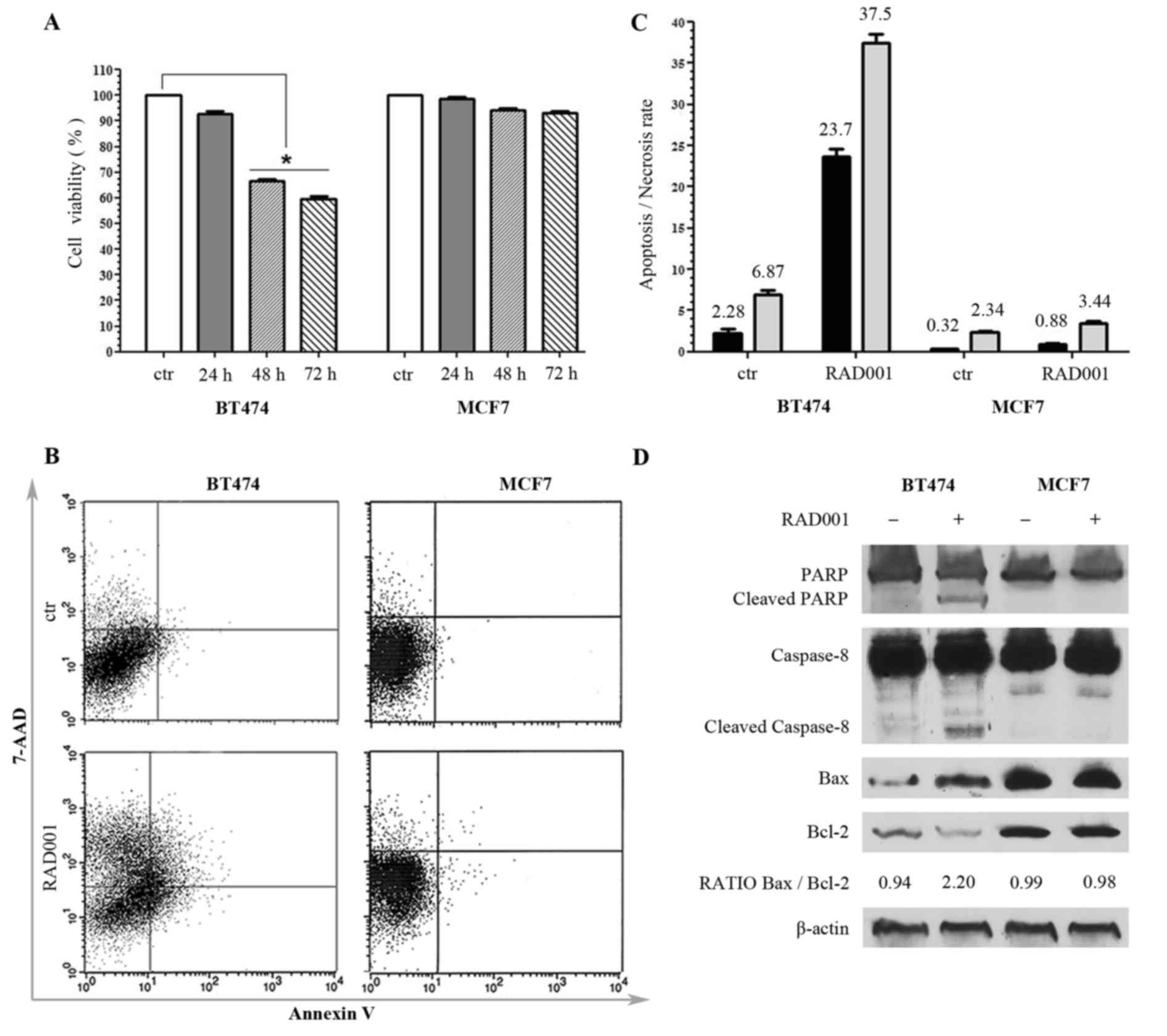
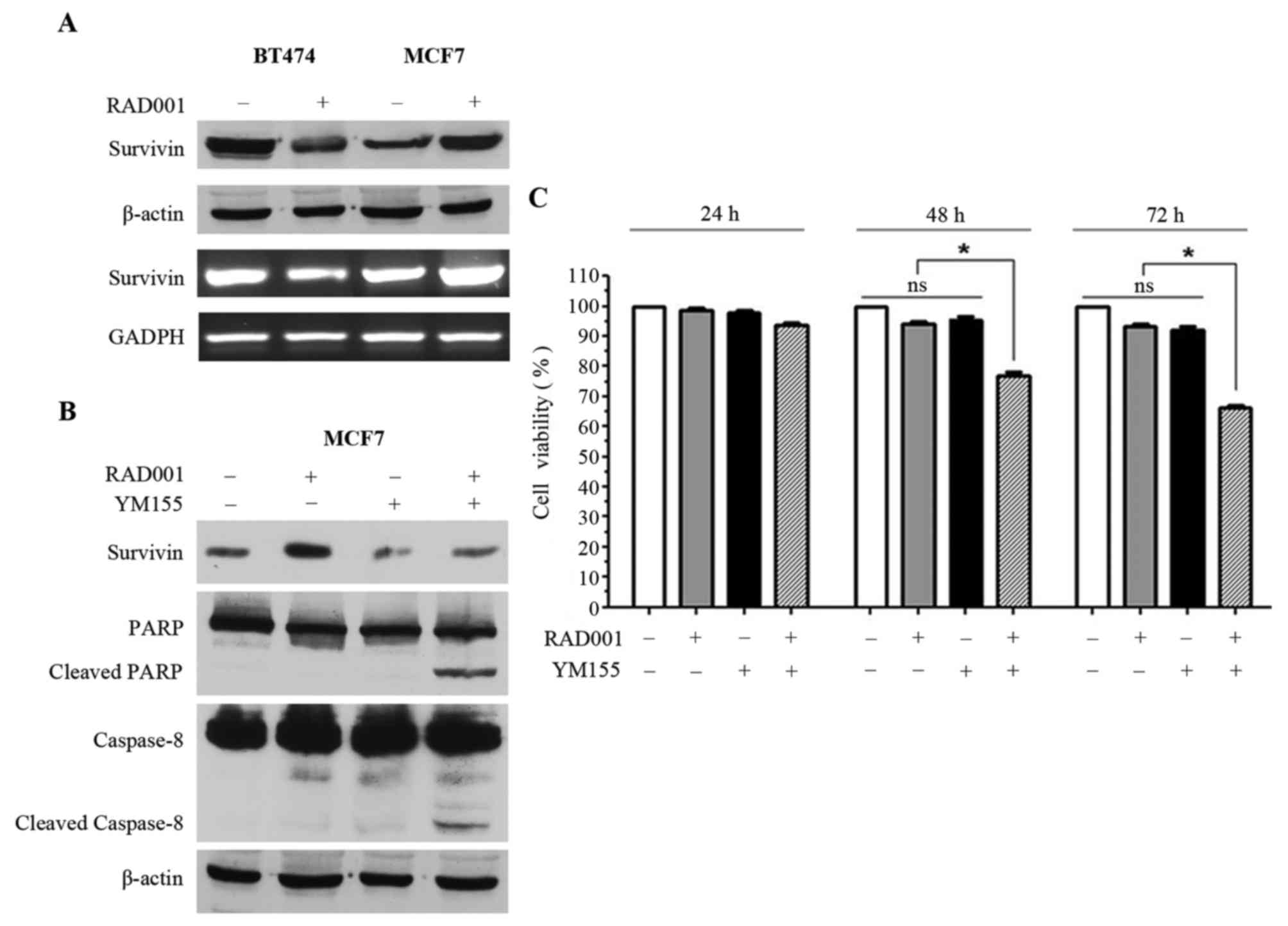
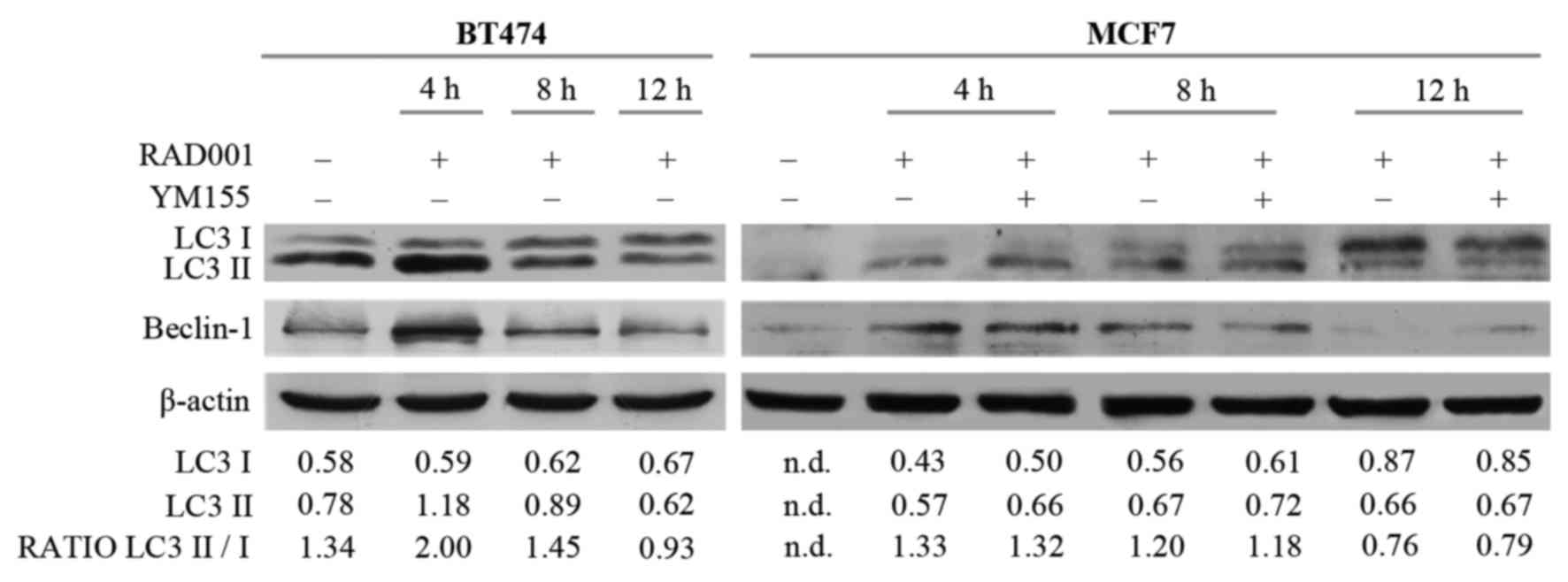
|
1
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network: Comprehensive
molecular portraits of human breast tumors. Nature. 490:61–70.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hurviz SA and Pietras RJ: Rational
management of endocrine resistance in breast cancer: A
comprehensive review of estrogen receptor biology, treatment
options, and future directions. Cancer. 113:2385–2397. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sobral AF, Amaral C, Correia-da-Silva G
and Teixeria N: Unravelling exemestane: From biology to clinical
prospects. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 163:1–11. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hunter AM, LaCasse EC and Korneluk RG: The
inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) as cancer targets. Apoptosis.
12:1543–1568. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ghayad SE, Bieche I, Vendrell JA, Keime C,
Lidereau R, Dumontet C and Cohen PA: mTOR inhibition reverses
acquired endocrine therapy resistance of breast cancer cells at the
cell proliferation and gene-expression levels. Cancer Sci.
99:1992–2003. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kajiwara M and Masuda S: Role of mTOR
inhibitors in kidney disease. Int J Mol Sci. 17:E9752016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kirchner GI, Meier-Wiedenbach I and Manns
MP: Clinical pharmacokinetics of everolimus. Clin Pharmacokinet.
