|
1
|
Chen MB, Wei MX, Han JY, Wu XY, Li C, Wang
J, Shen W and Lu PH: MicroRNA-451 regulates AMPK/mTORC1 signaling
and fascin1 expression in HT-29 colorectal cancer. Cell Signal.
26:102–109. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dong Y, Yu J and Ng SS: MicroRNA
dysregulation as a prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer.
Cancer Manag Res. 6:405–422. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gellad ZF and Provenzale D: Colorectal
cancer: National and international perspective on the burden of
disease and public health impact. Gastroenterology. 138:2177–2190.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cristóbal I, Caramés C, Madoz-Gúrpide J,
Rojo F, Aguilera O and García-Foncillas J: Downregulation of
miR-214 is specific of liver metastasis in colorectal cancer and
could play a role determining the metastatic niche. Int J
Colorectal Dis. 29:8852014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bonfrate L, Altomare DF, Di Lena M,
Travaglio E, Rotelli MT, De Luca A and Portincasa P: MicroRNA in
colorectal cancer: New perspectives for diagnosis, prognosis and
treatment. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 22:311–320. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Giordano S and Columbano A: MicroRNAs: New
tools for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy in hepatocellular
carcinoma? Hepatology. 57:840–847. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hur K, Toiyama Y, Okugawa Y, Ide S, Imaoka
H, Boland CR and Goel A: Circulating microRNA-203 predicts
prognosis and metastasis in human colorectal cancer. Gut.
66:654–665. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Croce CM: Causes and consequences of
microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 10:704–714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bai R, Weng C, Dong H, Li S, Chen G and Xu
Z: MicroRNA-409-3p suppresses colorectal cancer invasion and
metastasis partly by targeting GAB1 expression. Int J Cancer.
137:2310–2322. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jinushi T, Shibayama Y, Kinoshita I,
Oizumi S, Jinushi M, Aota T, Takahashi T, Horita S, Dosaka-Akita H
and Iseki K: Low expression levels of microRNA-124-5p correlated
with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer via targeting of SMC4.
Cancer Med. 3:1544–1552. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rokavec M, Öner MG, Li H, Jackstadt R,
Jiang L, Lodygin D, Kaller M, Horst D, Ziegler PK, Schwitalla S, et
al: IL-6R/STAT3/miR-34a feedback loop promotes EMT-mediated
colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis. J Clin Invest.
124:1853–1867. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Qiu Z, Guo W, Wang Q, Chen Z, Huang S,
Zhao F, Yao M, Zhao Y and He X: MicroRNA-124 reduces the pentose
phosphate pathway and proliferation by targeting PRPS1 and RPIA
mRNAs in human colorectal cancer cells. Gastroenterology.
149:1587–1598, e11. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hwang WL, Jiang JK, Yang SH, Huang TS, Lan
HY, Teng HW, Yang CY, Tsai YP, Lin CH, Wang HW and Yang MH:
MicroRNA-146a directs the symmetric division of Snail-dominant
colorectal cancer stem cells. Nat Cell Biol. 16:268–280. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang X, Schulz R, Edmunds S, Krüger E,
Markert E, Gaedcke J, Cormet-Boyaka E, Ghadimi M, Beissbarth T,
Levine AJ, et al: MicroRNA-101 suppresses tumor cell proliferation
by acting as an endogenous proteasome inhibitor via targeting the
proteasome assembly factor POMP. Mol Cell. 59:243–257. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Slaby O, Svoboda M, Michalek J and Vyzula
R: MicroRNAs in colorectal cancer: Translation of molecular biology
into clinical application. Mol Cancer. 8:1022009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Della Vittoria Scarpati G, Calura E, Di
Marino M, Romualdi C, Beltrame L, Malapelle U, Troncone G, De
Stefano A, Pepe S, De Placido S, et al: Analysis of differential
miRNA expression in primary tumor and stroma of colorectal cancer
patients. Biomed Res Int. 2014:8409212014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Betel D, Wilson M, Gabow A, Marks DS and
Sander C: The microRNA.org resource: Targets and expression.
