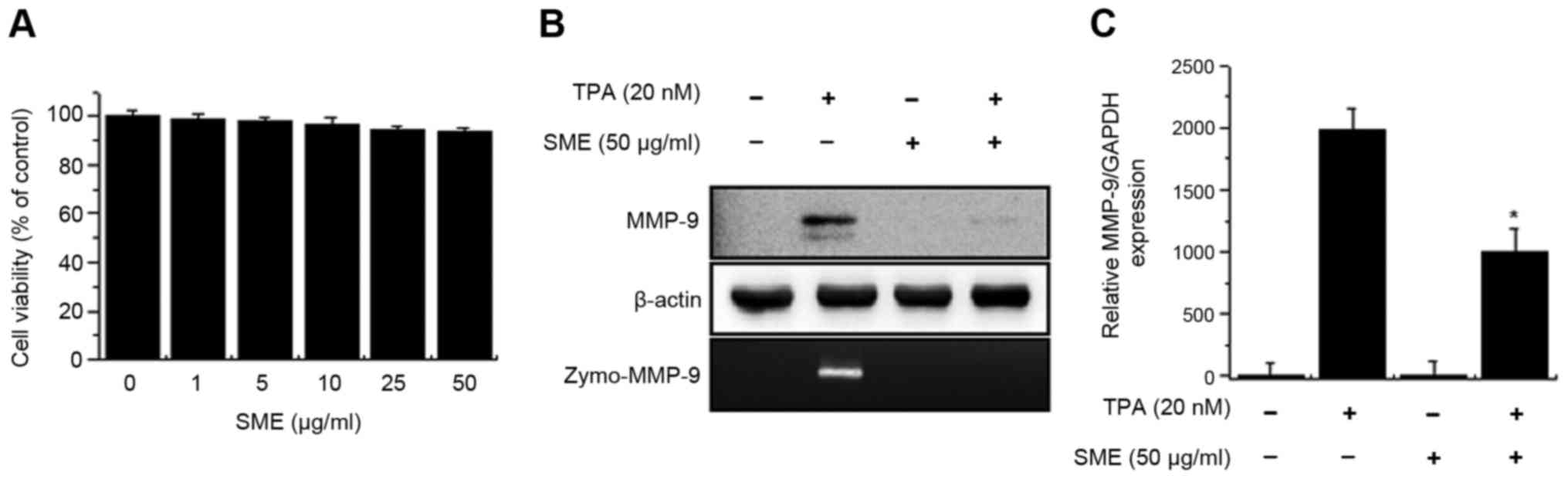
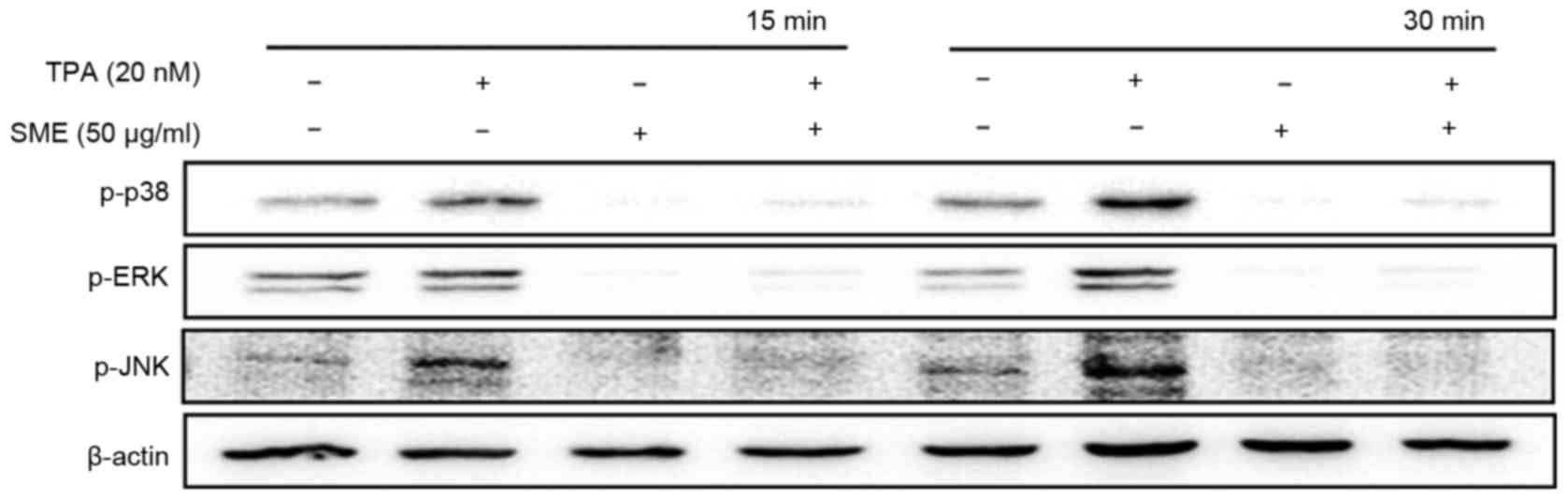
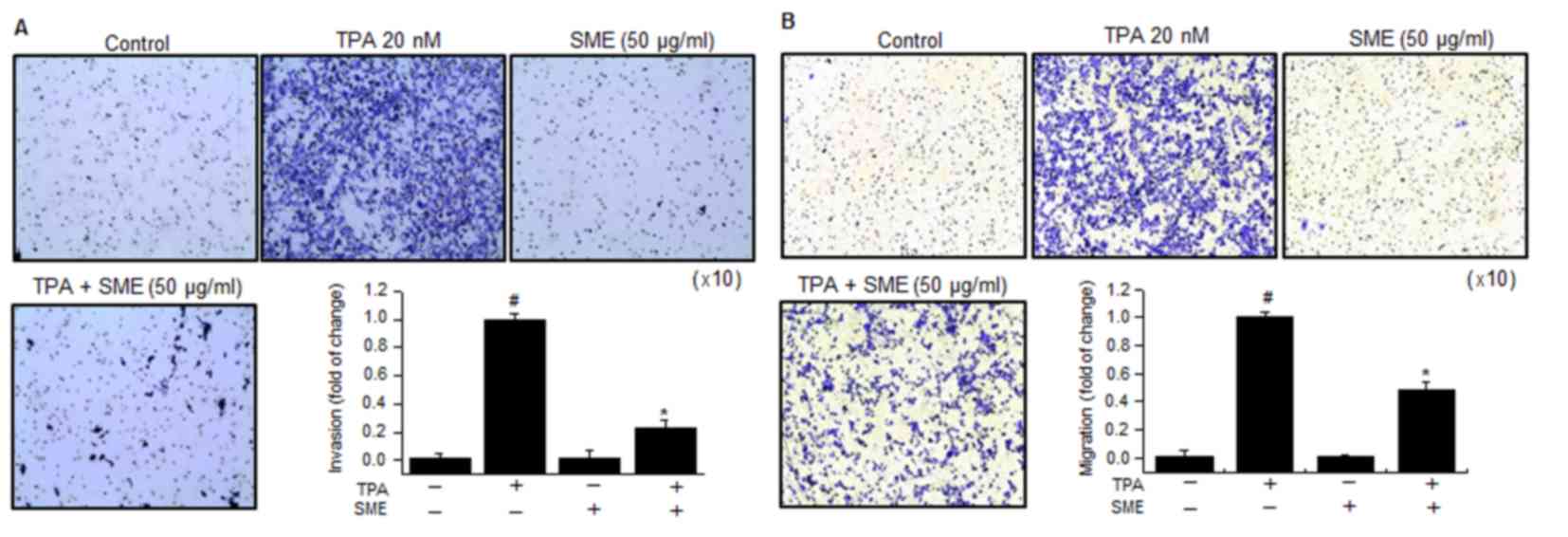
|
1
|
Yan X: Dan Shen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) in
Medicine. 1. Springer; The Netherlands: 2016
|
|
2
|
Park CH, Kim DH, Park MH, Kim MK, Kim ND,
Kim CM, Tanaka T, Yokozawa T, Chung HY and Moon HR: Chinese
prescription Kangen-karyu and Salviae Miltiorrhizae Radix improve
age-related oxidative stress and inflammatory response through the
PI3K/Akt or MAPK pathways. Am J Chin Med. 42:987–1005. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xiping Z, Yan P, Xinmei H, Guanghua F,
Meili M, Jie N and Fangjie Z: Effects of dexamethasone and Salvia
miltiorrhizae on the small intestine and immune organs of rats with
severe acute pancreatitis. Inflammation. 33:259–266. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gu J, Li JC, Tan R, Fan LN and Zhang X:
Effects of combination of Puerariae lobatae radix and Salviae
miltiorrhizae radix et rhizoma on lipid metabolism in
atherosclerotic quails. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 38:3939–3942.
