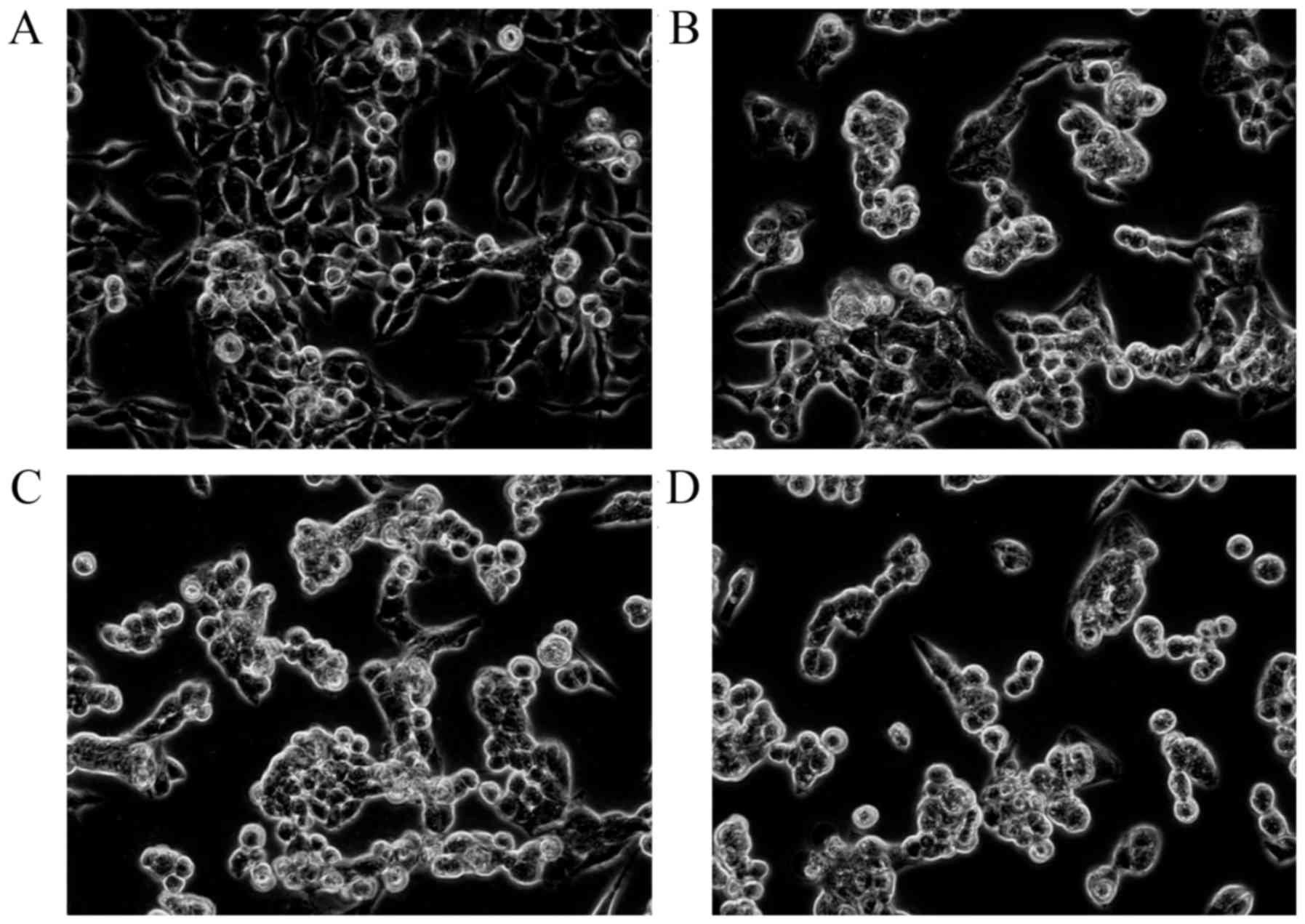
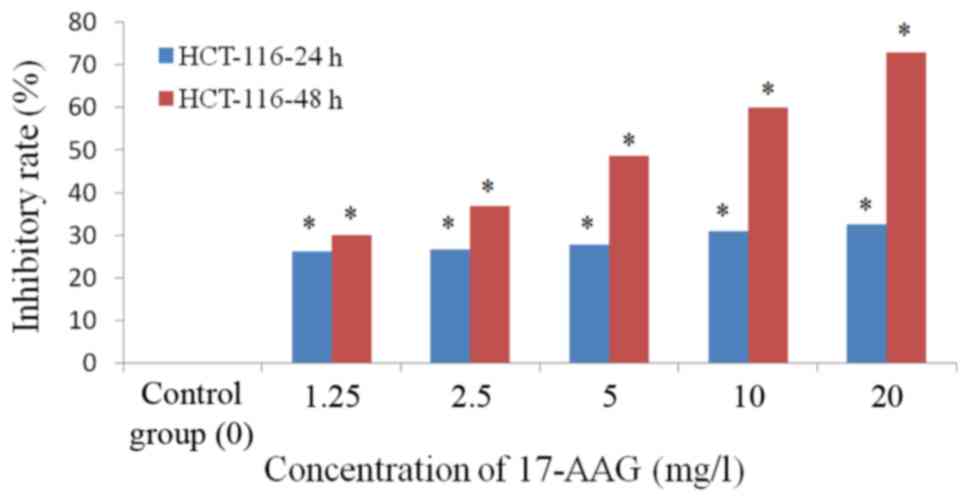
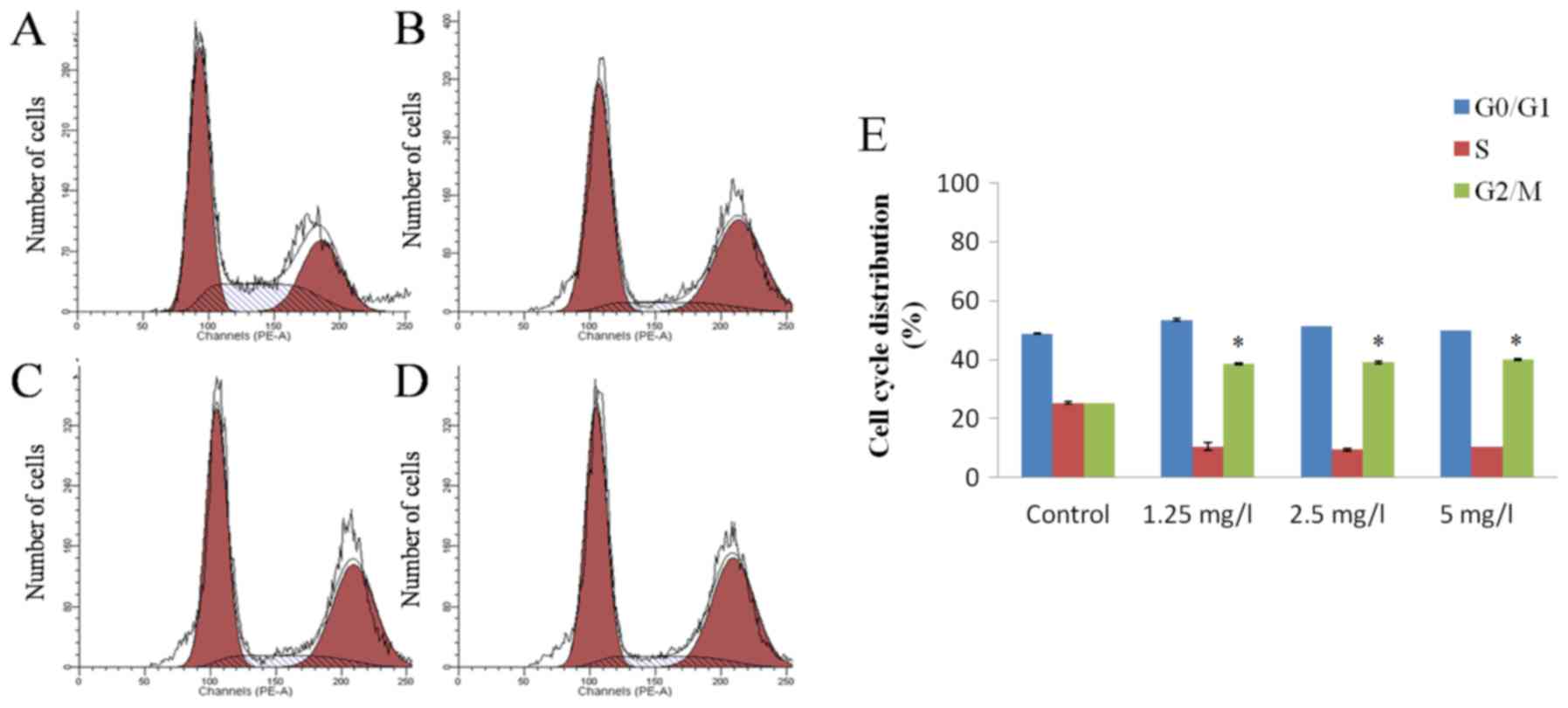
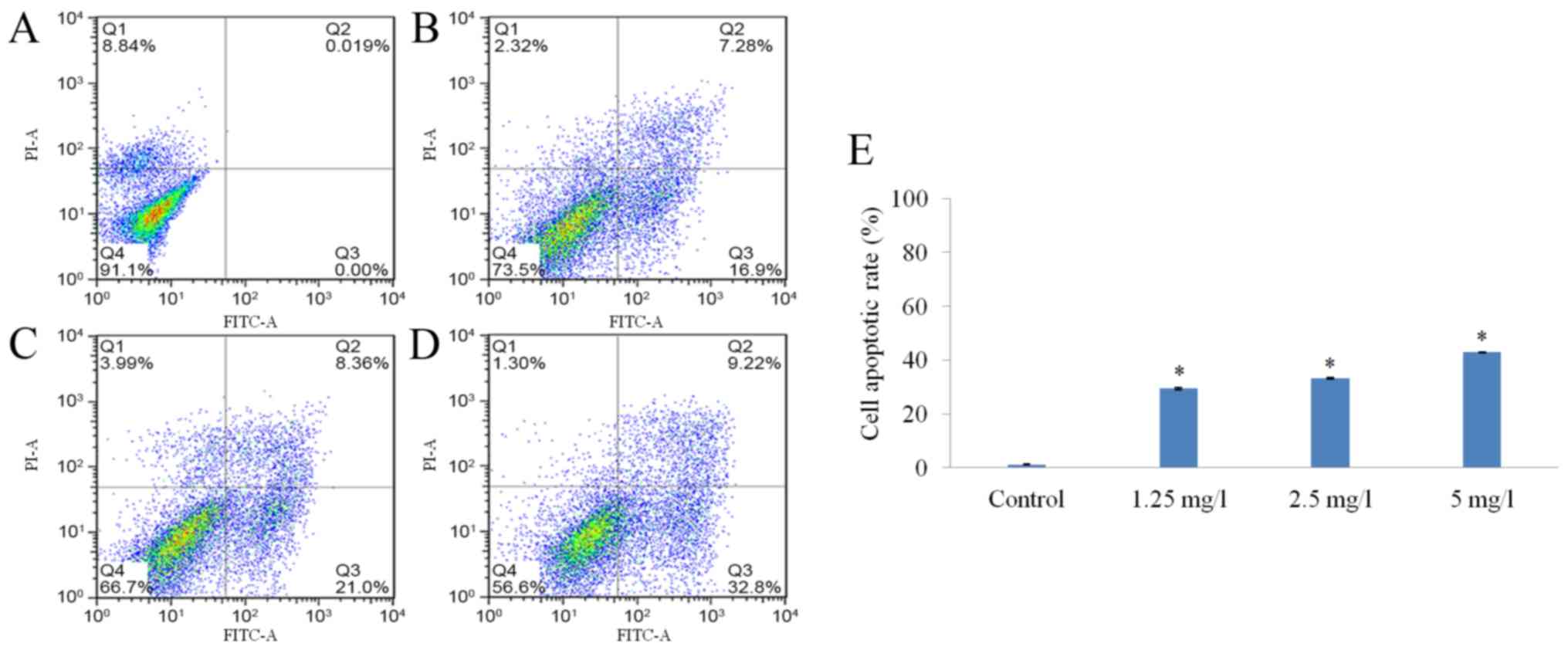
