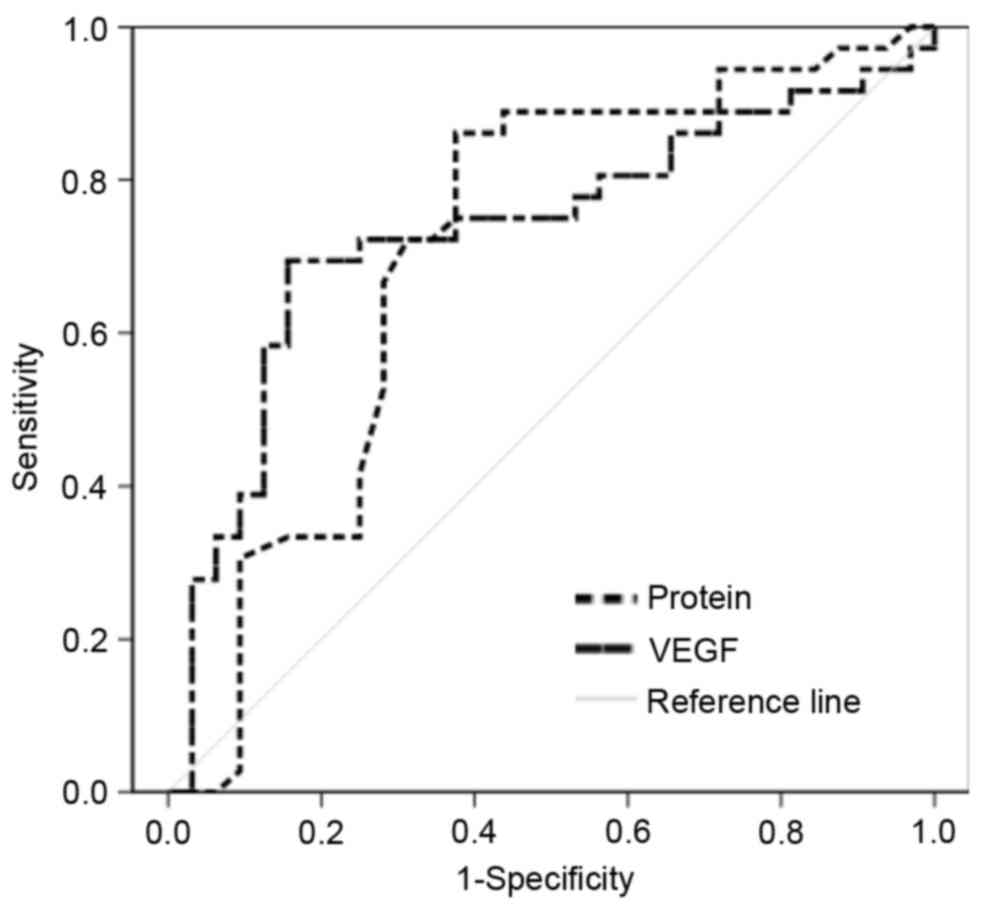
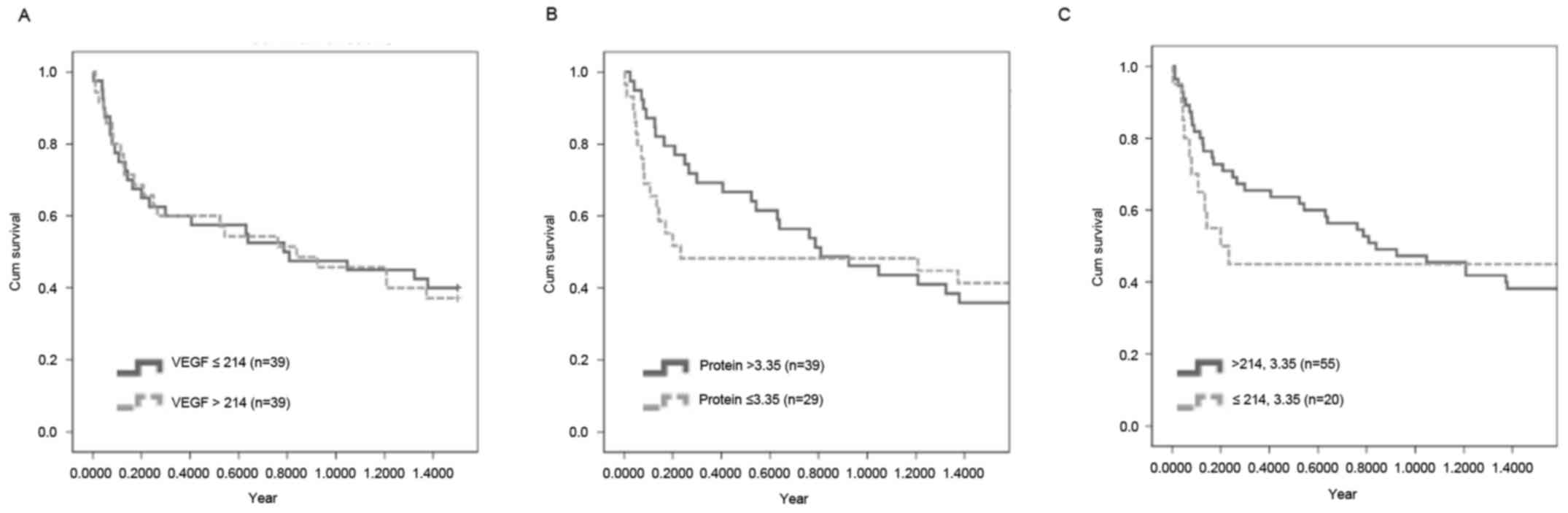
|
1
|
Medford AR and Maskell N: Pleural
effusion. Postgrad Med J. 81:702–710. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thomas R and Lee YC: Causes and management
of common benign pleural effusions. Thorac Surg Clin. 23:25–42.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
American Thoracic Society, . Management of
malignant pleural effusions. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
162:1987–2001. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Henschke CI, Yankelevitz DF and Davis SD:
Pleural diseases: Multimodality imaging and clinical management.
Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 20:155–181. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Martínez-Moragón E, Aparicio J, Sanchis J,
Menéndez R, Cruz Rogado M and Sanchis F: Malignant pleural
effusion: Prognostic factors for survival and response to chemical
pleurodesis in a series of 120 cases. Respiration. 65:108–113.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Heffner JE: Diagnosis and management of
malignant pleural effusions. Respirology. 13:5–20. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Heffner JE, Nietert PJ and Barbieri C:
Pleural fluid pH as a predictor of survival for patients with
malignant pleural effusions. Chest. 117:79–86. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bielsa S, Salud A, Martinez M, Esquerda A,
Martín A, Rodríguez-Panadero F and Porcel JM: Prognostic
significance of pleural fluid data in patients with malignant
effusion. Eur J Intern Med. 19:334–339. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chung CL, Chen YC and Chang SC: Effect of
repeated thoracenteses on fluid characteristics, cytokines, and
fibrinolytic activity in malignant pleural effusion. Chest.
123:1188–1195. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Stathopoulos GT and Kalomenidis I:
Malignant pleural effusion: Tumor-host interactions unleashed. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 186:487–492. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Stathopoulos GT, Psallidas I, Moustaki A,
Moschos C, Kollintza A, Karabela S, Porfyridis I, Vassiliou S,
Karatza M, Zhou Z, et al: A central role for tumor-derived monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 in malignant pleural effusion. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 100:1464–1476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hamed EA, El-Noweihi AM, Mohamed AZ and
Mahmoud A: Vasoactive mediators (VEGF and TNF-alpha) in patients
with malignant and tuberculous pleural effusions. Respirology.
