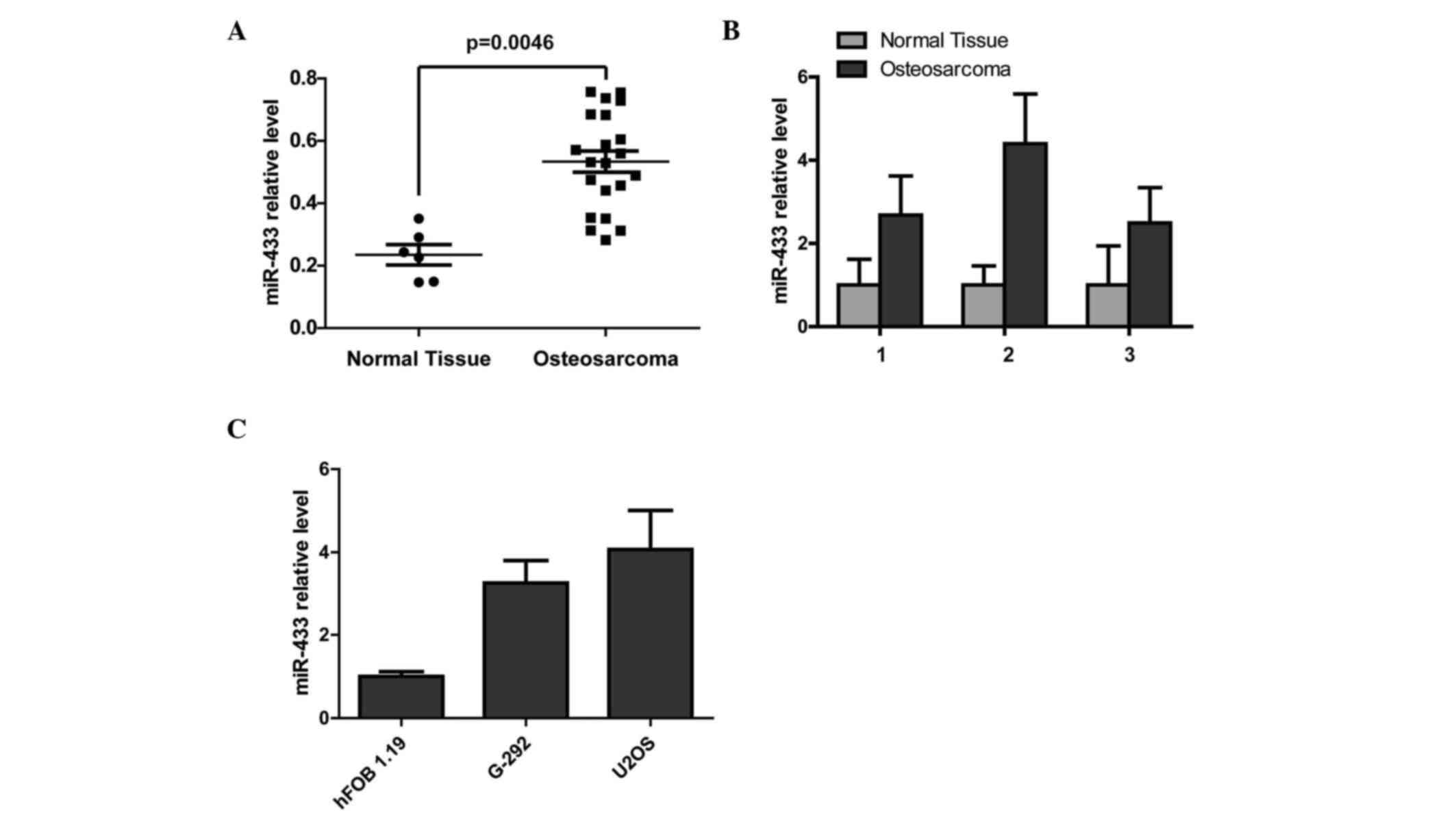
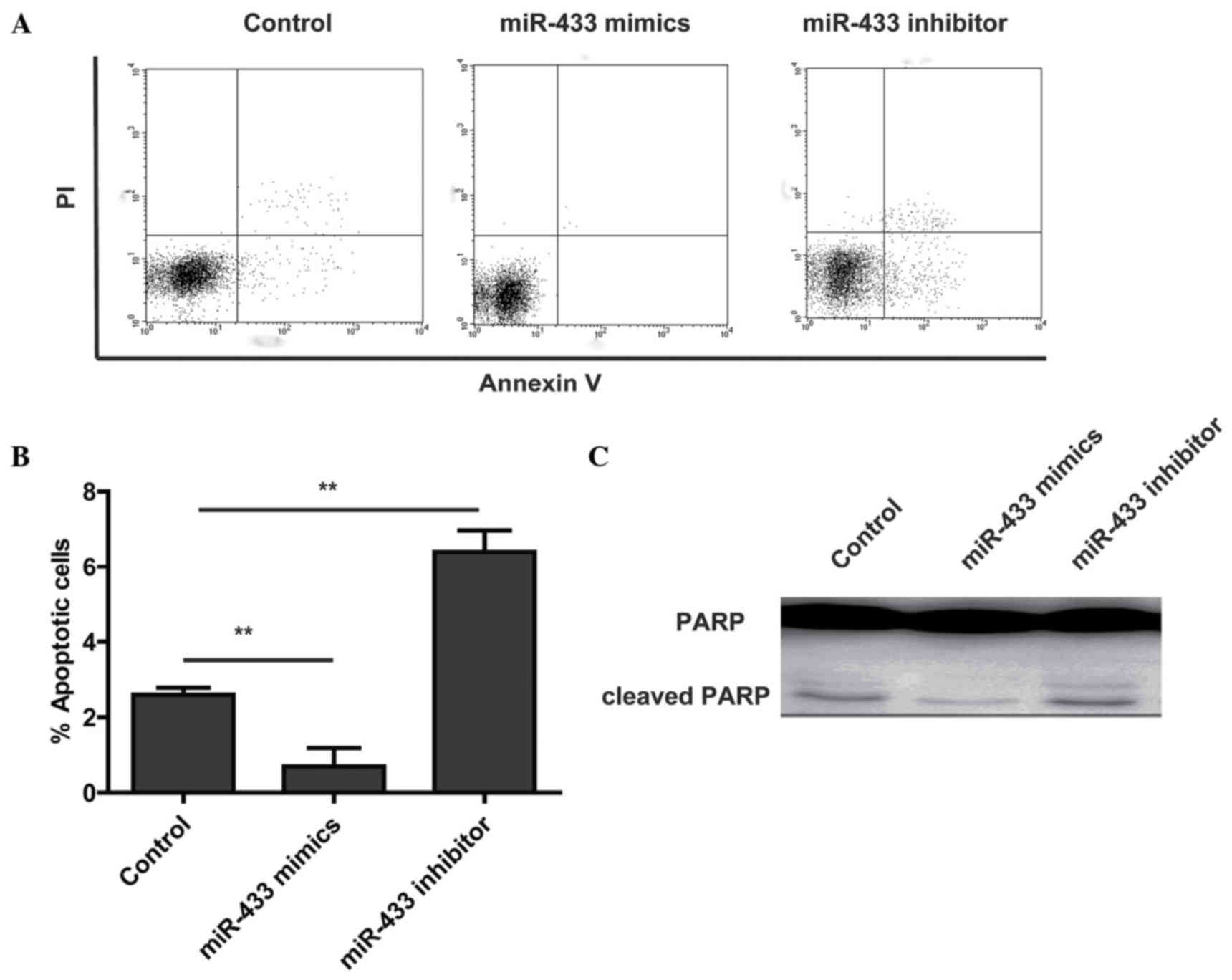
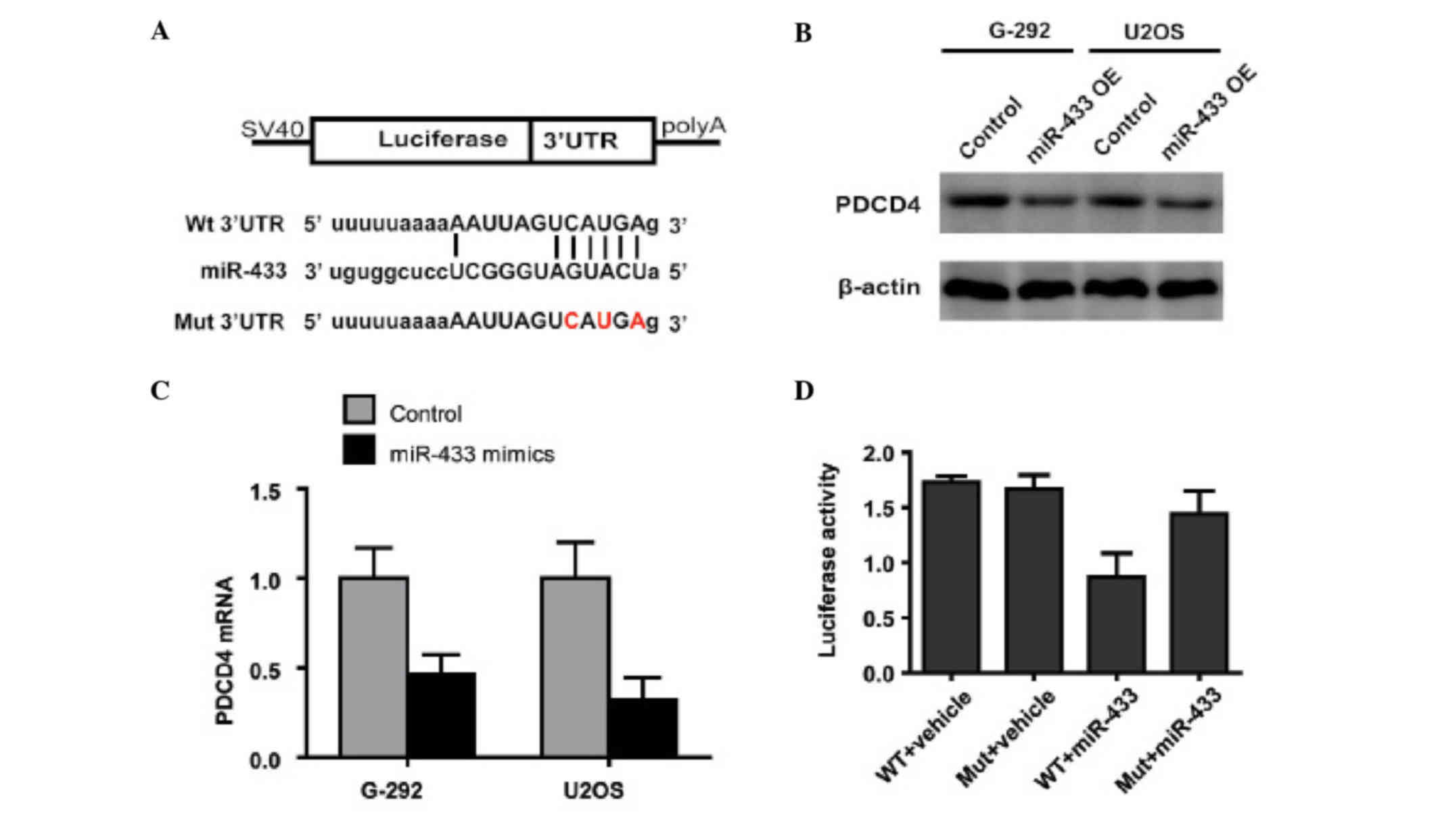
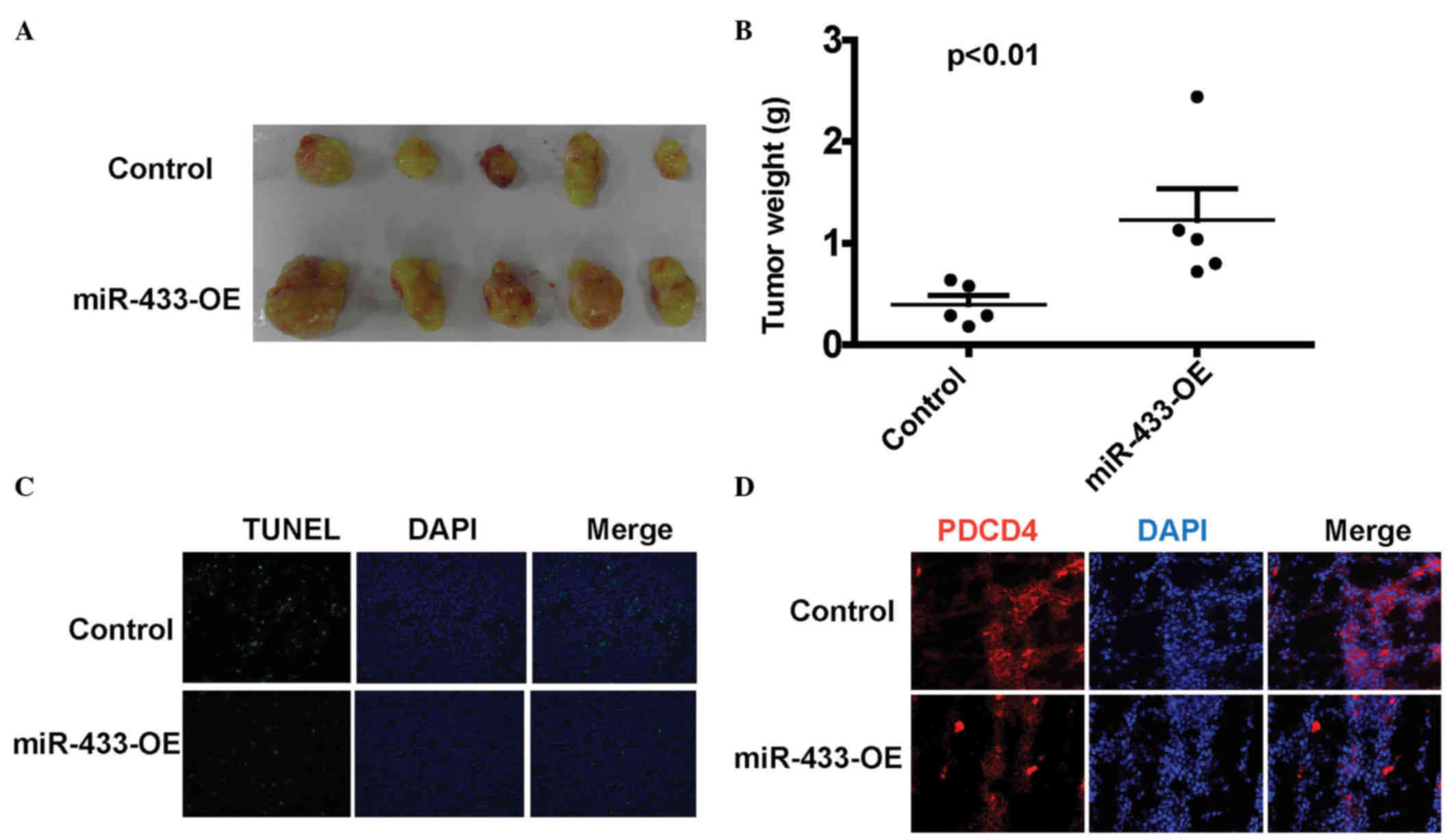
|
1
|
Ferguson WS and Goorin AM: Current
treatment of osteosarcoma. Cancer Invest. 19:292–315. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chou AJ and Gorlick R: Chemotherapy
resistance in osteosarcoma: Current challenges and future
directions. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 6:1075–1085. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Luetke A, Meyers PA, Lewis I and Juergens
H: Osteosarcoma treatment-where do we stand? A state of the art
review. Cancer Treat Rev. 40:523–532. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Aljubran AH, Griffin A, Pintilie M and
Blackstein M: Osteosarcoma in adolescents and adults: Survival
analysis with and without lung metastases. Ann Oncol. 20:1136–1141.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ghosh T, Aprea J, Nardelli J, Engel H,
Selinger C, Mombereau C, Lemonnier T, Moutkine I, Schwendimann L,
Dori M, et al: MicroRNAs establish robustness and adaptability of a
critical gene network to regulate progenitor fate decisions during
cortical neurogenesis. Cell Rep. 7:1779–1788. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mitra R, Sun J and Zhao Z: microRNA
regulation in cancer: One arm or two arms? Int J Cancer.
137:1516–1518. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Treiber T, Treiber N and Meister G:
Regulation of microRNA biogenesis and function. Thromb Haemost.
107:605–610. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guo LH, Li H, Wang F, Yu J and He JS: The
tumor suppressor roles of miR-433 and miR-127 in gastric cancer.
