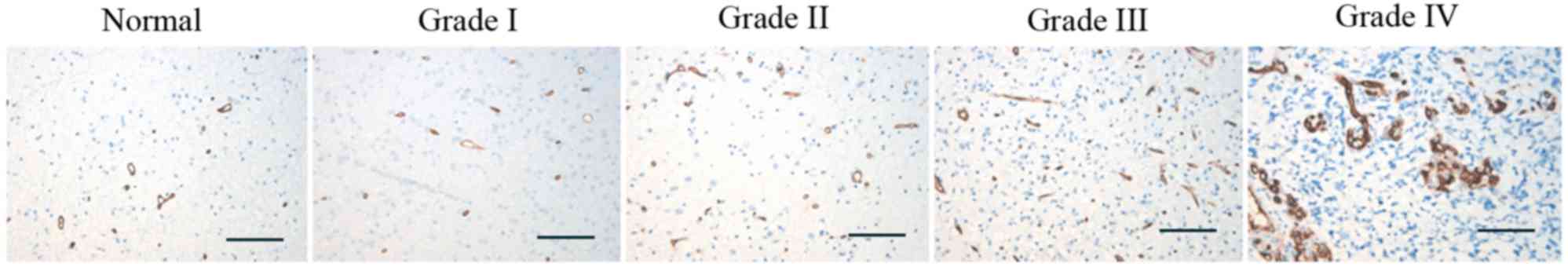
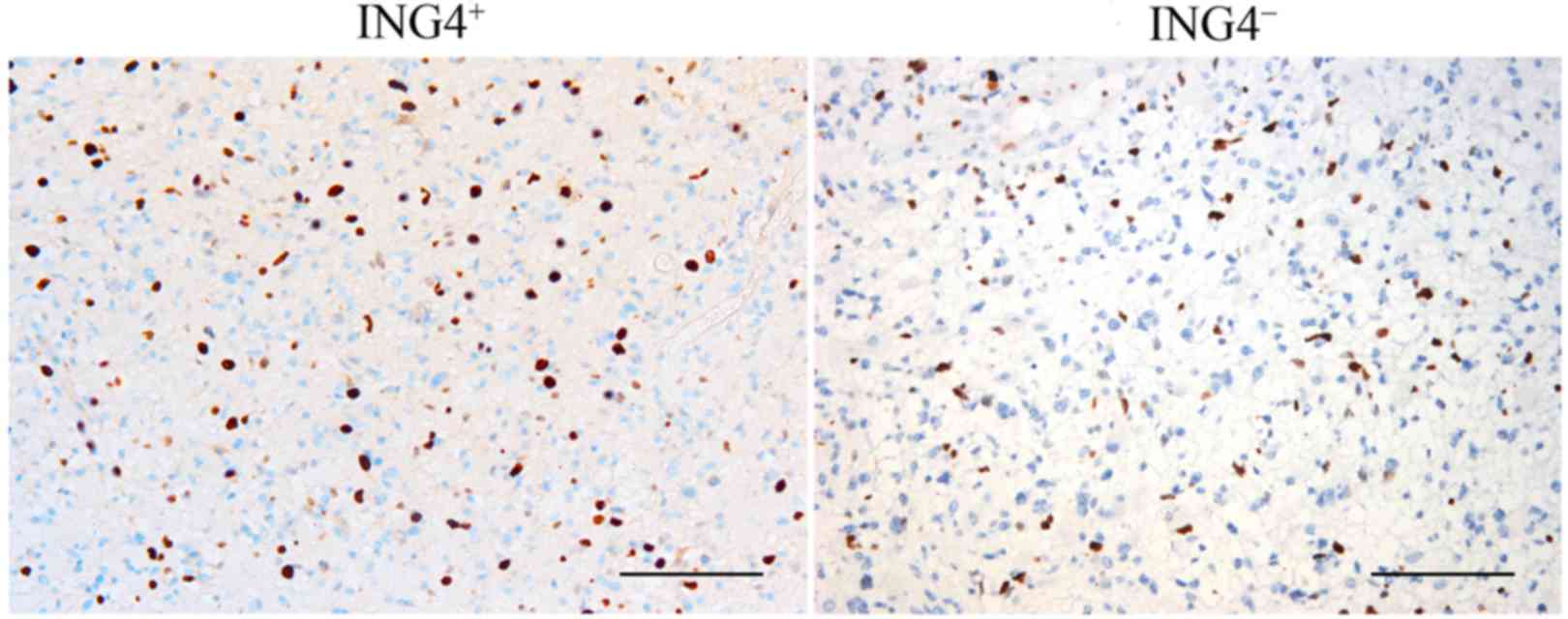
|
1
|
Wen PY and Kesari S: Malignant gliomas in
adults. N Engl J Med. 359:492–507. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ohgaki H and Kleihues P: Epidemiology and
etiology of gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 109:93–108. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Aggarwal R, Lu J, Kanji S, Das M, Joseph
M, Lustberg MB, Ray A, Pompili VJ, Shapiro CL and Das H: Human
Vγ2V∆2 T cells limit breast cancer growth by modulating cell
survival-, apoptosis-related molecules and microenvironment in
tumors. Int J Cancer. 133:2133–2144. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hou Y, Zhang Z, Xu Q, Wang H, Xu Y and
Chen K: Inhibitor of growth 4 induces NFκB/p65 ubiquitin-dependent
degradation. Oncogene. 33:1997–2003. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Culurgioni S, Muñoz IG, Moreno A, Palacios
A, Villate M, Palmero I, Montoya G and Blanco FJ: Crystal structure
of inhibitor of growth 4 (ING4) dimerization domain reveals
functional organization of ING family of chromatin-binding
proteins. J Biol Chem. 287:10876–10884. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao Y, Li Z, Sheng W, Miao J and Yang J:
Adenovirus-mediated ING4/IL-24 double tumor suppressor gene
co-transfer enhances antitumor activity in human breast cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 28:1315–1324. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tang Y, Cheng Y, Martinka M, Ong CJ and Li
G: Prognostic significance of KAI1/CD82 in human melanoma and its
role in cell migration and invasion through the regulation of ING4.
