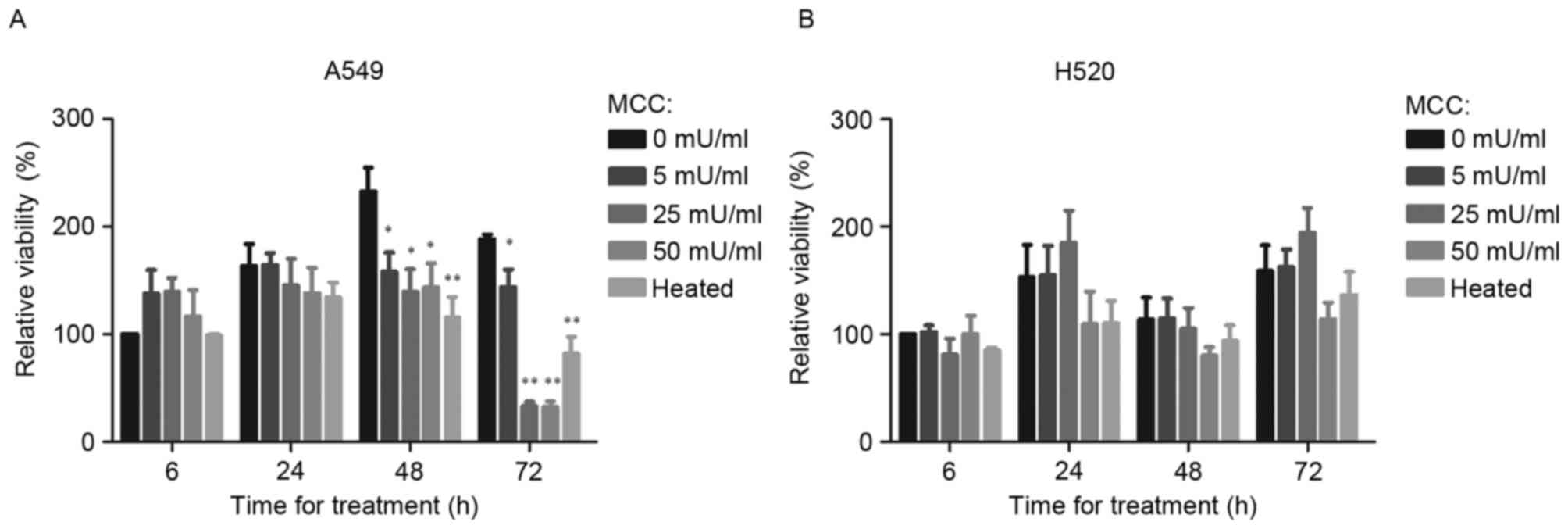
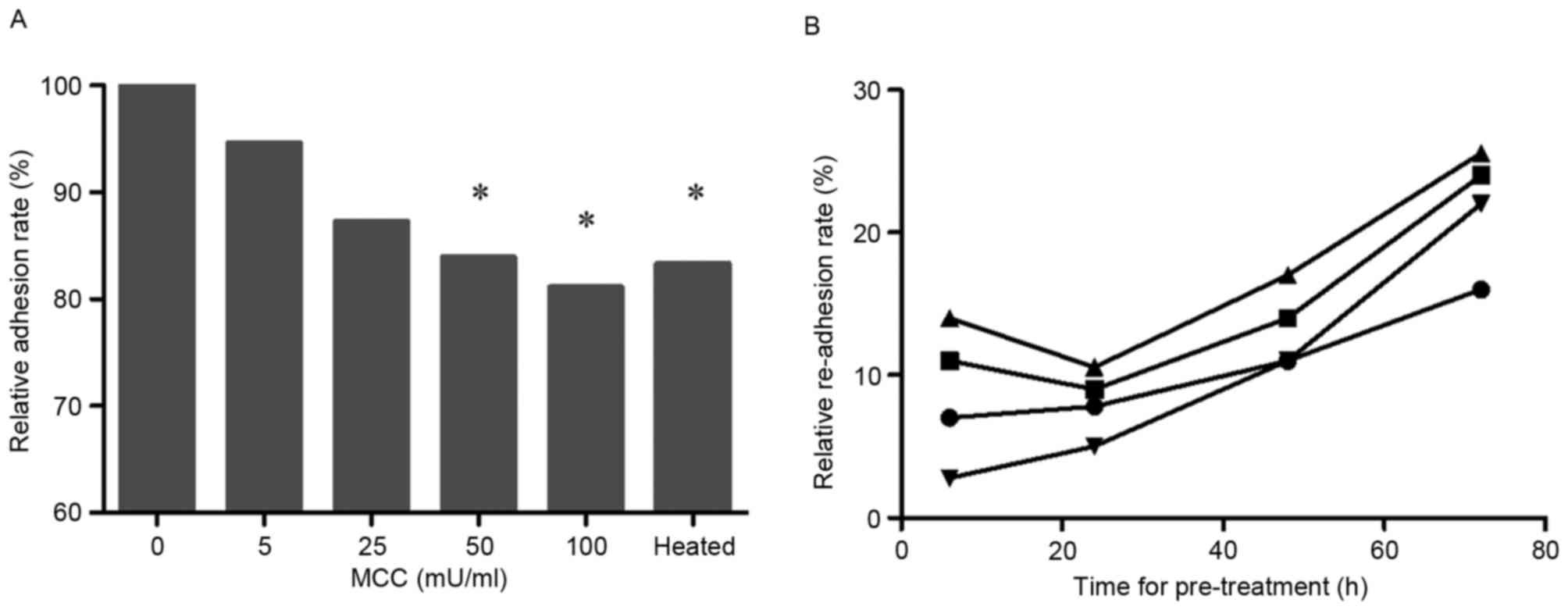
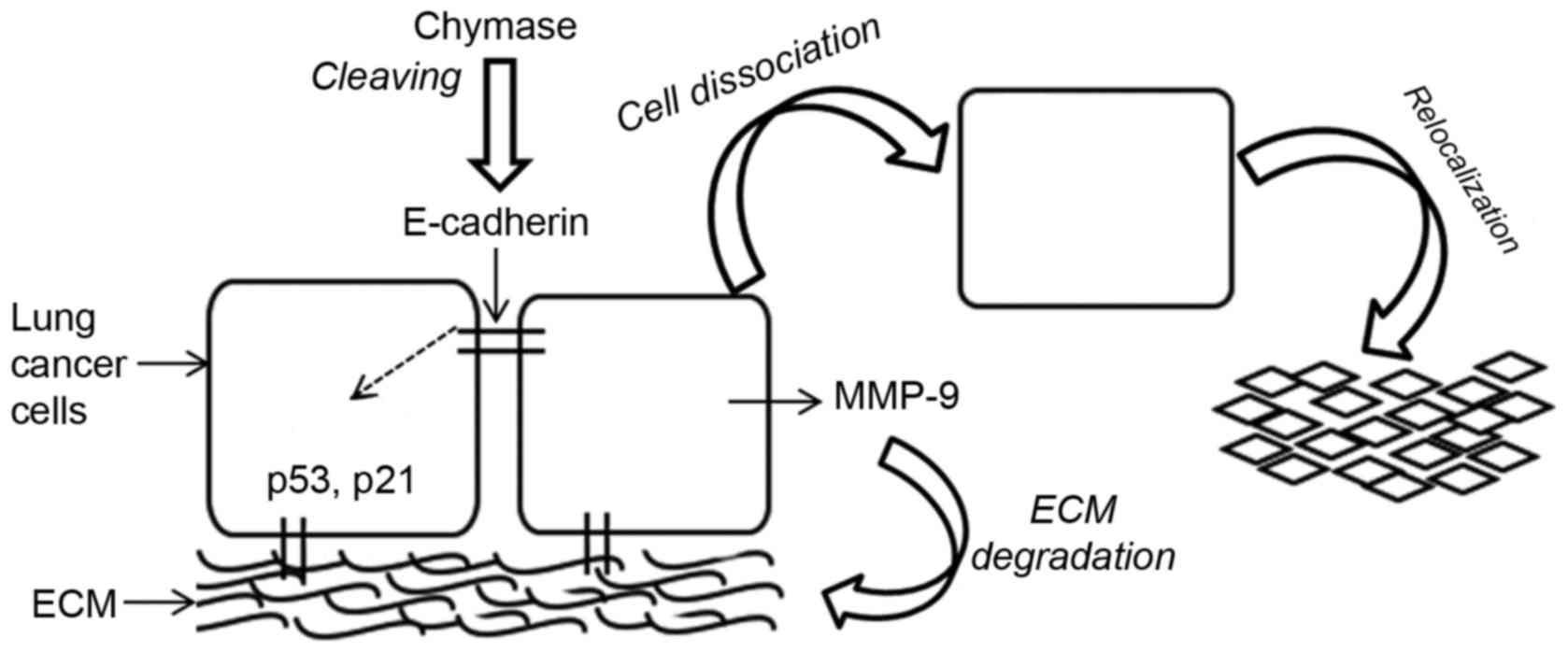
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Krishnaswamy G, Ajitawi O and Chi DS: The
human mast cell: An overview. Methods Mol Biol. 315:13–34.
