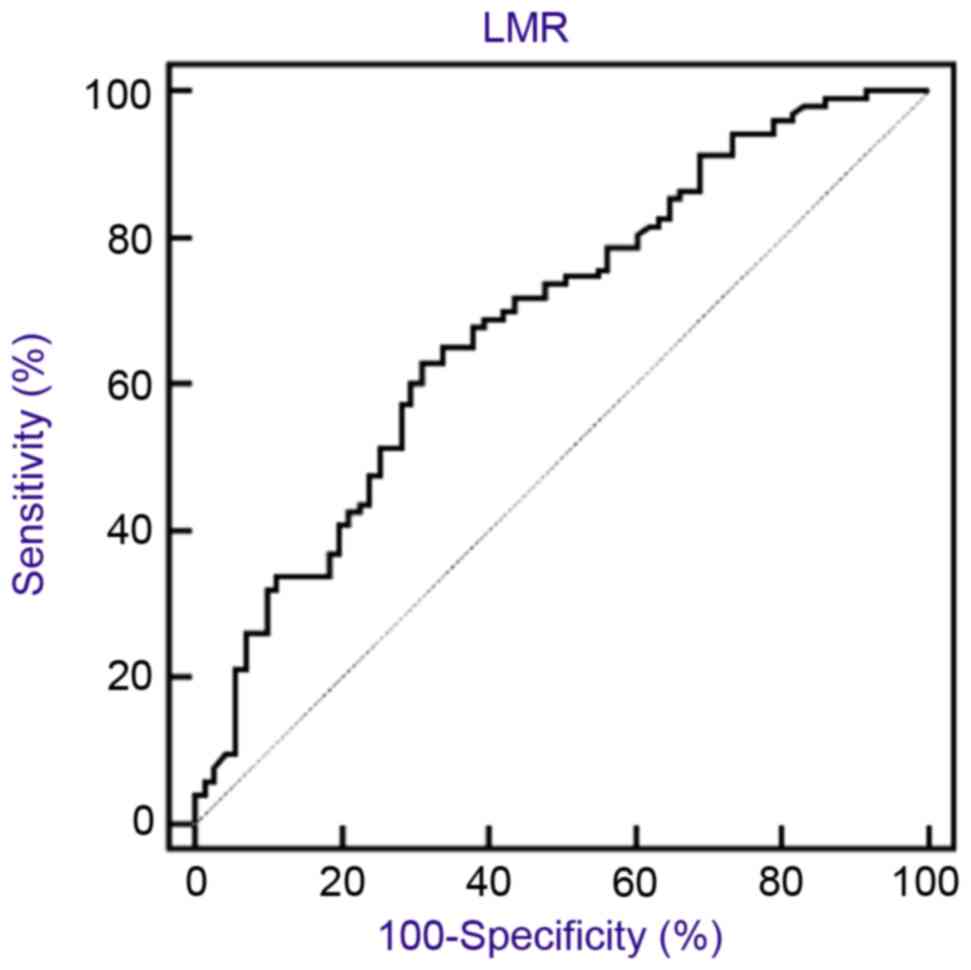
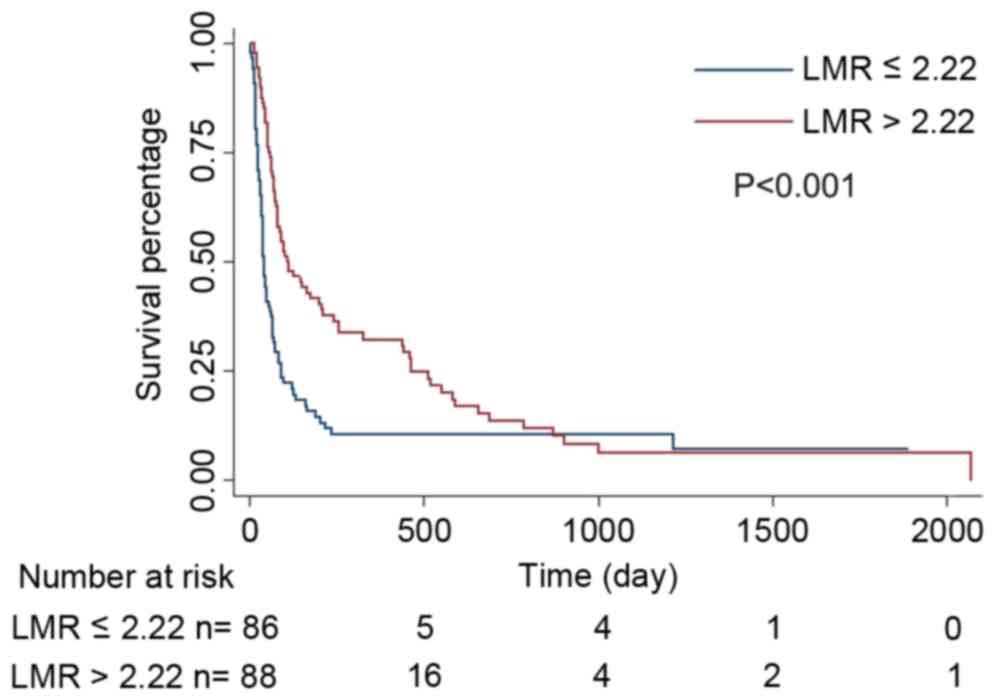
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yuan JM, Govindarajan S, Arakawa K and Yu
MC: Synergism of alcohol, diabetes and viral hepatitis on the risk
of hepatocellular carcinoma in blacks and whites in the U.S.
Cancer. 101:1009–1017. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bruix J and Sherman M: Practice Guidelines
Committee, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 42:1208–1236.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li J, Wang L, Cong N, Shi C, Bu W, Song J
and Chen H: Efficacy of sorafenib for advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma and prognostic factors. Hepatogastroenterology.
61:954–957. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ogasawara S, Chiba T, Ooka Y, Suzuki E,
Kanogawa N, Saito T, Motoyama T, Tawada A, Kanai F and Yokosuka O:
Post-progression survival in patients with advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma resistant to sorafenib. Invest New Drugs. 34:255–260.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hong YF, Chen ZH, Ma XK, Li X, Wu DH, Chen
J, Dong M, Wei L, Wang TT, Ruan DY, et al: Comparison of five
models for end-stage liver disease in predicting the survival rate
of patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol.
37:5265–5273. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sherman M: Hepatocellular carcinoma:
Epidemiology, surveillance, and diagnosis. Semin Liver Dis.
30:3–16. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bugada D, Allegri M, Lavand'homme P, De
