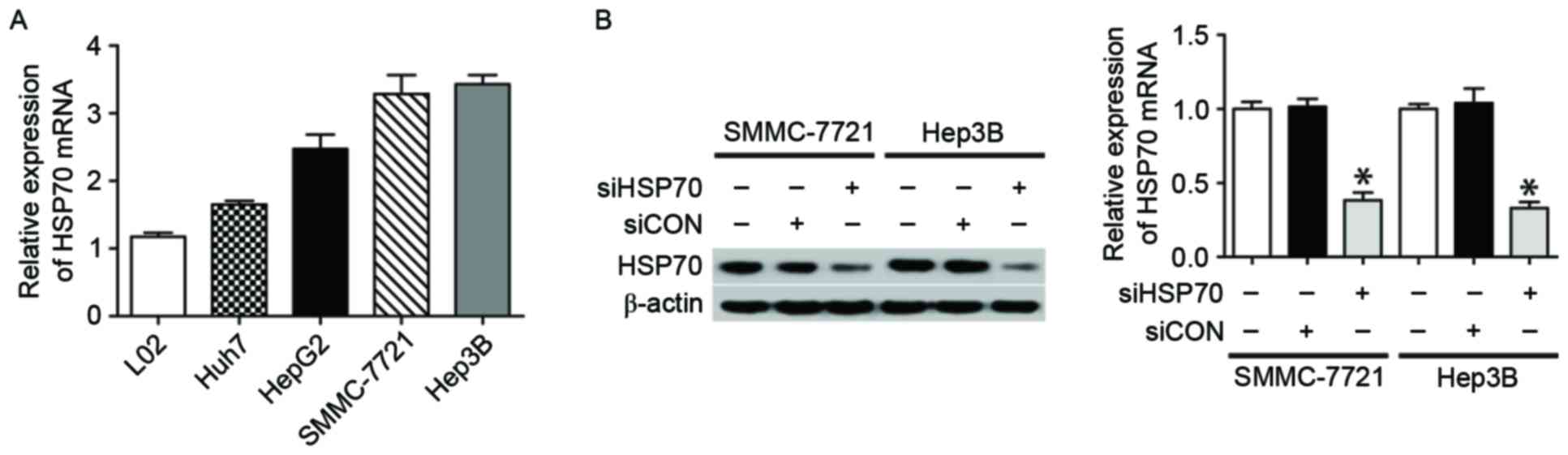
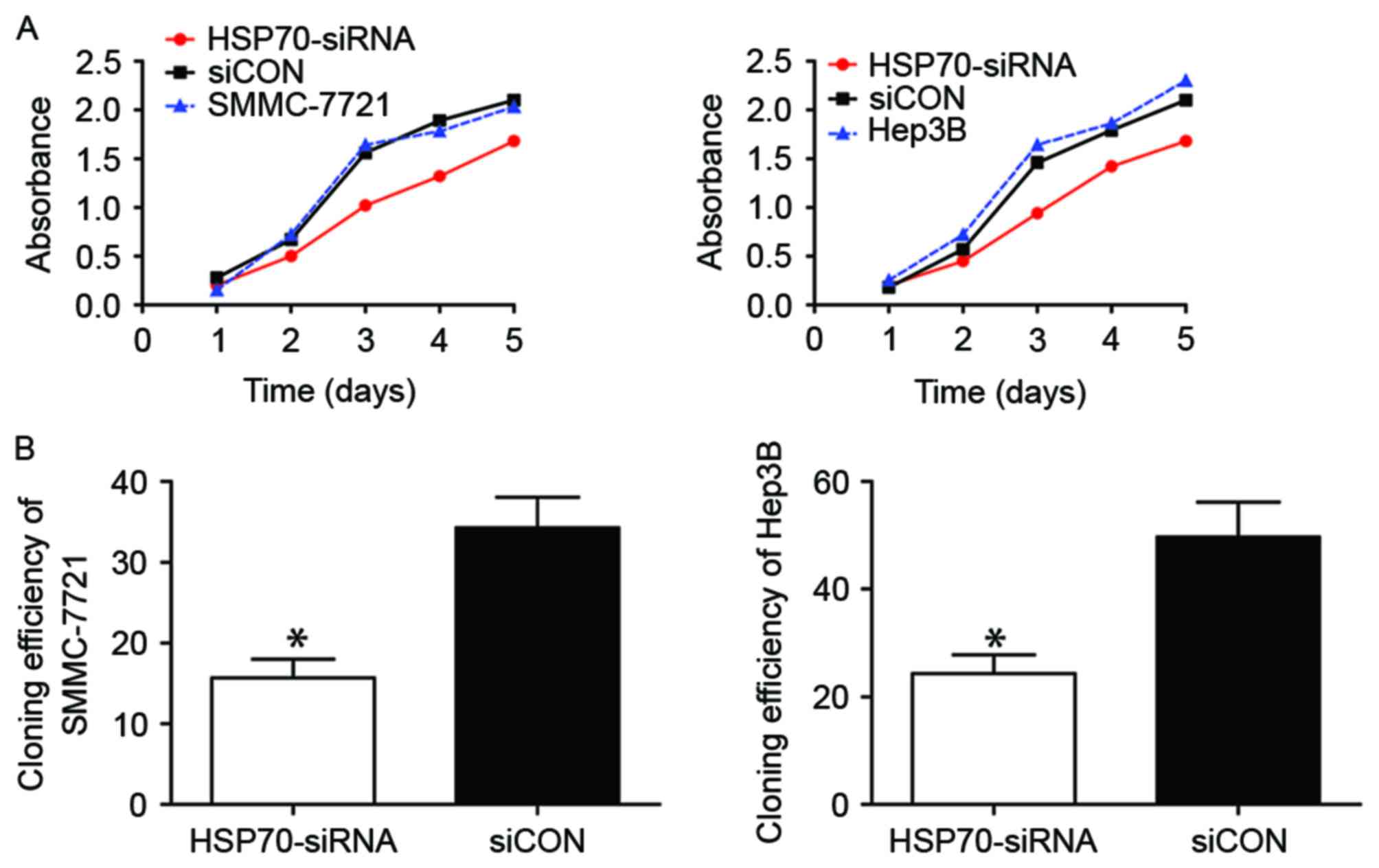
|
1
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
et al: Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J
Med. 359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yin J, Zhu JM and Shen XZ: The role and
therapeutic implications of RING-finger E3 ubiquitin ligases in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 136:249–257. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yasui W, Sentani K, Sakamoto N, Anami K,
Naito Y and Oue N: Molecular pathology of gastric cancer: Research
and practice. Pathol Res Pract. 207:608–612. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dawson MA and Kouzarides T: Cancer
epigenetics: From mechanism to therapy. Cell. 150:12–27. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Farazi PA and DePinho RA: Hepatocellular
carcinoma pathogenesis: From genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:674–687. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shi X, Zhu HR, Liu TT, Shen XZ and Zhu JM:
The Hippo pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma: Non-coding RNAs in
action. Cancer Lett. 400:175–182. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mosser DD and Morimoto RI: Molecular
chaperones and the stress of oncogenesis. Oncogene. 23:2907–2918.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vargas-Roig LM, Fanelli MA, López LA, Gago
FE, Tello O, Aznar JC and Ciocca DR: Heat shock proteins and cell
proliferation in human breast cancer biopsy samples. Cancer Detect
Prev. 21:441–451. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lazaris AC, Theodoropoulos GE, Aroni K,
Saetta A and Davaris PS: Immunohistochemical expression of C-myc
oncogene, heat shock protein 70 and HLA-DR molecules in malignant
cutaneous melanoma. Virchows Arch. 426:461–467. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kaur J, Srivastava A and Ralhan R:
Expression of 70-kDa heat shock protein in oral lesions: Marker of
biological stress or pathogenicity. Oral Oncol. 34:496–501. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Syrigos KN, Harrington KJ, Karayiannakis
AJ, Sekara E, Chatziyianni E, Syrigou EI and Waxman J: Clinical
significance of heat shock protein-70 expression in bladder cancer.
