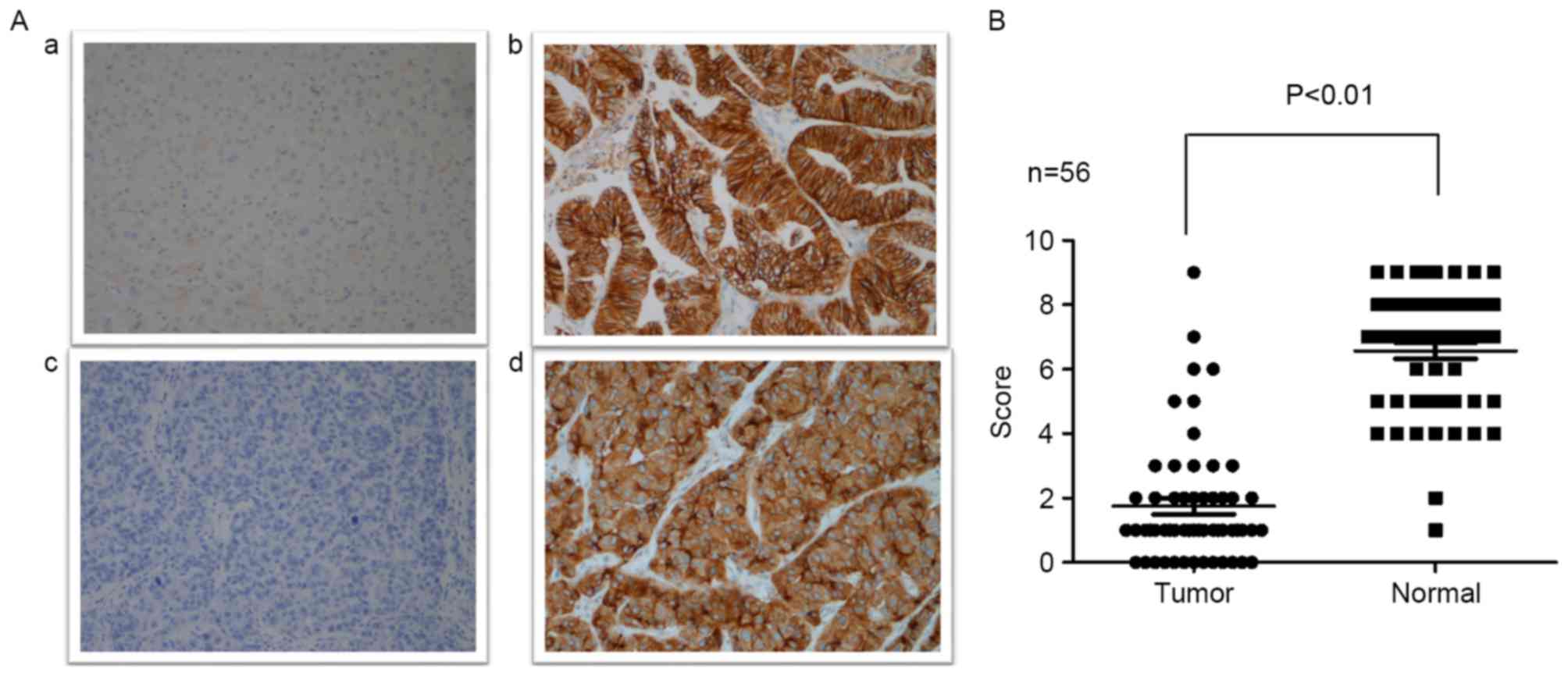
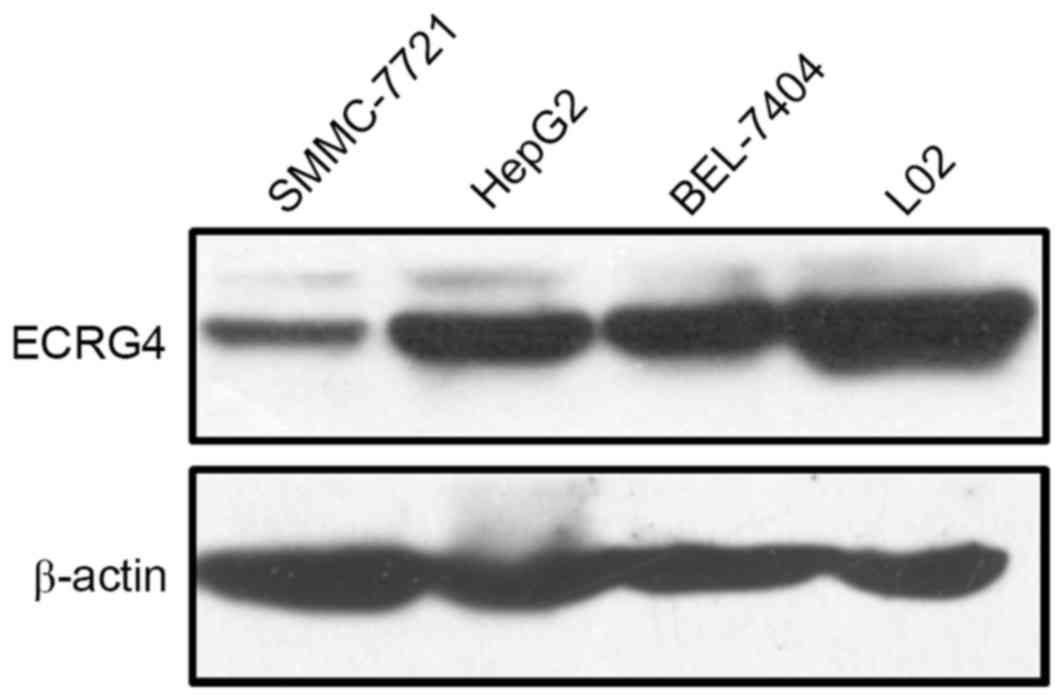
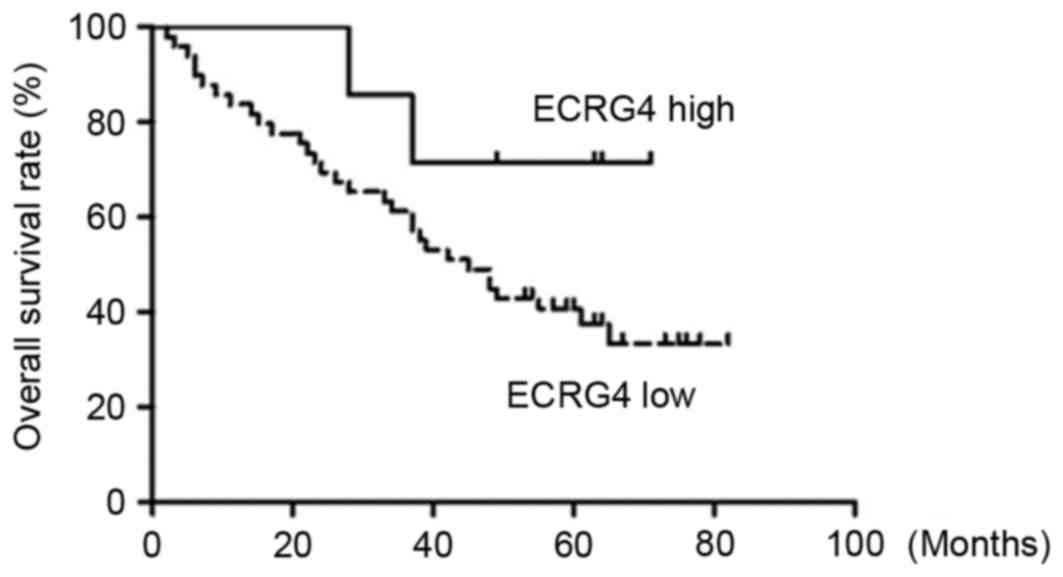
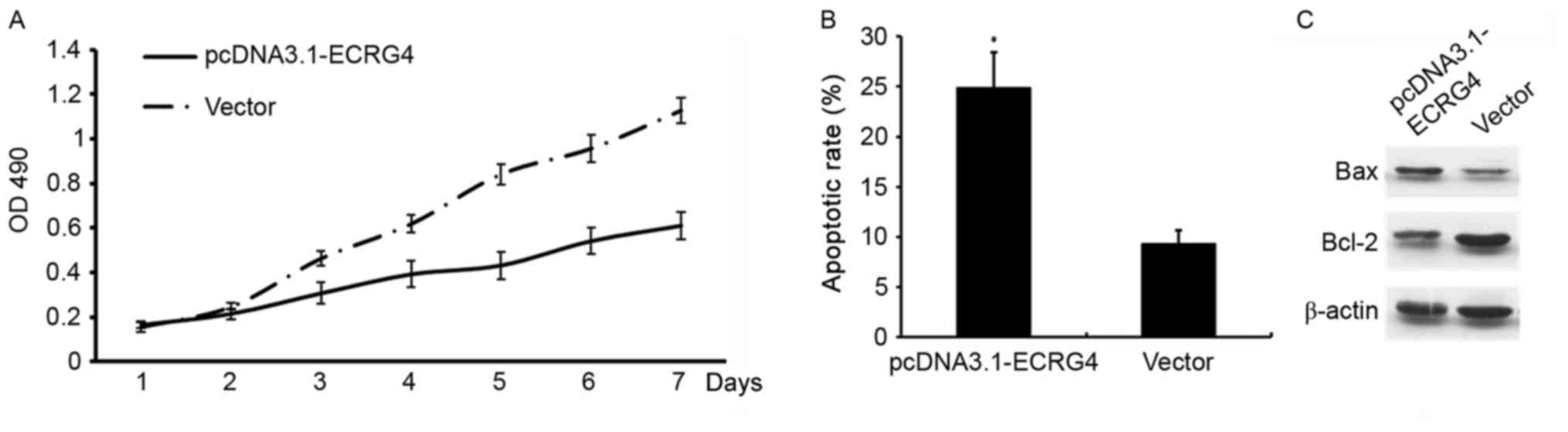
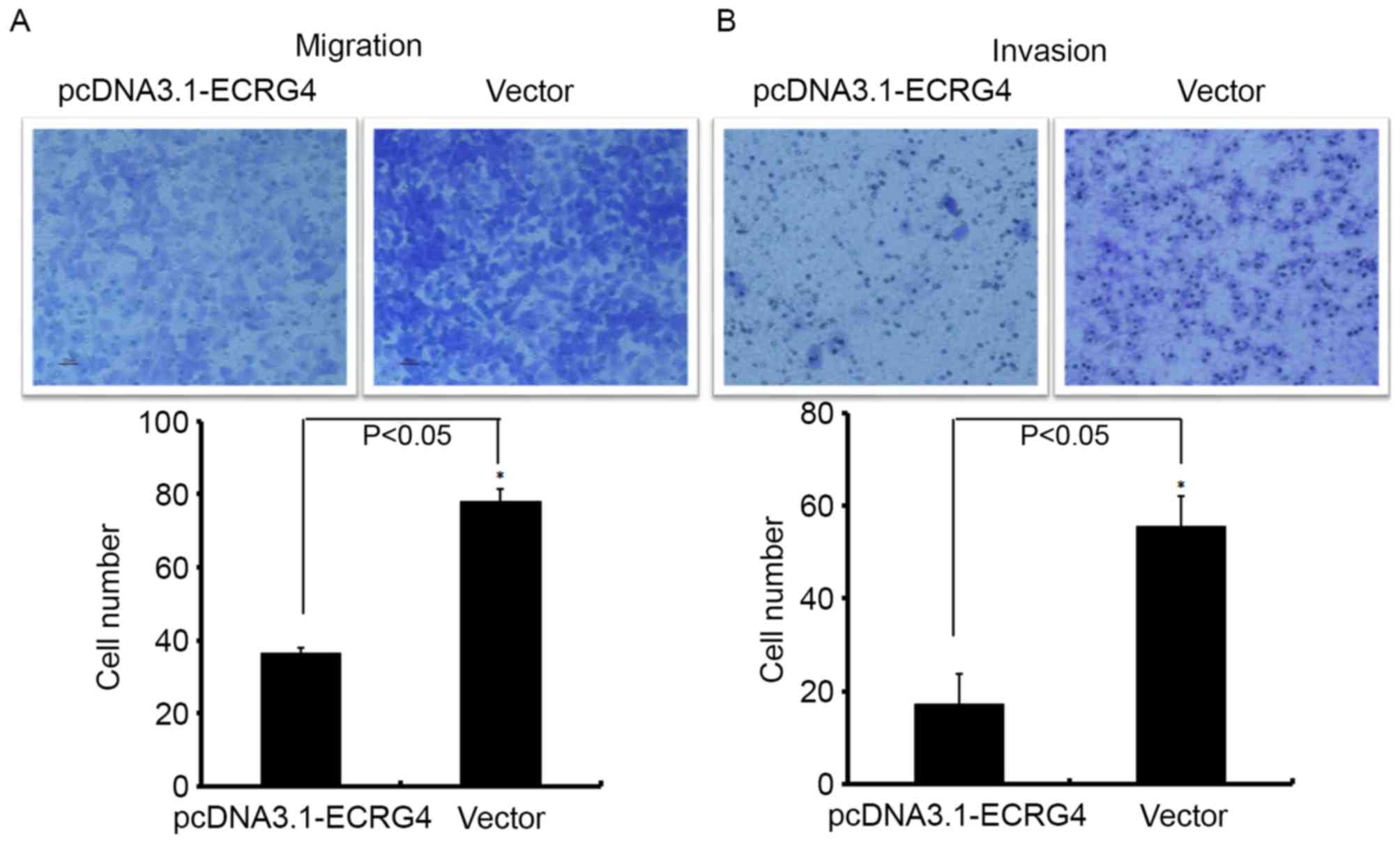
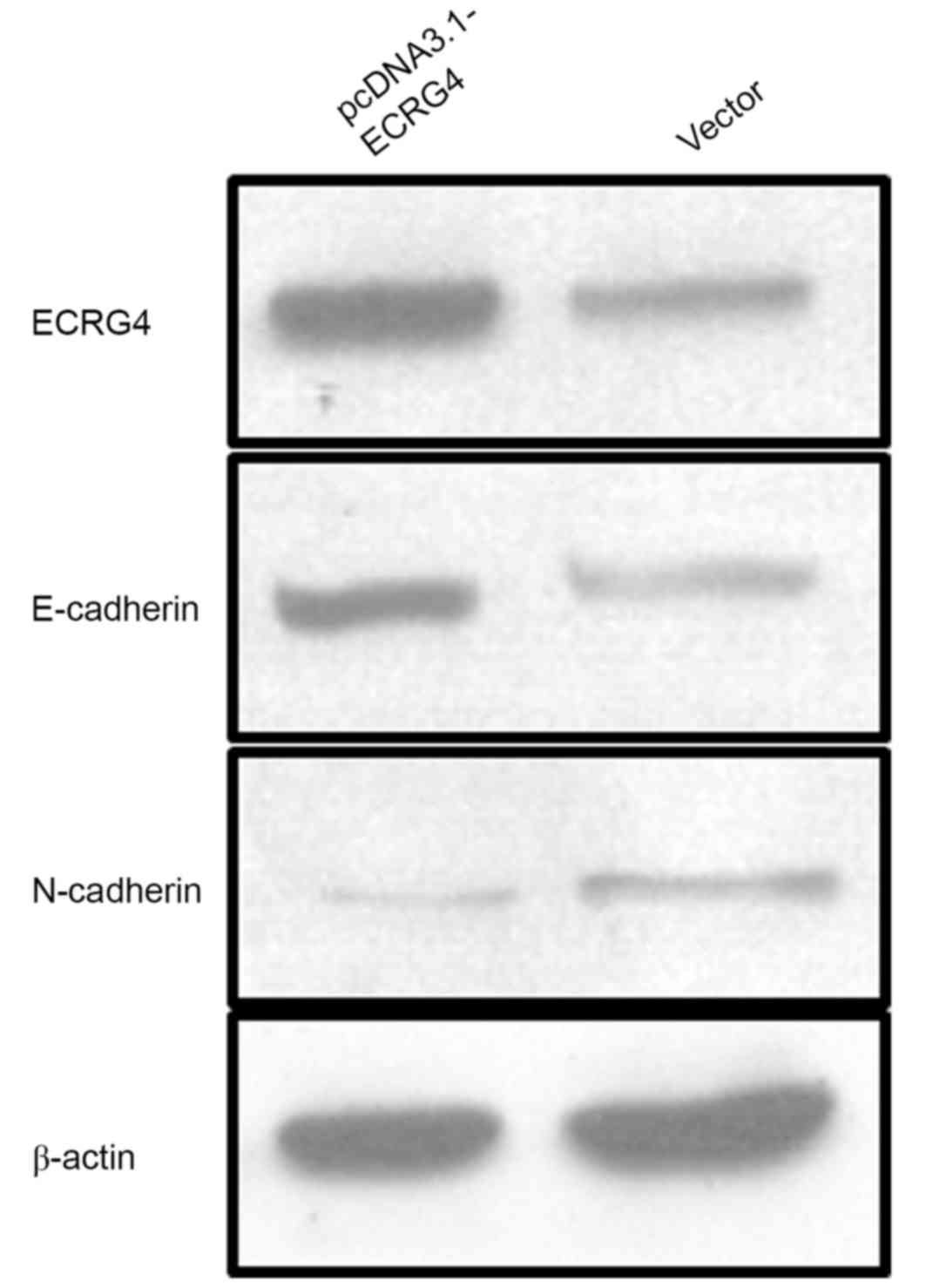
|
1
|
Bruix J, Gores GJ and Mazzaferro V:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Clinical frontiers and perspectives. Gut.
