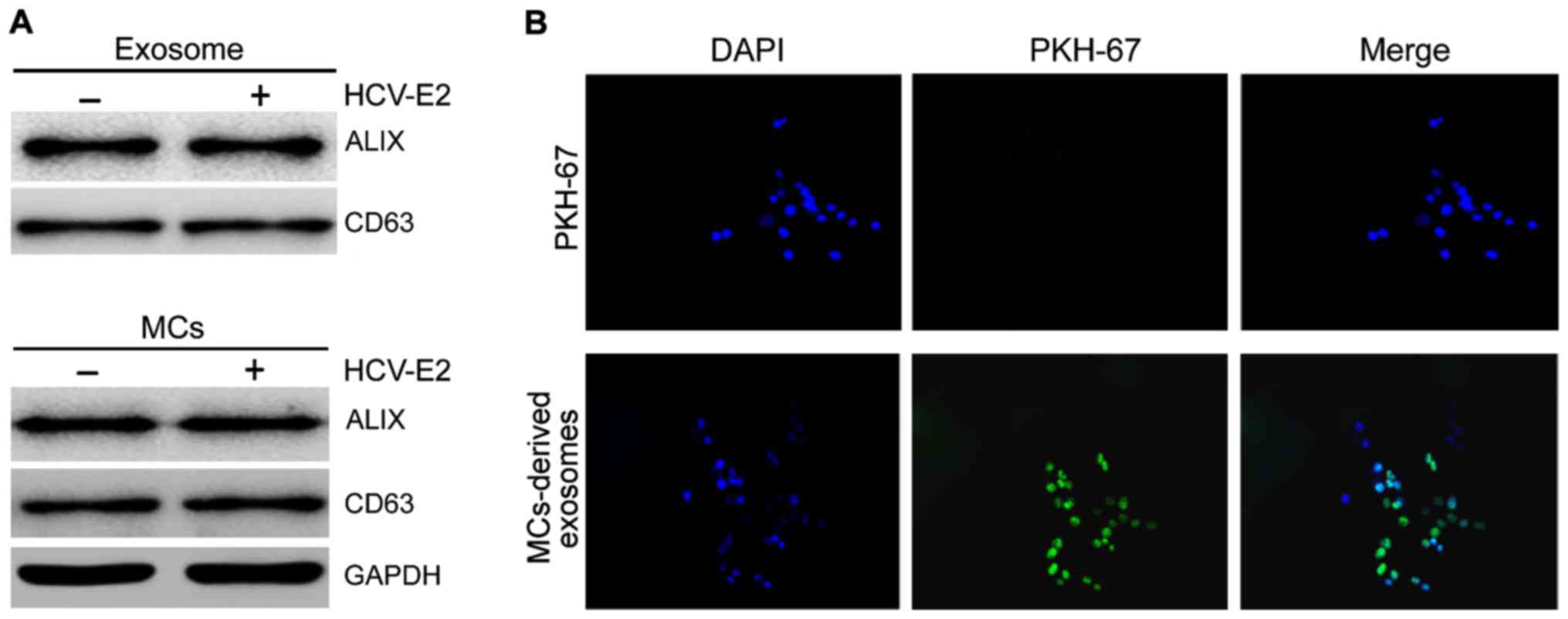
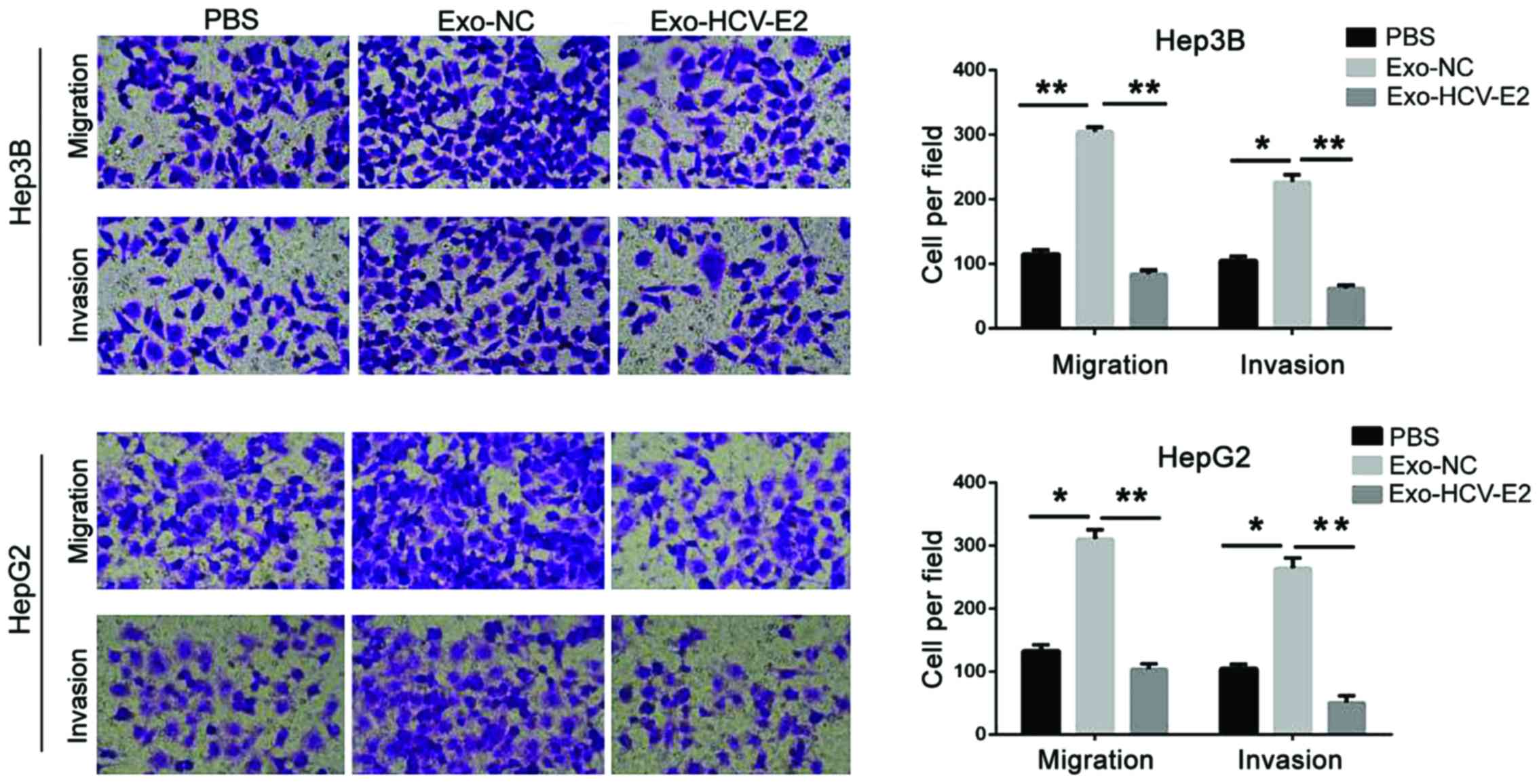
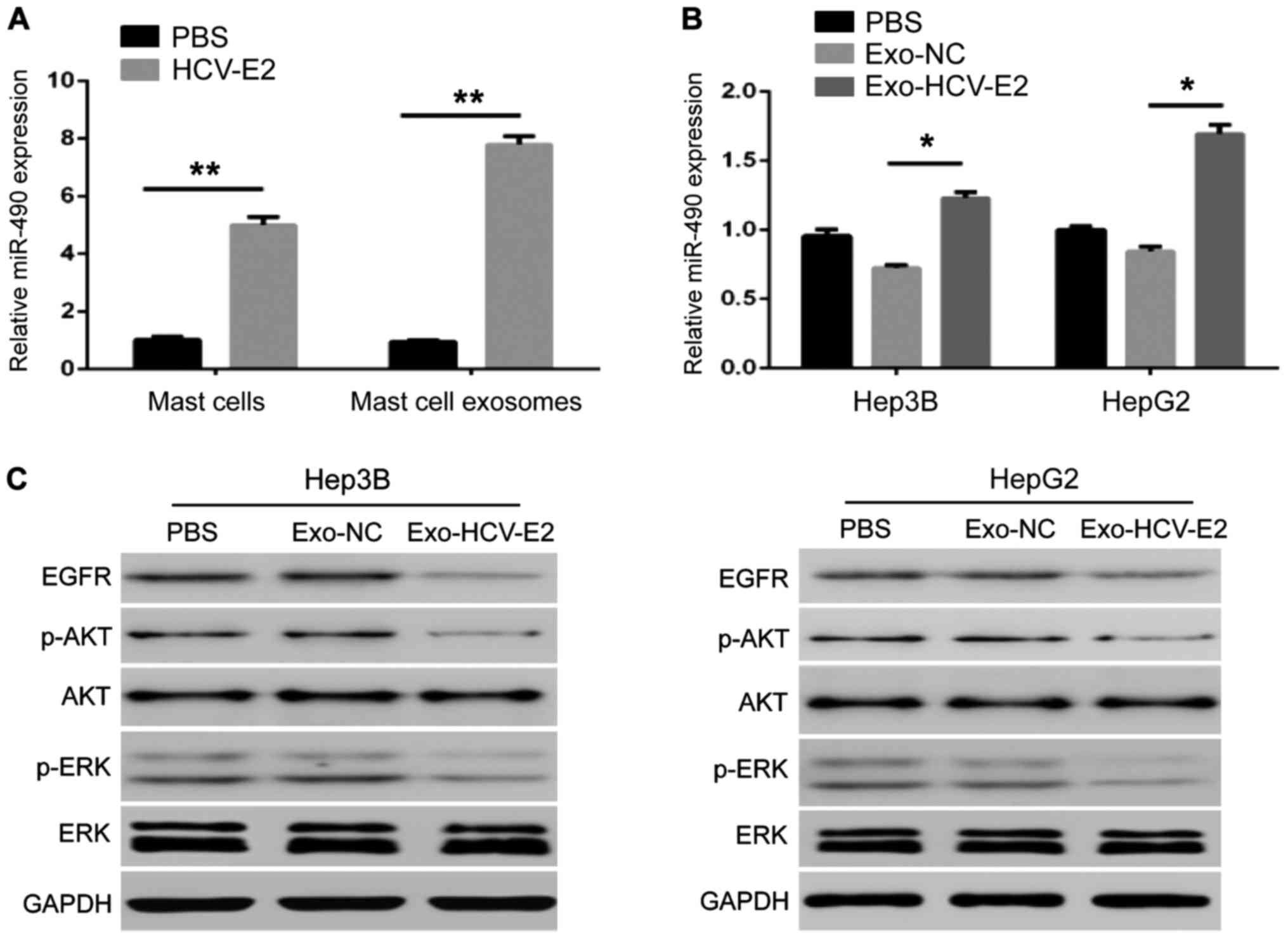
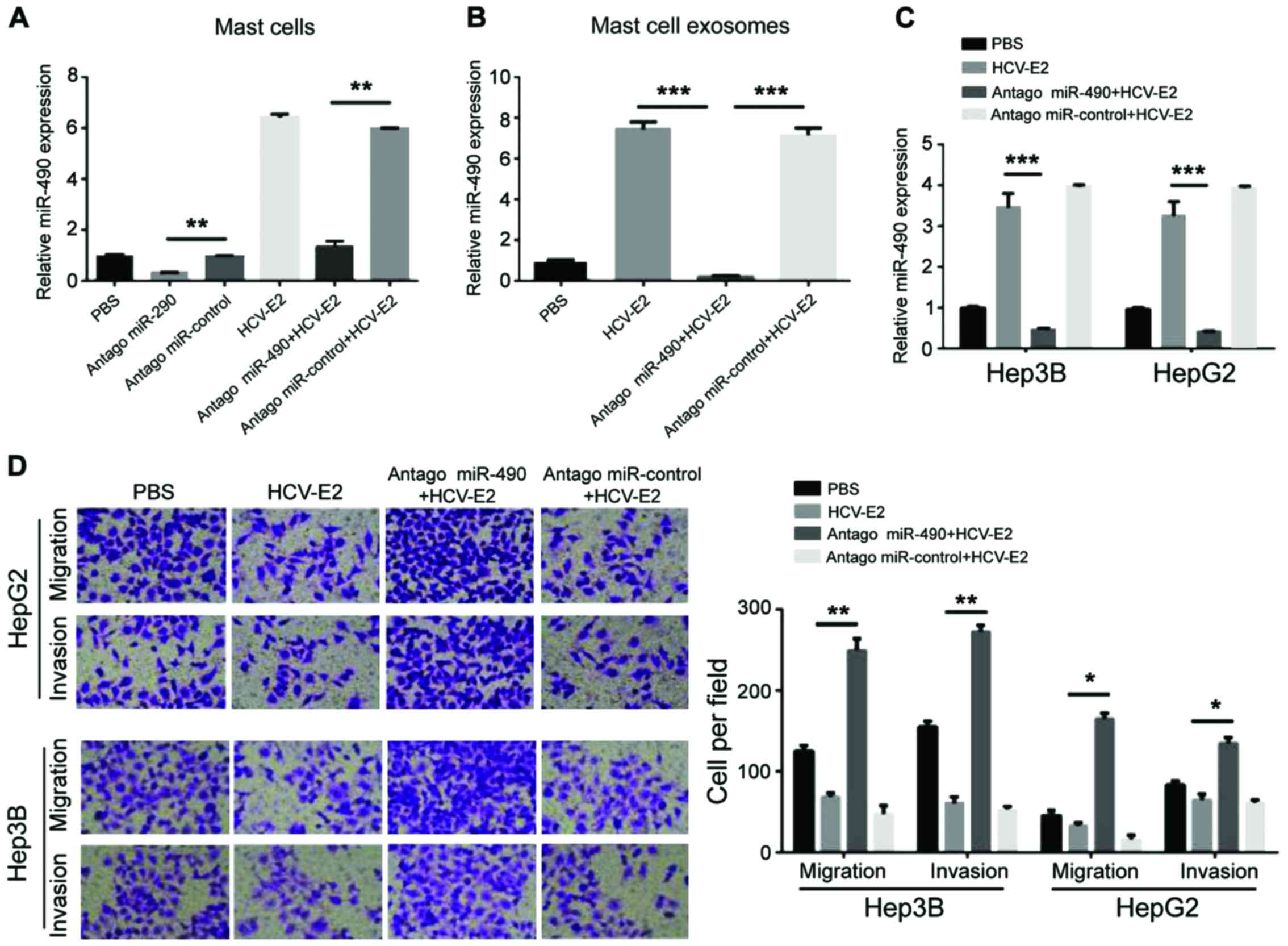
|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu Y, Zhang JB, Qin Y, Wang W, Wei L,
Teng Y, Guo L, Zhang B, Lin Z, Liu J, et al: PROX1 promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by way of up-regulating
hypoxia-inducible factor 1α expression and protein stability.
Hepatology. 58:692–705. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yamashita A, Saito T, Akaike K, Arakawa A,
Yoshida A, Kikuchi K, Sugitani M and Yao T: Mast cell sarcoma of
the sternum, clonally related to an antecedent germ cell tumor with
a novel D579del KIT mutation. Virchows Arch. 470:583–588. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Miłek K, Kaczmarczyk-Sekuła K, Strzępek A,
Dyduch G, Białas M, Szpor J, Gołąbek T, Szopiński T, Chłosta P and
Okoń K: Mast cells influence neoangiogenesis in prostatic cancer
independently of ERG status. Pol J Pathol. 67:244–249. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lampiasi N, Azzolina A, Montalto G and
Cervello M: Histamine and spontaneously released mast cell granules
affect the cell growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Exp
Mol Med. 39:284–294. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tu JF, Pan HY, Ying XH, Lou J, Ji JS and
Zou H: Mast cells comprise the major of interleukin 17-producing
cells and predict a poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e32202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Salido-Guadarrama I, Romero-Cordoba S,
Peralta-Zaragoza O, Hidalgo-Miranda A and Rodríguez-Dorantes M:
MicroRNAs transported by exosomes in body fluids as mediators of
intercellular communication in cancer. Onco Targets Ther.