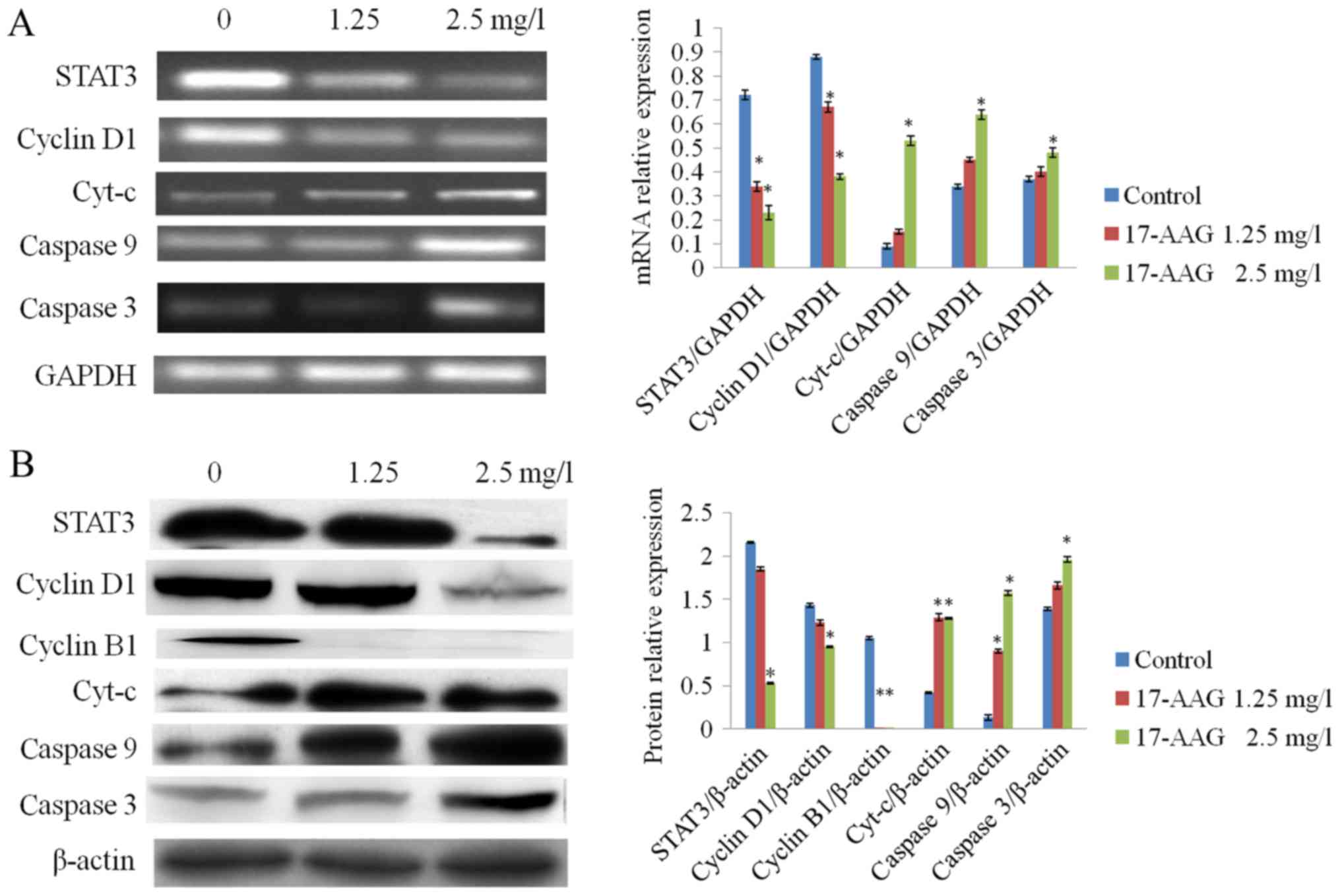
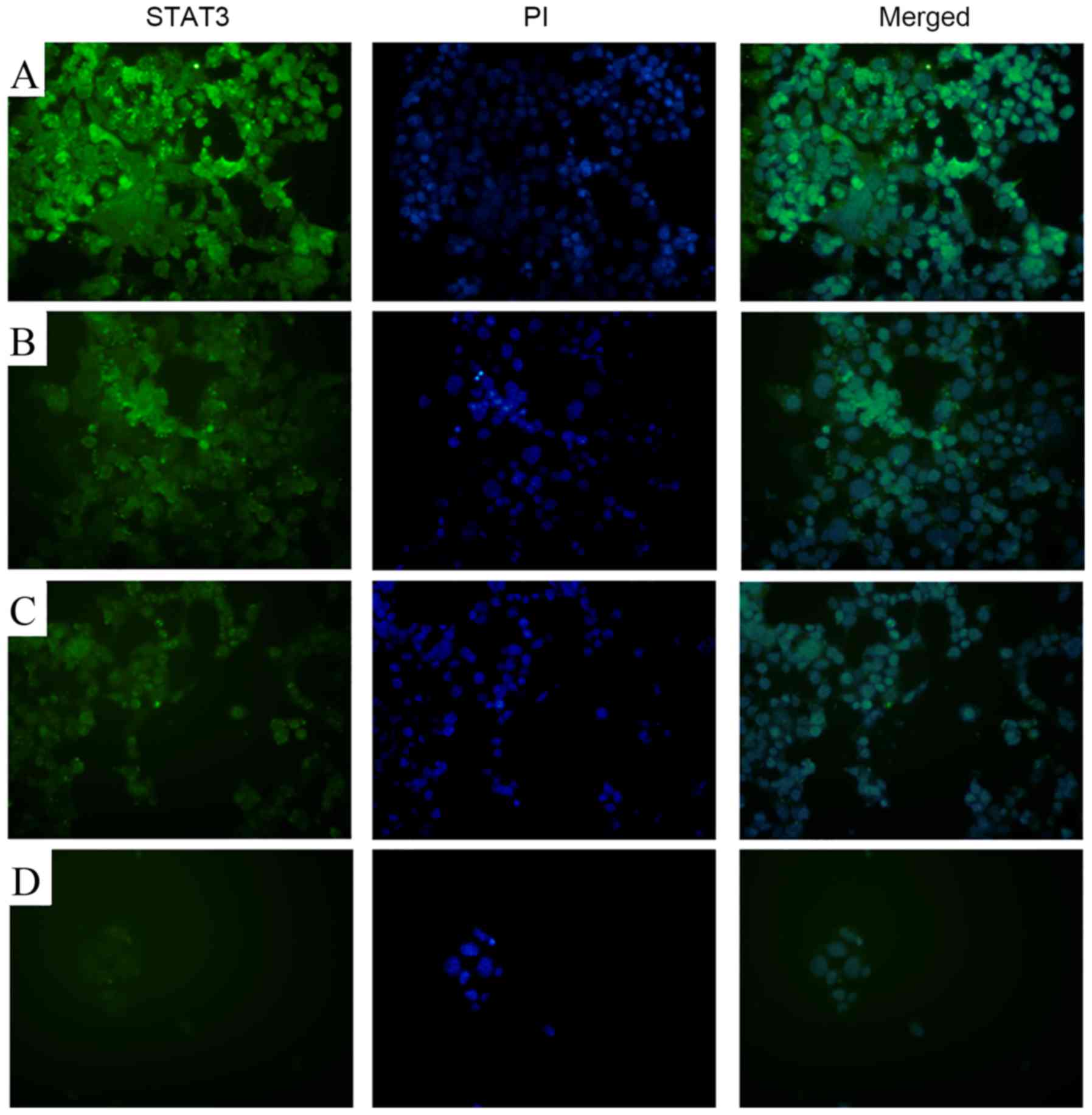
|
1
|
Haddock MG: Intraoperative radiation
therapy for colon and rectal cancers: A clinical review. Radiat
Oncol. 12:112017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Seeber A and Gastl G: Targeted therapy of
colorectal cancer. Oncol Res Treat. 39:796–802. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen G, Yang Z, Eshleman JR, Netto GJ and
Lin MT: Molecular diagnostics for precision medicine in colorectal
cancer: Current status and future perspective. Biomed Res Int.