63:844–855. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Akoad ME and Pomfret EA: Surgical
resection and liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Clin Liver Dis. 19:381–399. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mlynarsky L, Menachem Y and Shibolet O:
Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Steps forward but still a
long way to go. World J Hepatol. 7:566–574. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Su T, Liu H and Lu S: Cloning and
identification of cDNA fragments related to human esophageal
cancer. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 20:254–257. 1998.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Matsuzaki J, Torigoe T, Hirohashi Y,
Tamura Y, Asanuma H, Nakazawa E, Saka E, Yasuda K, Takahashi S and
Sato N: Expression of ECRG4 is associated with lower proliferative
potential of esophageal cancer cells. Pathol Int. 63:391–397. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sabatier R, Finetti P, Adelaide J, Guille
A, Borg JP, Chaffanet M, Lane L, Birnbaum D and Bertucci F:
Down-regulation of ECRG4, a candidate tumor suppressor gene, in
human breast cancer. PLoS One. 6:e276562011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang YB and Ba CF: Promoter methylation of
esophageal cancer-related gene 4 in gastric cancer tissue and its
clinical significance. Hepatogastroenterology. 59:1696–1698.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Matsuzaki J, Torigoe T, Hirohashi Y,
Kamiguchi K, Tamura Y, Tsukahara T, Kubo T, Takahashi A, Nakazawa
E, Saka E, et al: ECRG4 is a negative regulator of
caspase-8-mediated apoptosis in human T-leukemia cells.