2005.
|
|
4
|
Takanami I, Takeuchi K and Naruke M: Mast
cell density is associated with angiogenesis and poor prognosis in
pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Cancer. 88:2686–2692. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rajput AB, Turbin DA, Cheang MC, Voduc DK,
Leung S, Gelmon KA, Gilks CB and Huntsman DG: Stromal mast cells in
invasive breast cancer are a marker of favorable prognosis: A study
of 4,444 cases. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 107:249–257. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Johansson A, Rudolfsson S, Hammarsten P,
Halin S, Pietras K, Jones J, Stattin P, Egevad L, Granfors T,
Wikström P and Bergh A: Mast cells are novel independent prognostic
markers in prostate cancer and represent a target for therapy. Am J
Pathol. 177:1031–1041. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Blatner NR, Bonertz A, Beckhove P, Cheon
EC, Krantz SB, Strouch M, Weitz J, Koch M, Halverson AL, Bentrem DJ
and Khazaie K: In colorectal cancer mast cells contribute to
systemic regulatory T-cell dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:pp. 6430–6435. 2010; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ozdemir O: The role of mast cell density
in tumor-associated angiogenesis and survival of squamous cell
carcinoma of the lung. J Cancer Res Ther. 11:10412015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Khazaie K, Blatner NR, Khan MW, Gounari F,
Gounaris E, Dennis K, Bonertz A, Tsai FN, Strouch MJ, Cheon E, et
al: The significant role of mast cells in cancer. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 30:45–60. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nagata M, Shijubo N, Walls AF, Ichimiya S,
Abe S and Sato N: Chymase-positive mast cells in small sized
adenocarcinoma of the lung. Archiv Für Pathologische Anatomie Und
Physiologie Und Für Klinische Medicin. 443:565–573. 2003.
|
|
11
|
Maltby S, Khazaie K and McNagny KM: Mast
cells in tumor growth: Angiogenesis, tissue remodelling and
immune-modulation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1796:19–26.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Theoharides TC, Angelidou A and Zhang B:
Mast cells and tumor microenvironment. Cancer Drug Discovery
Development. 1–370. 2010.
|
|
13
|
Stewart JA Jr, Wei CC, Brower GL, Rynders
PE, Hankes GH, Dillon AR, Lucchesi PA, Janicki JS and Dell'Italia
LJ: Cardiac mast cell- and chymase-mediated matrix
metalloproteinase activity and left ventricular remodeling in
mitral regurgitation in the dog. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 35:311–319.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Seth D, D'Souza El-Guindy NB, Apte M, Mari
M, Dooley S, Neuman M, Haber PS, Kundu GC, Darwanto A, de Villiers
WJ, et al: Alcohol, signaling, and ECM turnover. Alcohol Clin Exp
Res. 34:4–18. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Christensen J and Shastri VP:
Matrix-metalloproteinase-9 is cleaved and activated by Cathepsin K.
Bmc Res Notes. 8:3222015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Murnane MJ, Cai J, Shuja S, McAneny D,
Klepeis V and Willett JB: Active MMP-2 effectively identifies the
presence of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 125:2893–2902. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cupić DF, Tesar EC, Ilijas KM, Nemrava J
and Kovacević M: Expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 in
primary and recurrent breast carcinomas. Coll Antropol. 35 Suppl
2:S7–S10. 2011.
|
|
18
|
Werner G, Daniele M, Gabriella N, Lorenzo
M, Giovanni T and Renato G: Association between metalloproteinases
2 and 9 activity and ERK1/2 phosphorylation status in head and neck
cancers: An ex vivo study. Oncol Rep. 24:1073–1078. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lecuit T and Yap AS: E-cadherin junctions
as active mechanical integrators in tissue dynamics. Nat Cell Biol.
17:533–539. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao P, Guo S, Tu Z, Di L, Zha X, Zhou H
and Zhang X: Grhl3 induces human epithelial tumor cell migration
and invasion via downregulation of E-cadherin. Acta Biochim Biophys
Sin (Shanghai). 48:266–274. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Techasen A, Loilome W, Namwat N, Khuntikeo
N, Puapairoj A, Jearanaikoon P, Saya H and Yongvanit P: Loss of
E-cadherin promotes migration and invasion of cholangiocarcinoma
cells and serves as a potential marker of metastasis. Tumour Biol.
