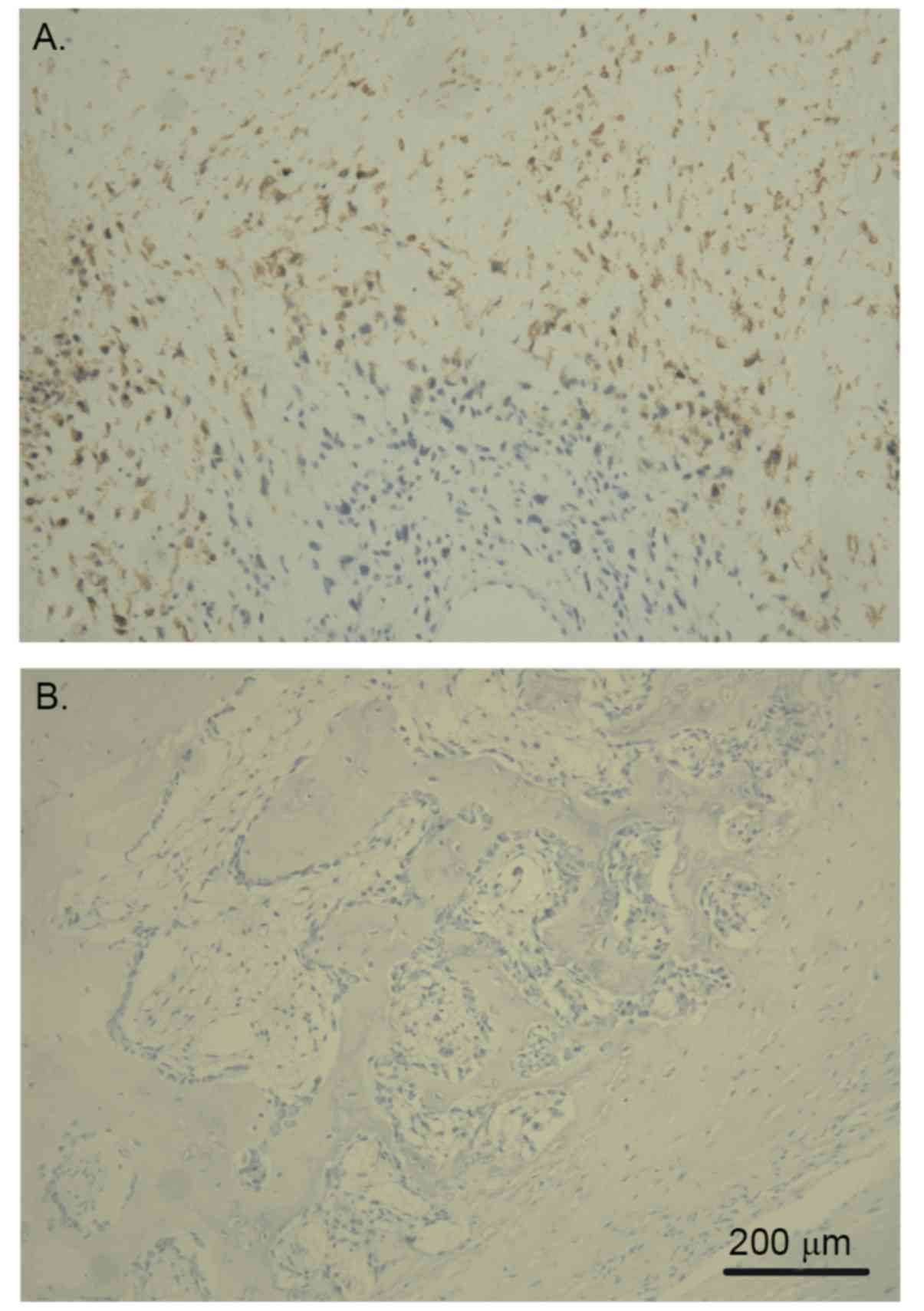
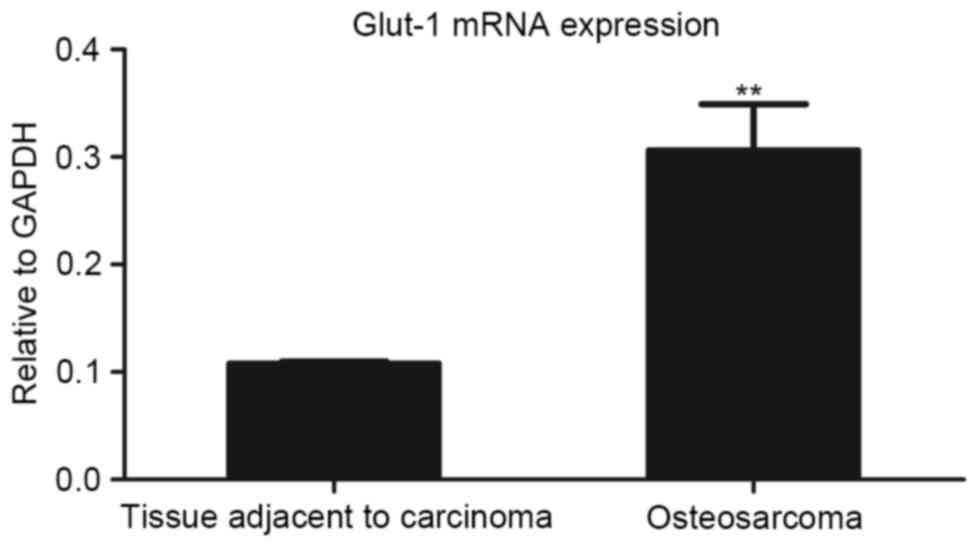
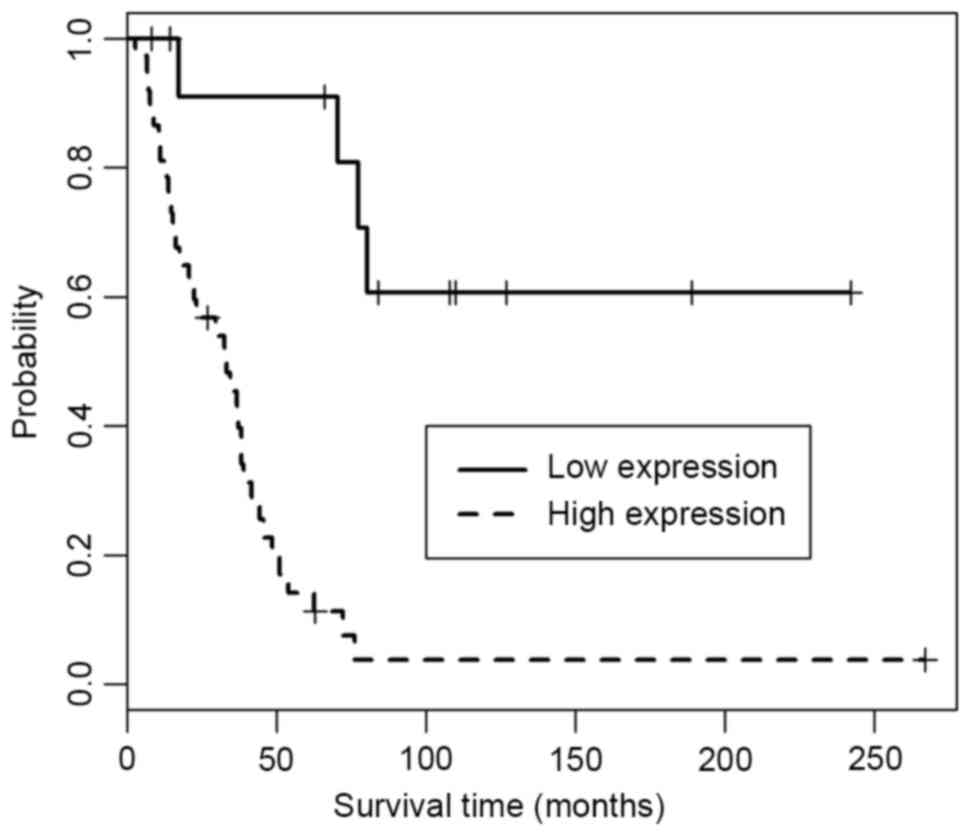
|
1
|
Arndt CA, Rose PS, Folpe AL and Laack NN:
Common musculoskeletal tumors of childhood and adolescence. Mayo
Clin Proc. 87:pp. 475–487. 2012; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mankin HJ, Hornicek FJ, Rosenberg AE,
Harmon DC and Gebhardt MC: Survival data for 648 patients with
osteosarcoma treated at one institution. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
1–291. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Longhi A, Errani C, De Paolis M, Mercuri M
and Bacci G: Primary bone osteosarcoma in the pediatric age: State
of the art. Cancer Treat Rev. 32:423–436. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Eselgrim M, Grunert H, Kühne T, Zoubek A,
Kevric M, Bürger H, Jürgens H, Mayer-Steinacker R, Gosheger G and
Bielack SS: Dose intensity of chemotherapy for osteosarcoma and
outcome in the Cooperative Osteosarcoma Study Group (COSS) trials.