Nucleic Acids Res. 36:D149–D153. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yan W, Wu K, Herman JG, Brock MV, Fuks F,
Yang L, Zhu H, Li Y, Yang Y and Guo M: Epigenetic regulation of
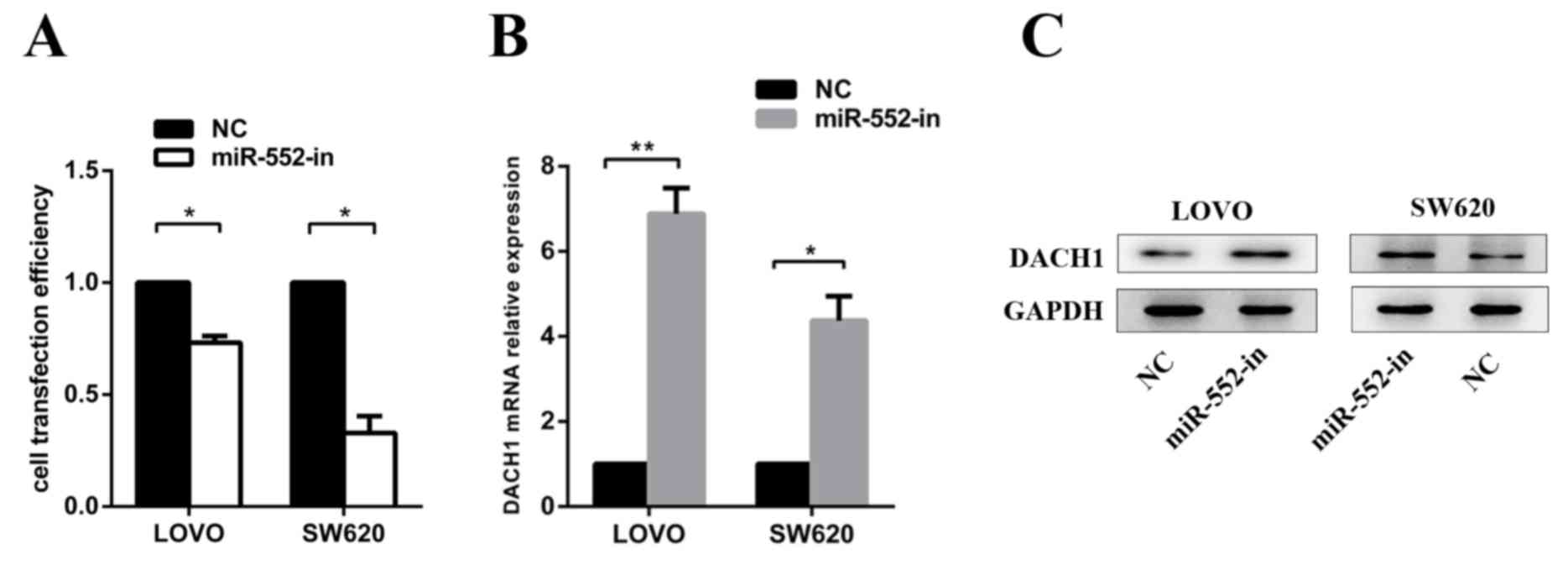
DACH1, a novel Wnt signaling component in colorectal cancer.
