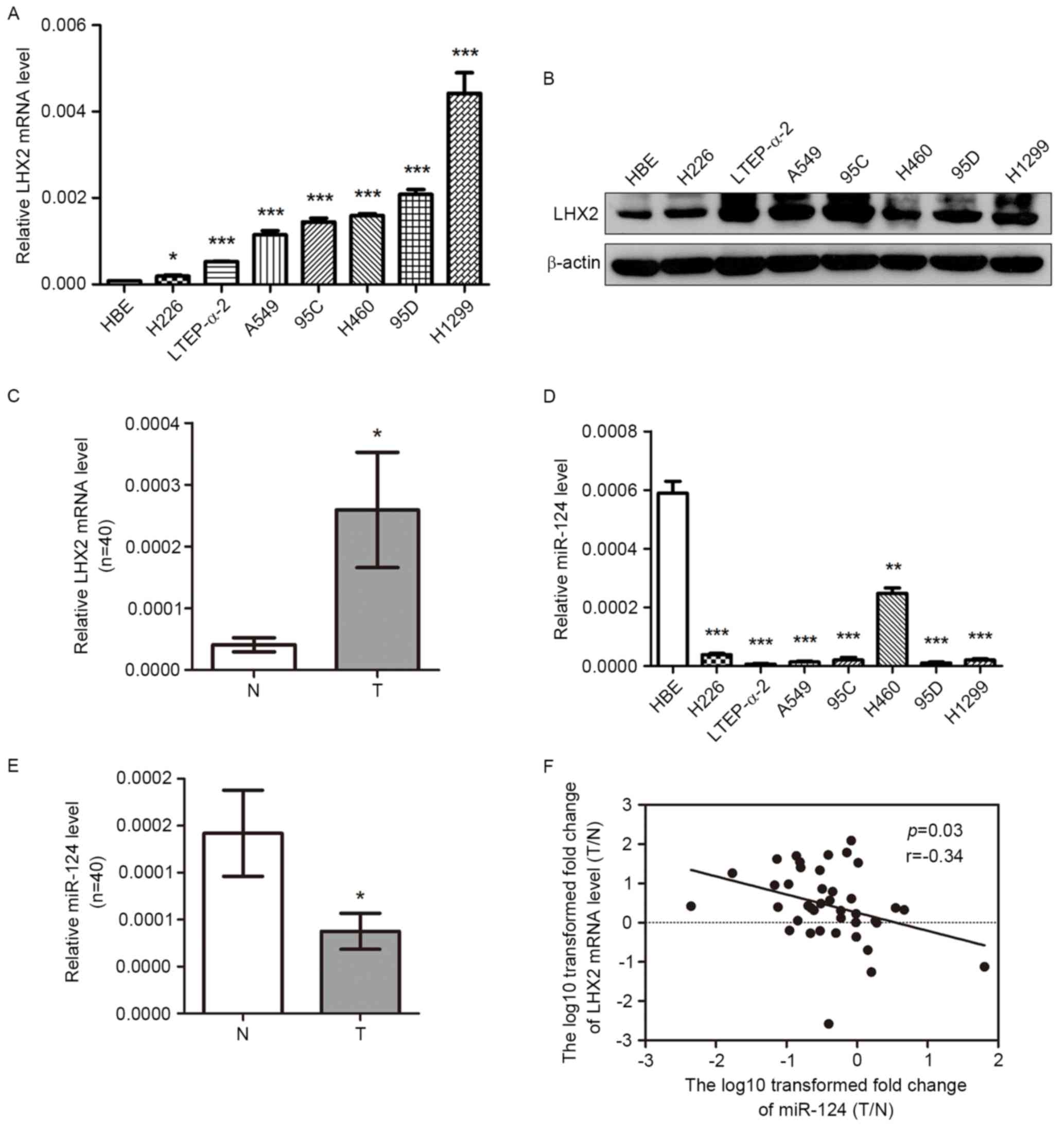
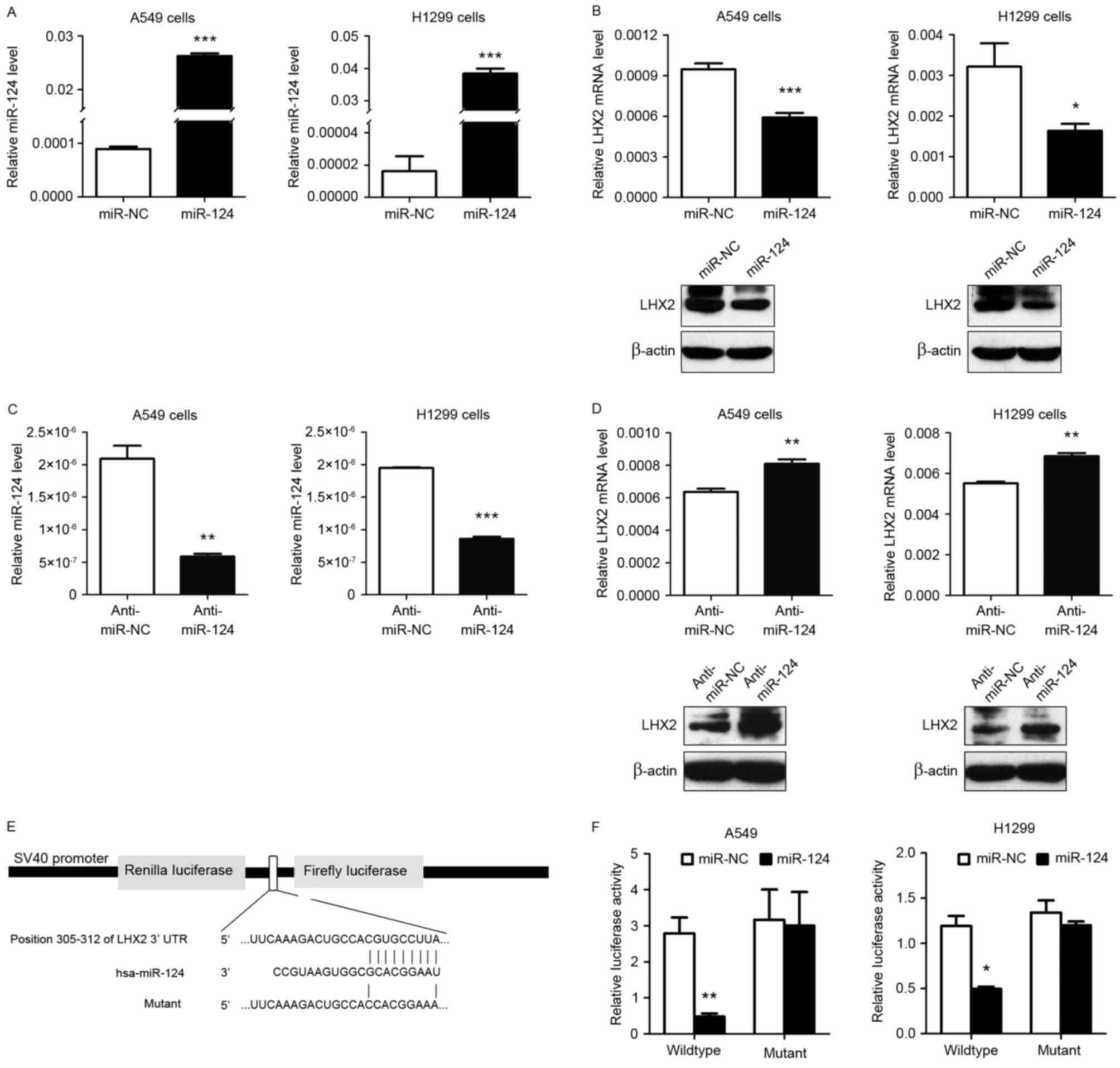
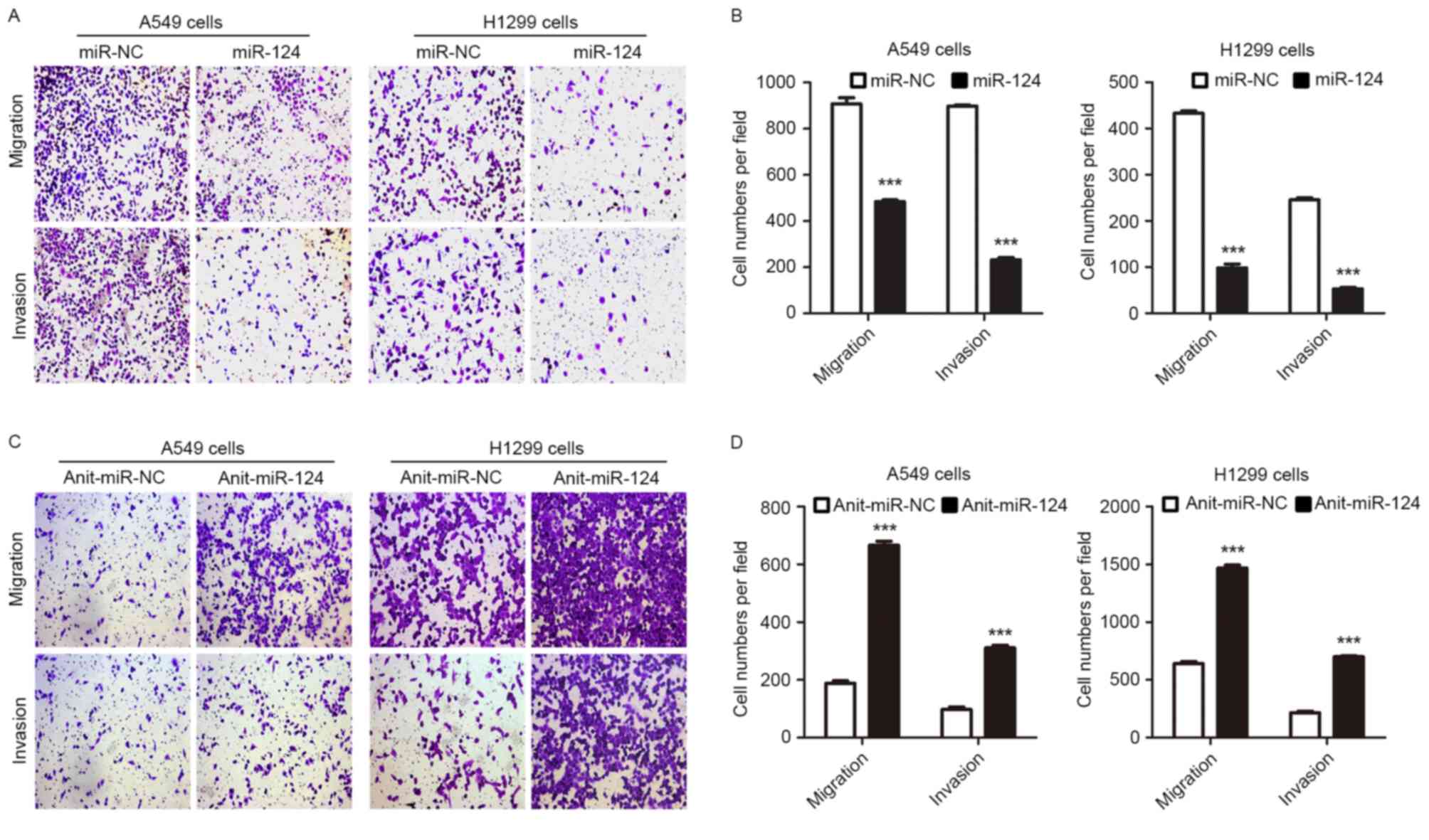
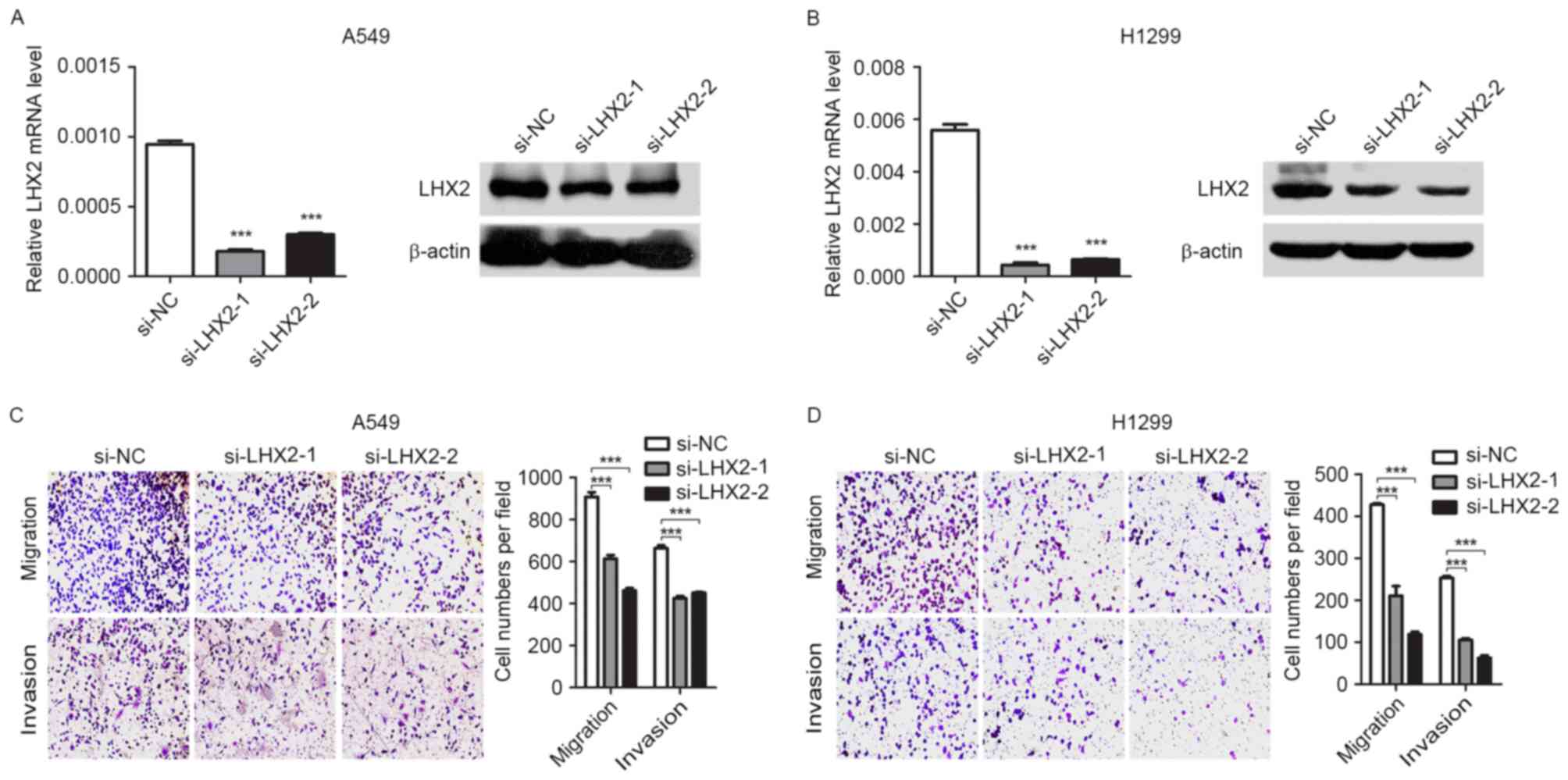
|
1
|
Herbst RS, Heymach JV and Lippman SM: Lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 359:1367–1380. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
DeSantis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Siegel
RL, Stein KD, Kramer JL, Alteri R, Robbins AS and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin.
64:252–271. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu RY, Zeng Y, Lei Z, Wang L, Yang H, Liu
Z, Zhao J and Zhang HT: JAK/STAT3 signaling is required for
TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer
cells. Int J Oncol. 44:1643–1651. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guo H, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS and Bartel
DP: Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA
levels. Nature. 466:835–840. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wilson RC and Doudna JA: Molecular
mechanisms of RNA interference. Annu Rev Biophys. 42:217–239. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Butz H, Racz K, Hunyady L and Patocs A:
Crosstalk between TGF-β signaling and the microRNA machinery.
