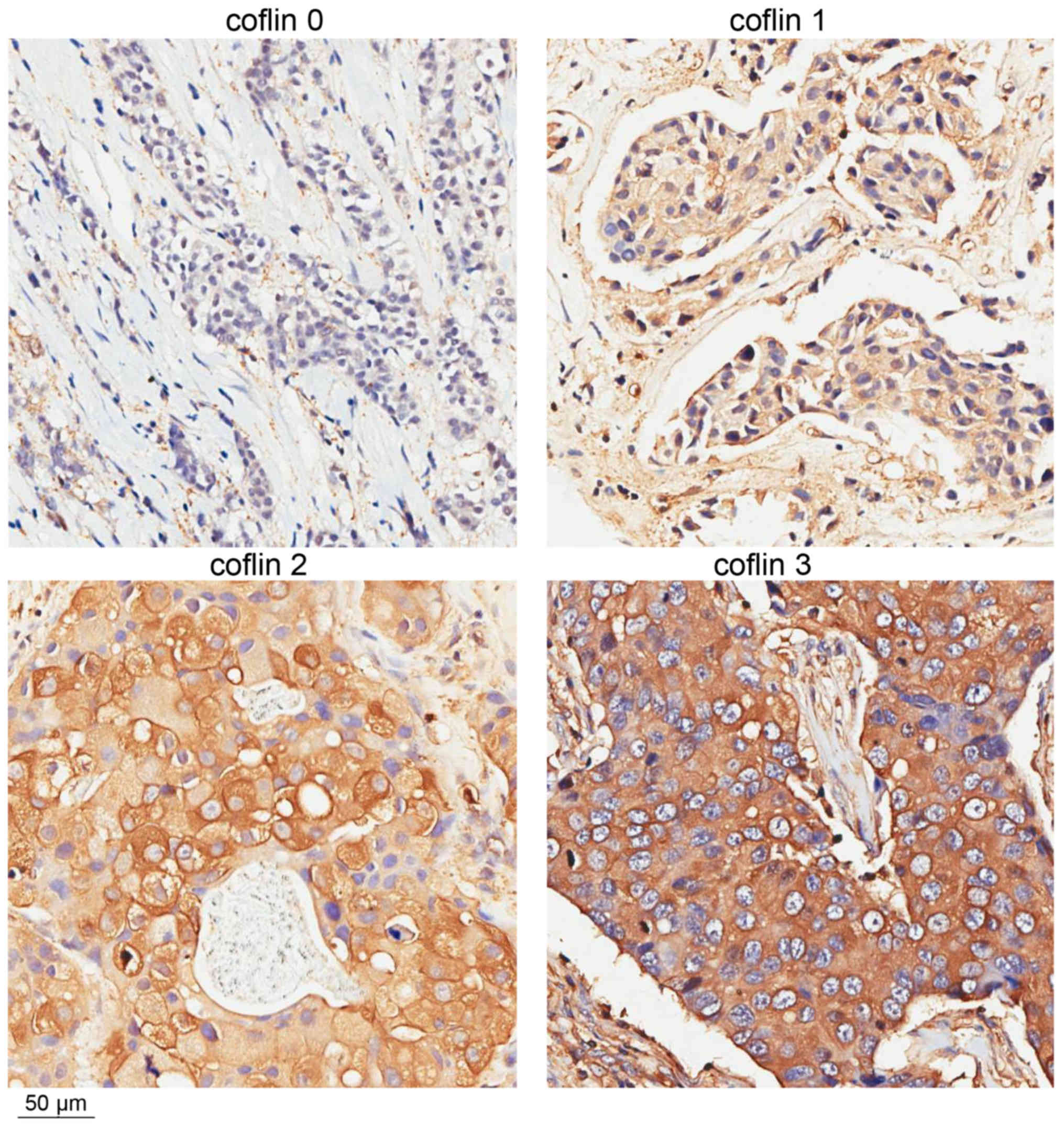
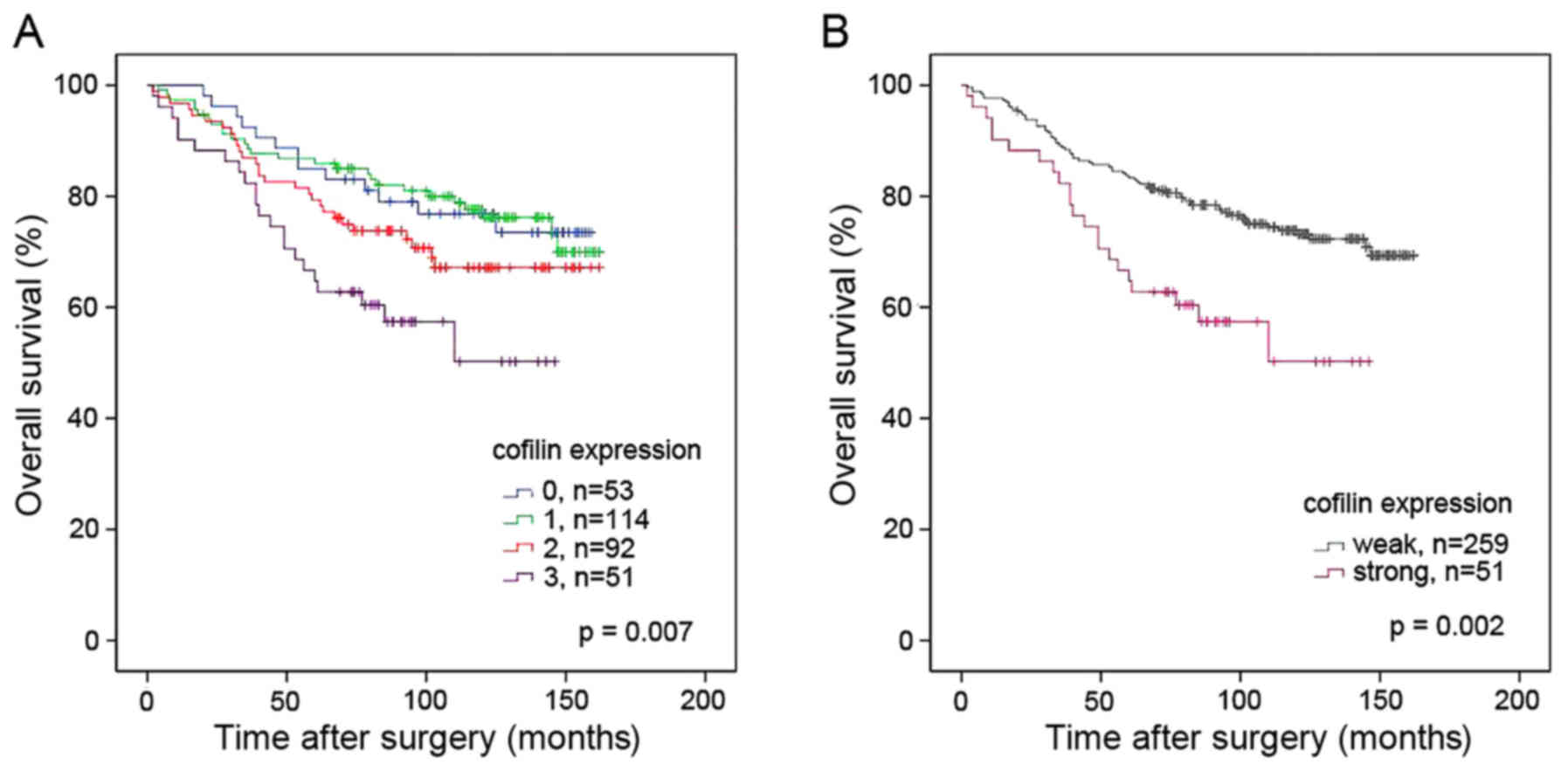
|
1
|
Guan X: Cancer metastases: Challenges and
opportunities. Acta Pharm Sin B. 5:402–418. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Roussos ET, Condeelis JS and Patsialou A:
Chemotaxis in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:573–587. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sidani M, Wessels D, Mouneimne G, Ghosh M,
Goswami S, Sarmiento C, Wang W, Kuhl S, El-Sibai M, Backer JM, et
al: Cofilin determines the migration behavior and turning frequency
of metastatic cancer cells. J Cell Biol. 179:777–791. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang W, Eddy R and Condeelis J: The
cofilin pathway in breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Nat Rev
Cancer. 7:429–440. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Moretti RM, Marelli M Montagnani, Mai S
and Limonta P: Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists suppress
melanoma cell motility and invasiveness through the inhibition of
α3 integrin and MMP-2 expression and activity. Int J Oncol.
33:405–413. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Limame R, de Beeck KO, Van Laere S, Croes
L, De Wilde A, Dirix L, Van Camp G, Peeters M, De Wever O, Lardon F
and Pauwels P: Expression profiling of migrated and invaded breast
cancer cells predicts early metastatic relapse and reveals
Krüppel-like factor 9 as a potential suppressor of invasive growth
in breast cancer. Oncoscience. 1:69–81. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Carlier MF, Ressad F and Pantaloni D:
Control of actin dynamics in cell motility. Role of ADF/cofilin. J
Biol Chem. 274:33827–33830. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Achard V, Martiel JL, Michelot A, Guérin
C, Reymann AC, Blanchoin L and Boujemaa-Paterski R: A
‘primer’-based mechanism underlies branched actin filament network
formation and motility. Curr Biol. 20:423–428. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bugyi B and Carlier MF: Control of actin
filament treadmilling in cell motility. Annu Rev Biophys.
