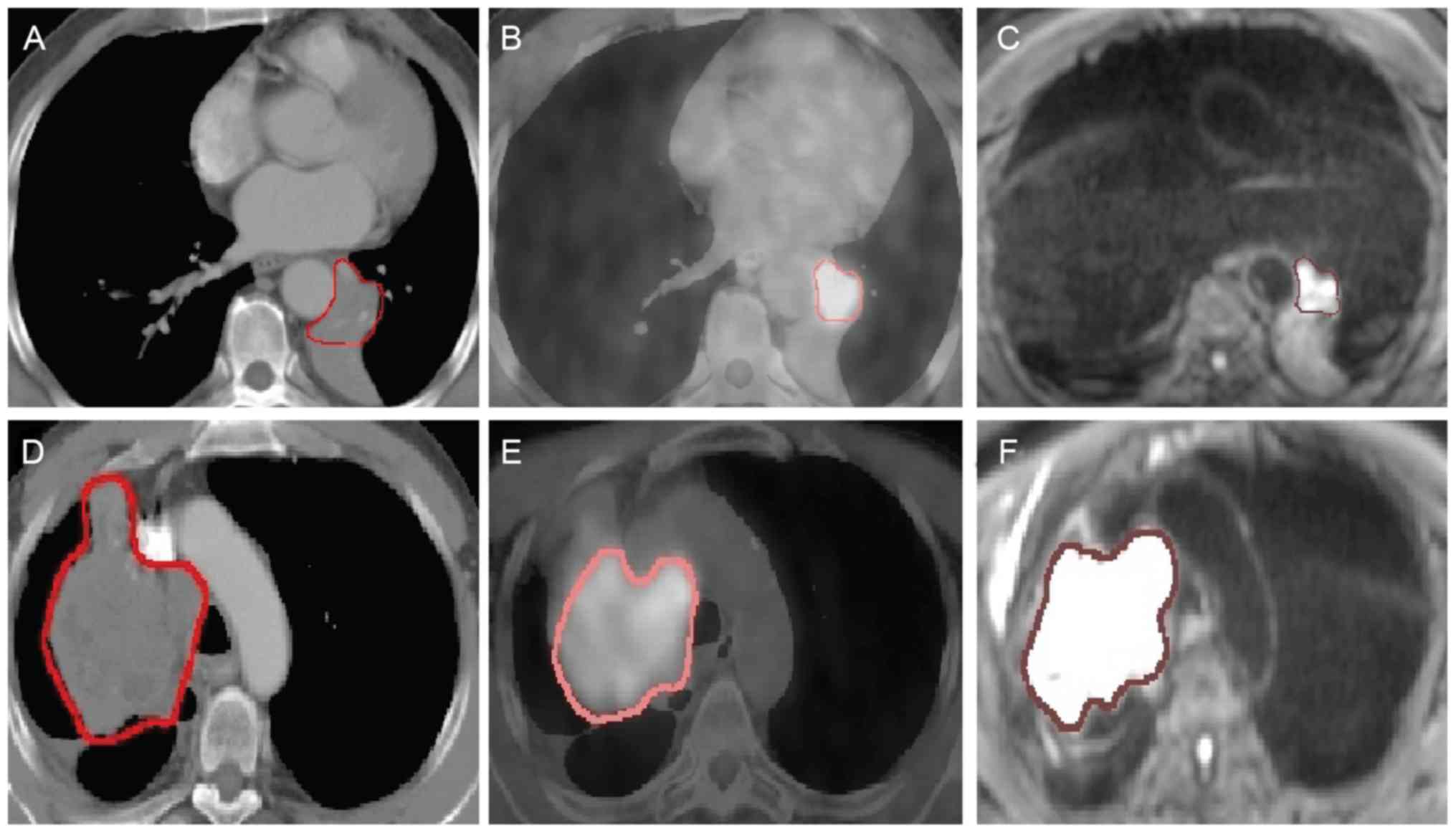
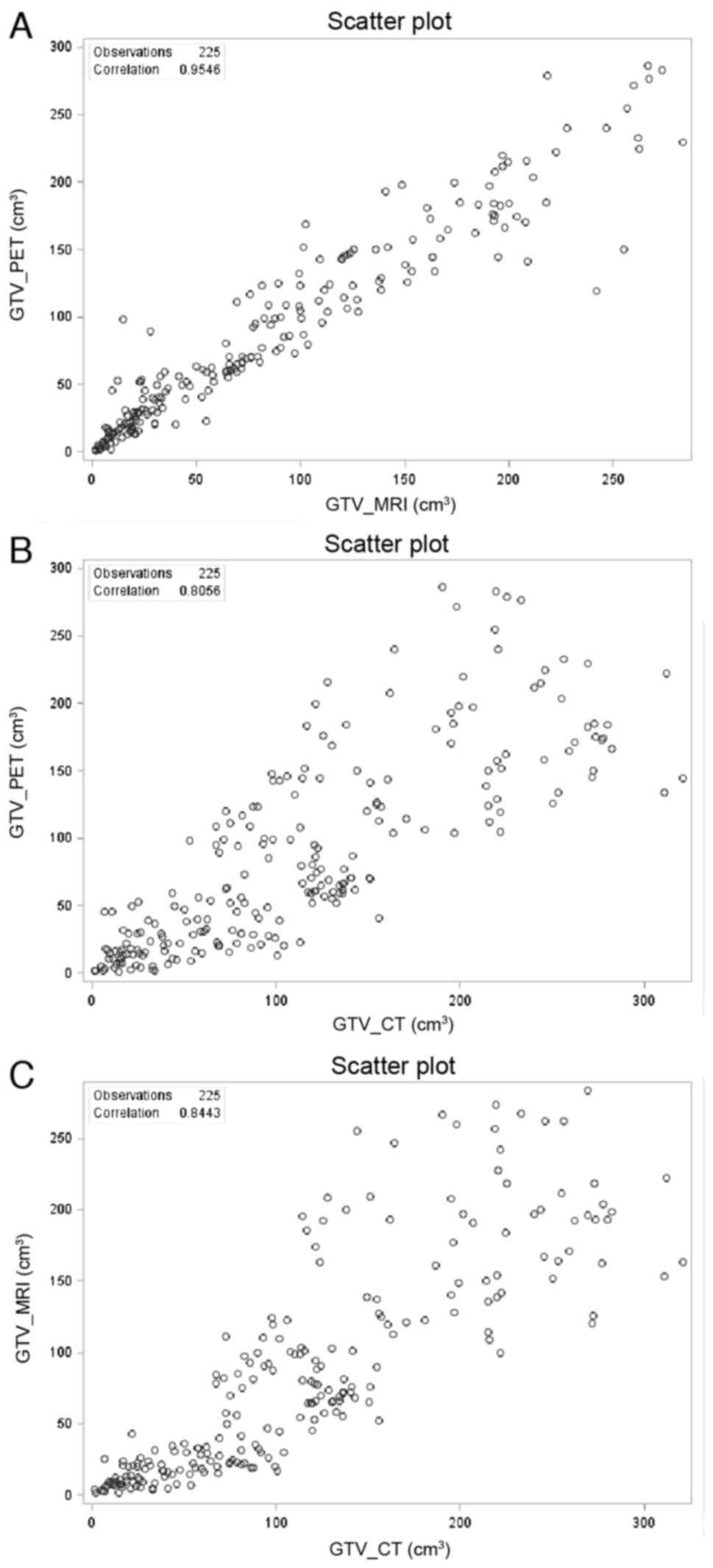
|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Senan S and De Ruysscher D: Critical
review of PET-CT for radiotherapy planning in lung cancer. Crit Rev
Oncol Hematol. 56:345–351. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dwamena BA, Sonnad SS, Angobaldo JO and
Wahl RL: Metastases from non-small cell lung cancer: Mediastinal
staging in the 1990s-meta-analytic comparison of PET and CT.
