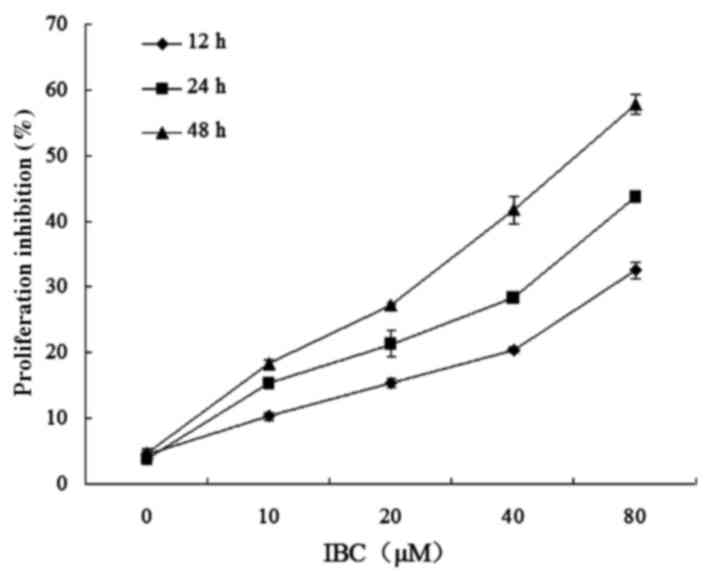
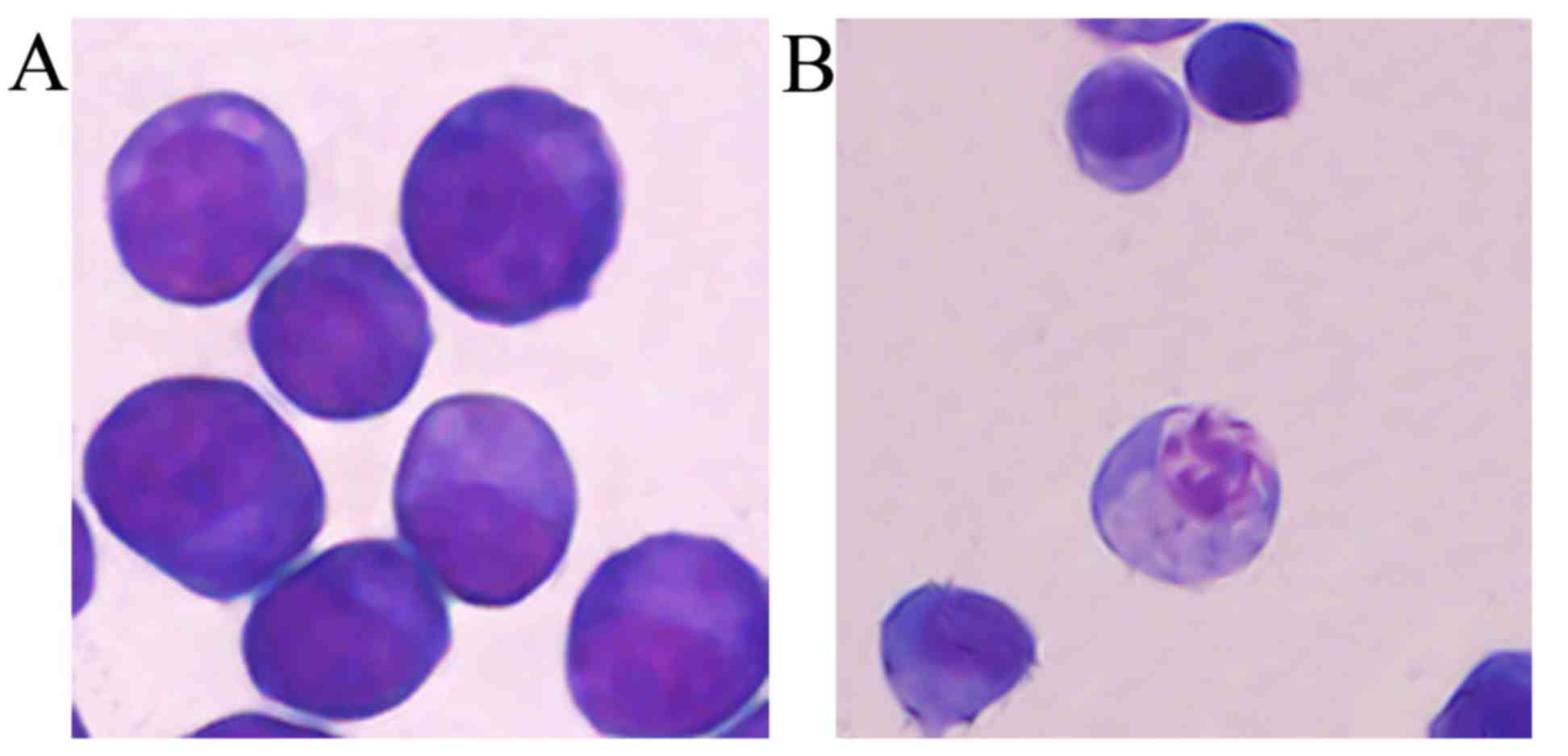
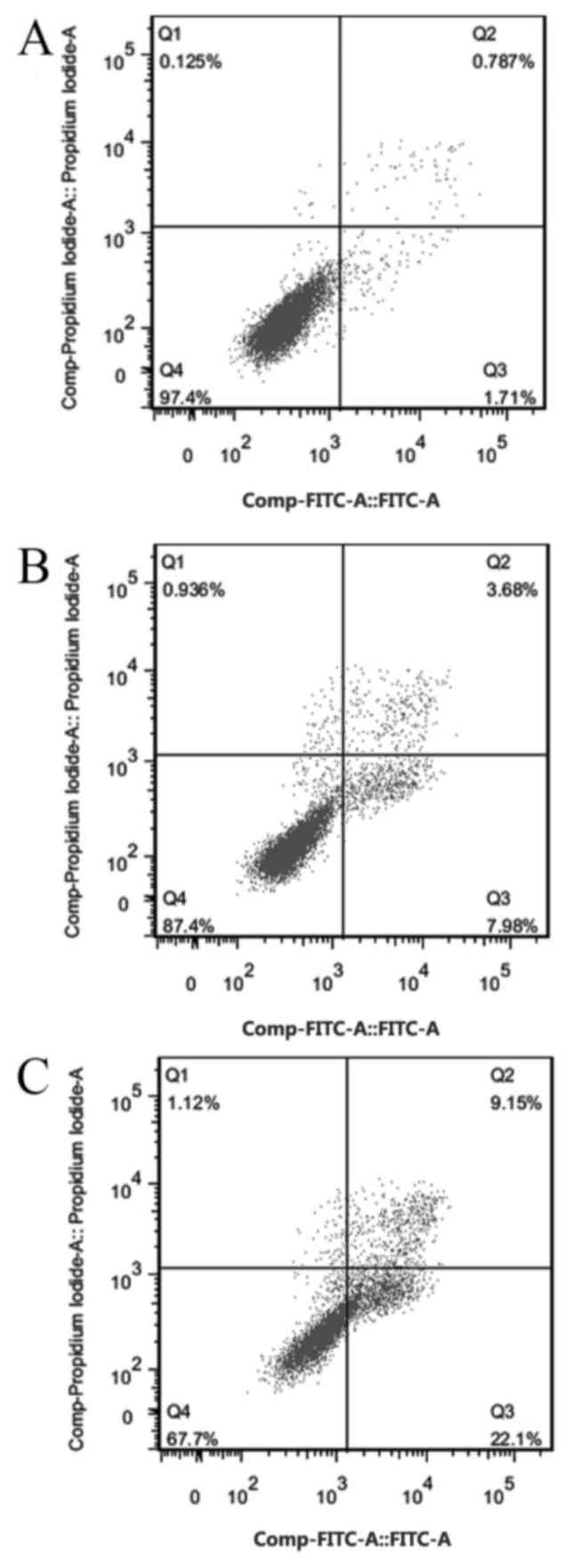
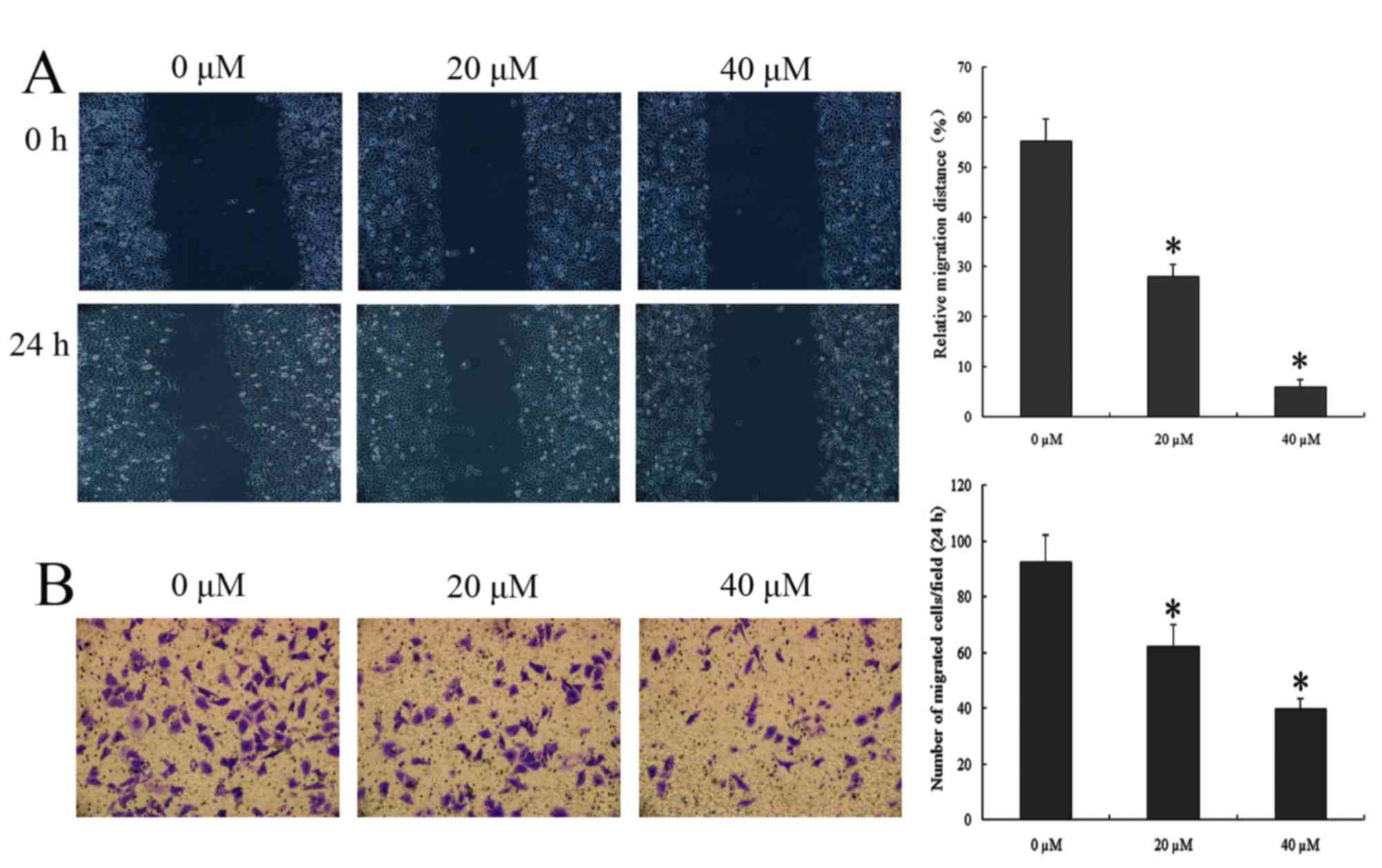
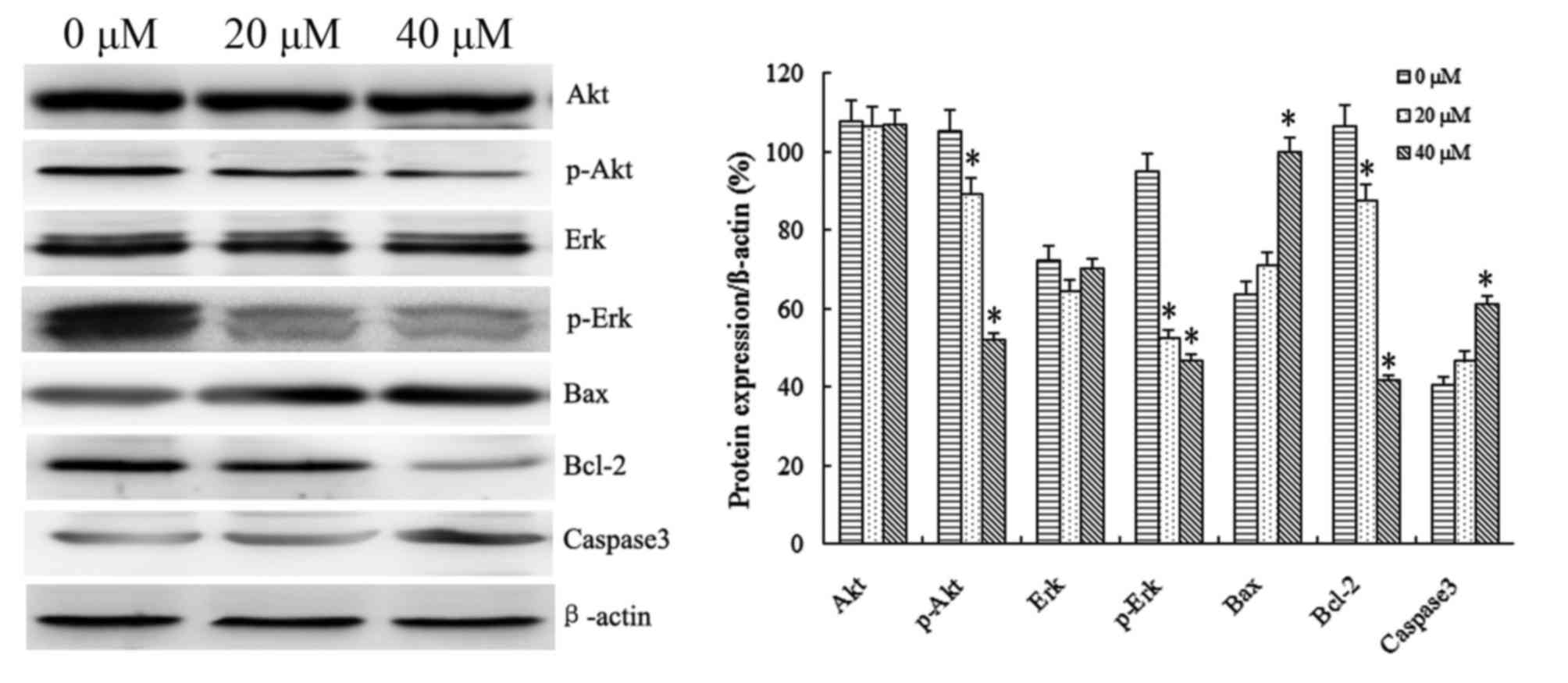
|
1
|
Clump DA, Bauman JE and Ferris RL: Cancer
of the oropharynx. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 24:509–520. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guo XH, Wang JY, Gao Y, Gao M, Yu GY,
Xiang RL, Li L, Yang NY, Cong X, Xu XY, et al: Decreased