9:81–86. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ozyurtkan MO, Balci AE and Cakmak M:
Predictors of mortality within three months in the patients with
malignant pleural effusion. Eur J Intern Med. 21:30–34. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu YC, Lee Shin-Jung S, Chen YS, Tu HZ,
Chen BC and Huang TS: Differential diagnosis of tuberculous and
malignant pleurisy using pleural fluid adenosine deaminase and
interferon gamma in Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 44:88–94.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Seiscento M, Vargas FS, Antonangelo L,
Acencio MM, Bombarda S, Capelozzi VL and Teixeira LR: Transforming
growth factor beta-1 as a predictor of fibrosis in tuberculous
pleurisy. Respirology. 12:660–663. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Light RW: Clinical practice. Pleural
effusion. N Engl J Med. 346:1971–1977. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hsu IL, Su WC, Yan JJ, Chang JM and Lai
WW: Angiogenetic biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer with
malignant pleural effusion: Correlations with patient survival and
pleural effusion control. Lung Cancer. 65:371–376. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hung TL, Chen FF, Liu JM, Lai WW, Hsiao
AL, Huang WT, Chen HH and Su WC: Clinical evaluation of HER-2/neu
protein in malignant pleural effusion-associated lung
adenocarcinoma and as a tumor marker in pleural effusion diagnosis.
Clin Cancer Res. 9:2605–2612. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee SH, Lee EJ, Min KH, Hur GY and Lee SY,
Kim JH, Shin C, Shim JJ, In KH, Kang KH and Lee SY: Procalcitonin
as a diagnostic marker in differentiating parapneumonic effusion
from tuberculous pleurisy or malignant effusion. Clin Biochem.
46:1484–1488. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Valdés L, San-José E, Ferreiro L, Golpe A,
González-Barcala FJ, Toubes ME, Rodríguez-Álvarez MX,
Álvarez-Dobaño JM, Rodríguez-Núñez N, Rábade C and Gude F:
Predicting malignant and tuberculous pleural effusions through
demographics and pleural fluid analysis of patients. Clin Respir J.
9:203–213. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Verma A, Abisheganaden J and Light RW:
Identifying malignant pleural effusion by a cancer ratio (serum
LDH: Pleural fluid ADA ratio). Lung. 194:147–153. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Thomas R, Cheah HM, Creaney J, Turlach BA
and Lee YC: Longitudinal measurement of pleural fluid biochemistry
and cytokines in malignant pleural effusions. Chest. 149:1494–1500.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bielsa S, Salud A, Martínez M, Esquerda A,
Martín A, Rodríguez-Panadero F and Porcel JM: Prognostic
significance of pleural fluid data in patients with malignant
effusion. Eur J Intern Med. 19:334–339. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ghayumi MA, Mojtahedi Z and Fattahi MJ:
Th1 and Th2 cytokine profiles in malignant pleural effusion. Iran J
Immunol. 8:195–200. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen YM, Yang WK, Whang-Peng J, Tsai CM
and Perng RP: An analysis of cytokine status in the serum and
effusions of patients with tuberculous and lung cancer. Lung
Cancer. 31:25–30. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Duysinx BC, Corhay JL, Hubin L, Nguyen D,
Henket M and Louis R: Diagnostic value of interleukine-6,
transforming growth factor-beta 1 and vascular endothelial growth
factor in malignant pleural effusions. Respir Med. 102:1708–1714.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fiorelli A, Vicidomini G, Di Domenico M,
Napolitano F, Messina G, Morgillo F, Ciardiello F and Santini M:
Vascular endothelial growth factor in pleural fluid for
differential diagnosis of benign and malignant origin and its
clinical applications. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 12:420–424.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Grove CS and Lee YC: Vascular endothelial
growth factor: The key mediator in pleural effusion formation. Curr
Opin Pulm Med. 8:294–301. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bradshaw M, Mansfield A and Peikert T: The
role of vascular endothelial growth factor in the pathogenesis,
diagnosis and treatment of malignant pleural effusion. Curr Oncol
Rep. 15:207–216. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cheng D, Kong H and Li Y: Prognostic
values of VEGF and IL-8 in malignant pleural effusion in patients
with lung cancer. Biomarkers. 18:386–390. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|