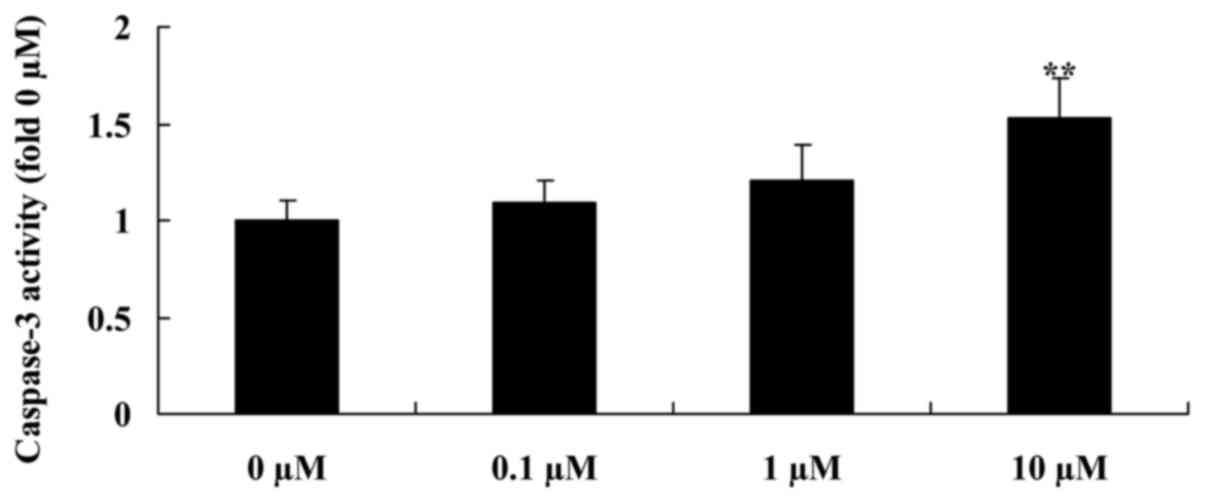
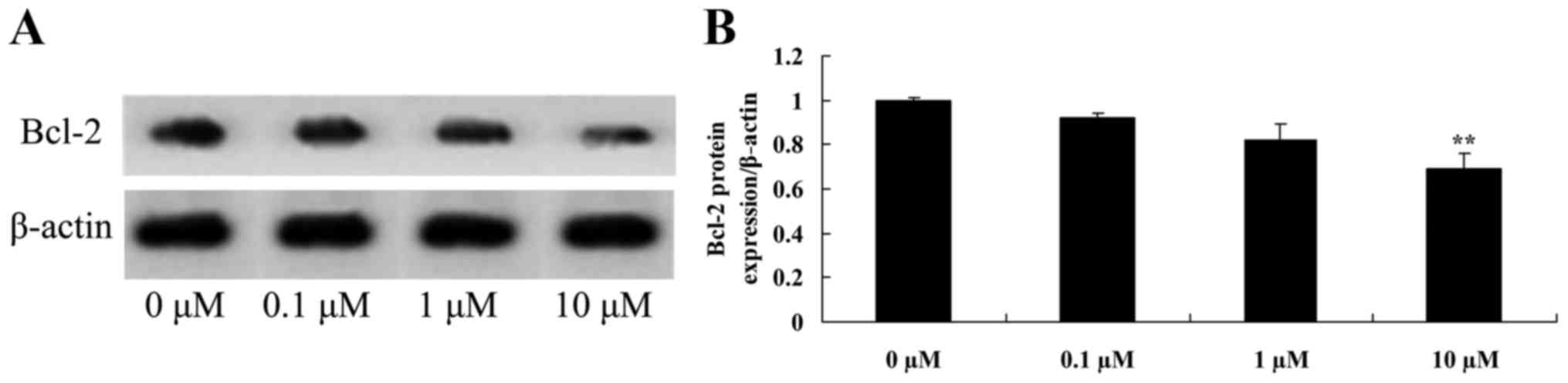
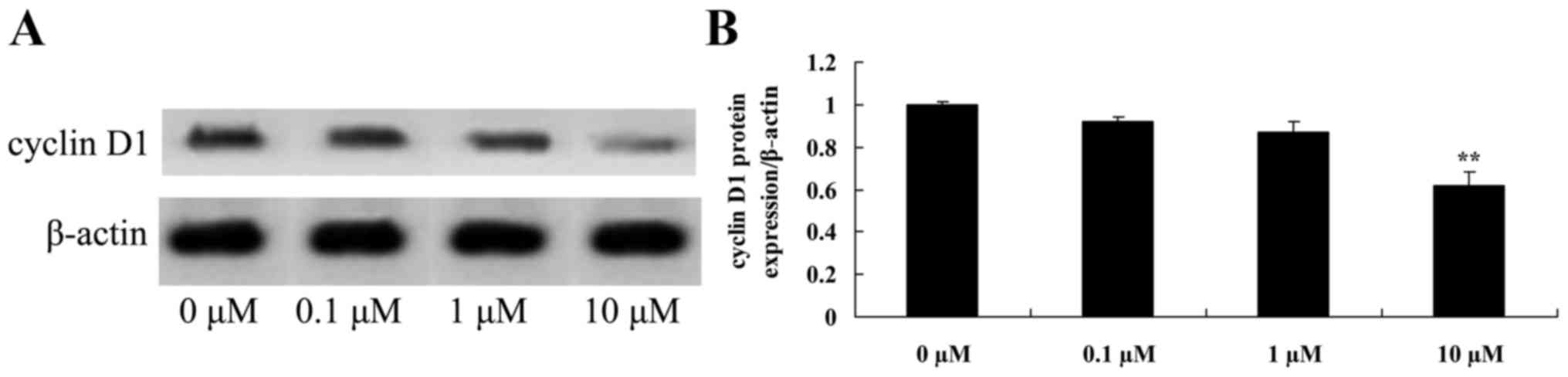
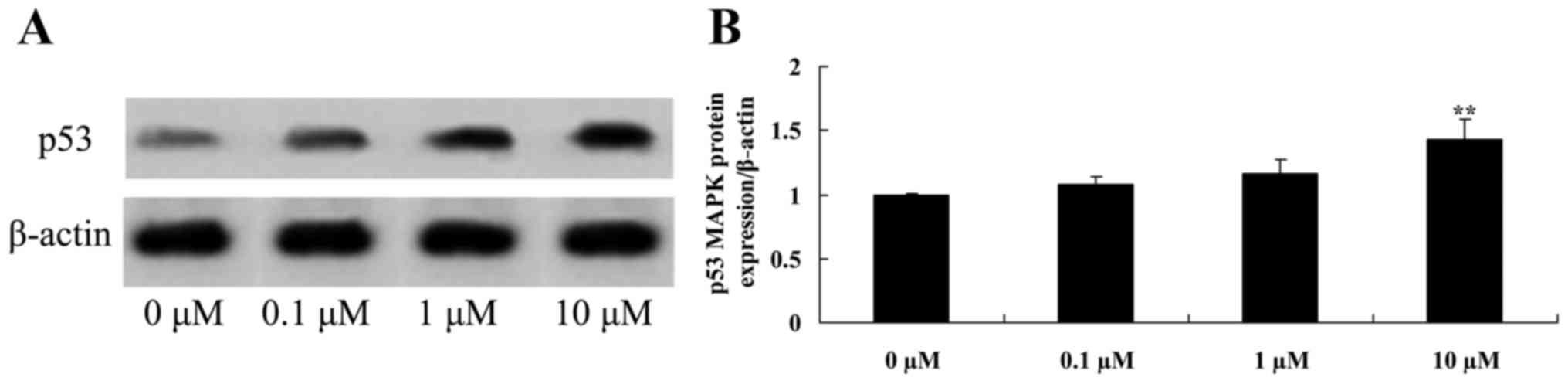
|
1
|
Metzger-Filho O, de Azambuja E, Bradbury
I, Saini KS, Bines J, Simon SD, Dooren VV, Aktan G, Pritchard KI,
Wolff AC, et al: Analysis of regional timelines to set up a global
phase III clinical trial in breast cancer: The adjuvant lapatinib
and/or trastuzumab treatment optimization experience. Oncologist.
18:134–140. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bower JE, Greendale G, Crosswell AD, Garet
D, Sternlieb B, Ganz PA, Irwin MR, Olmstead R, Arevalo J and Cole
SW: Yoga reduces inflammatory signaling in fatigued breast cancer
survivors: A randomized controlled trial. Psychoneuroendocrinology.
43:20–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Buckley A, McQuaid S, Johnson P and Buggy
DJ: Effect of anaesthetic technique on the natural killer cell
anti-tumour activity of serum from women undergoing breast cancer
surgery: A pilot study. Br J Anaesth. 113 Suppl 1:i56–i62. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ansari M, Porouhan P, Mohammadianpanah M,
Omidvari S, Mosalaei A, Ahmadloo N, Nasrollahi H and Hamedi SH:
Efficacy of ginger in control of chemotherapy induced nausea and
vomiting in breast cancer patients receiving doxorubicin-based
chemotherapy. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 17:3877–3880.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mrózek E, Layman R, Ramaswamy B, Lustberg
M, Vecchione A, Knopp MV and Shapiro CL: Phase II trial of
neoadjuvant weekly nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel,
carboplatin, and biweekly bevacizumab therapy in women with
clinical stage II or III HER2-negative breast cancer. Clin Breast
Cancer. 14:228–234. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pu Z, Zhang X, Chen Q, Yuan X and Xie H:
Establishment of an expression platform of OATP1B1 388GG and 521CC
genetic polymorphism and the therapeutic effect of tamoxifen in
MCF-7 cells. Oncol Rep. 33:2420–2428. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hu D, Su C, Jiang M, Shen Y, Shi A, Zhao
F, Chen R, Shen Z, Bao J and Tang W: Fenofibrate inhibited
pancreatic cancer cells proliferation via activation of p53
mediated by upregulation of LncRNA MEG3. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 471:290–295. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shokouh TZ, Ezatollah A and Barand P:
Interrelationships Between Ki67, HER2/neu, p53, ER, and PR status
and their associations with tumor grade and lymph node involvement
in breast carcinoma subtypes: Retrospective-observational
analytical study. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e13592015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Antony ML, Kim SH and Singh SV: Critical
role of p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis in benzyl
isothiocyanate-induced apoptotic cell death. PLoS One.