39:449–470. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bernstein BW and Bamburg JR: ADF/cofilin:
A functional node in cell biology. Trends Cell Biol. 20:187–195.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bravo-Cordero JJ, Magalhaes MA, Eddy RJ,
Hodgson L and Condeelis J: Functions of cofilin in cell locomotion
and invasion. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:405–415. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hotulainen P, Paunola E, Vartiainen MK and
Lappalainen P: Actin-depolymerizing factor and cofilin-1 play
overlapping roles in promoting rapid F-actin depolymerization in
mammalian nonmuscle cells. Mol Biol Cell. 16:649–664. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ghosh M, Song X, Mouneimne G, Sidani M,
Lawrence DS and Condeelis JS: Cofilin promotes actin polymerization
and defines the direction of cell motility. Science. 304:743–746.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yamaguchi H, Lorenz M, Kempiak S,
Sarmiento C, Coniglio S, Symons M, Segall J, Eddy R, Miki H,
Takenawa T and Condeelis J: Molecular mechanisms of invadopodium
formation: The role of the N-WASP-Arp2/3 complex pathway and
cofilin. J Cell Biol. 168:441–452. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yap CT, Simpson TI, Pratt T, Price DJ and
Maciver SK: The motility of glioblastoma tumour cells is modulated
by intracellular cofilin expression in a concentration-dependent
manner. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 60:153–165. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Y, Kuramitsu Y, Kitagawa T, Baron B,
Yoshino S, Maehara S, Maehara Y, Oka M and Nakamura K:
Cofilin-phosphatase slingshot-1L (SSH1L) is over-expressed in
pancreatic cancer (PC) and contributes to tumor cell migration.
Cancer Lett. 360:171–176. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Peng XC, Gong FM, Zhao YW, Zhou LX, Xie
YW, Liao HL, Lin HJ, Li ZY, Tang MH and Tong AP: Comparative
proteomic approach identifies PKM2 and cofilin-1 as potential
diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic targets for pulmonary
adenocarcinoma. PLoS One. 6:e273092011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li D, Zhang Y, Li Z, Wang X, Qu X and Liu
Y: Activated Pak4 expression correlates with poor prognosis in
human gastric cancer patients. Tumour Biol. 36:9431–9436. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nishimura S, Tsuda H, Kataoka F, Arao T,
Nomura H, Chiyoda T, Susumu N, Nishio K and Aoki D: Overexpression
of cofilin 1 can predict progression-free survival in patients with
epithelial ovarian cancer receiving standard therapy. Hum Pathol.
42:516–521. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang ZL, Miao X, Xiong L, Zou Q, Yuan Y,
Li J, Liang L, Chen M and Chen S: CFL1 and Arp3 are biomarkers for
metastasis and poor prognosis of squamous cell/adenosquamous
carcinomas and adenocarcinomas of gallbladder. Cancer Invest.
31:132–139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang W, Goswami S, Lapidus K, Wells AL,
Wyckoff JB, Sahai E, Singer RH, Segall JE and Condeelis JS:
Identification and testing of a gene expression signature of
invasive carcinoma cells within primary mammary tumors. Cancer Res.
64:8585–8594. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang W, Mouneimne G, Sidani M, Wyckoff J,
Chen X, Makris A, Goswami S, Bresnick AR and Condeelis JS: The
activity status of cofilin is directly related to invasion,
intravasation, and metastasis of mammary tumors. J Cell Biol.
173:395–404. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shaheed SU, Rustogi N, Scally A, Wilson J,
Thygesen H, Loizidou MA, Hadjisavvas A, Hanby A, Speirs V, Loadman
P, et al: Identification of stage-specific breast markers using
quantitative proteomics. J Proteome Res. 12:5696–5708. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Falck AK, Bendahl PO, Chebil G, Olsson H,
Fernö M and Rydén L: Biomarker expression and St Gallen molecular
subtype classification in primary tumours, synchronous lymph node
metastases and asynchronous relapses in primary breast cancer
patients with 10 years' follow-up. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
140:93–104. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rydén L, Jirström K, Bendahl PO, Fernö M,
Nordenskjöld B, Stål O, Thorstenson S, Jönsson PE and Landberg G:
Tumor-specific expression of vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor 2 but not vascular endothelial growth factor or human
epidermal growth factor receptor 2 is associated with impaired
response to adjuvant tamoxifen in premenopausal breast cancer. J
Clin Oncol. 23:4695–4704. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Edge S, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG,
Greene FL and Trotti A: AJCC Cancer Staging Handbook. 7th.