2016:98506902016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang C, Zhang Y, Guo K, Wang N, Jin H, Liu
Y and Qin W: Heat shock proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma:
Molecular mechanism and therapeutic potential. Int J Cancer.
138:1824–1834. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dimopoulos MA, Mitsiades CS, Anderson KC
and Richardson PG: Tanespimycin as antitumor therapy. Clin Lymphoma
Myeloma Leuk. 11:17–22. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Solárová Z, Mojžiš J and Solár P: Hsp90
inhibitor as a sensitizer of cancer cells to different therapies
(Review). Int J Oncol. 46:907–926. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hong DS, Banerji U, Tavana B, George GC,
Aaron J and Kurzrock R: Targeting the molecular chaperone heat
shock protein 90 (HSP90): Lessons learned and future directions.
Cancer Treat Rev. 39:375–387. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Soroka J, Wandinger SK, Mäusbacher N,
Schreiber T, Richter K, Daub H and Buchner J: Conformational
switching of the molecular chaperone Hsp90 via regulated
phosphorylation. Mol Cell. 45:517–528. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tian YZ, Usman T, Tian KC, Di J, Huang XX,
Xu XM, Tulafu H, Wu WW, Fu XF, Bai Y, et al: Comparative study of
13 candidate genes applying multi-reference normalization to detect
the expression of different fineness in skin tissues of wool sheep.
Genet Mol Res. 16:2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kathiria AS, Neumann WL, Rhees J,
Hotchkiss E, Cheng Y, Genta RM, Meltzer SJ, Souza RF and Theiss AL:
Prohibitin attenuates colitis-associated tumorigenesis in mice by
modulating p53 and STAT3 apoptotic responses. Cancer Res.
72:5778–5789. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pimienta G, Herbert KM and Regan L: A
compound that inhibits the HOP-Hsp90 complex formation and has
unique killing effects in breast cancer cell lines. Mol Pharm.