Kock M and Fanelli G: Inflammation-based scores: A new method for
patient-targeted strategies and improved perioperative outcome in
cancer patients. Biomed Res Int. 2014:1424252014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Deng Q, He B, Liu X, Yue J, Ying H, Pan Y,
Sun H, Chen J, Wang F, Gao T, et al: Prognostic value of
pre-operative inflammatory response biomarkers in gastric cancer
patients and the construction of a predictive model. J Transl Med.
13:662015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shiels MS, Katki HA, Hildesheim A,
Pfeiffer RM, Engels EA, Williams M, Kemp TJ, Caporaso NE, Pinto LA
and Chaturvedi AK: Circulating inflammation markers, risk of lung
cancer, and utility for risk stratification. J Natl Cancer Inst.
107:djv1992015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Morrison L, Laukkanen JA, Ronkainen K,
Kurl S, Kauhanen J and Toriola AT: Inflammatory biomarker score and
cancer: A population-based prospective cohort study. BMC Cancer.
16:802016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fang S, Wang Y, Sui D, Liu H, Ross MI,
Gershenwald JE, Cormier JN, Royal RE, Lucci A, Schacherer CW, et
al: C-reactive protein as a marker of melanoma progression. J Clin
Oncol. 33:1389–1396. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Aleksandrova K, Boeing H, Nöthlings U,
Jenab M, Fedirko V, Kaaks R, Lukanova A, Trichopoulou A,
Trichopoulos D, Boffetta P, et al: Inflammatory and metabolic
biomarkers and risk of liver and biliary tract cancer. Hepatology.