Springer; New York, NY: 2010
|
|
27
|
Krishnamurthy S, Mathews K, McClure S,
Murray M, Gilcrease M, Albarracin C, Spinosa J, Chang B, Ho J, Holt
J, et al: Multi-institutional comparison of whole slide digital
imaging and optical microscopy for interpretation of
hematoxylin-eosin-stained breast tissue sections. Arch Pathol Lab
Med. 137:1733–1739. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rakha EA, Reis-Filho JS, Baehner F, Dabbs
DJ, Decker T, Eusebi V, Fox SB, Ichihara S, Jacquemier J, Lakhani
SR, et al: Breast cancer prognostic classification in the molecular
era: The role of histological grade. Breast Cancer Res. 12:2072010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ono S: Mechanism of depolymerization and
severing of actin filaments and its significance in cytoskeletal
dynamics. Int Rev Cytol. 258:1–82. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
van Rheenen J, Song X, van Roosmalen W,
Cammer M, Chen X, Desmarais V, Yip SC, Backer JM, Eddy RJ and
Condeelis JS: EGF-induced PIP2 hydrolysis releases and activates
cofilin locally in carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol. 179:1247–1259.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Garg P, Verma R, Cook L, Soofi A,
Venkatareddy M, George B, Mizuno K, Gurniak C, Witke W and Holzman
LB: Actin-depolymerizing factor cofilin-1 is necessary in
maintaining mature podocyte architecture. J Biol Chem.
285:22676–22688. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tammana TV, Sahasrabuddhe AA, Bajpai VK
and Gupta CM: ADF/cofilin-driven actin dynamics in early events of
Leishmania cell division. J Cell Sci. 123:1894–1901. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ellsworth RE, Hooke JA, Love B, Ellsworth
DL and Shriver CD: Molecular changes in primary breast tumors and
the nottingham histologic score. Pathol Oncol Res. 15:541–547.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Niikura N, Iwamoto T, Masuda S, Kumaki N,
Xiaoyan T, Shirane M, Mori K, Tsuda B, Okamura T, Saito Y, et al:
Immuno-histochemical Ki67 labeling index has similar proliferation
predictive power to various gene signatures in breast cancer.
Cancer Sci. 103:1508–1512. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Volpi A, Nanni O, De Paola F, Granato AM,
Mangia A, Monti F, Schittulli F, De Lena M, Scarpi E, Rosetti P, et
al: HER-2 expression and cell proliferation: Prognostic markers in
patients with node-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
21:2708–2712. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mouneimne G, DesMarais V, Sidani M, Scemes
E, Wang W, Song X, Eddy R and Condeelis J: Spatial and temporal
control of cofilin activity is required for directional sensing
during chemotaxis. Curr Biol. 16:2193–2205. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Oser M, Yamaguchi H, Mader CC,
Bravo-Cordero JJ, Arias M, Chen X, Desmarais V, van Rheenen J,
Koleske AJ and Condeelis J: Cortactin regulates cofilin and N-WASp
activities to control the stages of invadopodium assembly and
maturation. J Cell Biol. 186:571–587. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang X, Sun D, Pan Q, Wen W, Chen Y, Xin
X, Huang M, Ding J and Geng M: JG6, a novel marine-derived
oligosaccharide, suppresses breast cancer metastasis via binding to
cofilin. Oncotarget. 5:3568–3578. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang Y and Tong X: Expression of the
actin-binding proteins indicates that cofilin and fascin are
related to breast tumour size. J Int Med Res. 38:1042–1048. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Polachini GM, Sobral LM, Mercante AM,
Paes-Leme AF, Xavier FC, Henrique T, Guimarães DM, Vidotto A,
Fukuyama EE, Góis-Filho JF, et al: Proteomic approaches identify
members of cofilin pathway involved in oral tumorigenesis. PLoS
One. 7:e505172012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lu LI, Fu NI, Luo XU, Li XY and Li XP:
Overexpression of cofilin 1 in prostate cancer and the
corresponding clinical implications. Oncol Lett. 9:2757–2761.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Naumann DN and Sintler M: The surgeon as
the most important factor in lymph node harvest during axillary
clearance. Anticancer Res. 33:3935–3939. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Olivotto IA, Gomi A, Bancej C, Brisson J,
Tonita J, Kan L, Mah Z, Harrison M and Shumak R: Influence of delay
to diagnosis on prognostic indicators of screen-detected breast
carcinoma. Cancer. 94:2143–2150. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|