8:2252–2261. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sharp SY, Roe SM, Kazlauskas E, Cikotienė
I, Workman P, Matulis D and Prodromou C: Cocrystalization and in
vitro biological characterization of
5-aryl-4-(5-substituted-2-4-dihydroxyphenyl)-1,2,3-thiadiazole
hsp90 inhibitors. PLoS One. 7:e446422012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Giubellino A, Sourbier C, Lee MJ,
Scroggins B, Bullova P, Landau M, Ying W, Neckers L, Trepel JB and
Pacak K: Targeting heat shock protein 90 for the treatment of
malignant pheochromocytoma. PLoS One. 8:e560832013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Barrott JJ and Haystead TA: Hsp90, an
unlikely ally in the war on cancer. FEBS J. 280:1381–1396. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ye XY, Luo QQ, Xu YH, Tang NW, Niu XM, Li
ZM, Shen SP, Lu S and Chen ZW: 17-AAG suppresses growth and
invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells via regulation of the
LATS1/YAP pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 19:651–663. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Guo W, Siegel D and Ross D: Stability of
the Hsp90 inhibitor 17AAG hydroquinone and prevention of
metal-catalyzed oxidation. J Pharm Sci. 97:5147–5157. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mita AC, Mita MM, Nawrocki ST and Giles
FJ: Survivin: Key regulator of mitosis and apoptosis and novel
target for cancer therapeutics. Clin Cancer Res. 14:5000–5005.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ambrosini G, Adida C and Altieri DC: A
novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and
lymphoma. Nat Med. 3:917–921. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yao JQ, Liu QH, Chen X, Yang Q, Xu ZY, Hu
F, Wang L and Li JM: Hsp90 inhibitor
17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin inhibits the proliferation
of ARPE-19 cells. J Biomed Sci. 17:302010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Napper JM and Sollars VE:
17-N-Allylamino-17-demeth-oxygeldanamycin induces a diverse
response in human acute myelogenous cells. Leuk Res. 34:1493–1500.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen M, Xu J and Zhao J: Effects of HSP90
inhibitor 17-AAG on cell cycle and apoptosis of human gastric
cancer cell lines SGC-7901. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao.
33:271–275. 2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Watanabe G, Behrns KE, Kim JS and Kim RD:
Heat shock protein 90 inhibition abrogates heaptocellular cancer
growth through cdc2-mediated G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
Cancer Chemother PHarmacol. 64:433–443. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Karkoulis PK, Stravopodis DJ, Margaritis
LH and Voutsinas GE: 17-Allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin induces
downregulation of critical Hsp90 protein clients and results in
cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of human urinary bladder cancer
cells. BMC Cancer. 10:4812010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mikhail S, Albanese C and Pishvaian MJ:
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors and the treatment of
gastrointestinal cancers. Am J Pathol. 185:1185–1197. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Swaffer MP, Jones AW, Flynn HR, Snijders
AP and Nurse P: CDK substrate phosphorylation and ordering the cell
cycle. Cell. 167:1750–1761.e16. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bilal I, Chowdhury A, Davidson J and
Whitehead S: Phytoestrogens and prevention of breast cancer: The
contentious debate. World J Clin Oncol. 5:705–712. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Poli A, Ramazzotti G, Matteucci A, Manzoli
L, Lonetti A, Suh PG, McCubrey JA and Cocco L: A novel
DAG-dependent mechanism links PKCa and Cyclin B1 regulating cell
cycle progression. Oncotarget. 5:11526–11540. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gong D and Ferrell JE Jr: The roles of
Cyclin A2, B1, and B2 in early and late mitotic events. Mol Biol
Cell. 21:3149–3161. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Powers MV, Valenti M, Miranda S, Maloney
A, Eccles SA, Thomas G, Clarke PA and Workman P: Mode of cell death
induced by the HSP90 inhibitor 17-AAG (tanespimycin) is dependent
on the expression of pro-apoptotic BAX. Oncotarget. 4:1963–1975.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Matos AJ and Santos AA: Advances in the
understanding of the clinically relevant genetic pathways and
molecular aspects of canine mammary tumours: Part 1. Proliferation,
apoptosis and DNA repair. Vet J. 205:136–143. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guicciardi ME, Malhi H, Mott JL and Gores
