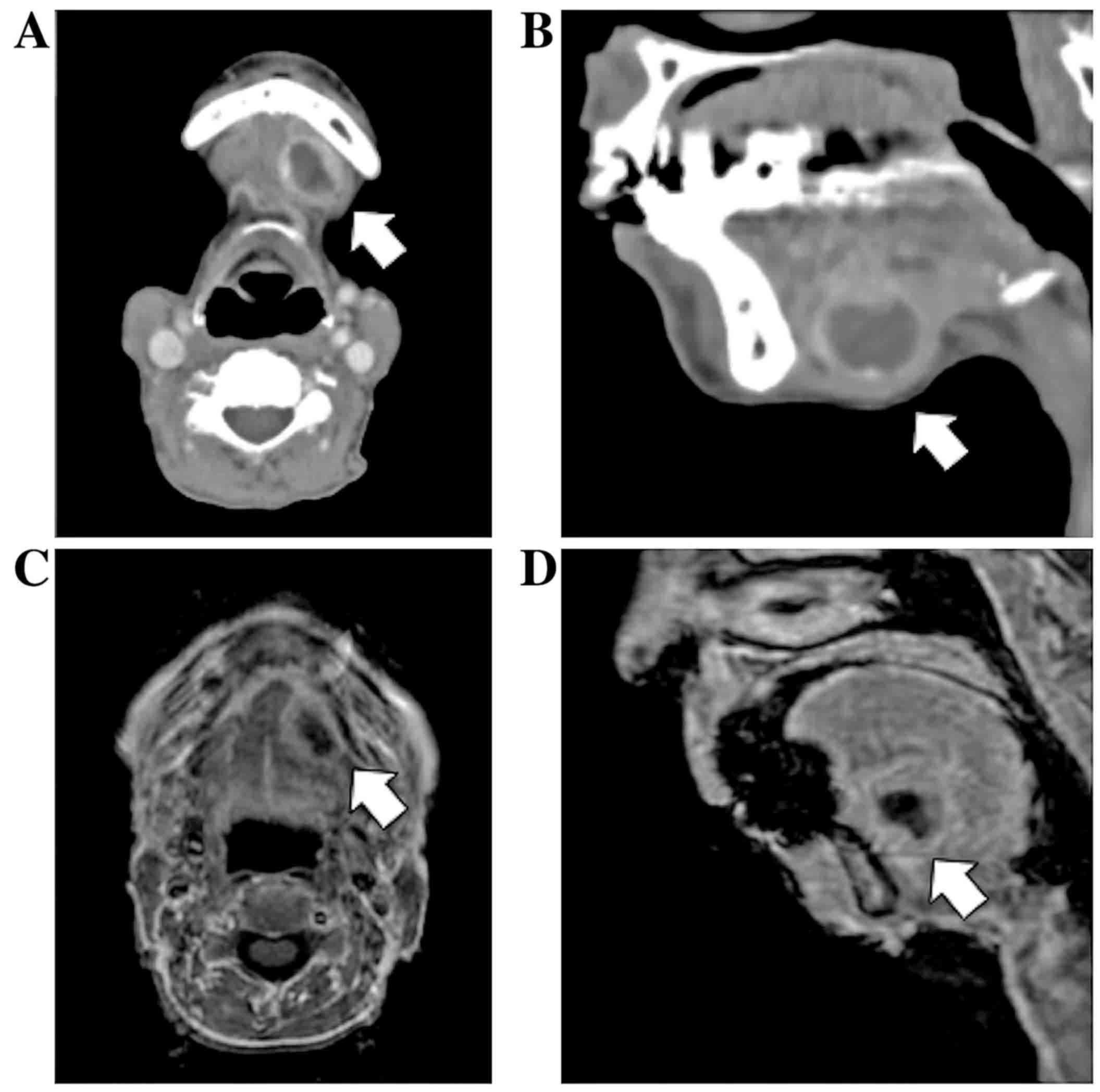
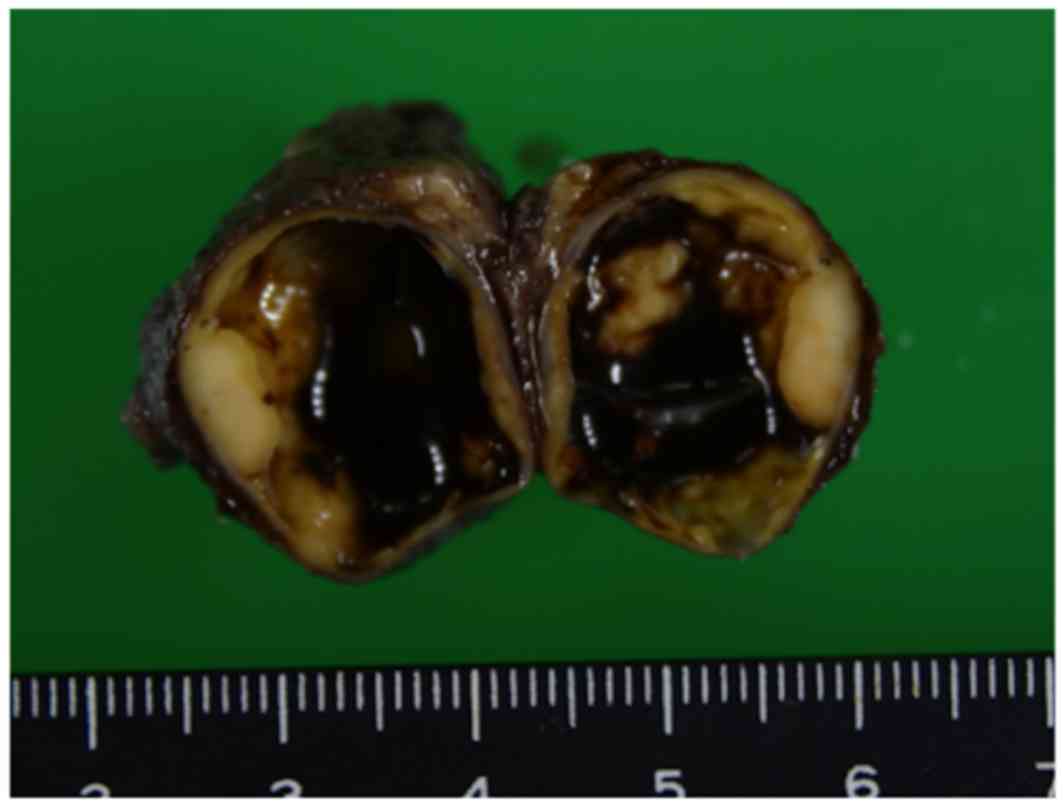
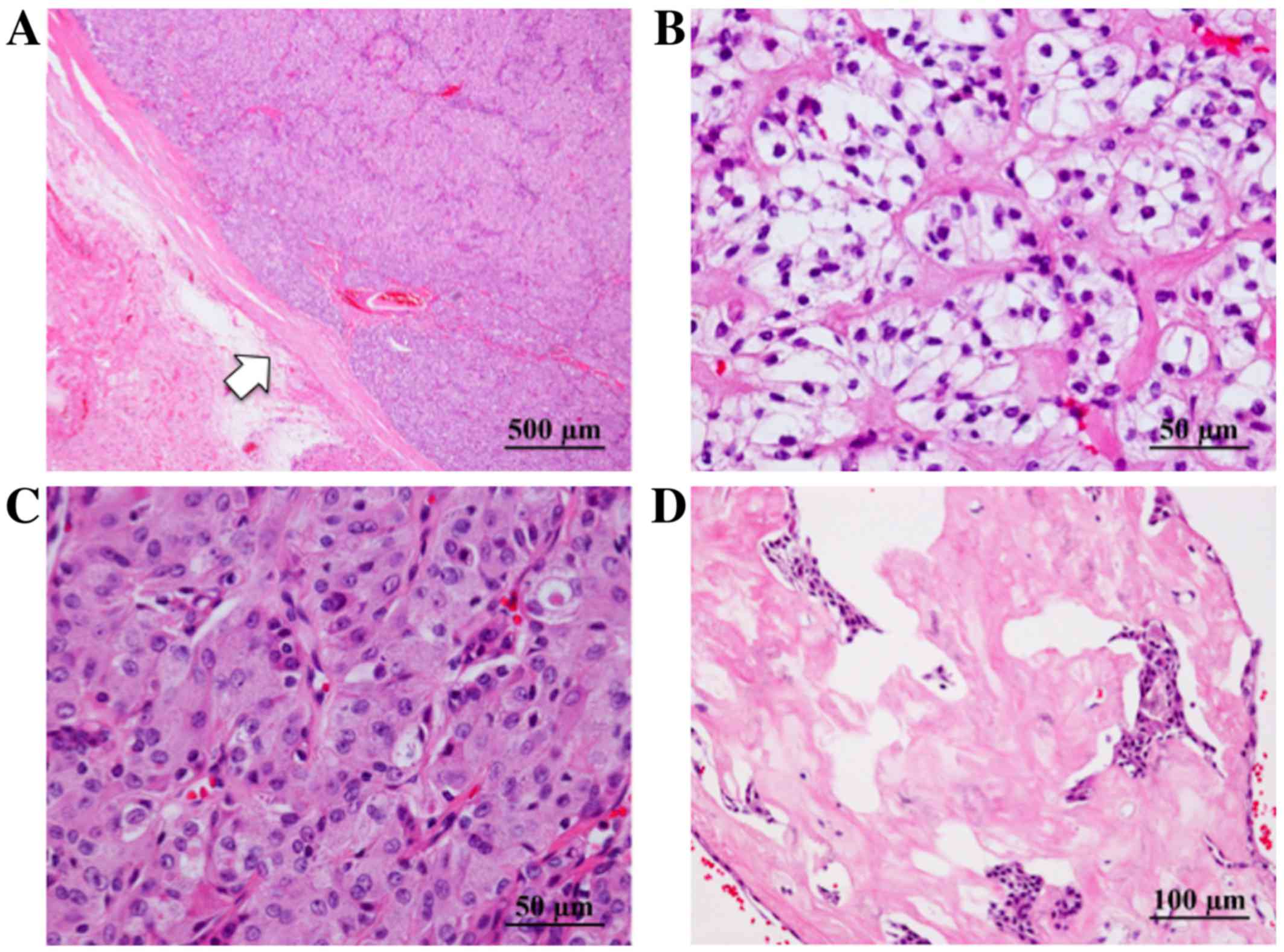
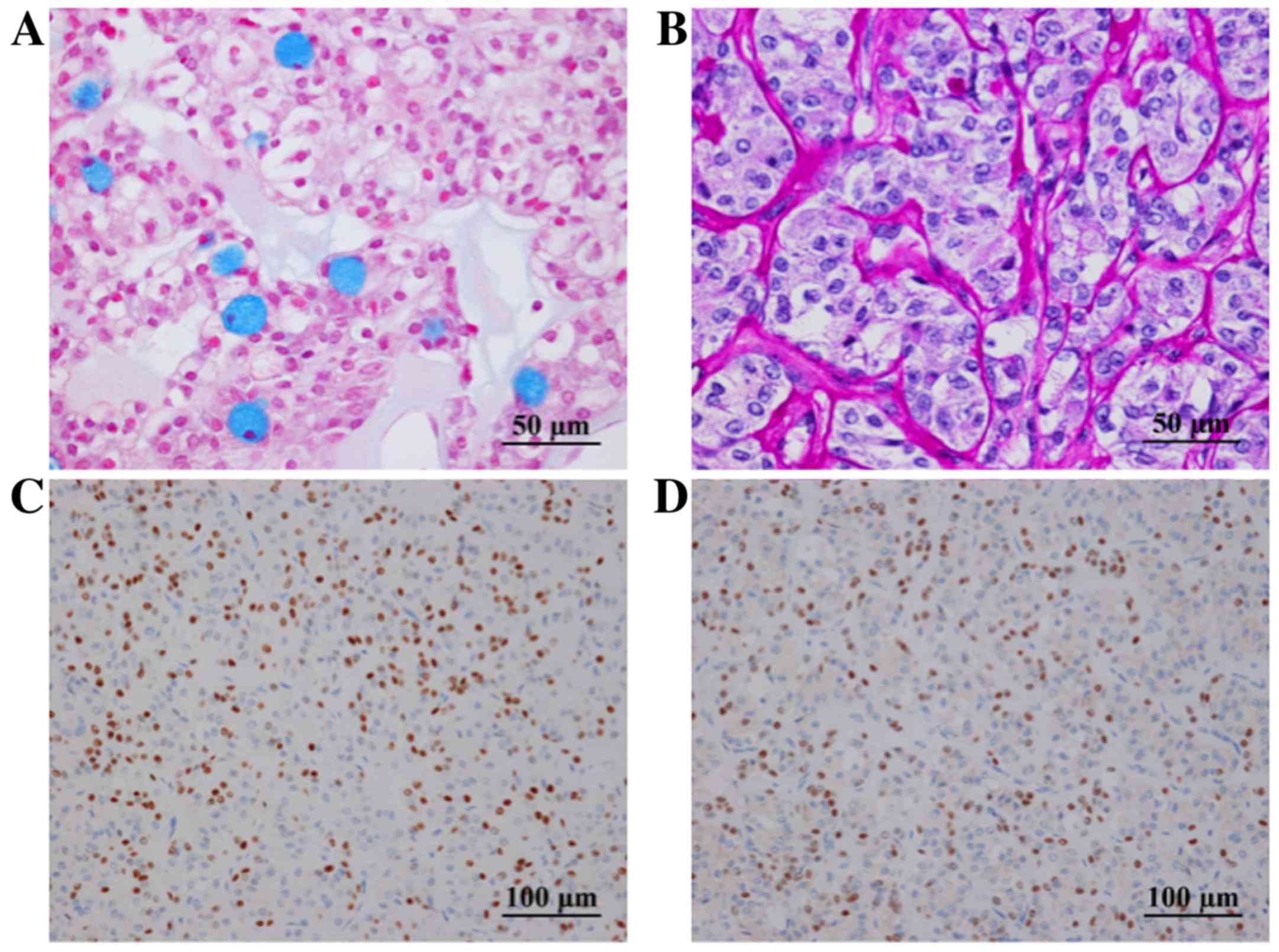
|
1
|
Eveson JW and Cawson RA: Salivary gland
tumours. A review of 2410 cases with particular reference to
histological types, site, age and sex distribution. J Pathol.
146:51–58. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gary LE and Paul LA: Tumor of the salivary
glandsAFIP Atlas of Tumor Pathology Series 4. AFIP ARP; Washington:
pp. 173–196. 2008
|
|
3
|
Goode RK and El-Naggar AK: Mucoepidermoid
carcinoma. In: World Health Organization Classification of
TumorsPathology and Genetics of Head and Neck Tumors. Barnes L,
Evenson JW, Reichart P and Sidransky D: IARC Press; Lyon: pp.
219–220. 2005
|
|
4
|
Stewart FW, Foote FW and Becker WF:
Muco-epidermoid tumors of salivary glands. Am J Surg. 122:820–844.