Epigenetics. 8:1373–1383. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu Y, Zhou R, Yuan X, Han N, Zhou S, Xu
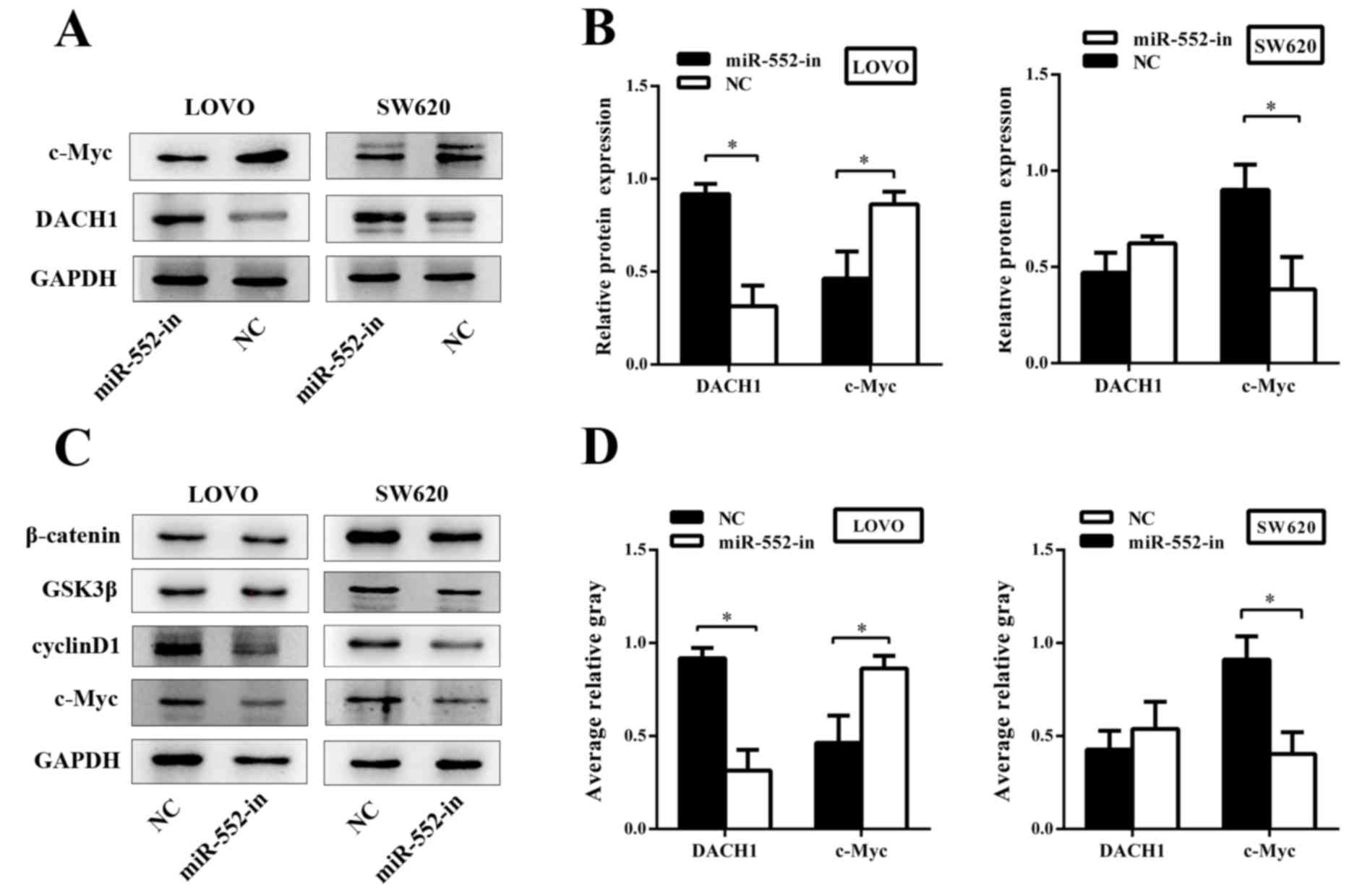
H, Guo M, Yu S, Zhang C, Yin T and Wu K: DACH1 is a novel
predictive and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma as
a negative regulator of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Oncotarget.
