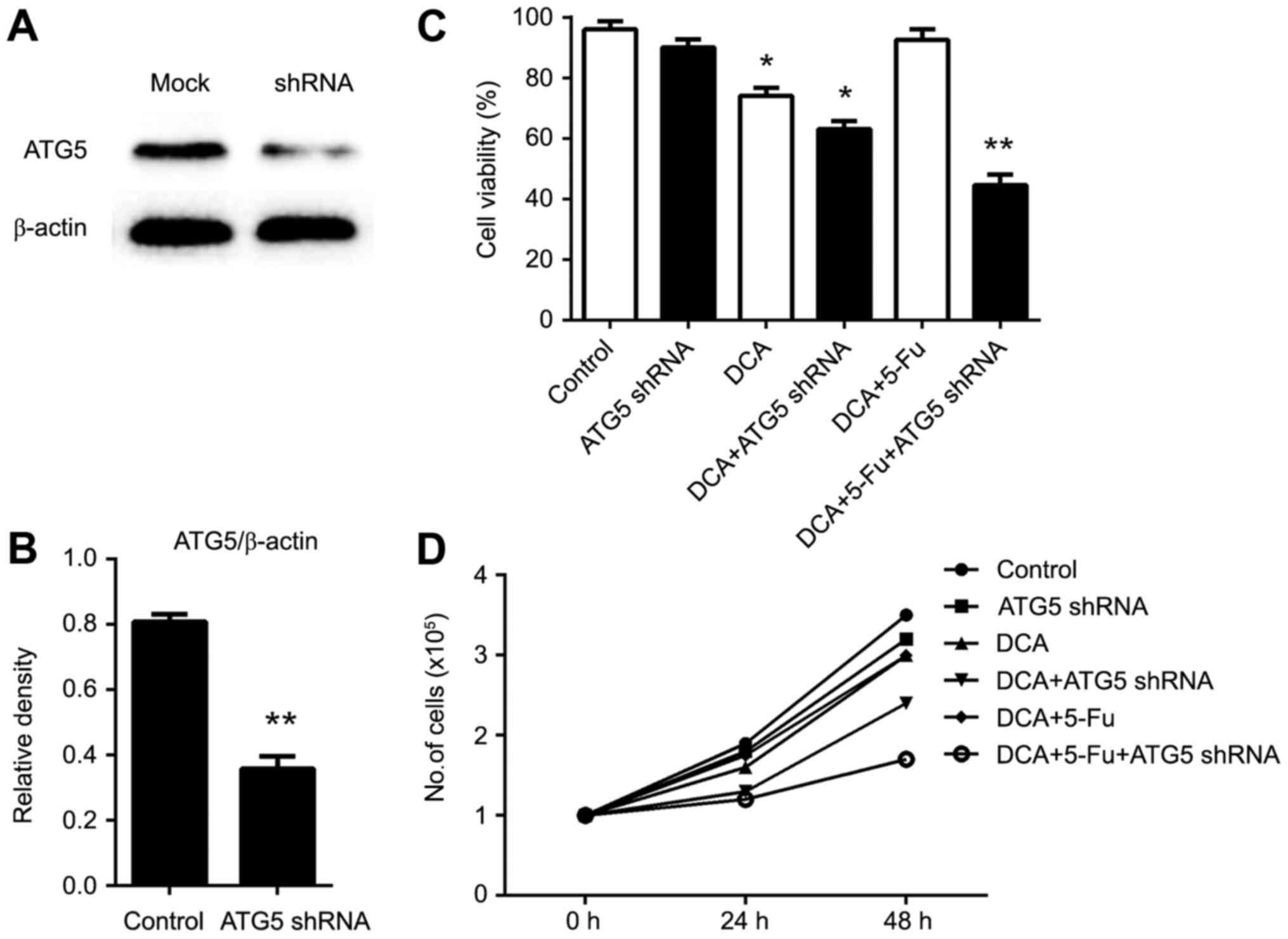
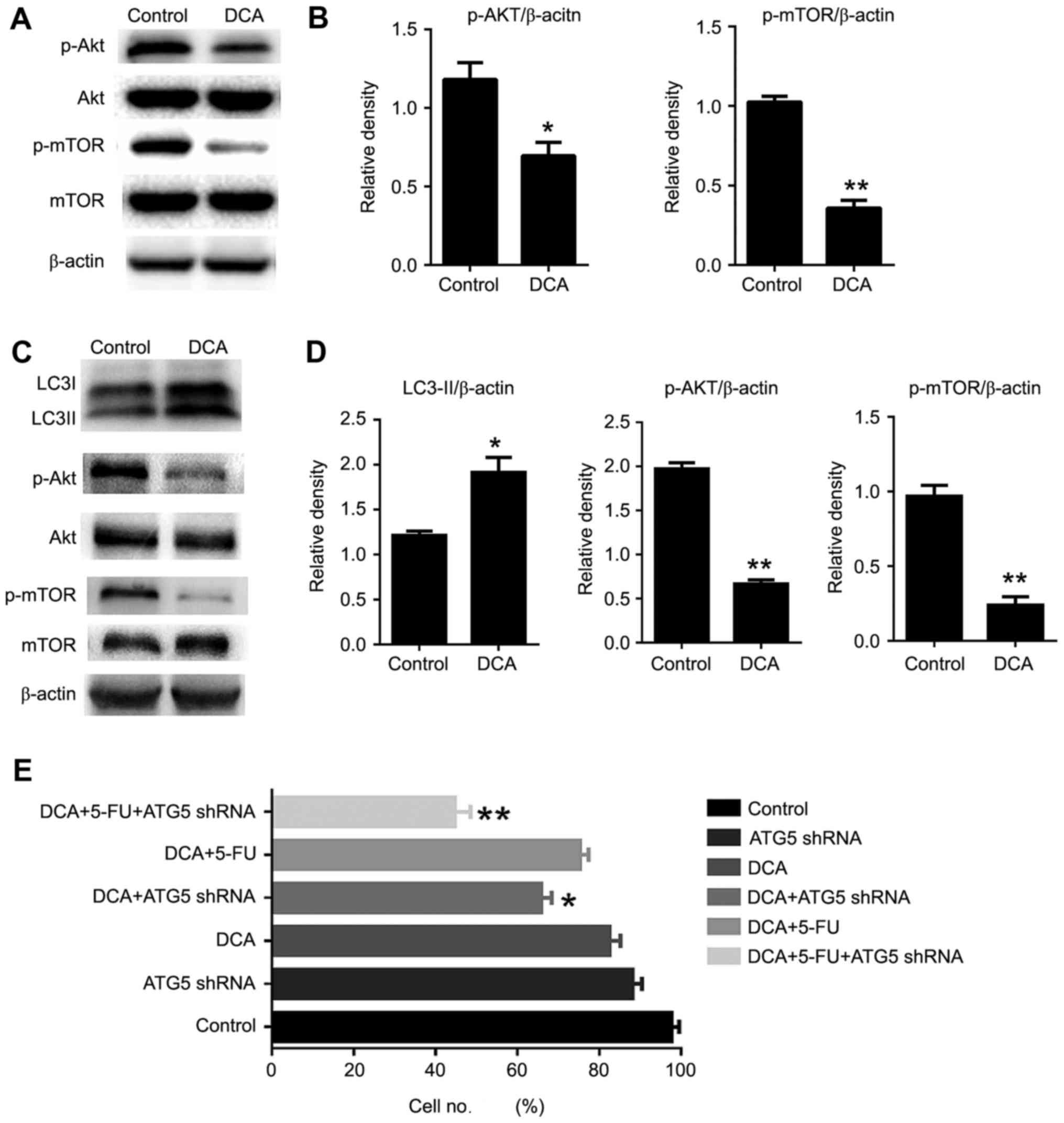
|
1
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gupta VK, Scheunemann L, Eisenberg T,
Mertel S, Bhukel A, Koemans TS, Kramer JM, Liu KS, Schroeder S,
Stunnenberg HG, et al: Restoring polyamines protects from
age-induced memory impairment in an autophagy-dependent manner. Nat
Neurosci. 16:1453–1460. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Denton D, Nicolson S and Kumar S: Cell
death by autophagy: Facts and apparent artifacts. Cell Death
Differ. 19:87–95. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Teng RJ, Du J, Welak S, Guan T, Eis A, Shi
Y and Konduri GG: Cross talk between NADPH oxidase and autophagy in
pulmonary artery endothelial cells with intrauterine persistent
pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
302:L651–L663. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Baehrecke EH: Autophagy: Dual roles in
life and death? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:505–510. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fan QW and Weiss WA: Autophagy and Akt
promote survival in glioma. Autophagy. 7:536–538. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang K, Liu R, Li J, Mao J, Lei Y, Wu J,
Zeng J, Zhang T, Wu H, Chen L, et al: Quercetin induces protective
autophagy in gastric cancer cells: Involvement of Akt-mTOR- and
hypoxia-induced factor 1α-mediated signaling. Autophagy. 7:966–978.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cheng P, Ni Z, Dai X, Wang B, Ding W, Rae
Smith A, Xu L, Wu D, He F and Lian J: The novel BH-3 mimetic
apogossypolone induces Beclin-1- and ROS-mediated autophagy in
human hepatocellular carcinoma [corrected] cells. Cell Death Dis.
