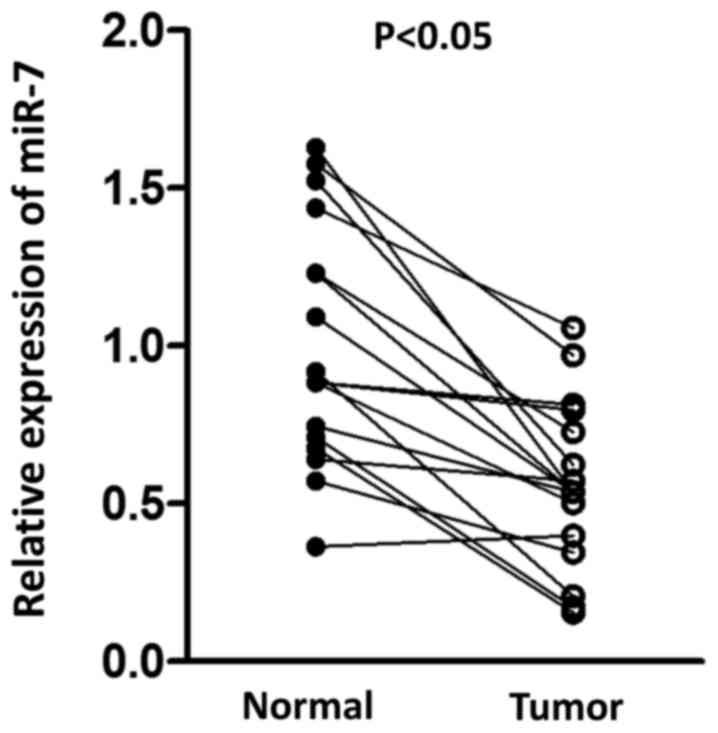
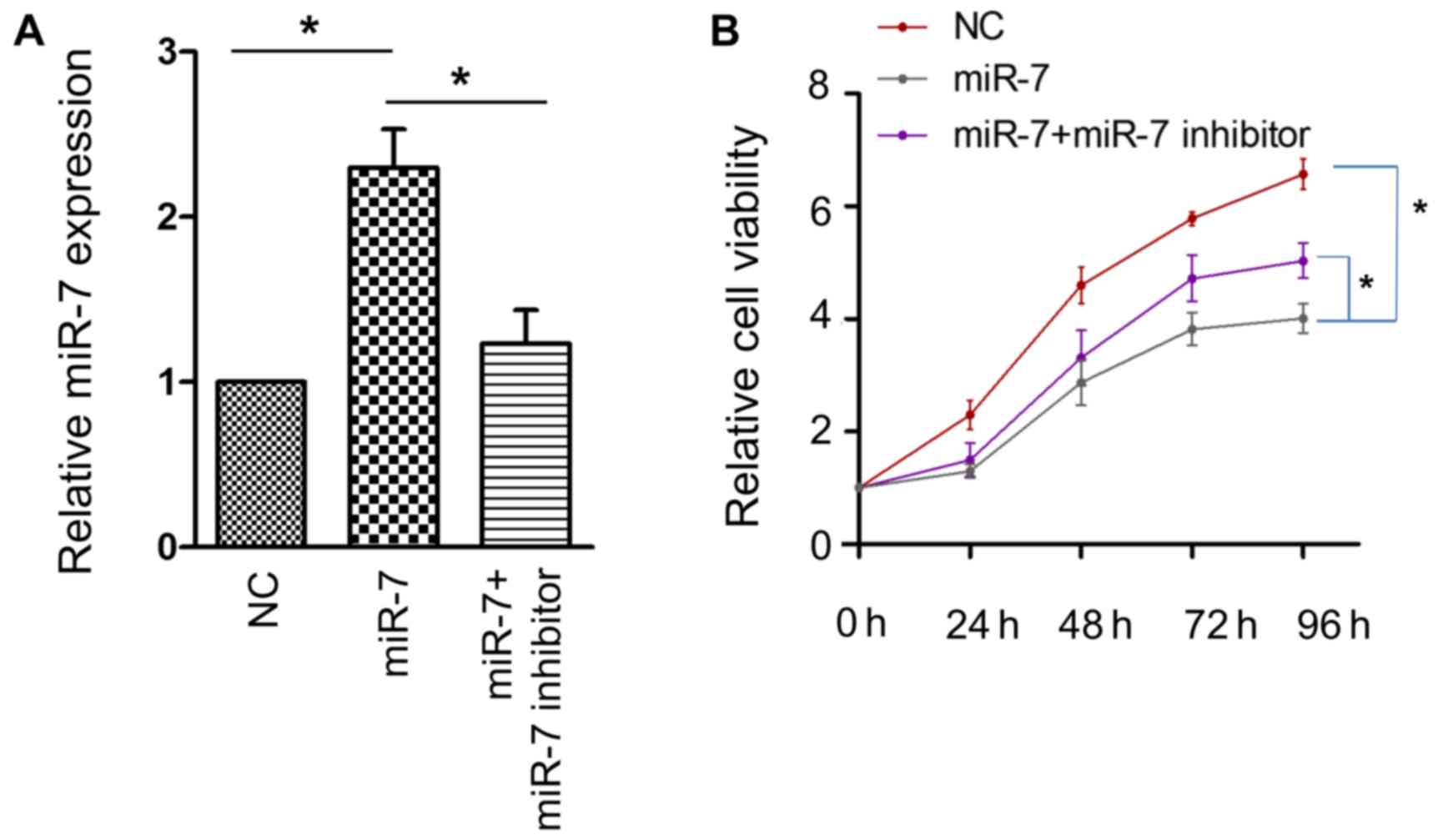
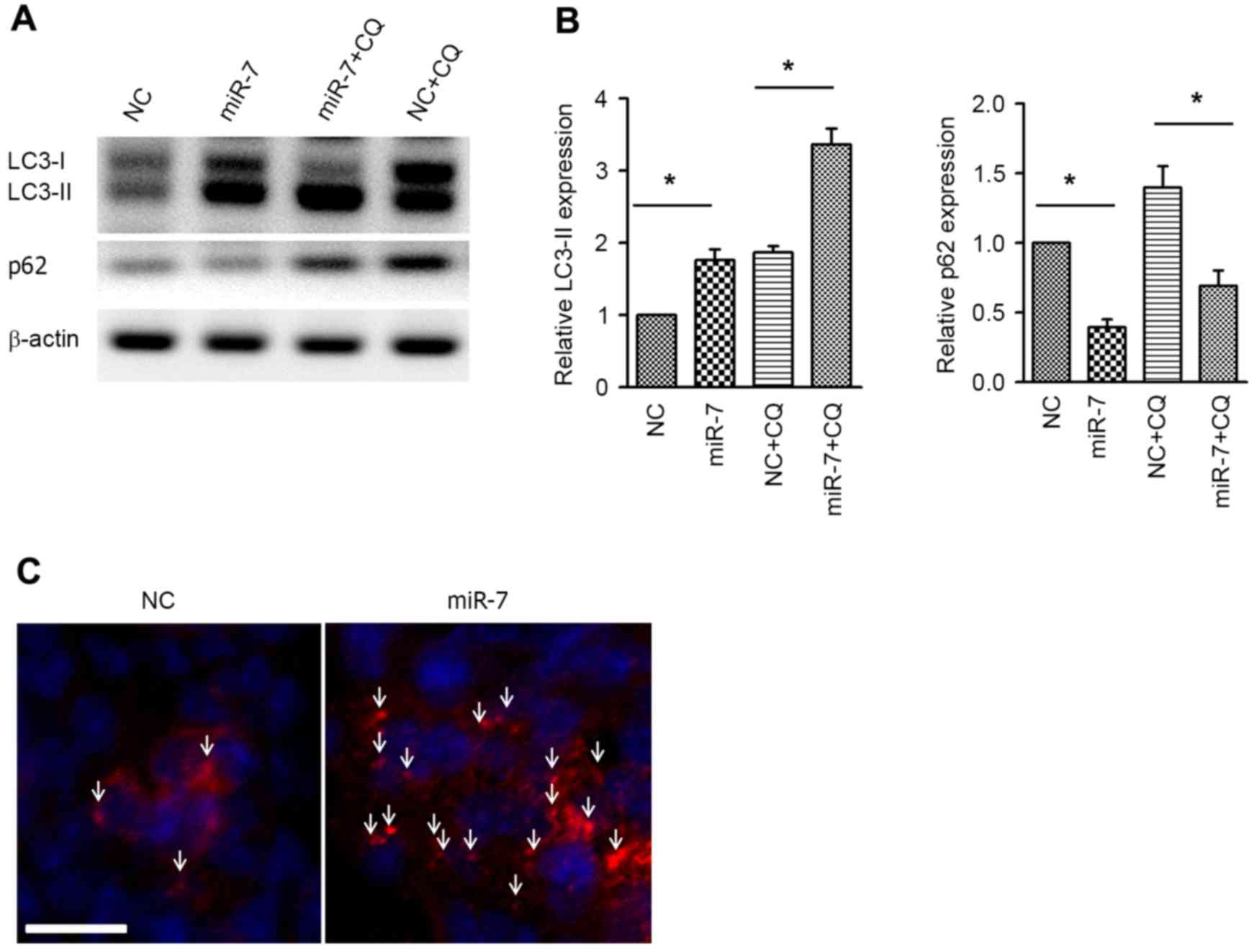
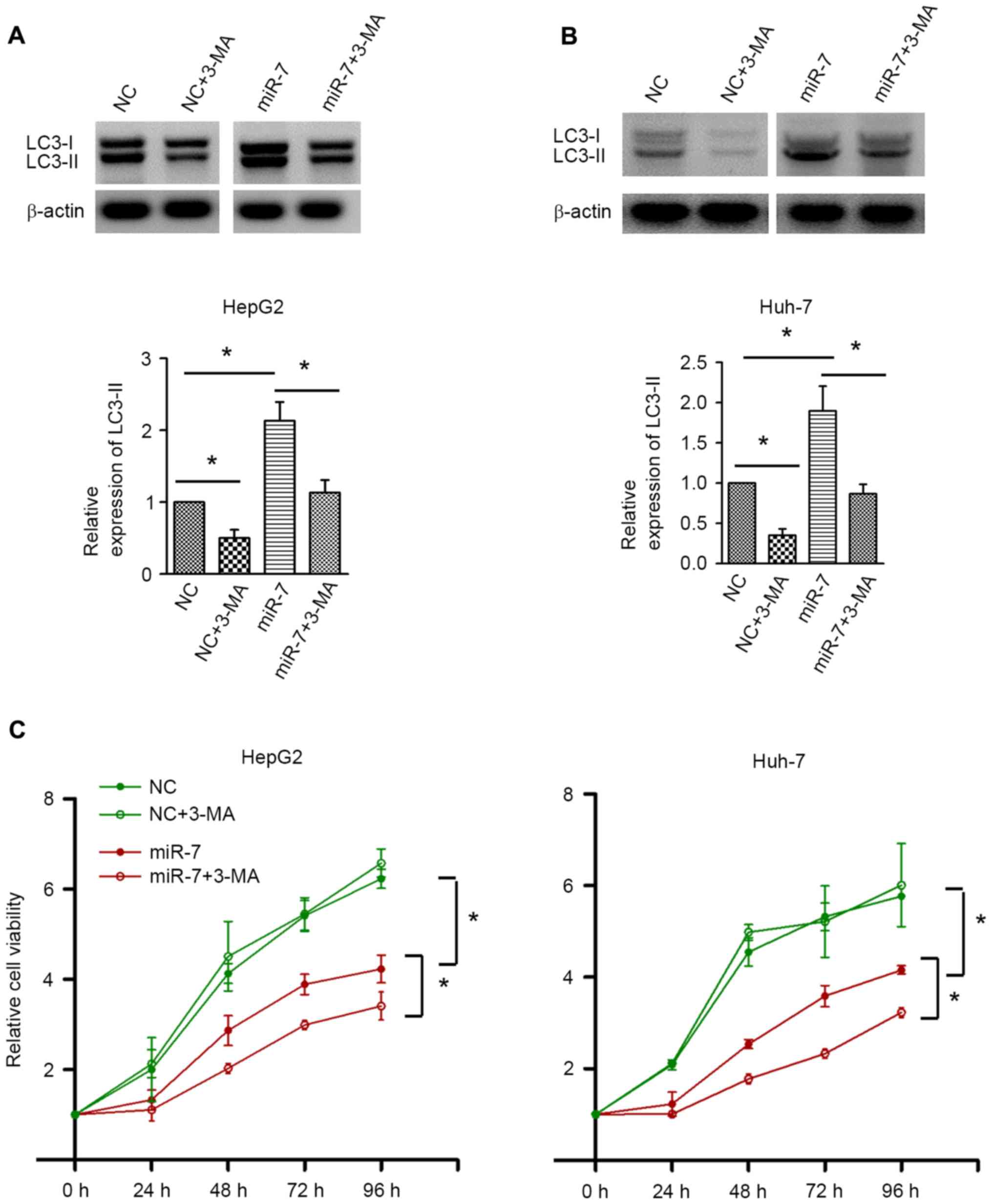
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Balogh J, Victor D III, Asham EH,
Burroughs SG, Boktour M, Saharia A, Li X, Ghobrial RM and Monsour
HP Jr: Hepatocellular carcinoma: a review. J Hepatocell Carcinoma.
3:41–53. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Levine B and Kroemer G: Autophagy in the
pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 132:27–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Puri P and Chandra A: Autophagy modulation
as a potential therapeutic target for liver diseases. J Clin Exp
Hepatol. 4:51–59. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kumar A, Singh UK and Chaudhary A:
Targeting autophagy to overcome drug resistance in cancer therapy.