43:83–95. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Granata S, Dalla Gassa A, Carraro A,
Brunelli M, Stallone G, Lupo A and Zaza G: Sirolimus and Everolimus
pathway: Reviewing candidate genes influencing their intracellular
effects. Int J Mol Sci. 17:E7352016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Baselga J, Campone M, Piccart M, Burris HA
III, Rugo HS, Sahmoud T, Noguchi S, Gnat M, Pritchard KI, Lebrun F,
et al: Everolimus in postmenopausal hormone-receptor-positive
advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 366:520–529. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hurvitz SA, Kalous O, Conklin D, Desai AJ,
Dering J, Anderson L, O'Brien NA, Kolarova T, Finn RS, Linnartz R,
et al: In vitro activity of the mTOR inhibitor everolimus, in a
large panel of breast cancer cell lines and analysis for predictor
response. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 149:669–680. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
De Iuliis F, Salerno G, Giuffrida A,
Milana B, Taglieri L, Rubinacci G, Giantulli S, Terella F,
Silvestri I and Scarpa S: Breast cancer cells respond differently
to docetaxel depending on their phenotype and on survivin
upregulation. Tumor Biol. 37:2603–2611. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
De Iuliis F, Taglieri L, Salerno G,
Giuffrida A, Milana B, Giantulli S, Carradori S, Silvestri I and
Scarpa S: The kinesin Eg5 inhibitor k858 induces apoptosis but also
survivin-related chemoresistance in breast cancer cells. Invest New
Drugs. 34:399–406. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang C, Cao X, Gei Y, Wang Y, Liu G,
Cheng G and Liu Q: Silencing of survivin by YM155 induces apoptosis
and growth arrest in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Lett.
10:1627–1631. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang S, Liu B, Fan Z, Wang D, Liu Y, Li
J, Wang N, Liu Y and Zhang B: Targeted inhibition of survivin with
YM155 promotes apoptosis of hypoxic human pulmonary arterial smooth
muscle cells via the upregulation of voltage-dependent
K+ channels. Mol Med Rep. 13:3415–3422. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li WL, Lee MR and Cho MY: The small
molecule survivin inhibitor YM155 may be an effective treatment
modality for colon cancer through increasing apoptosis. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 471:309–314. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Saran U, Foti M and Dufour JF: Cellular
and molecular effects of the mTOR inhibitor everolimus. Clin Sci
(Lond). 129:895–914. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tanida I: Autophagy basics. Microbiol
Immunol. 55:1–11. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ou DL, Lee BS, Lin LI, Liou JY, Liao SC,
Hsu C and Cheng AL: Vertical blockade of the IGFR-PI3 K/Akt/mTOR
pathway for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: The role of
survivin. Mol Cancer. 13:22014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pavlidou A, Kroupis C and Dimas K:
Association of survivin splice variants with prognosis and
treatment of breast cancer. World J Clin Oncol. 5:883–894. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Song J, Su H, Zhou YY and Guo LL:
Prognostic value of survivin expression in breast cancer patients:
A meta analysis. Tumor Biol. 34:2053–2062. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kim KW, Mutter RW, Cao C, Albert JM,
Freeman M, Hallahan DE and Lu B: Autophagy for cancer therapy
through inhibition of pro-apoptotic proteins and mammalian target
of rapamycin signaling. J Biol Chem. 281:36883–36890. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zarzynska JM: The importance of autophagy
regulation in breast cancer development and treatment. Biomed Res
Int. 2014:7103452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zambrano J and Yeh ES: Autophagy and
apoptotic crosstalk: Mechanism of therapeutic resistance in
HER2-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer (Auckl). 10:13–23.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hjelmeland A and Zhang J: Metabolic,
autophagic, and mitophagic activities in cancer initiation and
progression. Biomed J. 39:98–106. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jung YY, Lee YK and Koo JS: The potential
of Beclin 1 as a therapeutic target for the treatment of breast
cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 20:167–178. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rauch A, Henning D, Schäfer C, Wirth M,
Marx C, Heinzel T, Schneider G and Kramer OH: Survivin and YM155:
How faithful is the liaison? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1845:202–220.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Clemens MR, Gladkov OA, Gartner E,
Vladimirov V, Crown J, Steinberg J, Jie F and Keating A: Phase II,
multicenter, open-label, randomized study of YM155 plus docetaxel
as first-line treatment in patients with HER2-negative metastatic
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 149:171–179. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Papadopoulos KP, Lopez-Jimenez J, Smith
SE, Steinberg J, Keating A, Sasse C, Jie F and Thyss A: A
multicenter phase II study of sepantronium bromide (YM155) puls
rituximab in patients with relapsed aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin
lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 57:1848–1855. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|