Carcinogenesis. 33:996–1003. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Götze S, Feldhaus V, Traska T, Wolter M,
Reifenberger G, Tannapfel A, Kuhnen C, Martin D, Müller O and
Sievers S: ECRG4 is a candidate tumor suppressor gene frequently
hypermethylated in colorectal carcinoma and glioma. BMC Cancer.
9:4472009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH and
Theise ND: World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of
the Digestive System. 3. 4th. IARC Press; Lyon: 2010
|
|
11
|
Xu HB, Xu LZ, Li L, Fu J and Mao XP:
Reversion of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance by
guggulsterone in multidrug-resistant human cancer cell lines. Eur J
Pharmacol. 694:39–44. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Weinberg SE and Chandel NS: Targeting
mitochondria metabolism for cancer therapy. Nat Chem Biol. 11:9–15.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lu Z, Jiao D, Qiao J, Yang S, Yan M, Cui S
and Liu Z: Restin suppressed epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
tumor metastasis in breast cancer cells through upregulating
mir-200a/b expression via association with p73. Mol Cancer.
14:1022015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hu F, Deng X, Yang X, Jin H, Gu D, Lv X,
Wang C, Zhang Y, Huo X, Shen Q, et al: Hypoxia upregulates
Rab11-family interacting protein 4 through HIF-1α to promote the
metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 34:6007–6017.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu H, Li P, Zhai Y, Qu CF, Zhang LJ, Tan
YF, Li N and Ding HG: Diagnostic value of glypican-3 in serum and
liver for primary hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol.
16:4410–4415. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mori Y, Ishiguro H, Kuwabara Y, Kimura M,
Mitsui A, Kurehara H, Mori R, Tomoda K, Ogawa R, Katada T, et al:
Expression of ECRG4 is an independent prognostic factor for poor
survival in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol
Rep. 18:981–985. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li L, Zhang C, Li X, Lu S and Zhou Y: The
candidate tumor suppressor gene ECRG4 inhibits cancer cells
migration and invasion in esophageal carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 29:1332010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jiang CP, Wu BH, Wang BQ, Fu MY, Yang M,
Zhou Y and Liu F: Overexpression of ECRG4 enhances chemosensitivity
to 5-fluorouracil in the human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cell line.
Tumour Biol. 34:2269–2273. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li W, Liu X, Zhang B, Qi D, Zhang L, Jin Y
and Yang H: Overexpression of candidate tumor suppressor ECRG4
inhibits glioma proliferation and invasion. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
29:892010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu T, Xiao D and Zhang X: ECRG4 inhibits
growth and invasiveness of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and
neck in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Lett. 5:1921–1926.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jia J, Dai S, Sun X, Sang Y, Xu Z, Zhang
J, Cui X, Song J and Guo X: A preliminary study of the effect of
ECRG4 overexpression on the proliferation and apoptosis of human
laryngeal cancer cells and the underlying mechanisms. Mol Med Rep.
12:5058–5064. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen HW, Huang XD, Li HC, He S, Ni RZ,
Chen CH, Peng C, Wu G, Wang GH, Wang YY, et al: Expression of FOXJ1
in hepatocellular carcinoma: Correlation with patients' prognosis
and tumor cell proliferation. Mol Carcinog. 52:647–659. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang JY, Zhang K, Chen DQ, Chen J, Feng
B, Song H, Chen Y, Zhu Z, Lu L, De W, et al: MicroRNA-451:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition inhibitor and prognostic
biomarker of hepatocelluar carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:18613–18630.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Luo Y, He DL, Jiang YG, Ning L, Shen SL,
Zhao JH and Cui XH: Role of beta-catenin signaling pathway in EMT
of human prostate cancer induced by HIF-1alpha. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za
Zhi. 90:1131–1136. 2010.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|