Future Med Chem. 7:1535–1542. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Du H, Yang W, Chen L, Shi M, Seewoo V,
Wang J, Lin A, Liu Z and Qiu W: Role of autophagy in resistance to
oxaliplatin in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep.
27:143–150. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jung CH, Ro SH, Cao J, Otto NM and Kim DH:
mTOR regulation of autophagy. FEBS Lett. 584:1287–1295. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bupathi M, Kaseb A, Meric-Bernstam F and
Naing A: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Where there is unmet need. Mol
Oncol. 9:1501–1509. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang Z, Jin W, Jin H and Wang X: mTOR in
viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma: Function and
treatment. Biomed Res Int. 2014:7356722014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Inamura K: Diagnostic and therapeutic
potential of MicroRNAs in lung cancer. Cancers (Basel). 9:pii: E49.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cătană CS, Pichler M, Giannelli G, Mader
RM and Berindan-Neagoe I: Non-coding RNAs, the Trojan horse in
two-way communication between tumor and stroma in colorectal and
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:29519–29534.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Faller M and Guo F: MicroRNA biogenesis:
There's more than one way to skin a cat. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1779:663–667. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yao M, Wang L, Yao Y, Gu HB and Yao DF:
Biomarker-based MicroRNA therapeutic strategies for hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2:253–258. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Horsham JL, Kalinowski FC, Epis MR, Ganda
C, Brown RA and Leedman PJ: Clinical potential of microRNA-7 in
cancer. J Clin Med. 4:1668–1687. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kalinowski FC, Brown RA, Ganda C, Giles
KM, Epis MR, Horsham J and Leedman PJ: microRNA-7: A tumor
suppressor miRNA with therapeutic potential. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 54:312–317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang X, Hu S, Zhang X, Wang L, Zhang X,
Yan B, Zhao J, Yang A and Zhang R: MicroRNA-7 arrests cell cycle in
G1 phase by directly targeting CCNE1 in human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 443:1078–1084. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xiong S, Zheng Y, Jiang P, Liu R, Liu X
and Chu Y: MicroRNA-7 inhibits the growth of human non-small cell
lung cancer A549 cells through targeting BCL-2. Int J Biol Sci.
