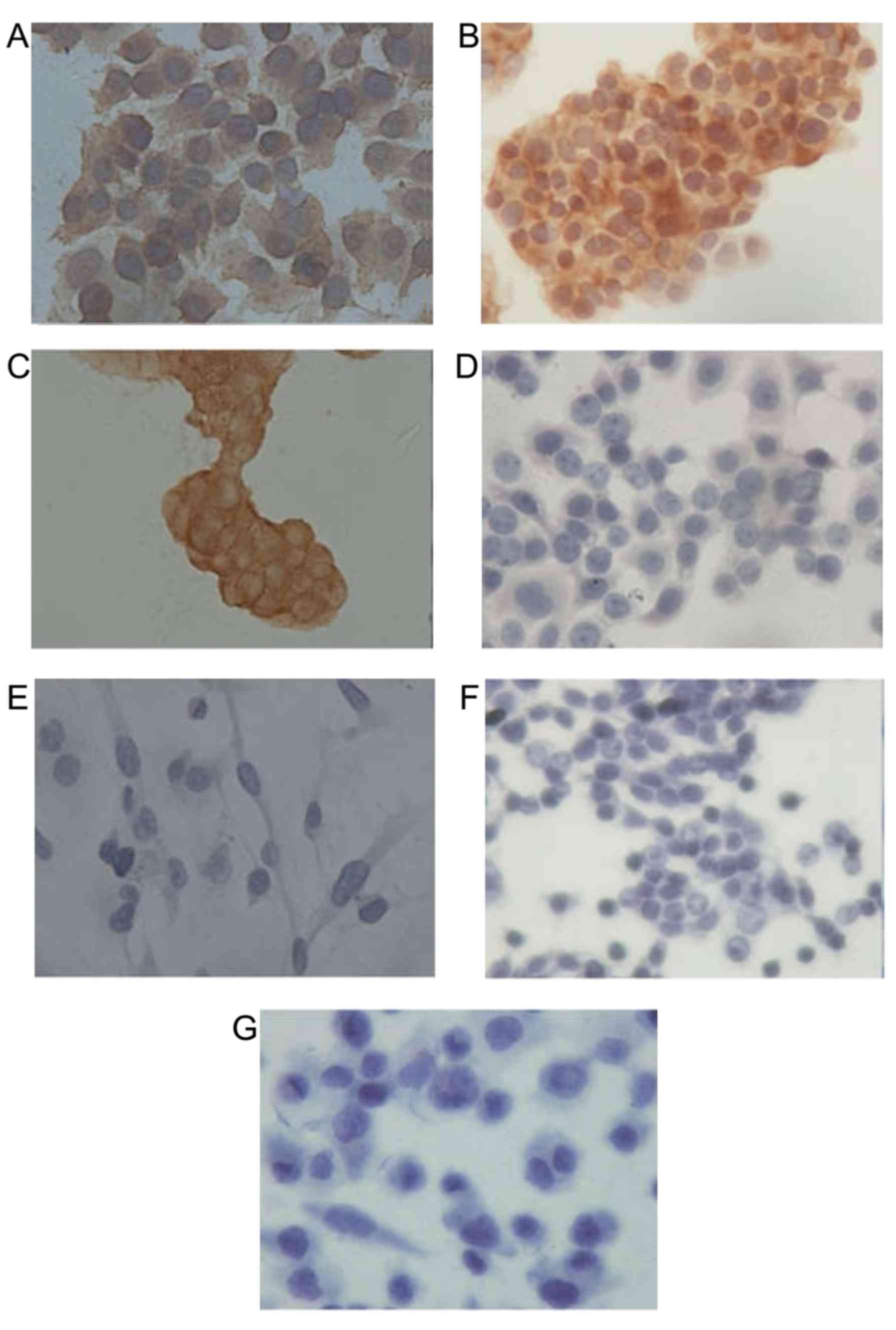
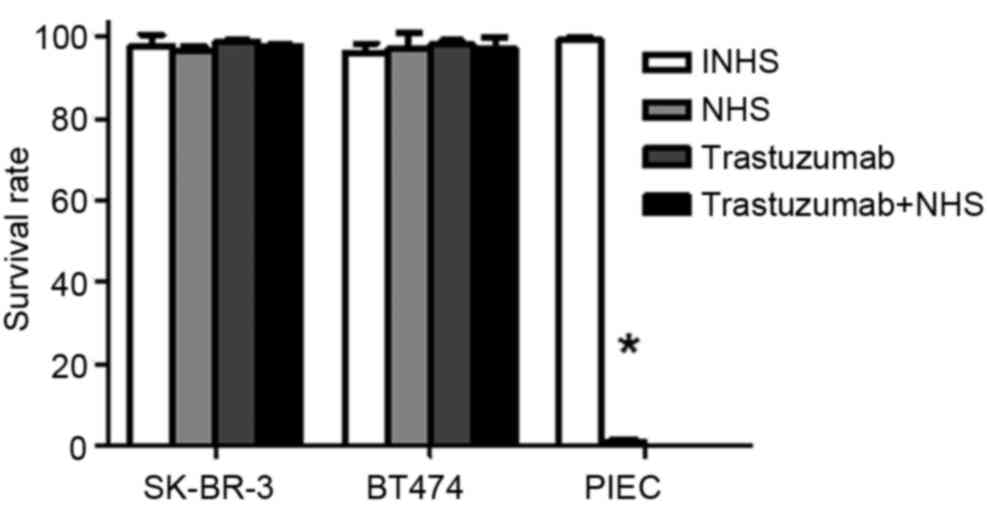
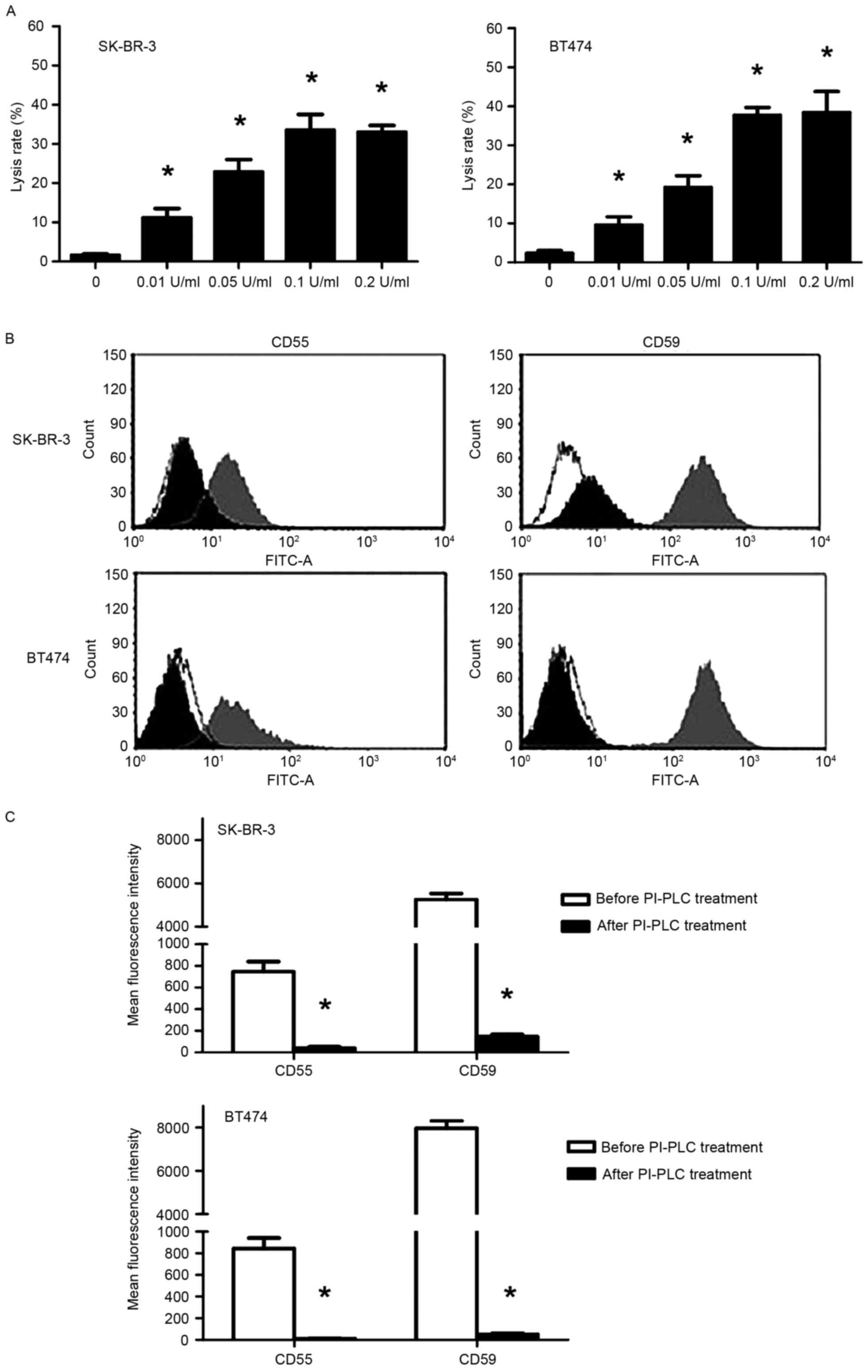
|
1
|
Servick K: Breast cancer. Breast cancer: A
world of differences. Science. 343:1452–1453. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thomas E and Berner G: Prognostic and
predictive implications of HER2 status for breast cancer patients.