60:858–871. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schumacher D, Strilic B, Sivaraj KK,
Wettschureck N and Offermanns S: Platelet-derived nucleotides
promote tumor-cell transendothelialmigration and metastasis via
p2y2 receptor. Cancer Cell. 24:130–137. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Grosse-Steffen T, Giese T, Giese N,
Longerich T, Schirmacher P, Hansch GM and Gaida MM:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma and pancreatic tumor cell lines: The role of
neutrophils and neutrophil-derived elastase. Clin Dev Immunol.
2012:7207682012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ren QQ, Fu SJ, Zhao Q, Guo ZY, Ji F, Chen
MG, Wu LW and He XS: Prognostic value of preoperative peripheral
monocyte count in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after
liver transplantation. Tumor Biol. 37:8973–8988. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Jia W, Wu J, Jia H, Yang Y, Zhang X, Chen
K and Su F: The peripheral blood Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte ratio is
superior to the Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte ratio for predicting the
long-term survival of triple-negative breast cancer patients. PLoS
One. 10:e01430612015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chang Y, Fu Q, Xu L, Zhou L, Liu Z, Yang
Y, Lin Z and Xu J: Prognostic value of preoperative lymphocyte to
monocyte ratio in patients with nonmetastatic clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 37:4613–4620. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chang Y, An H, Xu L, Zhu Y, Yang Y, Lin Z
and Xu J: Systemic inflammation score predicts postoperative
prognosis of patients with clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Br J
Cancer. 113:626–633. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen YM, Lai CH, Chang HC, Chao TY, Tseng
CC, Fang WF, Wang CC, Chung YH, Wang YH, Su MC, et al: Baseline and
trend of Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte ratio as prognostic factors in
epidermal growth factor receptor mutant non-small cell lung cancer
patients treated with first-line epidermal growth factor tyrosine
kinase inhibitors. PLoS One. 10:e01362522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shibutani M, Maeda K, Nagahara H, Ohtani
H, Sakurai K, Yamazoe S, Kimura K, Toyokawa T, Amano R, Tanaka H,
et al: Prognostic significance of the lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio
in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:9966–9973. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin ZX, Ruan DY, Li Y, Wu DH, Ma XK, Chen
J, Chen ZH, Li X, Wang TT, Lin Q, et al: Lymphocyte-to-monocyte
ratio predicts survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
after curative resection. World J Gastroenterol. 21:10898–10906.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Llovet JM, Brú C and Bruix J: Prognosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma: The BCLC staging classification. Semin
Liver Dis. 19:329–338. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
NCCN Guidelines Version 2.2105 Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
|
|
26
|
Schag CC, Heinrich RL and Ganz PA:
Karnofsky performance status revisited: Reliability, validity, and
guidelines. J Clin Oncol. 2:187–193. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fluss R, Faraggi D and Reiser B:
Estimation of the Youden Index and its associated cutoff point.
Biom J. 47:458–472. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Keibel A, Singh V and Sharma MC:
Inflammation, microenvironment, and the immune system in cancer
progression. Curr Pharm Des. 15:1949–1955. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Balkwill F and Mantovani A: Inflammation
and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet. 357:539–545. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A and
Balkwill F: Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 454:436–444. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Y, Niu XL, Qu Y, Wu J, Zhu YQ, Sun WJ
and Li LZ: Autocrine production of interleukin-6 confers cisplatin
and paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
295:110–123. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kuang DM, Zhao Q, Wu Y, Peng C, Wang J, Xu
Z, Yin XY and Zheng L: Peritumoral neutrophils link inflammatory
response to disease progression by fostering angiogenesis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 54:948–955. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee IK, Vansaun MN, Shim JH, Matrisian LM
and Gorden DL: Increased metastases are associated with
inflammation and matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity at incision
sites in a murine model of peritoneal dissemination of colorectal
cancer. J Surg Res. 180:252–259. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mishalian I, Granot Z and Fridlender ZG:
The diversity of circulating neutrophils in cancer. Immunobiology.
222:82–88. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dunn GP, Old LJ and Schreiber RD: The
immunobiology of cancer immunosurveillance and immunoediting.
