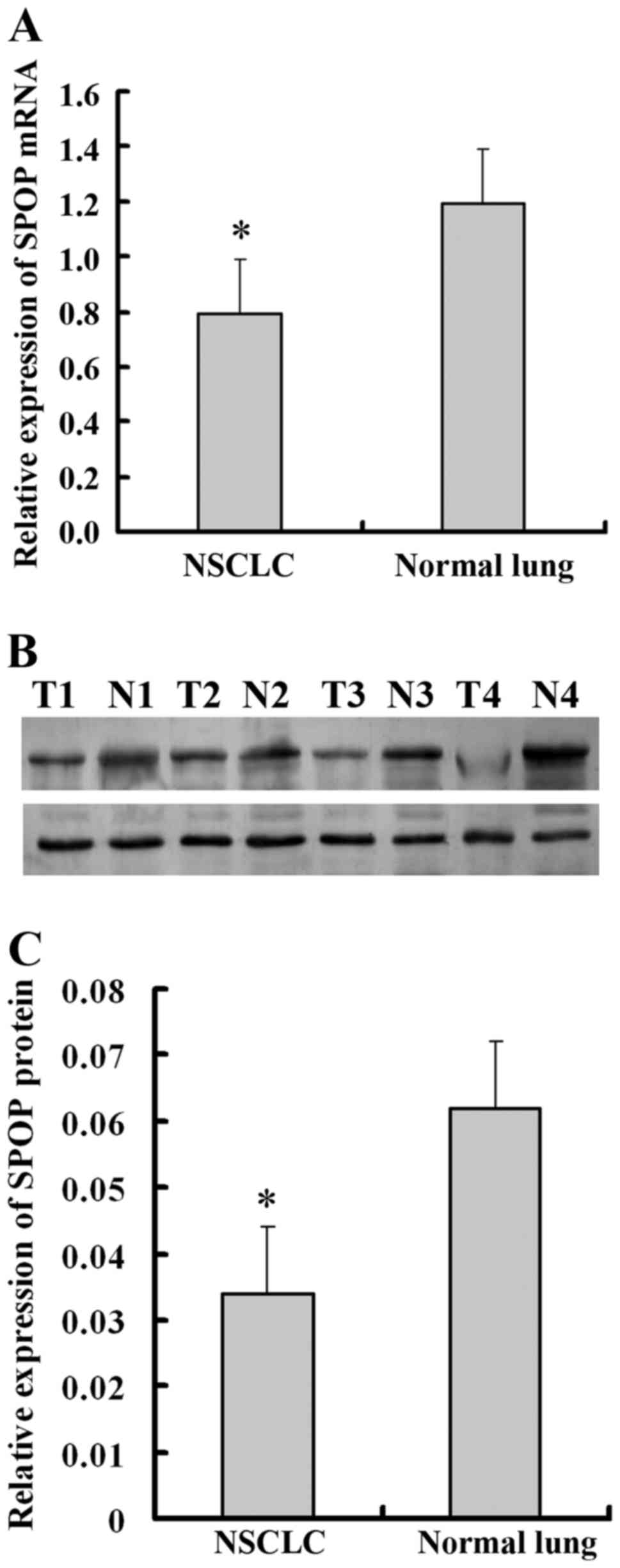
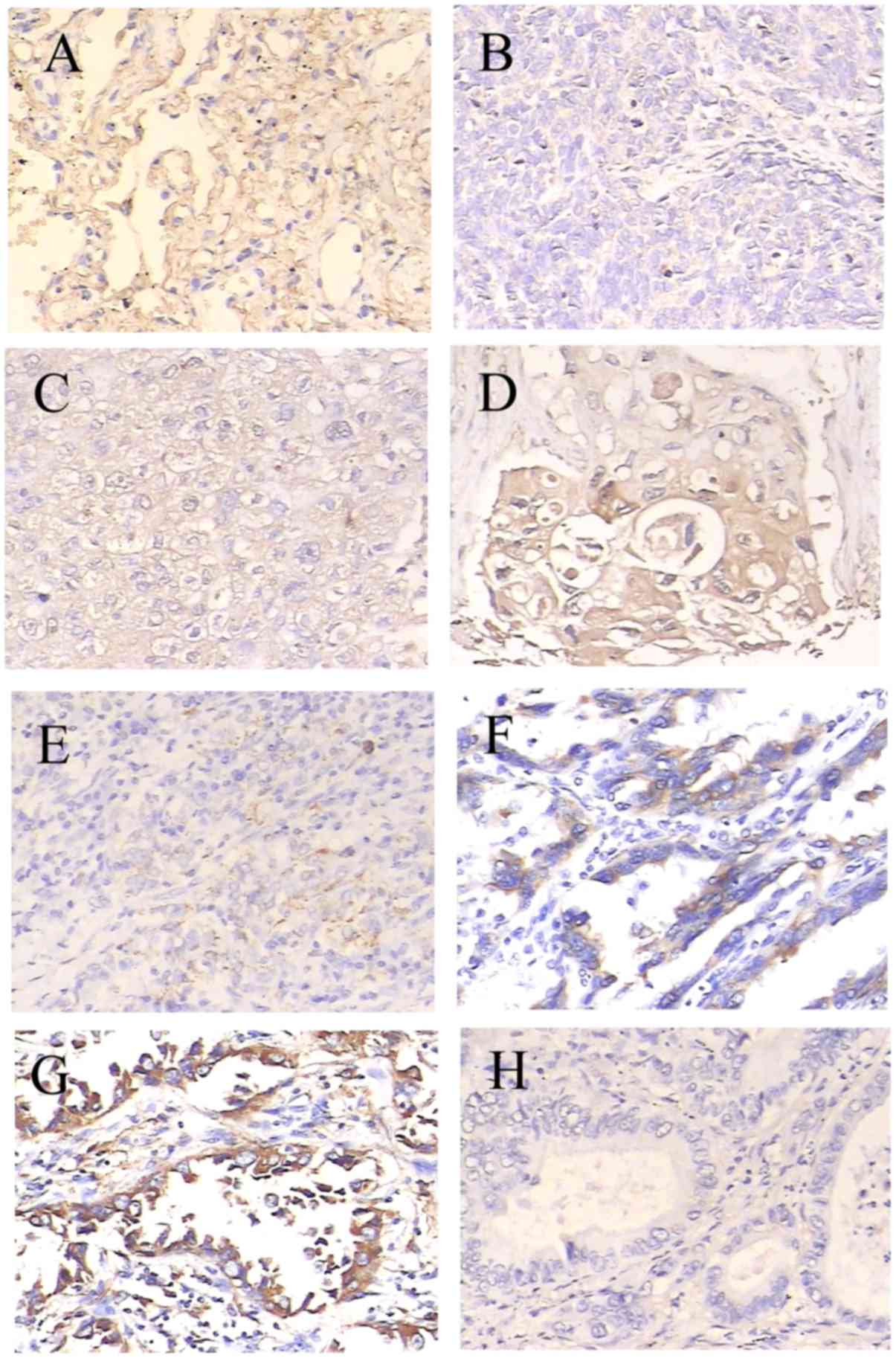
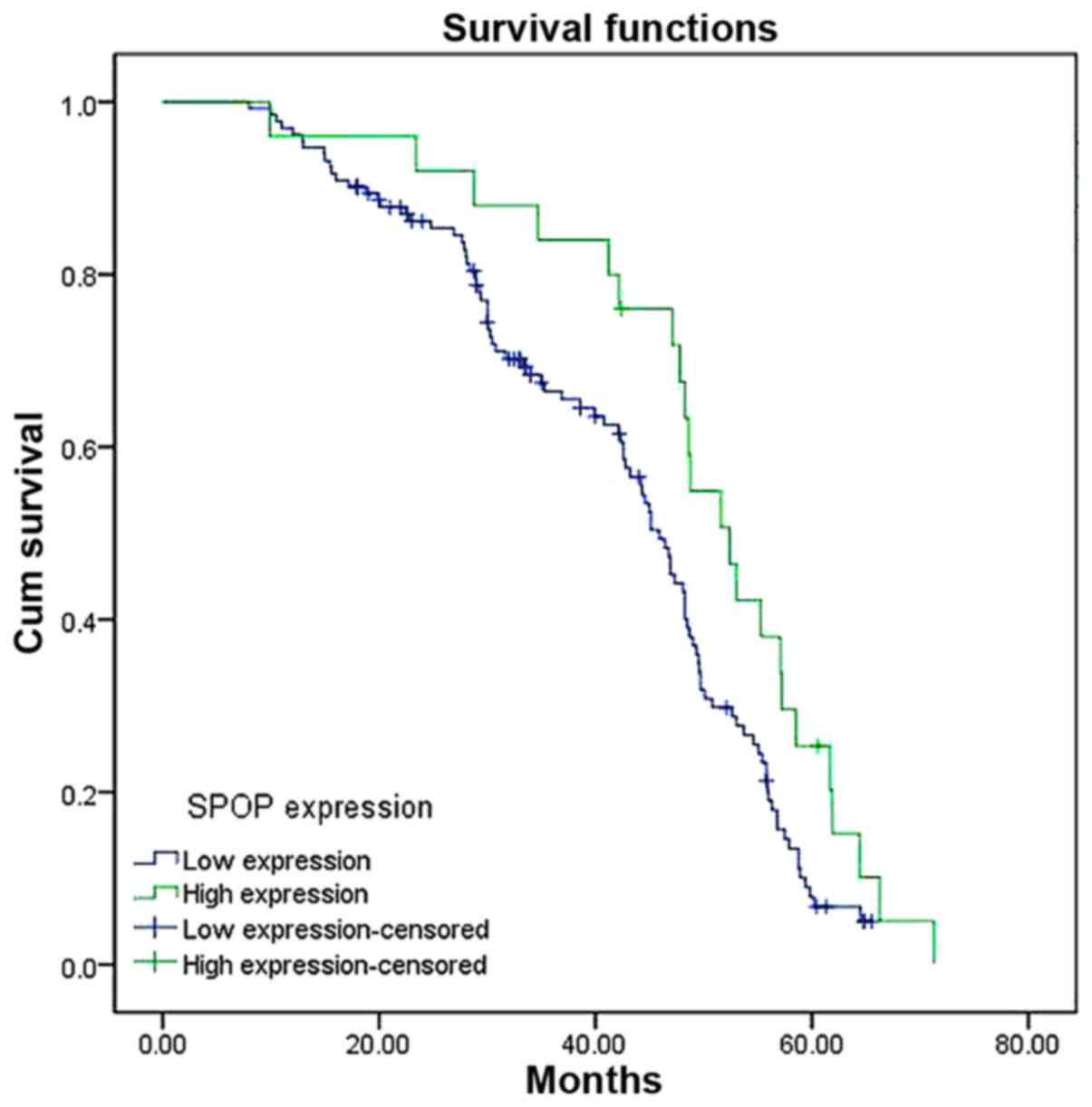
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang T, Zhang DM, Zhao D, Hou XM, Liu XJ,
Ling XL and Ma SC: The prognostic value of osteopontin expression
in non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. J Mol Histol.
45:533–540. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Esposito L, Conti D, Ailavajhala R, Khalil
N and Giordano A: Lung cancer: Are we up to the challenge? Curr
Genomics. 11:513–518. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nagai Y, Kojima T, Muro Y, Hachiya T,
Nishizawa Y, Wakabayashi T and Hagiwara M: Identification of a
novel nuclear speckle-type protein, SPOP. FEBS Lett. 418:23–26.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
De Marchis L, Cropp C, Sheng ZM, Bargo S
and Callahan R: Candidate target genes for loss of heterozygosity
on human chromosome 17q21. Br J Cancer. 90:2384–2389. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hernández-Muñoz I, Lund AH, van der Stoop
P, Boutsma E, Muijrers I, Verhoeven E, Nusinow DA, Panning B,
Marahrens Y and van Lohuizen M: Stable X chromosome inactivation
involves the PRC1 polycomb complex and requires histone MACROH2A1
and the CULLIN3/SPOP ubiquitin E3 ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:7635–7640. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kwon JE, La M, Oh KH, Oh YM, Kim GR, Seol
JH, Baek SH, Chiba T, Tanaka K, Bang OS, et al: BTB
domain-containing speckle-type POZ protein (SPOP) serves as an
adaptor of Daxx for ubiquitination by Cul3-based ubiquitin ligase.