adiponectin level is associated with aggressive phenotype of tongue
squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 104:206–213. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dzebo S, Mahmutovic J and Erkocevic H:
Quality of life of patients with oral cavity cancer. Mater
Sociomed. 29:30–34. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chan KK, Glenny AM, Weldon JC, Furness S,
Worthington HV and Wakeford H: Interventions for the treatment of
oral and oropharyngeal cancers: Targeted therapy and immunotherapy.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 1:CD0103412015.
|
|
5
|
Dashtdar M, Dashtdar MR, Dashtdar B, Kardi
K and Shirazi MK: The concept of wind in traditional chinese
medicine. J Pharmacopuncture. 19:293–302. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jing H, Zhou X, Dong X, Cao J, Zhu H, Lou
J, Hu Y, He Q and Yang B: Abrogation of Akt signaling by
Isobavachalcone contributes to its anti-proliferative effects
towards human cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 294:167–177. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nishimura R, Tabata K, Arakawa M, Ito Y,
Kimura Y, Akihisa T, Nagai H, Sakuma A, Kohno H and Suzuki T:
Isobavachalcone, a chalcone constituent of Angelica keiskei,
induces apoptosis in neuroblastoma. Biol Pharm Bull. 30:1878–1883.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Szliszka E, Jaworska D, Ksek M, Czuba ZP
and Król W: Targeting death receptor TRAIL-R2 by chalcones for
TRAIL-induced apoptosis in cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci.