Eur J Oncol Nurs. 4:10–17. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cardoso F, Piccart MJ, Durbecq V and Di
Leo A: Resistance to trastuzumab: A necessary evil or a temporary
challenge? Clin Breast Cancer. 3:247–259. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Scott AM, Wolchok JD and Old LJ: Antibody
therapy of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:278–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mineo JF, Bordron A, Quintin-Roué I,
Loisel S, Ster KL, Buhé V, Lagarde N and Berthou C: Recombinant
humanised anti-HER2/neu antibody (Herceptin) induces cellular death
of glioblastomas. Br J Cancer. 91:1195–1199. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Prang N, Preithner S, Brischwein K, Göster
P, Wöppel A, Müller J, Steiger C, Peters M, Baeuerle PA and da
Silva AJ: Cellular and complement-dependent cytotoxicity of
Ep-CAM-specific monoclonal antibody MT201 against breast cancer
cell lines. Br J Cancer. 92:342–349. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fishelson Z, Donin N, Zell S, Schultz S
and Kirschfink M: Obstacles to cancer immunotherapy: Expression of
membrane complement regulatory proteins (mCRPs) in tumors. Mol
Immunol. 40:109–123. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Macor P and Tedesco F: Complement as
effector system in cancer immunotherapy. Immunol Lett. 111:6–13.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu Y, Wang Y, Qin F, Wang Z, Wang Y, Yang
Y and Zheng H and Zheng H: CD55 limits sensitivity to
complement-dependent cytolysis triggered by heterologous expression
of α-gal xenoantigen in colon tumor cells. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 306:G1056–G1064. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu M, Yang YJ, Zheng H, Zhong XR, Wang Y,
Wang Z, Wang YG and Wang YP: Membrane-bound complement regulatory
proteins are prognostic factors of operable breast cancer treated
with adjuvant trastuzumab: A retrospective study. Oncol Rep.
32:2619–2627. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shi XX, Zhang B, Zang JL, Wang GY and Gao
MH: CD59 silencing via retrovirus-mediated RNA interference
enhanced complement-mediated cell damage in ovary cancer. Cell Mol
Immunol. 6:61–66. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Reichert JM: Antibody-based therapeutics
to watch in 2011. MAbs. 3:76–99. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Strome SE, Sausville EA and Mann D: A
mechanistic perspective of monoclonal antibodies in cancer therapy
beyond target-related effects. Oncologist. 12:1084–1095. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Clark MR: IgG effector mechanisms. Chem
Immunol. 65:88–110. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dalle S, Thieblemont C, Thomas L and
Dumontet C: Monoclonal antibodies in clinical oncology. Anticancer
Agents Med Chem. 8:523–532. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dean-Colomb W and Esteva FJ: Her2-positive
breast cancer: Herceptin and beyond. Eur J Cancer. 44:2806–2812.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
De Lorenzo C, Tedesco A, Terrazzano G,
Cozzolino R, Laccetti P, Piccoli R and D'Alessio G: A human,
compact, fully functional anti-ErbB2 antibody as a novel antitumour
agent. Br J Cancer. 91:1200–1204. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu J, Caragine T, Chen S, Morgan BP, Frey
AB and Tomlinson S: Protection of human breast cancer cells from
complement-mediated lysis by expression of heterologous CD59. Clin
Exp Immunol. 115:13–18. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gelderman KA, Tomlinson S, Ross GD and
Gorter A: Complement function in mAb-mediated cancer immunotherapy.