7:805–814. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Luo J, Li H and Zhang C: MicroRNA-7
inhibits the malignant phenotypes of non-small cell lung cancer
in vitro by targeting Pax6. Mol Med Rep. 12:5443–5448.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chang YL, Zhou PJ, Wei L, Li W, Ji Z, Fang
YX and Gao WQ: MicroRNA-7 inhibits the stemness of prostate cancer
stem-like cells and tumorigenesis by repressing KLF4/PI3K/Akt/p21
pathway. Oncotarget. 6:24017–24031. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fang Y, Xue JL, Shen Q, Chen J and Tian L:
MicroRNA-7 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by targeting the
phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 55:1852–1862. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xie J, Chen M, Zhou J, Mo MS, Zhu LH, Liu
YP, Gui QJ, Zhang L and Li GQ: miR-7 inhibits the invasion and
metastasis of gastric cancer cells by suppressing epidermal growth
factor receptor expression. Oncol Rep. 31:1715–1722.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bitto A, Lerner CA, Nacarelli T, Crowe E,
Torres C and Sell C: P62/SQSTM1 at the interface of aging,
autophagy, and disease. Age (Dordr). 36:96262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhu AX: Systemic treatment of
hepatocellular carcinoma: Dawn of a new era? Ann Surg Oncol.
17:1247–1256. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gandellini P, Doldi V and Zaffaroni N:
microRNAs as players and signals in the metastatic cascade:
Implications for the development of novel anti-metastatic
therapies. Semin Cancer Biol. Mar 23–2017.(Epub ahead of Print).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Denaro N, Merlano MC, Russi EG and Lo
Nigro C: Non coding RNAs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
(HNSCC): A clinical perspective. Anticancer Res. 34:6887–6896.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Karagonlar ZF, Korhan P and Atabey N:
Targeting c-Met in cancer by MicroRNAs: Potential therapeutic
applications in hepatocellular carcinoma. Drug Dev Res. 76:357–367.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Luo T, Fu J, Xu A, Su B, Ren Y, Li N, Zhu
J, Zhao X, Dai R, Cao J, et al: PSMD10/gankyrin induces autophagy
to promote tumor progression through cytoplasmic interaction with
ATG7 and nuclear transactivation of ATG7 expression. Autophagy.
12:1355–1371. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tian Y, Kuo CF, Sir D, Wang L,
Govindarajan S, Petrovic LM and Ou JH: Autophagy inhibits oxidative
stress and tumor suppressors to exert its dual effect on
hepatocarcinogenesis. Cell Death Differ. 22:1025–1034. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huang GM, Jiang QH, Cai C, Qu M and Shen
W: SCD1 negatively regulates autophagy-induced cell death in human
hepatocellular carcinoma through inactivation of the AMPK signaling
pathway. Cancer Lett. 358:180–190. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang Y, Wu J, Lin B, Li X, Zhang H, Ding
H, Chen X, Lan L and Luo H: Galangin suppresses HepG2 cell
proliferation by activating the TGF-β receptor/Smad pathway.
Toxicology. 326:9–17. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lan SH, Wu SY, Zuchini R, Lin XZ, Su IJ,
Tsai TF, Lin YJ, Wu CT and Liu HS: Autophagy suppresses
tumorigenesis of hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma through degradation of microRNA-224. Hepatology.
59:505–517. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gozuacik D, Akkoc Y, Ozturk DG and Kocak
M: Autophagy-Regulating microRNAs and cancer. Front Oncol.
7:652017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu L, Liao JZ, He XX and Li PY: The role
of autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma: Friend or foe.
Oncotarget. Apr 18–2017.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
36
|
He C, Dong X, Zhai B, Jiang X, Dong D, Li
B, Jiang H, Xu S and Sun X: MiR-21 mediates sorafenib resistance of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting autophagy via the
PTEN/Akt pathway. Oncotarget. 6:28867–28881. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tazawa H, Yano S, Yoshida R, Yamasaki Y,
Sasaki T, Hashimoto Y, Kuroda S, Ouchi M, Onishi T, Uno F, et al:
Genetically engineered oncolytic adenovirus induces autophagic cell
death through an E2F1-microRNA-7-epidermal growth factor receptor
axis. Int J Cancer. 131:2939–2950. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|