Immunity. 21:137–148. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Condeelis J and Pollard JW: Macrophages:
Obligate partners for tumor cell migration, invasion, and
metastasis. Cell. 124:263–266. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Leek RD and Harris AL: Tumor-associated
macrophages in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia.
7:177–189. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gay LJ and Felding-Habermann B:
Contribution of platelets to tumour metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:123–134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Buergy D, Wenz F, Groden C and Brockmann
MA: Tumor-platelet interaction in solid tumors. Int J Cancer.
130:2747–2760. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen XF, Qian J, Pei D, Zhou C, Røe OD,
Zhu F, He SH, Qian YY, Zhou Y, Xu J, et al: Prognostic value of
perioperative leukocyte count in resectable gastric cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 22:2818–2827. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kitayama J, Yasuda K, Kawai K, Sunami E
and Nagawa H: Circulating lymphocyte number has a positive
association with tumor response in neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy
for advanced rectal cancer. Radiat Oncol. 5:472010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gu L, Li H, Chen L, Ma X, Li X, Gao Y,
Zhang Y, Xie Y and Zhang X: Prognostic role of lymphocyte to
monocyte ratio for patients with cancer: Evidence from a systematic
review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 7:31926–31942.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hoffmann TK, Dworacki G, Tsukihiro T,
Meidenbauer N, Gooding W, Johnson JT and Whiteside TL: Spontaneous
apoptosis of circulating T lymphocytes in patients with head and
neck cancer and its clinical importance. Clin Cancer Res.
8:2553–2562. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rabinowich H, Cohen R, Bruderman I,
Steiner Z and Klajman A: Functional analysis of mononuclear cells
infiltrating into tumors: Lysis of autologous human tumor cells by
cultured infiltrating lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 47:173–177.
1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Stotz M, Pichler M, Absenger G, Szkandera
J, Arminger F, Schaberl-Moser R, Samonigg H, Stojakovic T and
Gerger A: The preoperative lymphocyte to monocyte ratio predicts
clinical outcome in patients with stage III colon cancer. Br J
Cancer. 110:435–440. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Unitt E, Marshall A, Gelson W, Rushbrook
SM, Davies S, Vowler SL, Morris LS, Coleman N and Alexander GJ:
Tumour lymphocytic infiltrate and recurrence of hepatocellular
carcinoma following liver transplantation. J Hepatol. 45:246–253.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zikos TA, Donnenberg AD, Landreneau RJ,
Luketich JD and Donnenberg VS: Lung T-cell subset composition at
the time of surgical resection is a prognostic indicator in
nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 60:819–827.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gao Q, Qiu SJ, Fan J, Zhou J, Wang XY,
Xiao YS, Xu Y, Li YW and Tang ZY: Intratumoral balance of
regulatory and cytotoxic T cells is associated with prognosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. J Clin Oncol.
25:2586–2593. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Evani SJ, Prabhu RG, Gnanaruban V, Finol
EA and Ramasubramanian AK: Monocytes mediate metastatic breast
tumor cell adhesion to endothelium under flow. FASEB J.
27:3017–3029. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Shi C and Pamer EG: Monocyte recruitment
during infection and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 11:762–774.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Pollard JW: Tumour-educated macrophages
promote tumour progression and metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:71–78.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hagemann T and Lawrence T: Investigating
macrophage and malign interactions in vitro. Methods Mol Biol.
512:325–332. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Tadmor T: Does monocyte count have
prognostic significance in cancer? Leuk Res. 37:1193–1194. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Sasaki A, Iwashita Y, Shibata K, Matsumoto
T, Ohta M and Kitano S: Prognostic value of preoperative peripheral
blood monocyte count inpatients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
Surgery. 139:755–764. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lin GN, Jiang XM, Peng JW, Xiao JJ, Liu DY
and Xia ZJ: Prognostic significance of the peripheral blood
absolute monocyte count inpatients with locally advanced or
metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma receiving systemic
chemotherapy. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:6387–6390. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhang J, Feng G, Zhao Y, Zhang J, Feng L
and Yang J: Association between lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR)
and the mortality of HBV-related liver cirrhosis: A retrospective
cohort study. BMJ Open. 5:e0080332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|