|
1
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: Epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Diaz M and Cléries R:
Primary liver cancer: Worldwide incidence and trends.
Gastroenterology. 127 5 Suppl 1:1–16. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Koike K: Hepatitis B virus HBx gene and
hepatocarcinogenesis. Intervirology. 38:134–142. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huang P, Zhuang B, Zhang H, Yan H, Xiao Z,
Li W, Zhang J, Tang Q, Hu K, Koeffler HP, et al: Hepatitis B virus
X protein (HBx) is responsible for resistance to targeted therapies
in hepatocellular carcinoma: Ex vivo culture evidence. Clin Cancer
Res. 21:4420–4430. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rajput P, Shukla SK and Kumar V: The HBx
oncoprotein of hepatitis B virus potentiates cell transformation by
inducing c-Myc-dependent expression of the RNA polymerase I
transcription factor UBF. Virol J. 12:622015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang J, Wang Y, Guo Y and Sun S:
Down-regulated microRNA-152 induces aberrant DNA methylation in
hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting DNA
methyltransferase 1. Hepatology. 52:60–70. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yuan JH, Yang F, Chen BF, Lu Z, Huo XS,
Zhou WP, Wang F and Sun SH: The histone deacetylase
4/SP1/microrna-200a regulatory network contributes to aberrant
histone acetylation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
54:2025–2035. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Moyo B, Nicholson SA and Arbuthnot PB: The
role of long non-coding RNAs in hepatitis B virus-related
hepatocellular carcinoma. Virus Res. 212:103–113. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nagano T and Fraser P: No-nonsense
functions for long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 145:178–181. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wilusz JE, Sunwoo H and Spector DL: Long
noncoding RNAs: Functional surprises from the RNA world. Genes Dev.
23:1494–1504. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mercer TR, Dinger ME and Mattick JS: Long
non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet.
10:155–159. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pandey RR, Mondal T, Mohammad F, Enroth S,
Redrup L, Komorowski J, Nagano T, Mancini-Dinardo D and Kanduri C:
Kcnq1ot1 antisense noncoding RNA mediates lineage-specific
transcriptional silencing through chromatin-level regulation. Mol
Cell. 32:232–246. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang X, Arai S, Song X, Reichart D, Du K,
Pascual G, Tempst P, Rosenfeld MG, Glass CK and Kurokawa R: Induced
ncRNAs allosterically modify RNA-binding proteins in cis to inhibit
transcription. Nature. 454:126–130. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao Z, Li S, Song E and Liu S: The roles
of ncRNAs and histone-modifiers in regulating breast cancer stem
cells. Protein Cell. 7:89–99. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ji P, Diederichs S, Wang W, Böing S,
Metzger R, Schneider PM, Tidow N, Brandt B, Buerger H, Bulk E, et
al: MALAT-1, a novel noncoding RNA, and thymosin beta4 predict
metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer.
Oncogene. 22:8031–8041. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fu X, Ravindranath L, Tran N, Petrovics G
and Srivastava S: Regulation of apoptosis by a prostate-specific
and prostate cancer-associated noncoding gene, PCGEM1. DNA Cell
Biol. 25:135–141. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Du Y, Kong G, You X, Zhang S, Zhang T, Gao
Y, Ye L and Zhang X: Elevation of highly up-regulated in liver
cancer (HULC) by hepatitis B virus X protein promotes hepatoma cell
proliferation via down-regulating p18. J Biol Chem.
287:26302–26311. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang F, Zhang L, Huo XS, Yuan JH, Xu D,
Yuan SX, Zhu N, Zhou WP, Yang GS, Wang YZ, et al: Long noncoding
RNA high expression in hepatocellular carcinoma facilitates tumor
growth through enhancer of zeste homolog 2 in humans. Hepatology.
54:1679–1689. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yuan JH, Yang F, Wang F, Ma JZ, Guo YJ,
Tao QF, Liu F, Pan W, Wang TT, Zhou CC, et al: A long noncoding RNA
activated by TGF-β promotes the invasion-metastasis cascade in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 25:666–681. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ishibashi M, Kogo R, Shibata K, Sawada G,
Takahashi Y, Kurashige J, Akiyoshi S, Sasaki S, Iwaya T, Sudo T, et
al: Clinical significance of the expression of long non-coding RNA
HOTAIR in primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 29:946–950.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang JL, Ren TY, Cao SW, Zheng SH, Hu XM,
Hu YW, Lin L, Chen J, Zheng L and Wang Q: HBx-related long
non-coding RNA DBH-AS1 promotes cell proliferation and survival by
activating MAPK signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget.