Pediatr Blood Cancer. 47:42–50. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lewis IJ, Nooij MA, Whelan J, Sydes MR,
Grimer R, Hogendoorn PC, Memon MA, Weeden S, Uscinska BM, van
Glabbeke M, et al: Improvement in histologic response but not
survival in osteosarcoma patients treated with intensified
chemotherapy: A randomized phase III trial of the European
Osteosarcoma Intergroup. J Natl Cancer Inst. 99:112–128. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou SH, Fan J, Chen XM, Cheng KJ and Wang
SQ: Inhibition of cell proliferation and glucose uptake in human
laryngeal carcinoma cells by antisense oligonucleotides against
glucose transporter-1. Head Neck. 31:1624–1633. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hasegawa T, Yamamoto S, Yokoyama R, Umeda
T, Matsuno Y and Hirohashi S: Prognostic significance of grading
and staging system using MIB-1 score in adult patients with soft
tissue sarcoma of the extremities and trunk. Cancer. 95:843–851.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen J, Sun MX, Hua YQ and Cai ZD:
Prognostic significance of serum lactate dehydrogenase level in
osteosarcoma: A meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
140:1205–1210. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim MS, Lee SY, Cho WH, Song WS, Koh JS,
Lee JA, Yoo JY, Jung ST and Jeon DG: Effect of increases in tumor
volume after neoadjuvant chemotherapy on the outcome of stage II
osteosarcoma regardless of histological response. J Orthop Sci.
14:292–297. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ito H, Duxbury M, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW and
Whang EE: Glucose transporter-1 gene expression is associated with
pancreatic cancer invasiveness and MMP-2 activity. Surgery.
136:548–556. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vleugel MM, Greijer AE, Shvarts A, van der
Groep P, van Berkel M, Aarbodem Y, van Tinteren H, Harris AL, van
Diest PJ and van der Wall E: Differential prognostic impact of
hypoxia induced and diffuse HIF-1alpha expression in invasive
breast cancer. J Clin Pathol. 58:172–177. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mao ZP, Zhao LJ, Zhou SH, Liu MQ, Tan WF
and Yao HT: Expression and significance of glucose transporter-1,
P-glycoprotein, multidrug resistance-associated protein and
glutathione S-transferase-π in laryngeal carcinoma. Oncol Let.
9:806–810. 2015.
|
|
13
|
Stewart GD, Gray K, Pennington CJ, Edwards
DR, Riddick AC, Ross JA and Habib FK: Analysis of
hypoxia-associated gene expression in prostate cancer: Lysyl
oxidase and glucose transporter-1 expression correlate with Gleason
score. Oncol Rep. 20:1561–1567. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kunkel M, Reichert TE, Benz P, Lehr HA,
Jeong JH, Wieand S, Bartenstein P, Wagner W and Whiteside TL:
Overexpression of Glut-1 and increased glucose metabolism in tumors
are associated with a poor prognosis in patients with oral squamous
cell carcinoma. Cancer. 97:1015–1024. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Manolescu AR, Witkowska K, Kinnaird A,
Cessford T and Cheeseman C: Facilitated hexose transporters: New
perspectives on form and function. Physiology (Bethesda).