7:e322672012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wong FC, Woo CC, Hsu A and Tan BK: The
anti-cancer activities of Vernonia amygdalina extract in human
breast cancer cell lines are mediated through caspase-dependent and
p53-independent pathways. PLoS One. 8:e780212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ali A, Shah AS and Ahmad A:
Gain-of-function of mutant p53: Mutant p53 enhances cancer
progression by inhibiting KLF17 expression in invasive breast
carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 354:87–96. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hsieh TJ, Liu TZ, Chern CL, Tsao DA, Lu
FJ, Syu YH, Hsieh PY, Hu HS, Chang TT and Chen CH: Liriodenine
inhibits the proliferation of human hepatoma cell lines by blocking
cell cycle progression and nitric oxide-mediated activation of p53
expression. Food Chem Toxicol. 43:1117–1126. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nordin N, Majid NA, Hashim NM, Rahman MA,
Hassan Z and Ali HM: Liriodenine, an aporphine alkaloid from
Enicosanthellum pulchrum, inhibits proliferation of human ovarian
cancer cells through induction of apoptosis via the mitochondrial
signaling pathway and blocking cell cycle progression. Drug Des
Devel Ther. 9:1437–1448. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hufford CD, Sharma AS and Oguntimein BO:
Antibacterial and antifungal activity of liriodenine and related
oxoaporphine alkaloids. J Pharm Sci. 69:1180–1183. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
De la Cruz-Chacón I, González-Esquinca AR,
Fefer P Guevara and Garcia LF Jimenez: Liriodenine, early
antimicrobial defence in Annona diversifolia. Z Naturforsch C.
66:377–384. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li L, Xu Y and Wang B: Liriodenine induces
the apoptosis of human laryngocarcinoma cells via the upregulation
of p53 expression. Oncol Lett. 9:1121–1127. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zuo S, Liu C, Wang J, Wang F, Xu W, Cui S,
Yuan L, Chen X, Fan W, Cui M and Song G: IGFBP-rP1 induces p21
expression through a p53-independent pathway, leading to cellular
senescence of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
138:1045–1055. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Verma S and Rao BJ: p53 suppresses
BRCA2-stimulated ATPase and strand exchange functions of human
RAD51. J Biochem. 154:237–248. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chang HC, Chang FR, Wu YC and Lai YH:
Anti-cancer effect of liriodenine on human lung cancer cells.
Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 20:365–371. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Saxena NK, Vertino PM, Anania FA and
Sharma D: Leptin-induced growth stimulation of breast cancer cells
involves recruitment of histone acetyltransferases and mediator
complex to CYCLIN D1 promoter via activation of Stat3. J Biol Chem.
282:13316–13325. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Feldt M, Bjarnadottir O, Kimbung S,
Jirström K, Bendahl PO, Veerla S, Grabau D, Hedenfalk I and
Borgquist S: Statin-induced anti-proliferative effects via cyclin
D1 and p27 in a window-of-opportunity breast cancer trial. J Transl
Med. 13:1332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mohammadizadeh F, Hani M, Ranaee M and
Bagheri M: Role of cyclin D1 in breast carcinoma. J Res Med Sci.
18:1021–1025. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gonzalez-Sarrias A, Ma H, Edmonds ME and
Seeram NP: Maple polyphenols, ginnalins A-C, induce S- and
G2/M-cell cycle arrest in colon and breast cancer cells mediated by
decreasing cyclins A and D1 levels. Food Chem. 136:636–642. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Coates AS, Millar EK, O'Toole SA, Molloy
TJ, Viale G, Goldhirsch A, Regan MM, Gelber RD, Sun Z,
Castiglione-Gertsch M, et al: Prognostic interaction between
expression of p53 and estrogen receptor in patients with
node-negative breast cancer: Results from IBCSG Trials VIII and IX.
Breast Cancer Res. 14:R1432012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang Z, Wang CZ, Du GJ, Qi LW, Calway T,
He TC, Du W and Yuan CS: Genistein induces G2/M cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis via ATM/p53-dependent pathway in human colon cancer
cells. Int J Oncol. 43:289–296. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu S and Qian W: Need for clarification
of data in a recent meta-analysis on vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF) and risk of breast cancer. Cytokine. 60:5962012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Groves MD, Hess KR, Puduvalli VK, Colman
H, Conrad CA, Gilbert MR, Weinberg J, Cristofanilli M, Yung WK and
Liu TJ: Biomarkers of disease: Cerebrospinal fluid vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and stromal cell derived factor
(SDF)-1 levels in patients with neoplastic meningitis (NM) due to
breast cancer, lung cancer and melanoma. J Neurooncol. 94:229–234.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|