Carcinogenesis. 35:86–95. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu Y, Yu L, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y and
Zhang G: Expression of tumor suppressor gene ING4 in ovarian
carcinoma is correlated with microvessel density. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 138:647–655. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ling C, Xie Y, Zhao D, Zhu Y, Xiang J and
Yang J: Enhanced radiosensitivity of non-small-cell lung cancer
(NSCLC) by adenovirus-mediated ING4 gene therapy. Cancer Gene Ther.
19:697–706. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Garkavtsev I, Kozin SV, Chernova O, Xu L,
Winkler F, Brown E, Barnett GH and Jain RK: The candidate tumour
suppressor protein ING4 regulates brain tumour growth and
angiogenesis. Nature. 428:328–332. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bhattacharya A, Turowski SG, San Martin
ID, Rajput A, Rustum YM, Hoffman RM and Seshadri M: Magnetic
resonance and fluorescence-protein imaging of the anti-angiogenic
and anti-tumor efficacy of selenium in an orthotopic model of human
colon cancer. Anticancer Res. 31:387–393. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Folkman J: How is blood vessel growth
regulated in normal and neoplastic tissue? G.H.A. clowes memorial
award lecture. Cancer Res. 46:467–473. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rubatt JM, Darcy KM, Hutson A, Bean SM,
Havrilesky LJ, Grace LA, Berchuck A and Secord AA: Independent
prognostic relevance of microvessel density in advanced epithelial
ovarian cancer and associations between CD31, CD105, p53status, and
angiogenic marker expression: A Gynecologic Oncology Group study.
Gynecol Oncol. 112:469–474. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao S, Jin C, Zhao X, Jin B, Hui L, Zhou
W, Niu G and Tao S: Expression and clinical significance of ING4
and HIF-1 alpha in brain astrocytoma. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.
95:3533–3536. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fuller GN: The WHO classification of
tumours of the central nervous system, 4th edition. Arch Pathol Lab
Med. 132:9062008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu H, Wan D, Pan Z, Cao L, Wu X, Lu Z and
Kang T: Expression and biological significance of leptin, leptin
receptor, VEGF, and CD34 in colorectal carcinoma. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 60:241–244. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fang F, Luo LB, Tao YM, Wu F and Yang LY:
Decreased expression of inhibitor of growth 4 correlated with poor
prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 18:409–416. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li XH, Kikuchi K, Zheng Y, Noguchi A,
Takahashi H, Nishida T, Masuda S, Yang XH and Takano Y:
Downregulation and translocation of nuclear ING4 is correlated with
tumorigenesis and progression of head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 47:217–223. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Klironomos G, Bravou V, Papachristou DJ,
Gatzounis G, Varakis J, Parassi E, Repanti M and Papadaki H: Loss
of inhibitor of growth (ING-4) is implicated in the pathogenesis
and progression of human astrocytomas. Brain Pathol. 20:490–497.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
You Q, Wang XS, Fu SB and Jin XM:
Downregulated expression of inhibitor of growth 4 (ING4) in
advanced colorectal cancers: A non-randomized experimental study.
Pathol Oncol Res. 17:473–477. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gong A, Ye S, Xiong E, Guo W, Zhang Y,
Peng W, Shao G, Jin J, Zhang Z, Yang J and Gao J: Autophagy
contributes to ING4-induced glioma cell death. Exp Cell Res.
319:1714–1723. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Colla S, Tagliaferri S, Morandi F, Lunghi
P, Donofrio G, Martorana D, Mancini C, Lazzaretti M, Mazzera L,
Ravanetti L, et al: The new tumor-suppressor gene inhibitor of
growth family member 4 (ING4) regulates the production of
proangiogenic molecules by myeloma cells and suppresses
hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1alpha) activity: Involvement
in myeloma-induced angiogenesis. Blood. 110:4464–4475. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lou C, Jiang S, Guo X and Dong XS: ING4 is
negatively correlated with microvessel density in colon cancer.
Tumor Biol. 33:2357–2364. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhang X, Xu LS, Wang ZQ, Wang KS, Li N,
Cheng ZH, Huang SZ, Wei DZ and Han ZG: ING4 induces G2/M cell cycle
arrest and enhances the chemosensitivity to DNA-damage agents in
HepG2 cells. FEBS Lett. 570:7–12. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu E, Wu J, Cao W, Zhang J, Liu W, Jiang
X and Zhang X: Curcumin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest in a
p53-dependent manner and upregulates ING4 expression in human
glioma. J Neurooncol. 85:263–270. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Goodheart MJ, Ritchie JM, Rose SL,
Fruehauf JP, De Young BR and Buller RE: The relationship of
molecular markers of p53 function and angiogenesis to prognosis of
stage I epithelial ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 11:3733–3742.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Luo Y, Jiang F, Cole TB, Hradil VP, Reuter
D, Chakravartty A, Albert DH, Davidsen SK, Cox BF, McKeegan EM and
Fox GB: A novel multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor, linifanib
(ABT-869), produces functional and structural changes in tumor
vasculature in an orthotopic rat glioma model. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 69:911–921. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brat DJ, Bellail AC and Van Meir EG: The
role of interleukin-8 and its receptors in gliomagenesis and
tumoral angiogenesis. Neuro Oncol. 7:122–133. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|