Trends Immunol. 25:158–164. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yan J, Allendorf DJ, Li B, Yan R, Hansen R
and Donev R: The role of membrane complement regulatory proteins in
cancer immunotherapy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 632:159–174.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jurianz K, Ziegler S, Garcia-Schüler H,
Kraus S, Bohana-Kashtan O, Fishelson Z and Kirschfink M: Complement
resistance of tumor cells: Basal and induced mechanisms. Mol
Immunol. 36:929–939. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gancz D and Fishelson Z: Cancer resistance
to complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC): Problem-oriented
research and development. Mol Immunol. 46:2794–2800. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rushmere NK, Knowlden JM, Gee JM, Harper
ME, Robertson JF, Morgan BP and Nicholson RI: Analysis of the level
of mRNA expression of the membrane regulators of complement, CD59,
CD55, and CD46, in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 108:930–936. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ravindranath NM and Shuler C: Cell-surface
density of complement restriction factors (CD46, CD55 and CD59):
Oral squamous cell carcinoma versus other solid tumors. Oral Surg
Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 103:231–239. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Loberg RD, Wojno KJ, Day LL and Pienta KJ:
Analysis of membrane-bound complement regulatory proteins in
prostate cancer. Urology. 66:1321–1326. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Madjd Z, Durrant LG, Bradley R, Spendlove
I, Ellis IO and Pinder SE: Loss of CD55 is associated with
aggressive breast tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 10:2797–2803. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zell S, Geis N, Rutz R, Schultz S, Giese T
and Kirschfink M: Down-regulation of CD55 and CD46 expression by
anti-sense phosphorothioate oligonucleotides (S-ODNs) sensitizes
tumour cells to complement attack. Clin Exp Immunol. 150:576–584.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jurianz K, Maslak S, Garcia-Schuler H,
Fishelson Z and Kirschfink M: Neutralization of complement
regulatory proteins augments lysis of breast carcinoma cells
targeted with rhumAb anti-HER2. Immunopharmacology. 42:209–218.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Macor P, Tripodo C, Zorzet S, Piovan E,
Bossi F, Marzari R, Amadori A and Tedesco F: In vivo targeting of
human neutralizing antibodies against CD55 and CD59 to lymphoma
cells increases the antitumor activity of rituximab. Cancer Res.
67:10556–10563. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Golay J, Lazzari M, Facchinetti V,
Bernasconi S, Borleri G, Barbui T, Rambaldi A and Introna M: CD20
levels determine the in vitro susceptibility to rituximab and
complement of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Further
regulation by CD55 and CD59. Blood. 98:3383–3389. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou X, Hu W and Qin X: The role of
complement in the mechanism of action of rituximab for B-cell
lymphoma: Implications for therapy. Oncologist. 13:954–966. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nicholson-Weller A and Wang CE: Structure
and function of decay accelerating factor CD55. J Lab Clin Med.
123:485–491. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fonsatti E, Altomonte M, Coral S, De Nardo
C, Lamaj E, Sigalotti L, Natali PG and Maio M: Emerging role of
protectin (CD59) in humoral immunotherapy of solid malignancies.
Clin Ter. 151:187–193. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Brasoveanu LI, Altomonte M, Fonsatti E,
Colizzi F, Coral S, Nicotra MR, Cattarossi I, Cattelan A, Natali PG
and Maio M: Levels of cell membrane CD59 regulate the extent of
complement-mediated lysis of human melanoma cells. Lab Invest.
74:33–42. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Azuma A, Yamano Y, Yoshimura A, Hibino T,
Nishida T, Yagita H, Okumura K, Seya T, Kannagi R, Shibuya M, et
al: Augmented lung adenocarcinoma cytotoxicity by the combination
of a genetically modified anti-Lewis Y antibody and antibodies to
complement regulatory proteins. Scand J Immunol. 42:202–208. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bjorge L, Hakulinen J, Wahlström T, Matre
R and Meri S: Complement-regulatory proteins in ovarian
malignancies. Int J Cancer. 70:14–25. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Aagaard L and Rossi JJ: RNAi therapeutics:
Principles, prospects and challenges. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 59:75–86.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bellone S, Roque D, Cocco E, Gasparrini S,
Bortolomai I, Buza N, Abu-Khalaf M, Silasi DA, Ratner E, Azodi M,
et al: Downregulation of membrane complement inhibitors CD55 and
CD59 by siRNA sensitises uterine serous carcinoma overexpressing
Her2/neu to complement and antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity in
vitro: Implications for trastuzumab-based immunotherapy. Br J
Cancer. 106:1543–1550. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mamidi S, Cinci M, Hasmann M, Fehring V
and Kirschfink M: Lipoplex mediated silencing of membrane
regulators (CD46, CD55 and CD59) enhances complement-dependent
anti-tumor activity of trastuzumab and pertuzumab. Mol Oncol.
7:580–594. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|