GJ: Apoptosis and necrosis in the liver. Compr Physiol. 3:977–1010.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
McCracken JM and Allen LA: Regulation of
human neutrophil apoptosis and lifespan in health and disease. J
Cell Death. 7:15–23. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Apostolova N and Victor VM: Molecular
Strategies for targeting antioxidants to mitochondria: Therapeutic
implications. Antioxid Redox Signal. 22:686–729. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hilgendorf KI, Leshchiner ES, Nedelcu S,
Maynard MA, Calo E, Ianari A, Walensky LD and Lees JA: The
retinoblastoma protein induces apoptosis directly at the
mitochondria. Genes Dev. 27:1003–1015. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hassan M, Watari H, AbuAlmaaty A, Ohba Y
and Sakuragi N: Apoptosis and molecular targeting therapy in
cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2014:1508452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hong S, Mehta KP and Laimins LA:
Suppression of STAT-1 expression by human papillomaviruses is
necessary for differentiation-dependent genome amplification and
plasmid Maintenance. J Virol. 85:9486–1994. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kamran MZ, Patil P and Gude RP: Role of
STAT3 in cancer metastasis and translational advances. Biomed Res
Int. 2013:4218212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yuan J, Zhang F and Niu R: Multiple
regulation pathways and pivotal biological functions of STAT3 in
cancer. Sci Rep. 5:176632015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Giordano C, Vizza D, Panza S, Barone I,
Bonofiglio D, Lanzino M, Sisci D, De Amicis F, Fuqua SA, Catalano S
and Andò S: Leptin increases HER2 protein levels through a
STAT3-mediated up-regulation of Hsp90 in breast cancer cells. Mol
Oncol. 7:379–391. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Huang W, Dong Z, Wang F, Peng H, Liu JY
and Zhang JT: A small molecule compound targeting STAT3 DNA-binding
domain inhibits cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion.
ACS Chem Biol. 9:1188–1196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li Y, Guo G, Song J, Cai Z, Yang J, Chen
Z, Wang Y, Huang Y and Gao Q: B7-H3 promotes the migration and
invasion of human bladder cancer cells via the PI3K/Akt/STAT3
signaling Pathway. J Cancer. 8:816–824. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chaudhari N, Talwar P, Parimisetty A,
d'Hellencourt C Lefebvre and Ravanan P: A molecular web:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress, inflammation, and oxidative stress.
Front Cell Neurosci. 8:2132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Qin A, Yu Q, Gao Y, Tan J, Huang H, Qiao Z
and Qian W: Inhibition of STAT3/cyclinD1 pathway promotes
chemotherapeutic sensitivity of colorectal caner. Biochem BiopHys
Res Commun. 457:681–687. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kamran MZ, Patil P and Gude RP: Role of
STAT3 in cancer metastasis and translational advances. Biomed Res
Int. 2013:4218212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cimica V, Chen HC, Iyer JK and Reich NC:
Dynamics of the STAT3 transcription factor: Nuclear import
dependent on ran and importin-β1. PLoS One. 6:e201882011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Duan J, Jiang XP, Li MQ, Fan DX, Wang Y,
Li DJ and Jin LP: Thymic stromal lympHopoietin suppresses the
apoptosis of decidual gamma-delta T cells via regulation of the
signal transduction and activation of transcription 3/caspase-3
signaling pathway. Am J Reprod Immunol. 70:464–471. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhu Y, Doornebal EJ, Pirtskhalava T,
Giorgadze N, Wentworth M, Fuhrmann-Stroissnigg H, Niedernhofer LJ,
Robbins PD, Tchkonia T and Kirkland JL: New agents that target
senescent cells: The flavone, fisetin, and the BCL-XL inhibitors,
A1331852 and A1155463. Aging (Albany NY). 9:955–963.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Do DV, Ueda J, Messerschmidt DM,
Lorthongpanich C, Zhou Y, Feng B, Guo G, Lin PJ, Hossain MZ, Zhang
W, et al: A genetic and developmental pathway from STAT3 to the
OCT4-NANOG circuit is essential for maintenance of ICM lineages in
vivo. Genes Dev. 27:1378–1390. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ren Z, Zou W, Cui J, Liu L, Qing Y and Li
Y: Geraniin suppresses tumor cell growth and triggers apoptosis in
human glioma via inhibition of STAT3 signaling. Cytotechnology.
2017.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Carbognin E, Betto RM, Soriano ME, Smith
AG and Martello G: Stat3 promotes mitochondrial transcription and
oxidative respiration during maintenance and induction of naive
pluripotency. EMBO J. 35:618–634. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|