6:8621–8634. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Amirkhah R, Schmitz U, Linnebacher M,
Wolkenhauer O and Farazmand A: MicroRNA-mRNA interactions in
colorectal cancer and their role in tumor progression. Genes
Chromosomes Cancer. 54:129–141. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shen G, Rong X, Zhao J, Yang X, Li H,
Jiang H, Zhou Q, Ji T, Huang S, Zhang J and Jia H: MicroRNA-105
suppresses cell proliferation and inhibits PI3K/AKT signaling in
human hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 35:2748–2755. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim J, Lim NJ, Jang SG, Kim HK and Lee GK:
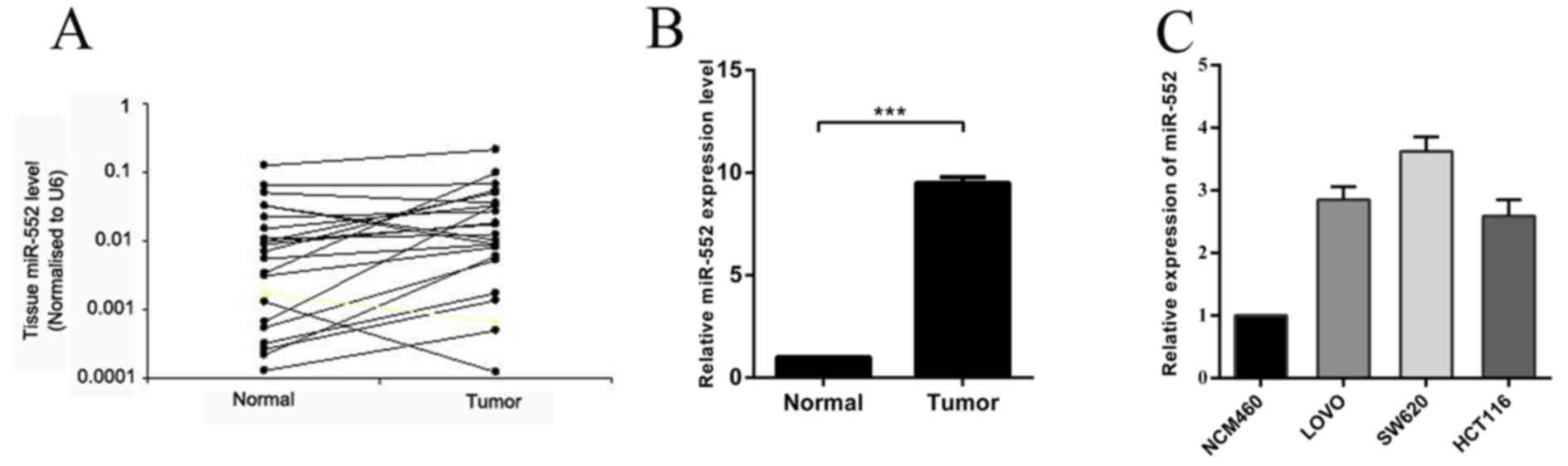
miR-592 and miR-552 can distinguish between primary lung
adenocarcinoma and colorectal cancer metastases in the lung.
Anticancer Res. 34:2297–2302. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xia ZS, Wang L, Yu T, Zhong W, Lian GD, Wu
D, Zhou HM and Chen GC: MiR-5000-3p, miR-5009-3P and miR-552:
Potential microRNA biomarkers of side population cells in colon
cancer. Oncol Rep. 32:589–596. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Atkins M, Jiang Y, Sansores-Garcia L,