Urology. 61:677–680. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Udono H and Srivastava PK: Heat shock
protein 70-associated peptides elicit specific cancer immunity. J
Exp Med. 178:1391–1396. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lindquist S and Craig EA: The heat-shock
proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 22:631–677. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lim SO, Park SG, Yoo JH, Park YM, Kim HJ,
Jang KT, Cho JW, Yoo BC, Jung GH and Park CK: Expression of heat
shock proteins (HSP27, HSP60, HSP70, HSP90, GRP78, GRP94) in
hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinomas and dysplastic
nodules. World J Gastroenterol. 11:2072–2079. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ciocca DR, Green S, Elledge RM, Clark GM,
Pugh R, Ravdin P, Lew D, Martino S and Osborne CK: Heat shock
proteins hsp27 and hsp70: Lack of correlation with response to
tamoxifen and clinical course of disease in estrogen
receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer (a Southwest Oncology
Group Study). Clin Cancer Res. 4:1263–1266. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nylandsted J, Brand K and Jäättelä M: Heat
shock protein 70 is required for the survival of cancer cells. Ann
N Y Acad Sci. 926:122–125. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Murphy ME: The HSP70 family and cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 34:1181–1188. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Malusecka E, Zborek A, Krzyzowska-Gruca S
and Krawczyk Z: Expression of heat shock proteins HSP70 and HSP27
in primary non-small cell lung carcinomas. An immunohistochemical
study. Anticancer Res. 21:1015–1021. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lazaris ACh, Chatzigianni EB,
Panoussopoulos D, Tzimas GN, Davaris PS and Golematis BCh:
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen and heat shock protein 70
immunolocalization in invasive ductal breast cancer not otherwise
specified. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 43:43–51. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hwang TS, Han HS, Choi HK, Lee YJ, Kim YJ,
Han MY and Park YM: Differential, stage-dependent expression of
Hsp70, Hsp110 and Bcl-2 in colorectal cancer. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 18:690–700. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Thompson MD and Monga SP: WNT/beta-catenin
signaling in liver health and disease. Hepatology. 45:1298–1305.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wands JR and Kim M: WNT/beta-catenin
signaling and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 60:452–454.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Botrugno OA, Fayard E, Annicotte JS, Haby
C, Brennan T, Wendling O, Tanaka T, Kodama T, Thomas W, Auwerx J
and Schoonjans K: Synergy between LRH-1 and beta-catenin induces G1
cyclin-mediated cell proliferation. Mol Cell. 15:499–509. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tetsu O and McCormick F: Beta-catenin
regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature.
398:422–426. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Buckley MF, Sweeney KJ, Hamilton JA, Sini
RL, Manning DL, Nicholson RI, deFazio A, Watts CK, Musgrove EA and
Sutherland RL: Expression and amplification of cyclin genes in
human breast cancer. Oncogene. 8:2127–2133. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ray A, James MK, Larochelle S, Fisher RP
and Blain SW: p27Kip1 inhibits cyclin D-cyclin-dependent kinase 4
by two independent modes. Mol Cell Biol. 29:986–999. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yachida S, Sakamoto M, Imaida K, Yokohira
M, Saoo K, Okano K, Wakabayashi H, Maeta H and Suzuki Y:
p27(Kip1)is overexpressed in very early stages of
hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Sci. 99:2152–2159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Poon RT, Fan ST, Ng IO, Lo CM, Liu CL and
Wong J: Different risk factors and prognosis for early and late
intrahepatic recurrence after resection of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer. 89:500–507. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Calderwood SK, Khaleque MA, Sawyer DB and
Ciocca DR: Heat shock proteins in cancer: Chaperones of
tumorigenesis. Trends Biochem Sci. 31:164–172. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Karlsson R, Pedersen ED, Wang Z and
Brakebusch C: Rho GTPase function in tumorigenesis. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1796:91–98. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nikfarjam M, Muralidharan V, Su K,
Malcontenti-Wilson C and Christophi C: Patterns of heat shock
protein (HSP70) expression and Kupffer cell activity following
thermal ablation of liver and colorectal liver metastases. Int J
Hyperthermia. 21:319–332. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fang F, Chang R and Yang L: Heat shock
factor 1 promotes invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular
carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Cancer. 118:1782–1794. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hartmann S, Günther N, Biehl M, Katzer A,
Kuger S, Worschech E, Sukhorukov VL, Krohne G, Zimmermann H,
Flentje M and Djuzenova CS: Hsp90 inhibition by NVP-AUY922 and
NVP-BEP800 decreases migration and invasion of irradiated normoxic
and hypoxic tumor cell lines. Cancer Lett. 331:200–210. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|