2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu CF, Bohnert S, Thines E and Efferth T:
Cytotoxicity of Salvia miltiorrhiza against multidrug-resistant
cancer cells. Am J Chin Med. 44:871–894. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ge Y, Yang B, Chen Z and Cheng R:
Cryptotanshinone suppresses the proliferation and induces the
apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells via the STAT3 signaling
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 12:7782–7788. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gao H, Sun W, Zhao W, Hao W, Leung CH, Lu
J and Chen X: Total tanshinones-induced apoptosis and autophagy via
reactive oxygen species in lung cancer 95D Cells. Am J Chin Med.
43:1265–1279. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yuxian X, Feng T, Ren L and Zhengcai L:
Tanshinone II-A inhibits invasion and metastasis of human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Tumori.
95:789–795. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shan YF, Shen X, Xie YK, Chen JC, Shi HQ,
Yu ZP, Song QT, Zhou MT and Zhang QY: Inhibitory effects of
tanshinone II-A on invasion and metastasis of human colon carcinoma
cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 30:1537–1542. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nizamutdinova IT, Lee GW, Lee JS, Cho MK,
Son KH, Jeon SJ, Kang SS, Kim YS, Lee JH, Seo HG, et al: Tanshinone
I suppresses growth and invasion of human breast cancer cells,
MDA-MB-231, through regulation of adhesion molecules.
Carcinogenesis. 29:1885–1892. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nizamutdinova IT, Lee GW, Son KH, Jeon SJ,
Kang SS, Kim YS, Lee JH, Seo HG, Chang KC and Kim HJ: Tanshinone I
effectively induces apoptosis in estrogen receptor-positive (MCF-7)
and estrogen receptor-negative (MDA-MB-231) breast cancer cells.
Int J Oncol. 33:485–491. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Redig AJ and McAllister SS: Breast cancer
as a systemic disease: A view of metastasis. J Intern Med.
274:113–126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Leber MF and Efferth T: Molecular
principles of cancer invasion and metastasis (Review). Int J Oncol.
34:881–895. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chambers AF and Matrisian LM: Changing
views of the role of matrix metalloproteinases in metastasis. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 89:1260–1270. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Woodhouse EC, Chuaqui RF and Liotta LA:
General mechanisms of metastasis. Cancer. 80:(8 Suppl).