13:15343–15359. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Szliszka E, Czuba ZP, Mazur B, Sedek L,
Paradysz A and Krol W: Chalcones enhance TRAIL-induced apoptosis in
prostate cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 11:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dzoyem JP, Hamamoto H, Ngameni B, Ngadjui
BT and Sekimizu K: Antimicrobial action mechanism of flavonoids
from Dorstenia species. Drug Discov Ther. 7:66–72. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jin X, Zhu Z and Shi Y: Metastasis
mechanism and gene/protein expression in gastric cancer with
distant organs metastasis. Bull Cancer. 101:E1–E12. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Akihisa T, Tokuda H, Hasegawa D, Ukiya M,
Kimura Y, Enjo F, Suzuki T and Nishino H: Chalcones and other
compounds from the exudates of Angelica keiskei and their cancer
chemopreventive effects. J Nat Prod. 69:38–42. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bhalla VX, Nayak UR and Dev S: Some new
fiavonoids from Psoralea corylifolia. Tetrahedron Lett.
20:2401–2406. 1968. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Nowakowska Z: A review of anti-infective
and anti-inflammatory chalcones. Eur J Med Chem. 42:125–137. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Green DR and Reed JC: Mitochondria and
apoptosis. Science. 281:1309–1312. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Scott N, Hale A, Deakin M, Hand P, Adab
FA, Hall C, Williams GT and Elder JB: A histopathological
assessment of the response of rectal adenocarcinoma to combination
chemo-radiotherapy: Relationship to apoptotic activity, p53 and
bcl-2 expression. Eur J Surg Oncol. 24:169–173. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang B, Liu M, Tang HK, Ma HB, Wang C,
Chen X and Huang HZ: The expression and significance of MRP1, LRP,
TOPOIIβ, and BCL2 in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol
Med. 41:141–148. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Meterissian SH, Kontogiannea M, Po J,
Jensen G and Ferdinand B: Apoptosis induced in human colorectal
carcinoma by anti-Fas antibody. Ann Surg Oncol. 4:169–175. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Y, Jiang XY, Liu L and Jiang HQ:
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway regulates hepatic
stellate cell apoptosis. World J Gastroenterol. 14:5186–5191. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chong ZZ and Maises K: Targeting WNT
protein kinase B, and mitochondrial membrane integrity to foster
cellular survival in the nervous system. Histol Histopathol.
19:495–504. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Aranda F, Vacchelli E, Eggermont A, Galon
J, Fridman WH, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G and Galluzzi L: Trial Watch:
Immunostimulatory monoclonal antibodies in cancer therapy.
Oncoimmunology. 3:e272972014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jin X and Shi YI: Isobavachalcone induces
the apoptosis of gastric cancer cells via inhibition of the Akt and
Erk pathways. Exp Ther Med. 11:403–408. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rao JS: Molecular mechanisms of glioma
invasiveness: The role of proteases. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:489–501.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Aparna M, Rao L, Kunhikatta V and
Radhakrishnan R: The role of MMP-2 and MMP-9 as prognostic markers
in the early stages of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral
Pathol Med. 44:345–352. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yin B, Liu Z, Wang Y, Wang X, Liu W, Yu P,
Duan X, Liu C, Chen Y, Zhang Y, et al: RON and c-Met facilitate
metastasis through the ERK signaling pathway in prostate cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 37:3209–3218. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang D, Wang D, Wang N, Long Z and Ren X:
Long non-coding RNA BANCR promotes endometrial cancer cell
proliferation and invasion by regulating MMP2 and MMP1 via ERK/MAPK
signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 40:644–656. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cheng CY, Hsieh HL, Hsiao LD and Yang CM:
PI3-K/Akt/JNK/NF-κB is essential for MMP-9 expression and outgrowth
in human limbal epithelial cells on intact amniotic membrane. Stem
Cell Res. 9:9–23. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|