Int J Mol Sci. 14:14171–14184. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gotanda K, Hirota T, Matsumoto N and Ieiri
I: MicroRNA-433 negatively regulates the expression of thymidylate
synthase (TYMS) responsible for 5-fluorouracil sensitivity in HeLa
cells. BMC Cancer. 13:3692013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lin X, Rice KL, Buzzai M, Hexner E, Costa
FF, Kilpivaara O, Mullally A, Soares MB, Ebert BL, Levine R and
Licht JD: miR-433 is aberrantly expressed in myeloproliferative
neoplasms and suppresses hematopoietic cell growth and
differentiation. Leukemia. 27:344–352. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pfaffl MW: A new mathematical model for
relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res.
29:e452001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin SM, Du P, Huber W and Kibbe WA:
Model-based variance-stabilizing transformation for Illumina
microarray data. Nucleic Acids Res. 36:e112008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Luo F, Du X, Weng T, Wen X, Huang J and
Chen L: Efficient multi-site-directed mutagenesis directly from
genomic template. J Biosci. 37:965–969. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Betel D, Wilson M, Gabow A, Marks DS and
Sander C: The microRNA.org resource: targets and expression.
Nucleic Acids Res. 36:D149–D153. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lankat-Buttgereit B and Göke R: The tumour
suppressor Pdcd4: Recent advances in the elucidation of function
and regulation. Biol Cell. 101:309–317. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen X, Bahrami A, Pappo A, Easton J,
Dalton J, Hedlund E, Ellison D, Shurtleff S, Wu G, Wei L, et al:
Recurrent somatic structural variations contribute to tumorigenesis
in pediatric osteosarcoma. Cell Rep. 7:104–112. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Duong LM and Richardson LC: Descriptive
epidemiology of malignant primary osteosarcoma using
population-based registries, United States, 1999–2008. J Registry
Manag. 40:59–64. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao H, Ma B, Wang Y, Han T, Zheng L, Sun
C, Liu T, Zhang Y, Qiu X and Fan Q: miR-34a inhibits the metastasis
of osteosarcoma cells by repressing the expression of CD44. Oncol
Rep. 29:1027–1036. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang Q, Cai J, Wang J, Xiong C and Zhao J:
MiR-143 inhibits EGFR-signaling-dependent osteosarcoma invasion.
Tumour Biol. 35:12743–12748. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Song B, Wang Y, Xi Y, Kudo K, Bruheim S,
Botchkina GI, Gavin E, Wan Y, Formentini A, Kornmann M, et al:
Mechanism of chemoresistance mediated by miR-140 in human
osteosarcoma and colon cancer cells. Oncogene. 28:4065–4074. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou C, Tan W, Lv H, Gao F and Sun J4:
Hypoxia-inducible microRNA-488 regulates apoptosis by targeting Bim
in osteosarcoma. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 39:463–471. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin Z, Song D, Wei H, Yang X, Liu T, Yan W
and Xiao J: TGF-β1-induced miR-202 mediates drug resistance by
inhibiting apoptosis in human osteosarcoma. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 142:239–246. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang GC, He QY, Tong DK, Wang CF, Liu K,
Ding C, Ji F and Zhang H: MiR-367 negatively regulates apoptosis
induced by adriamycin in osteosarcoma cells by targeting KLF4. J
Bone Oncol. 5:51–56. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang Y, Duan G and Feng S: MicroRNA-301a
modulates doxorubicin resistance in osteosarcoma cells by targeting
AMP-activated protein kinase alpha 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
459:367–373. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ram Kumar RM, Boro A and Fuchs B:
Involvement and clinical aspects of microRNA in osteosarcoma. Int J
Mol Sci. 17:E8772016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kelly AD, Haibe-Kains B, Janeway KA, Hill
KE, Howe E, Goldsmith J, Kurek K, Perez-Atayde AR, Francoeur N, Fan
JB, et al: MicroRNA paraffin-based studies in osteosarcoma reveal
reproducible independent prognostic profiles at 14q32. Genome Med.
5:22013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Weiner-Gorzel K, Dempsey E, Milewska M,
McGoldrick A, Toh V, Walsh A, Lindsay S, Gubbins L, Cannon A,
Sharpe D, et al: Overexpression of the microRNA miR-433 promotes
resistance to paclitaxel through the induction of cellular
senescence in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Med. 4:745–758. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Guo LH, Li H, Wang F, Yu J and He JS: The
tumor suppressor roles of mir-433 and mir-127 in gastric cancer.
Int J Mol Sci. 14:14171–14184. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|