S1529–S1537. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yan C and Boyd DD: Regulation of matrix
metalloproteinase gene expression. J Cell Physiol. 211:19–26. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Overall CM and Dean RA: Degradomics:
Systems biology of the protease web. Pleiotropic roles of MMPs in
cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 25:69–75. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hong S, Park KK, Magae J, Ando K, Lee TS,
Kwon TK, Kwak JY, Kim CH and Chang YC: Ascochlorin inhibits matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression by suppressing activator
protein-1-mediated gene expression through the ERK1/2 signaling
pathway: Inhibitory effects of ascochlorin on the invasion of renal
carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 280:25202–25209. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Roy R, Yang J and Moses MA: Matrix
metalloproteinases as novel biomarkers and potential therapeutic
targets in human cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:5287–5297. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu JF, Crépin M, Liu JM, Barritault D and
Ledoux D: FGF-2 and TPA induce matrix metalloproteinase-9 secretion
in MCF-7 cells through PKC activation of the Ras/ERK pathway.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 293:1174–1182. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Przybylowska K, Kluczna A, Zadrozny M,
Krawczyk T, Kulig A, Rykala J, Kolacinska A, Morawiec Z, Drzewoski
J and Blasiak J: Polymorphisms of the promoter regions of matrix
metalloproteinases genes MMP-1 and MMP-9 in breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 95:65–72. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim S, Choi JH, Kim JB, Nam SJ, Yang JH,
Kim JH and Lee JE: Berberine suppresses TNF-alpha-induced MMP-9 and
cell invasion through inhibition of AP-1 activity in MDA-MB-231
human breast cancer cells. Molecules. 13:2975–2985. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim S, Choi JH, Lim HI, Lee SK, Kim WW,
Cho S, Kim JS, Kim JH, Choe JH, Nam SJ, et al: EGF-induced MMP-9
expression is mediated by the JAK3/ERK pathway, but not by the
JAK3/STAT-3 pathway in a SKBR3 breast cancer cell line. Cell
Signal. 21:892–898. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chung TW, Moon SK, Chang YC, Ko JH, Lee
YC, Cho G, Kim SH, Kim JG and Kim CH: Novel and therapeutic effect
of caffeic acid and caffeic acid phenyl ester on hepatocarcinoma
cells: Complete regression of hepatoma growth and metastasis by
dual mechanism. FASEB J. 18:1670–1681. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Noh EM, Chung EY, Youn HJ, Jung SH, Hur H,
Lee YR and Kim JS: Cis-guggulsterone inhibits the IKK/NF-kappaB
pathway, whereas trans-guggulsterone inhibits MAPK/AP-1 in MCF-7
breast cancer cells: Guggulsterone regulates MMP-9 expression in an
isomer-specific manner. Int J Mol Med. 31:393–399. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hess J, Angel P and Schorpp-Kistner M:
AP-1 subunits: Quarrel and harmony among siblings. J Cell Sci.
117:5965–5973. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lin CW, Hou WC, Shen SC, Juan SH, Ko CH,
Wang LM and Chen YC: Quercetin inhibition of tumor invasion via
suppressing PKC delta/ERK/AP-1-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-9
activation in breast carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis. 29:1807–1815.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee SO, Jeong YJ, Kim M, Kim CH and Lee
IS: Suppression of PMA-induced tumor cell invasion by capillarisin
via the inhibition of NF-kappaB-dependent MMP-9 expression. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 366:1019–1024. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oh JH, Chung AS, Steinbrenner H, Sies H
and Brenneisen P: Thioredoxin secreted upon ultraviolet A
irradiation modulates activities of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and
tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 in human dermal
fibroblasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 423:218–226. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Himelstein BP, Lee EJ, Sato H, Seiki M and
Muschel RJ: Tumor cell contact mediated transcriptional activation
of the fibroblast matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene: Involvement of
multiple transcription factors including Ets and an alternating
purine-pyrimidine repeat. Clin Exp Metastasis. 16:169–177. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jacobs MD and Harrison SC: Structure of an
IkappaBalpha/NF-kappaB complex. Cell. 95:749–758. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim HR, Kim JM, Kim MS, Hwang JK, Park YJ,
Yang SH, Kim HJ, Ryu DG, Lee DS, Oh H, et al: Saussurea lappa
extract suppresses TPA-induced cell invasion via inhibition of
NF-kappaB-dependent MMP-9 expression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.
BMC Complement Altern Med. 14:1702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee YR, Noh EM, Oh HJ, Hur H, Kim JM, Han
JH, Hwang JK, Park BH, Park JW, Youn HJ, et al:
Dihydroavenanthramide D inhibits human breast cancer cell invasion
through suppression of MMP-9 expression. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 405:552–557. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim JM, Noh EM, Kim HR, Kim MS, Song HK,
Lee M, Yang SH, Lee GS, Moon HC, Kwon KB and Lee YR: Suppression of
TPA-induced cancer cell invasion by peucedanum japonicum thunb.