35:8645–8652. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen A, Beetham H, Black MA, Priya R,
Telford BJ, Guest J, Wiggins GA, Godwin TD, Yap AS and Guilford PJ:
E-cadherin loss alters cytoskeletal organization and adhesion in
non-malignant breast cells but is insufficient to induce an
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Bmc Cancer. 14:5522014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Muller PA and Vousden KH: Mutant p53 in
cancer: New functions and therapeutic opportunities. Cancer Cell.
25:304–317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sivoňová MK, Vilčková M, Kliment J,
Mahmood S, Jurečeková J, Dušenková S, Waczulíková I, Slezák P and
Dobrota D: Association of p53 and p21 polymorphisms with prostate
cancer. Biomed Rep. 3:707–714. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ribatti D and Crivellato E: Mast cells,
angiogenesis, and tumour growth. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1822:2–8.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou X, Cox C, Rajenthirar S, Mahrous AA,
Masters B, Roche WR and Walls AF: Mast cell Chymase Can Disrupt the
human bronchial epithelium and stimulate the loss of adhesion
molecules. J Allergy Clinical Immunol. 121:S1102008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lee HS and Daar IO: EphrinB reverse
signaling in cell-cell adhesion: Is it just par for the course?
Cell Adh Migr. 3:250–255. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Segal L, Katz LS, Shapira H, Sandbank J,
Geras-Raaka E, Gershengorn MC and Oron Y: PAR-3 knockdown enhances
adhesion rate of PANC-1 cells via increased expression of
integrinαv and E-cadherin. PLoS One. 9:e938792014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cui T, Srivastava AK, Han C, Yang L, Zhao
R, Zou N, Qu M, Duan W, Zhang X and Wang QE: XPC inhibits NSCLC
cell proliferation and migration by enhancing E-Cadherin
expression. Oncotarget. 6:10060–10072. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Waldum HL, Ringnes E, Nordbø H, Sørdal Ø,
Nordrum IS and Hauso Ø: The normal neuroendocrine cells of the
upper gastrointestinal tract lack E-cadherin. Scand J Gastroentero.
49:974–978. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yamashita N, Tokunaga E, Inoue Y, Tanaka
K, Ueo H, Saeki H, Oki K and Maehara Y: Abstract P2-05-12:
Epithelial paradox; clinical significance of co-expression of
E-cadherin and vimentin in invasive breast cancer. Cancer Res.
76:2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wu CL, Ho JY, Chou SC and Yu DS: MiR-429
reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition by restoring E-cadherin
expression in bladder cancer. Oncotarget. 7:26593–26603. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dass SD, Cheah PL, Ong DB, Teoh KH and
Looi LM: E-cadherin downregulation at the infiltrating tumour front
is associated with histological grade and stage in colorectal
carcinoma of Malaysians. Malays J Pathol. 37:19–24. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nam RK, Benatar T, Wallis CJ, Amemiya Y,
Yang W, Garbens A, Naeim M, Sherman C, Sugar L and Seth A: MiR-301a
regulates E-cadherin expression and is predictive of prostate
cancer recurrence. Prostate. 76:869–884. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ma B, Zhang HY, Bai X, Wang F, Ren XH,
Zhang L and Zhang MZ: ADAM10 mediates the cell invasion and
metastasis of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via
regulation of E-cadherin activity. Oncol Rep. 35:2785–2794.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang X, Simpson ER and Brown KA: p53:
Protection against tumor growth beyond effects on cell cycle and
apoptosis. Cancer Res. 75:5001–5007. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
McNaughton M, Pitman M, Pitson SM, Pyne NJ
and Pyne S: Proteasomal degradation of sphingosine kinase 1 and
inhibition of dihydroceramidedesaturase by the sphingosine kinase
inhibitors, SKi or ABC294640, induces growth arrest in
androgen-independent LNCaP-AI prostate cancer cells. Oncotarget.
7:16663–16673. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu Z, Liu Z, Zhang X, Xue P and Zhang H:
RY10-4 suppressed metastasis of MDA-MB-231 by stabilizing ECM and
E-cadherin. Biomed Pharmacother. 68:439–445. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sullu Y, Demirag GG, Yildirim A, Karagoz F
and Kandemir B: Matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and MMP-9
expression in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Pathol Res
Pract. 207:747–753. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Peng WJ, Zhang JQ, Wang BX, Pan HF, Lu MM
and Wang J: Prognostic value of matrix metalloproteinase 9
expression in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Clinica
Chim Acta. 413:1121–1126. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|