22:234–240. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cooper R, Sarioğlu S, Sökmen S, Füzün M,
Küpelioğlu A, Valentine H, Görken IB, Airley R and West C: Glucose
transporter-1 (GLUT-1): A potential marker of prognosis in rectal
carcinoma? Br J Cancer. 89:870–876. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Amann T, Maegdefrau U, Hartmann A, Agaimy
A, Marienhagen J, Agaimy A, Marienhagen J, Weiss TS, Stoeltzing O,
Warnecke C, et al: GLUT1 expression is increased in hepatocellular
carcinoma and promotes tumorigenesis. Am J Pathol. 174:1544–1552.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Endo M, Tateishi U, Seki K, Yamaguchi U,
Nakatani F, Kawai A, Chuman H and Beppu Y: Prognostic implications
of glucose transporter protein-1 (Glut-1) overexpression in bone
and soft-tissue sarcomas. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 37:955–960. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kubo T, Shimose S, Fujimori J, Furuta T,
Arihiro K and Ochi M: Does expression of glucose transporter
protein-1 relate to prognosis and angiogenesis in osteosarcoma?
Clin Orthop Relat Res. 473:305–310. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fan J, Zhou JQ, Yu GR and Lu DD: Glucose
transporter protein 1-targeted RNA interference inhibits growth and
invasion of the osteosarcoma cell line MG63 in vitro. Cancer
Biother Radiopharm. 25:521–527. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fan J, Yuan F, Jiong M, Zhu XZ, Yu GR and
Lu DD: Silencing of glucose transporter protein-1 by RNA
interference inhibits human osteosarcoma Mg63 cells growth in vivo.
Technol Cancer Res Treat. 14:243–248. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huvos AG: Osteogenic sarcoma: Pathologic
assessment of preoperative (neoadjuvant) chemotherapyBone Tumors:
Diagnosis, Treatment and Prognosis. 2nd. WB Saunders; Philadelphia,
PA: pp. 122–128. 1991
|
|
23
|
Enneking WF, Spanier SS and Goodman MA: A
system for the surgical staging of musculoskeletal sarcoma. Clin
Orthop Relat Res. 153:106–120. 1980.
|
|
24
|
Yarbro JW, Page DL, Fielding LP, Partridge
EE and Murphy GP: American Joint Committee on Cancer prognostic
factors consensus conference. Cancer. 86:2436–2446. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pourhoseingholi MA, Hajizadeh E, Dehkordi
B Moghimi, Safaee A, Abadi A and Zali MR: Comparing Cox regression
and parametric models for survival of patients with gastric
carcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 8:412–416. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tateishi U, Yamaguchi U, Seki K, Terauchi
T, Arai Y and Hasegawa T: Glut-1 expression and enhanced glucose
metabolism are associated with tumour grade in bone and soft tissue
sarcomas: A prospective evaluation by [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose
positron emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.
33:683–691. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sasaki H, Shitara M, Yokota K, Hikosaka Y,
Moriyama S, Yano M and Fujii Y: Overexpression of GLUT1 correlates
with Kras mutations in lung carcinomas. Med Rep. 5:599–602.
2012.
|
|
29
|
Sadlecki P, Bodnar M, Grabiec M, Marszalek
A, Walentowicz P, Sokup A, Zegarska J and Walentowicz-Sadlecka M:
The role of Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 α, glucose transporter-1,
(GLUT-1) and carbon anhydrase IX in endometrial cancer patients.
Biomed Res Int. 2014:6168502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Melstrom LG, Salabat MR, Ding XZ, Strouch
MJ, Grippo PJ, Mirzoeva S, Pelling JC and Bentrem DJ: Apigenin
down-regulates the hypoxia response genes: HIF-1α, GLUT-1, and VEGF
in human pancreatic cancer cells. J Surg Res. 167:173–181. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|