Jusiak B, Halder G and Mardon G: Dynamic rewiring of the Drosophila
retinal determination network switches its function from selector
to differentiation. PLoS Genet. 9:e10037312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang P: Suppression of DACH1 promotes
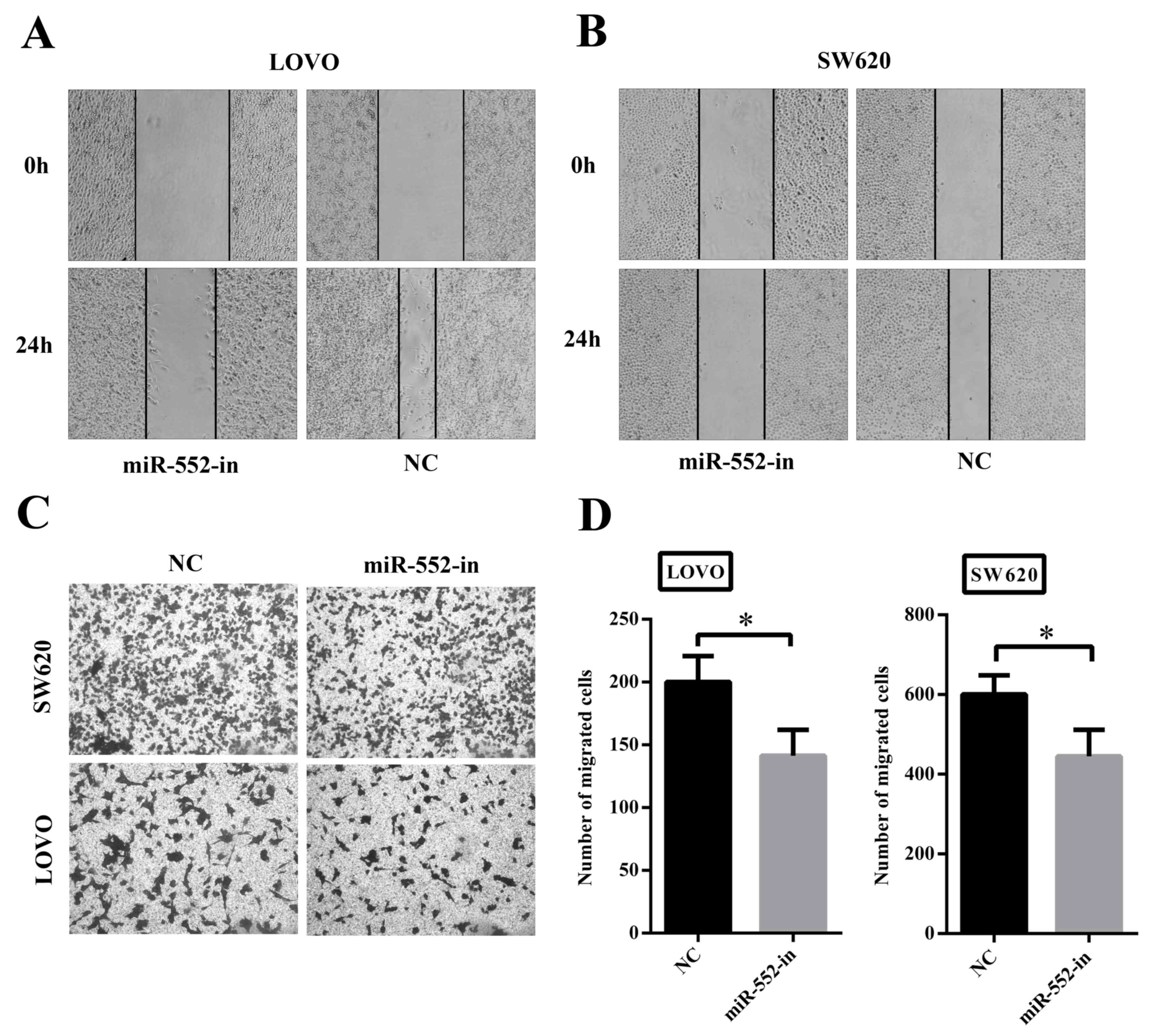
migration and invasion of colorectal cancer via activating
TGF-β-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 460:314–319. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chu Q, Han N, Yuan X, Nie X, Wu H, Chen Y,
Guo M, Yu S and Wu K: DACH1 inhibits cyclin D1 expression, cellular
proliferation and tumor growth of renal cancer cells. J Hematol
Oncol. 7:732014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mohammed MK, Shao C, Wang J, Wei Q, Wang
X, Collier Z, Tang S, Liu H, Zhang F, Huang J, et al: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling plays an ever-expanding role in stem cell self-renewal,
tumorigenesis and cancer chemoresistance. Genes Dis. 3:11–40. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|