J Biol Chem. 281:12664–12672. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ande SR, Chen J and Maddika S: The
ubiquitin pathway: An emerging drug target in cancer therapy. Eur J
Pharmacol. 625:199–205. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kan Z, Jaiswal BS, Stinson J, Janakiraman
V, Bhatt D, Stern HM, Yue P, Haverty PM, Bourgon R, Zheng J, et al:
Diverse somatic mutation patterns and pathway alterations in human
cancers. Nature. 466:869–873. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Berger MF, Lawrence MS, Demichelis F,
Drier Y, Cibulskis K, Sivachenko AY, Sboner A, Esgueva R, Pflueger
D, Sougnez C, et al: The genomic complexity of primary human
prostate cancer. Nature. 470:214–220. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Barbieri CE, Baca SC, Lawrence MS,
Demichelis F, Blattner M, Theurillat JP, White TA, Stojanov P, Van
Allen E, Stransky N, et al: Exome sequencing identifies recurrent
SPOP, FOXA1 and MED12 mutations in prostate cancer. Nat Genet.
44:685–689. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Le GM, O'Hara AJ, Rudd ML, Urick ME,
Hansen NF, O'Neil NJ, Price JC, Zhang S, England BM, Godwin AK, et
al: Exome sequencing of serous endometrial tumors identifies
recurrent somatic mutations in chromatin-remodeling and ubiquitin
ligase complex genes. Nat Genet. 44:1310–1315. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li C, Ao J, Fu J, Lee DF, Xu J, Lonard D
and O'Malley BW: Tumor-suppressor role for the SPOP ubiquitin
ligase in signal-dependent proteolysis of the oncogenic
co-activator SRC-3/AIB1. Oncogene. 30:4350–4364. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim MS, Je EM, Oh JE, Yoo NJ and Lee SH:
Mutational and expressional analyses of SPOP, a candidate tumor
suppressor gene, in prostate, gastric and colorectal cancers.
APMIS. 121:626–633. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Nicholson AG,
Yatabe Y, Austin JH, Beasley MB, Chirieac LR, Dacic S, Duhig E,
Flieder DB, et al: The 2015 World Health Organization
classification of lung tumors: Impact of genetic, clinical and
radiologic advances since the 2004 classification. J Thorac Oncol.
10:1243–1260. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American joint
committee on cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mani RS: The emerging role of speckle-type
POZ protein (SPOP) in cancer development. Drug Discov Today.
19:1498–1502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ding D, Song T, Jun W, Tan Z and Fang J:
Decreased expression of the SPOP gene is associated with poor
prognosis in glioma. Int J Oncol. 46:333–341. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Grasso CS, Wu YM, Robinson DR, Cao X,
Dhanasekaran SM, Khan AP, Quist MJ, Jing X, Lonigro RJ, Brenner JC,
et al: The mutational landscape of lethal castration-resistant
prostate cancer. Nature. 487:239–243. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Varshavsky A: Discovery of the biology of
the ubiquitin system. JAMA. 311:1969–1970. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pei XH, Bai F, Li Z, Smith MD, Whitewolf
G, Jin R and Xiong Y: Cytoplasmic CUL9/PARC ubiquitin ligase is a
tumor suppressor and promotes p53-dependent apoptosis. Cancer Res.
71:2969–2977. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hoeller D and Dikic I: Targeting the
ubiquitin system in cancer therapy. Nature. 458:438–444. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cohen P and Tcherpakov M: Will the
ubiquitin system furnish as many drug targets as protein kinases?
Cell. 143:686–693. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|