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 33:382–393. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lei Z, Xu G, Wang L, Yang H, Liu X, Zhao J
and Zhang HT: MiR-142-3p represses TGF-β-induced growth inhibition
through repression of TGFβR1 in non-small cell lung cancer. FASEB
J. 28:2696–2704. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Arabkheradmand A, Safari A, Seifoleslami
M, Yahaghi E and Gity M: Down-regulated microRNA-124 expression as
predictive biomarker and its prognostic significance with
clinicopathological features in breast cancer patients. Diagn
Pathol. 10:1782015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ibarrola-Villava M, Llorca-Cardeñosa MJ,
Tarazona N, Mongort C, Fleitas T, Perez-Fidalgo JA, Roselló S,
Navarro S, Ribas G and Cervantes A: Deregulation of ARID1A, CDH1,
cMET and PIK3CA and target-related microRNA expression in gastric
cancer. Oncotarget. 6:26935–26945. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang X, Wu Q, Xu B, Wang P, Fan W, Cai Y,
Gu X and Meng F: miR-124 exerts tumor suppressive functions on the
cell proliferation, motility and angiogenesis of bladder cancer by
fine-tuning UHRF1. FEBS J. 282:4376–4388. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang M, Piao L, Datta J, Lang JC, Xie X,
Teknos TN, Mapp AK and Pan Q: miR-124 regulates the
epithelial-restricted with serine box/epidermal growth factor
receptor signaling axis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Mol Cancer Ther. 14:2313–2320. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xi ZW, Xin SY, Zhou LQ, Yuan HX, Wang Q
and Chen KX: Downregulation of rho-associated protein kinase 1 by
miR-124 in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 21:5454–5464.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun Y, Ai X, Shen S and Lu S:
NF-κB-mediated miR-124 suppresses metastasis of non-small-cell lung
cancer by targeting MYO10. Oncotarget. 6:8244–8254. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dong LL, Chen LM, Wang WM and Zhang LM:
Decreased expression of microRNA-124 is an independent unfavorable
prognostic factor for patients with breast cancer. Diagn Pathol.
10:452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Y, Li H, Han J and Zhang Y:
Down-regulation of microRNA-124 is correlated with tumor metastasis
and poor prognosis in patients with lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:1967–1972. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Porter FD, Drago J, Xu Y, Cheema SS,
Wassif C, Huang SP, Lee E, Grinberg A, Massalas JS, Bodine D, et
al: Lhx2, a LIM homeobox gene, is required for eye, forebrain, and
definitive erythrocyte development. Development. 124:2935–2944.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kuzmanov A, Hopfer U, Marti P,
Meyer-Schaller N, Yilmaz M and Christofori G: LIM-homeobox gene 2
promotes tumor growth and metastasis by inducing autocrine and
paracrine PDGF-B signaling. Mol Oncol. 8:401–416. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shi X, Zhan L, Xiao C, Lei Z, Yang H, Wang
L, Zhao J and Zhang HT: miR-1238 inhibits cell proliferation by
targeting LHX2 in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget.
6:19043–19054. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mountain CF: Revisions in the
international system for staging lung cancer. Chest. 111:1710–1717.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
do Pinto OP, Kolterud A and Carlsson L:
Expression of the LIM-homeobox gene LH2 generates immortalized
steel factor-dependent multipotent hematopoietic precursors. EMBO
J. 17:5744–5756. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chou SJ and O'Leary DD: Role for Lhx2 in
corticogenesis through regulation of progenitor differentiation.
Mol Cell Neurosci. 56:1–9. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou F, Gou S, Xiong J, Wu H, Wang C and
Liu T: Oncogenicity of LHX2 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Mol Biol Rep. 41:8163–8167. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ohtsuka M, Ling H, Doki Y, Mori M and
Calin GA: MicroRNA processing and human cancer. J Clin Med.
4:1651–1667. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson
A, Schelter JM, Castle J, Bartel DP, Linsley PS and Johnson JM:
Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large
numbers of target mRNAs. Nature. 433:769–773. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang W, Mao YQ, Wang H, Yin WJ, Zhu SX
and Wang WC: MiR-124 suppresses cell motility and adhesion by
targeting talin 1 in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int.
15:492015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|