4:e4892013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lin JF, Tsai TF, Liao PC, Lin YH, Lin YC,
Chen HE, Chou KY and Hwang TI: Benzyl isothiocyanate induces
protective autophagy in human prostate cancer cells via inhibition
of mTOR signaling. Carcinogenesis. 34:406–414. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bonnet S, Archer SL, Allalunis-Turner J,
Haromy A, Beaulieu C, Thompson R, Lee CT, Lopaschuk GD, Puttagunta
L, Bonnet S, et al: A mitochondria-K+ channel axis is suppressed in
cancer and its normalization promotes apoptosis and inhibits cancer
growth. Cancer Cell. 11:37–51. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cao W, Yacoub S, Shiverick KT, Namiki K,
Sakai Y, Porvasnik S, Urbanek C and Rosser CJ: Dichloroacetate
(DCA) sensitizes both wild-type and over expressing Bcl-2 prostate
cancer cells in vitro to radiation. Prostate. 68:1223–1231. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sun RC, Fadia M, Dahlstrom JE, Parish CR,
Board PG and Blackburn AC: Reversal of the glycolytic phenotype by
dichloroacetate inhibits metastatic breast cancer cell growth in
vitro and in vivo. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 120:253–260. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun W, Zhou S, Chang SS, McFate T, Verma A
and Califano JA: Mitochondrial mutations contribute to HIF1alpha
accumulation via increased reactive oxygen species and up-regulated
pyruvate dehydrogenease kinase 2 in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:476–484. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yuan K, Huang C, Fox J, Laturnus D,
Carlson E, Zhang B, Yin Q, Gao H and Wu M: Autophagy plays an
essential role in the clearance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by
alveolar macrophages. J Cell Sci. 125:507–515. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jiang X, Overholtzer M and Thompson CB:
Autophagy in cellular metabolism and cancer. J Clin Invest.
125:47–54. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tong J, Xie G, He J, Li J, Pan F and Liang
H: Synergistic antitumor effect of dichloroacetate in combination
with 5-fluorouracil in colorectal cancer. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2011:7405642011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rubinsztein DC, Codogno P and Levine B:
Autophagy modulation as a potential therapeutic target for diverse
diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 11:709–730. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin G, Hill DK, Andrejeva G, Boult JK,
Troy H, Fong AC, Orton MR, Panek R, Parkes HG, Jafar M, et al:
Dichloroacetate induces autophagy in colorectal cancer cells and
tumours. Br J Cancer. 111:375–385. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Michelakis ED, Webster L and Mackey JR:
Dichloroacetate (DCA) as a potential metabolic-targeting therapy
for cancer. Br J Cancer. 99:989–994. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Papandreou I, Goliasova T and Denko NC:
Anticancer drugs that target metabolism: Is dichloroacetate the new
paradigm? Int J Cancer. 128:1001–1008. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Michelakis ED, Sutendra G, Dromparis P,
Webster L, Haromy A, Niven E, Maguire C, Gammer TL, Mackey JR,
Fulton D, et al: Metabolic modulation of glioblastoma with
dichloroacetate. Sci Transl Med. 2:31ra342010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shahrzad S, Lacombe K, Adamcic U, Minhas K
and Coomber BL: Sodium dichloroacetate (DCA) reduces apoptosis in
colorectal tumor hypoxia. Cancer Lett. 297:75–83. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|