7:1327–1338. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang J, Yao Y, Wu J and Li G:
Identification and analysis of exosomes secreted from macrophages
extracted by different methods. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:6135–6142.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cocucci E, Racchetti G and Meldolesi J:
Shedding microvesicles: Artefacts no more. Trends Cell Biol.
19:43–51. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dreyer F and Baur A: Biogenesis and
functions of exosomes and extracellular vesicles. Methods Mol Biol.
1448:201–216. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sabahi A, Uprichard SL, Wimley WC, Dash S
and Garry RF: Unexpected structural features of the hepatitis C
virus envelope protein 2 ectodomain. J Virol. 88:10280–10288. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Valadi H, Ekström K, Bossios A, Sjöstrand
M, Lee JJ and Lötvall JO: Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and
microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells.
Nat Cell Biol. 9:654–659. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou W, Fong MY, Min Y, Somlo G, Liu L,
Palomares MR, Yu Y, Chow A, O'Connor ST, Chin AR, et al:
Cancer-secreted miR-105 destroys vascular endothelial barriers to
promote metastasis. Cancer Cell. 25:501–515. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Y, Yi J, Chen X, Zhang Y, Xu M and
Yang Z: The regulation of cancer cell migration by lung cancer
cell-derived exosomes through TGF-β and IL-10. Oncol Lett.
11:1527–1530. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ko SF, Yip HK, Zhen YY, Lee CC, Lee CC,
Huang CC, Ng SH and Lin JW: Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell
exosomes suppress hepatocellular carcinoma growth in a rat model:
Apparent diffusion coefficient, natural killer T-cell responses,
and histopathological features. Stem Cells Int. 2015:8535062015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cheung KL, Jarrett R, Subramaniam S,
Salimi M, Gutowska-Owsiak D, Chen YL, Hardman C, Xue L, Cerundolo V
and Ogg G: Psoriatic T cells recognize neolipid antigens generated
by mast cell phospholipase delivered by exosomes and presented by
CD1a. J Exp Med. 213:2399–2412. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jia Z, Liu Y, Gao Q, Han Y, Zhang G, Xu S,
Cheng K and Zou W: miR-490-3p inhibits the growth and invasiveness
in triple-negative breast cancer by repressing the expression of
TNKS2. Gene. 593:41–47. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xu X, Chen R, Li Z, Huang N, Wu X, Li S,
Li Y and Wu S: MicroRNA-490-3p inhibits colorectal cancer
metastasis by targeting TGFβR1. BMC Cancer. 15:10232015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen S, Chen X, Xiu YL, Sun KX and Zhao Y:
MicroRNA-490-3P targets CDK1 and inhibits ovarian epithelial
carcinoma tumorigenesis and progression. Cancer Lett. 362:122–130.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang LY, Liu M, Li X and Tang H:
miR-490-3p modulates cell growth and epithelial to mesenchymal
transition of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting
endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment protein 3
(ERGIC3). J Biol Chem. 288:4035–4047. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu J, Zhang X, Wang H, Ge S, Gao T, Song
L, Wang X, Li H, Qin Y and Zhang Z: HCRP1 downregulation promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through the
induction of EGFR activation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Biomed Pharmacother. 88:421–429. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Guo T, Zhao L, Zhang Y, Liu G, Yao Y and
Li H: A monoclonal antibody targeting the dimer interface of
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Immunol Lett. 180:39–45.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cao C, Lu S, Sowa A, Kivlin R, Amaral A,
Chu W, Yang H, Di W and Wan Y: Priming with EGFR tyrosine kinase
inhibitor and EGF sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to respond to
chemotherapeutical drugs. Cancer Lett. 266:249–262. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Higuchi T, Todaka H, Sugiyama Y, Ono M,
Tamaki N, Hatano E, Takezaki Y, Hanazaki K, Miwa T, Lai S, et al:
Suppression of microRNA-7 (miR-7) biogenesis by nuclear factor
90-nuclear factor 45 complex (NF90-NF45) controls cell
proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Biol Chem.
291:21074–21084. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|