Radiology. 213:530–536. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Devic S: MRI simulation for radiotherapy
treatment planning. Med Phys. 39:6701–6711. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Toloza EM, Harpole L and McCrory DC:
Noninvasive staging of non-small cell lung cancer: A review of the
current evidence. Chest. 123 1 Suppl:137S–146S. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gould MK, Kuschner WG, Rydzak CE, Maclean
CC, Demas AN, Shigemitsu H, Chan JK and Owens DK: Test performance
of positron emission tomography and computed tomography for
mediastinal staging in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: A
meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 139:879–892. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Roberts PF, Follette DM, von Haag D, Park
JA, Valk PE, Pounds TR and Hopkins DM: Factors associated with
false-positive staging of lung cancer by positron emission
tomography. Ann Thorac Surg. 70:1154–1160. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Silvestri GA, Gould MK, Margolis ML,
Tanoue LT, McCrory D, Toloza E and Detterbeck F: American College
of Chest Physicians: Noninvasive staging of non-small cell lung
cancer: ACCP evidenced-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd
edition). Chest. 132 3 Suppl:178S–201S. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Al-Jahdali H, Khan AN, Loutfi S and
Al-Harbi AS: Guidelines for the role of FDG-PET/CT in lung cancer
management. J Infect Public Health. 5 Suppl 1:S35–S40. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Aristei C, Falcinelli L, Palumbo B and
Tarducci R: PET and PET-CT in radiation treatment planning for lung
cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 10:571–584. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Aubin
ML, Vignaud J and Laval-Jeantet M: Separation of diffusion and
perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology.
168:497–505. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Usuda K, Zhao XT, Sagawa M, Matoba M,
Kuginuki Y, Taniguchi M, Ueda Y and Sakuma T: Diffusion-weighted
imaging is superior to positron emission tomography in the
detection and nodal assessment of lung cancers. Ann Thorac Surg.
91:1689–1695. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Komori T, Narabayashi I, Matsumura K,
Matsuki M, Akagi H, Ogura Y, Aga F and Adachi I:
2-[Fluorine-18]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission
tomography/computed tomography versus whole-body diffusion-weighted
MRI for detection of malignant lesions: Initial experience. Ann
Nucl Med. 21:209–215. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nomori H, Mori T, Ikeda K, Kawanaka K,
Shiraishi S, Katahira K and Yamashita Y: Diffusion-weighted
magnetic resonance imaging can be used in place of positron
emission tomography for N staging of non-small cell lung cancer
with fewer false-positive results. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
135:816–822. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Klingensmith WC III, Perlman D and Baum K:
Intrapatient comparison of 2-deoxy-2-[F-18]fluoro-D-glucose with
positron emissiontomography/computed tomography to Tc-99 m
fanolesomab (NeutroSpec) for localization of infection. Mol Imaging
Biol. 9:295–299. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Subesinghe M, Scarsbrook AF, Sourbron S,
Wilson DJ, McDermott G, Speight R, Roberts N, Carey B, Forrester R,
Gopal SV, et al: Alterations in anatomic and functional imaging
parameters with repeated FDG PET-CT and MRI during radiotherapy for
head and neck cancer: A pilot study. BMC Cancer. 15:1372015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sander L, Langkilde NC, Holmberg M and
Carl J: MRI target delineation may reduce long-term toxicity after
prostate radiotherapy. Acta Oncol. 53:809–814. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Navarria P, Reggiori G, Pessina F,
Ascolese AM, Tomatis S, Mancosu P, Lobefalo F, Clerici E, Lopci E,
Bizzi A, et al: Investigation on the role of integrated PET/MRI for
target volume definition and radiotherapy planning in patients with
high grade glioma. Radiother Oncol. 112:425–429. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Karnofsky DA, Abelman WH, Craver LF and
Burchenal JH: The use of nitrogen mustards in the palliative
treatment of carcinoma. With particular reference to bronchogenic
carcinoma. Cancer. 1:634–656. 1948. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Qi LP, Zhang XP, Tang L, Li J, Sun YS and
Zhu GY: Using diffusion-weighted MR imaging for tumor detection in
the collapsed lung: A preliminary study. Eur Radiol. 19:333–341.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang RM, Li L, Wei XH, Guo YM, Huang YH,
Lai LS, Chen AM, Liu GS, Xiong WF, Luo LP and Jiang XQ:
Differentiation of central lung cancer from atelectasis: Comparison
of diffusion-weighted MRI with PET/CT. PLoS One. 8:e602792013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Onitsuka H, Tsukuda M, Araki A, Murakami
J, Torii Y and Masuda K: Differentiation of central lung tumor from
postobstructive lobar collapse by rapid sequence computed
tomography. J Thorac Imaging. 6:28–31. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
McAdams HP, Erasums JJ, Patz EF, Goodman
PC and Coleman RE: Evaluation of patients with round atelectasis
using 2-[18F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose PET. J Comput Assist Tomogr.