1945.
|
|
5
|
John WE and Lester DRT: Malignant
neoplasms of the salivary glandsHead and Neck Pathology. Lester
DRT: 2nd. Elsevier Sauners; Philadelphia: pp. 270–277. 2013
|
|
6
|
Luna MA: Salivary mucoepidermoid
carcinoma: Revisited. Adv Anat Pathol. 13:293–307. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Whatley WS, Thompson JW and Rao B:
Salivary gland tumors in survivors of childhood cancer. Otolaryngol
Head Neck Surg. 134:385–388. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Noda H, Okamura Y, Nakayama T, Miyabe S,
Fujiyoshi Y, Hattori H, Shimozato K and Inagaki H:
Clinicopathological significance of MAML2 gene split in
mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 104:85–92. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fehr A, Röser K, Heidorn K, Hallas C,
Löning T and Bullerdiek J: A new type of MAMAL2 fusion in
mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 47:203–206.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Goode RK, Alclair PL and Ellis GL:
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the major salivary glands. Clinical and
histopathologic analysis of 234 cases with evaluation of grading
criteria. Cancer. 82:1217–1224. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kumar AN, Nair PP, Thomas S, Raman PS and
Bhambal A: Mucoepidemoid carcinoma of sublingual gland: A malignant
neoplasm in an uncommon region. BMJ Case Rep May.
2011:bcr02201138642011.
|
|
12
|
Murase Y, Kawano S, Kiyoshima T, Goto Y,
Matsubara R, Chikui T, Yoshiga D and Nakamura S: Case of
mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the sublingual gland accompanied with
extensive dystrophic calcification and intratumoral bone formation.
Head Neck. 37:E161–E164. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sumanth KN, Mainali A, Ongole R and Pai
MR: Mucoepidermoid carcinoma: ‘A Mimicker’? J Nepal Dent Assoc.
10:31–34. 2009.
|
|
14
|
Furuse C, Sousa SO, Nunes FD, Magalhães MH
and Araújo VC: Myoepithelial cell markers in salivary gland
neoplasms. Int J Surg Pathol. 13:57–65. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Owosho AA, Aguilar CE and Seethala RR:
Comparison of p63 and p40 (ΔNp63) as basal, squamoid, and
myoepithelial markers in salivary gland tumors. Appl
Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 24:501–508. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tajima S, Namiki I and Koda K: A clear
cell variant of mucoepidermoid carcinoma harboring CRTC1-MAML2
fusion gene found in buccal mucosa: Report of a case showing a
large clear cell component and lacking typical epidermoid cells and
intermediate cells. Med Mol Morphol. 50:117–121. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fujimaki M, Fukumura Y, Saito T, Mitani K,
Uchida S, Yokoyama J, Yao T and Ikeda K: Oncocytic mucoepidermoid
carcinoma of the parotid gland with CRTC1-MAML2 fusion transcript:
Report of a case with review of literature. Hum Pathol.
42:2052–2055. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu L, Liu J, Gao P, Nakamura M, Cao Y,
Shen H and Griffin JD: Transforming activity of MECT1-MAML2 fusion
oncoprotein is mediated by constitutive CREB activation. EMBO J.
24:2391–2402. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Stenman G, Persson F and Andersson MK:
Diagnostic and therapeutic implications of new molecular biomarkers
in salivary gland cancers. Oral Oncol. 50:683–690. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Seethala RR and Chiosea SI: MAML2 status
in mucoepidermoid carcinoma can no longer be considered a
prognostic marker. Am J Surg Pathol. 40:1151–1153. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Spiro RH, Huvos AG, Berk R and Strong EW:
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of salivary gland origin. A
clinicopathologic study of 367 cases. Am J Surg. 136:461–468. 1978.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nance MA, Seethala RR, Wang Y, Chiosea SI,
Myers EN, Johnson JT and Lai SY: Treatment and survival outcomes
based on histologic grading in patients with head and neck
mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Cancer. 113:2082–2089. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Elnayal A, Moran CA, Fox PS, Mawlawi O,
Swisher SG and Marom EM: Primary salivary gland-type lung cancer:
Imaging and clinical predictors of outcome. AJR Am J Roentgenol.
201:W57–W63. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ishizumi T, Tateishi U, Watanabe S, Maeda
T and Arai Y: F-18 FDG PET/CT imaging of low-grade mucoepidermoid
carcinoma of the bronchus. Ann Nucl Med. 21:299–302. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|