6:33791–33804. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang JF, Guo YJ, Zhao CX, Yuan SX, Wang
Y, Tang GN, Zhou WP and Sun SH: Hepatitis B virus X protein
(HBx)-related long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) down-regulated expression
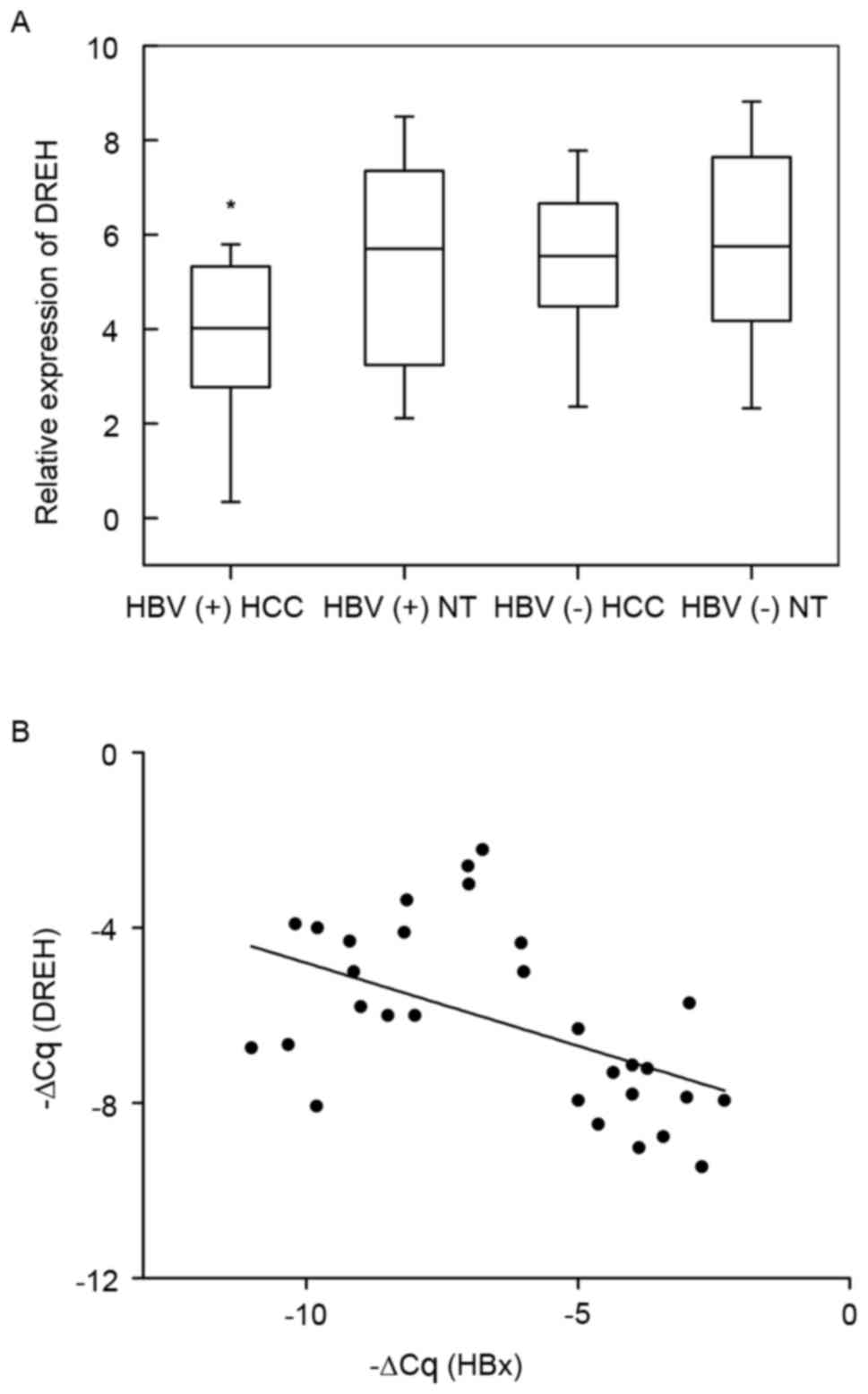
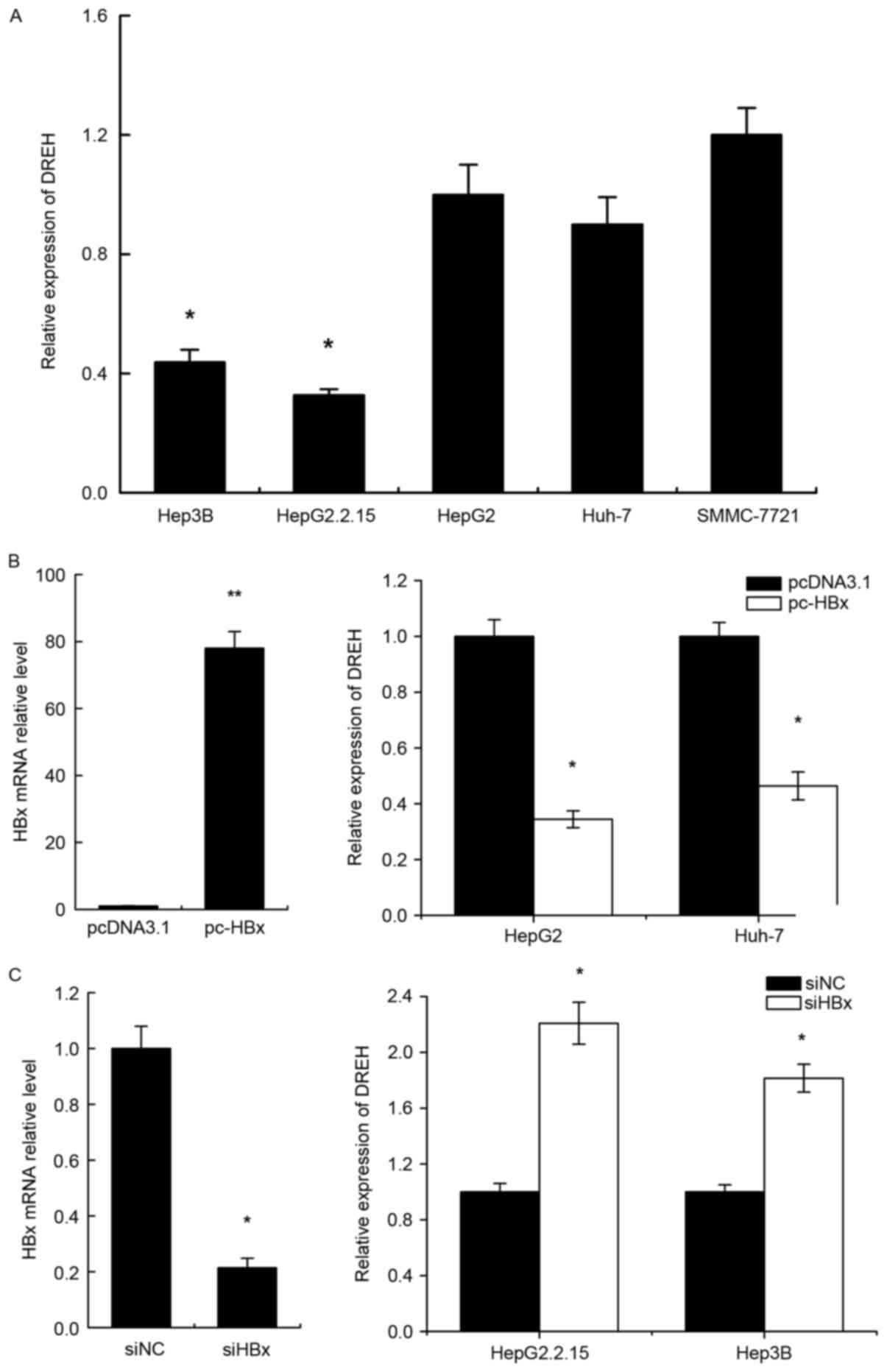
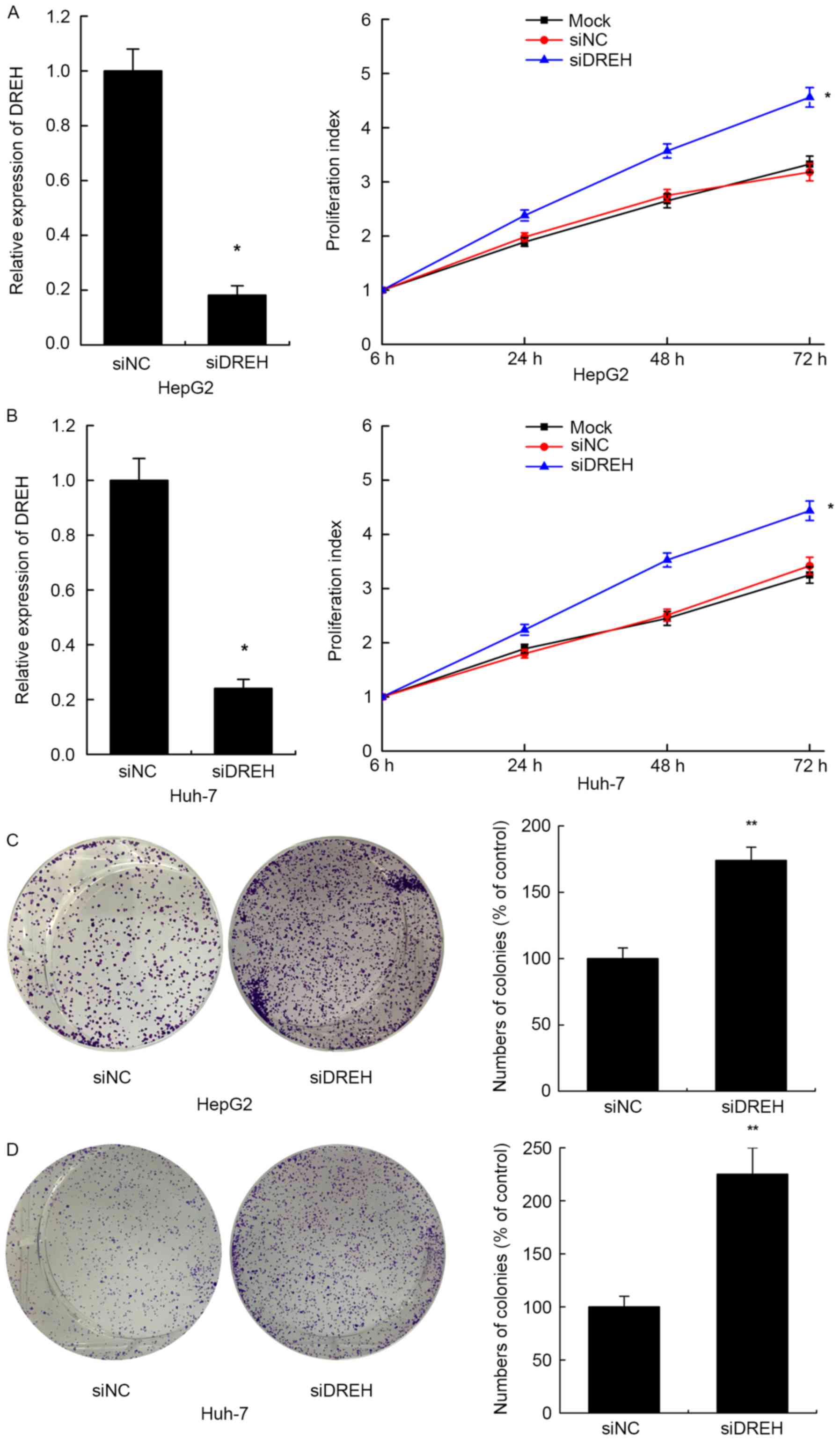
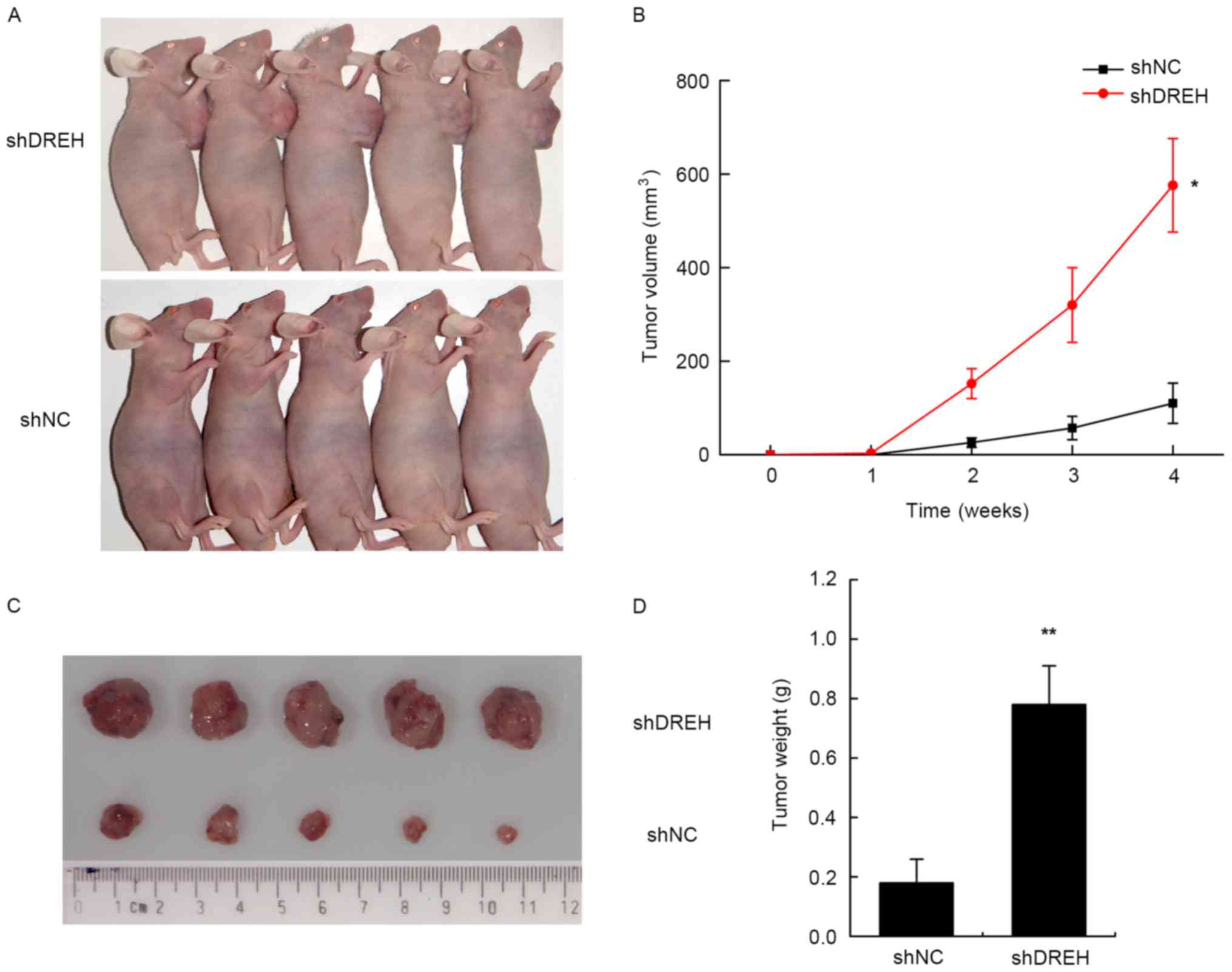
by HBx (Dreh) inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by
targeting the intermediate filament protein vimentin. Hepatology.
57:1882–1892. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Murata S, Mine T, Sugihara F, Yasui D,
Yamaguchi H, Ueda T, Onozawa S and Kumita S: Interventional
treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:13453–13465. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Margini C and Dufour JF: The story of HCC
in NAFLD: From epidemiology, across pathogenesis, to prevention and
treatment. Liver Int. 36:317–324. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Greten TF, Wang XW and Korangy F: Current
concepts of immune based treatments for patients with HCC: From
basic science to novel treatment approaches. Gut. 64:842–848. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dufour JF, Bargellini I, De Maria N, De
Simone P, Goulis I and Marinho RT: Intermediate hepatocellular
carcinoma: Current treatments and future perspectives. Ann Oncol.
24 Suppl 2:ii24–ii29. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu Y, Sarkissyan M and Vadgama JV:
Epigenetics in breast and prostate cancer. Methods Mol Biol.
1238:425–466. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kanwal R, Gupta K and Gupta S: Cancer
epigenetics: An introduction. Methods Mol Biol. 1238:3–25. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dawson MA and Kouzarides T: Cancer
epigenetics: From mechanism to therapy. Cell. 150:12–27. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang N, Ekanem NR, Sakyi CA and Ray SD:
Hepatocellular carcinoma and microRNA: New perspectives on
therapeutics and diagnostics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 81:62–74. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Batista PJ and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs: Cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell.
152:1298–1307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee JT: Epigenetic regulation by long
noncoding RNAs. Science. 338:1435–1439. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Huarte M: The emerging role of lncRNAs in
cancer. Nat Med. 21:1253–1261. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Protzer U: Hepatitis: Epigenetic control
of HBV by HBx protein-releasing the break? Nat Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 12:558–559. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Park IY, Sohn BH, Yu E, Suh DJ, Chung YH,
Lee JH, Surzycki SJ and Lee YI: Aberrant epigenetic modifications
in hepatocarcinogenesis induced by hepatitis B virus X protein.
Gastroenterology. 132:1476–1494. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|