22:601–604. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schmidt S, Nestle U, Walter K, Licht N,
Ukena D, Schnabel K and Kirsch CM: Optimization of radiotherapy
planning for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) using 18FDG-PET.
Nuklearmedizin. 41:217–220. 2002.(In German). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Senan S, van Sörnsen de Koste J, Samson M,
Tankink H, Jansen P, Nowak PJ, Krol AD, Schmitz P and Lagerwaard
FJ: Evaluation of a target contouring protocol for 3D conformal
radiotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol.
53:247–255. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Van de Steene J, Linthout N, de Mey J,
Vinh-Hung V, Claassens C, Noppen M, Bel A and Storme G: Definition
of gross tumor volume in lung cancer: Inter-observer variability.
Radiother Oncol. 62:37–49. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Al-Jahdali H, Khan AN, Loutfi S and
Al-Harbi AS: Guidelines for the role of FDG-PET/CT in lung cancer
management. J Infect Public Health. 5 Suppl 1:S35–S40. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ling CC, Humm J, Larson S, Amols H, Fuks
Z, Leibel S and Koutcher JA: Towards multidimensional radiotherapy
(MD-CRT): Biological imaging and biological conformality. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 47:551–560. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gao Z, Wilkins D, Eapen L, Morash C,
Wassef Y and Gerig L: A study of prostate delineation referenced
against a gold standard created from the visible human data.
Radiother Oncol. 85:239–246. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
McLaughlin PW, Evans C, Feng M and
Narayana V: Radiographic and anatomic basis for prostate contouring
errors and methods to improve prostate contouring accuracy. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 76:369–378. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Seppälä T, Visapää H, Collan J, Kapanen M,
Beule A, Kouri M, Tenhunen M and Saarilahti K: Converting from CT-
to MRI-only-based target definition in radiotherapy of localized
prostate cancer: A comparison between two modalities. Strahlenther
Onkol. 191:862–868. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bradley J, Bae K, Choi N, Forster K,
Siegel BA, Brunetti J, Purdy J, Faria S, Vu T, Thorstad W and Choy
H: A phase II comparative study of gross tumor volume definition
with or without PET/CT fusion in dosimetric planning for
non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Primary analysis of radiation
therapy oncology group (RTOG) 0515. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
82:435–41.e1. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tyng CJ, Chojniak R, Pinto PN, Borba MA,
Bitencourt AG, Fogaroli RC, Castro DG and Novaes PE: Conformal
radiotherapy for lung cancer: Interobservers' variability in the
definition of gross tumor volume between radiologists and
radiotherapists. Radiat Oncol. 4:282009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rodríguez N, Sanz X, Trampal C, Foro P,
Reig A, Lacruz M, Membrive I, Lozano J, Quera J and Algara M:
18F-FDG PET definition of gross tumor volume for radiotherapy of
lung cancer: Is the tumor uptake value-based approach appropriate
for lymph node delineation? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
78:659–666. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|