Extract through the inhibition of PKCα/NF-κB-dependent MMP-9
expression in MCF-7 cells. Int J Mol Med. 37:108–114.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Livak KL and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Noh EM, Lee YR, Hong OY, Jung SH, Youn HJ
and Kim JS: Aurora kinases are essential for PKC-induced invasion
and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in MCF-7 breast cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 34:803–810. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Woessner JF Jr: Matrix metalloproteinases
and their inhibitors in connective tissue remodeling. FASEB J.
5:2145–2154. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zwiefel K and Janni W: Current standards
in the treatment of breast cancer. Med Monatsschr Pharm.
34:280–288; quiz 289–290. 2011.(In German). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Deryugina EI and Quigley JP: Matrix
metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
25:9–34. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Köhrmann A, Kammerer U, Kapp M, Dietl J
and Anacker J: Expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in
primary human breast cancer and breast cancer cell lines: New
findings and review of the literature. BMC Cancer. 9:1882009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lombard C, Saulnier J and Wallach J:
Assays of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) activities: A review.
Biochimie. 87:265–272. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Duffy MJ and McCarthy K: Matrix
metalloproteinases in cancer: Prognostic markers and targets for
therapy (Review). Int J Oncol. 12:1343–1348. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mignatti P and Rifkin DB: Biology and
biochemistry of proteinases in tumor invasion. Physiol Rev.
73:161–195. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cho HJ, Kang JH, Kwak JY, Lee TS, Lee IS,
Park NG, Nakajima H, Magae J and Chang YC: Ascofuranone suppresses
PMA-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene activation through the
Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK- and Ap1-dependent mechanisms. Carcinogenesis.
28:1104–1110. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Mo N, Li ZQ, Li J and Cao YD: Curcumin
inhibits TGF-β1-induced MMP-9 and invasion through ERK and Smad
signaling in breast cancer MDA- MB-231 cells. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 13:5709–5714. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lungu G, Covaleda L, Mendes O,
Martini-Stoica H and Stoica G: FGF-1-induced matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression in breast cancer cells is mediated
by increased activities of NF-kappaB and activating protein-1. Mol
Carcinog. 47:424–435. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Huang XY, Wang L, Huang ZL, Zheng Q, Li QS
and Tang ZY: Herbal extract ‘Songyou Yin’ inhibits tumor growth and
prolongs survival in nude mice bearing human hepatocellular
carcinoma xenograft with high metastatic potential. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 135:1245–1255. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yang W, Ju JH, Jeon MJ, Han X and Shin I:
Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) extract inhibits proliferation of
breast cancer cells via modulation of Akt activity and p27 level.
Phytother Res. 24:198–204. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Cobb MH and Goldsmith EJ: How MAP kinases
are regulated. J Biol Chem. 270:14843–14846. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Seger R, Biener Y, Feinstein R, Hanoch T,
Gazit A and Zick Y: Differential activation of mitogen-activated
protein kinase and S6 kinase signaling pathways by
12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) and insulin. Evidence
for involvement of a TPA-stimulated protein-tyrosine kinase. J Biol
Chem. 270:28325–28330. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jemal A, Murray T, Ward E, Samuels A,
Tiwari RC, Ghafoor A, Feuer EJ and Thun MJ: Cancer statistics,
2005. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:10–30. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yao J, Xiong S, Klos K, Nguyen N, Grijalva
R, Li P and Yu D: Multiple signaling pathways involved in
activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) by heregulin-beta1
in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 20:8066–8074. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Smith LM, Wise SC, Hendricks DT, Sabichi
AL, Bos T, Reddy P, Brown PH and Birrer MJ: cJun overexpression in
MCF-7 breast cancer cells produces a tumorigenic, invasive and
hormone resistant phenotype. Oncogene. 18:6063–6070. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Eberhardt W, Huwiler A, Beck KF, Walpen S
and Pfeilschifter J: Amplification of IL-1 beta-induced matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression by superoxide in rat glomerular
mesangial cells is mediated by increased activities of NF-kappa B
and activating protein-1 and involves activation of the
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. J Immunol.
165:5788–5797. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|