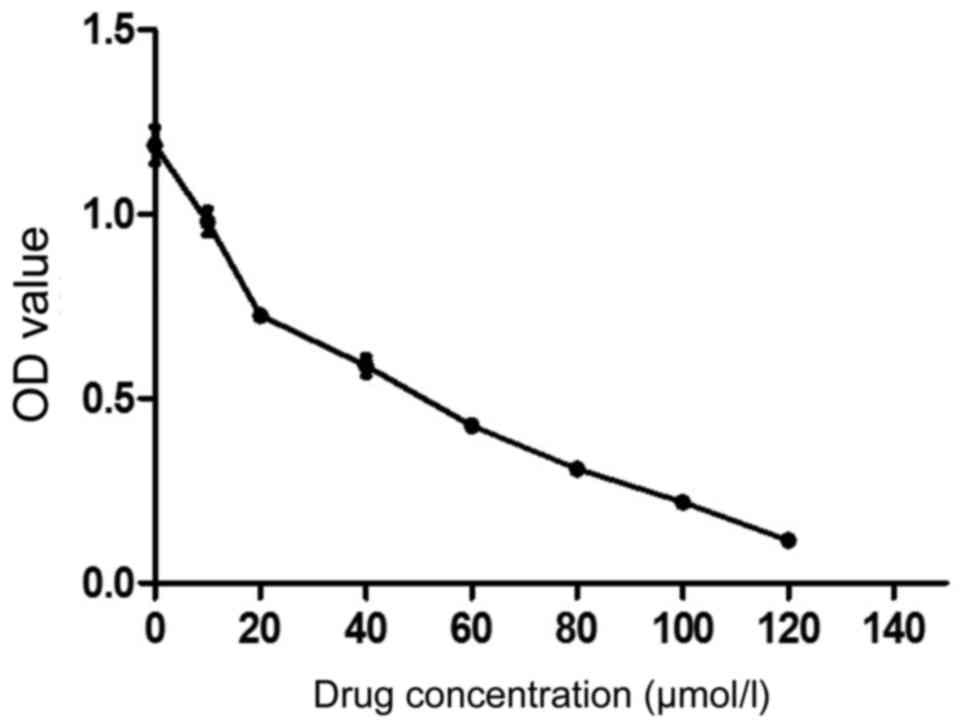
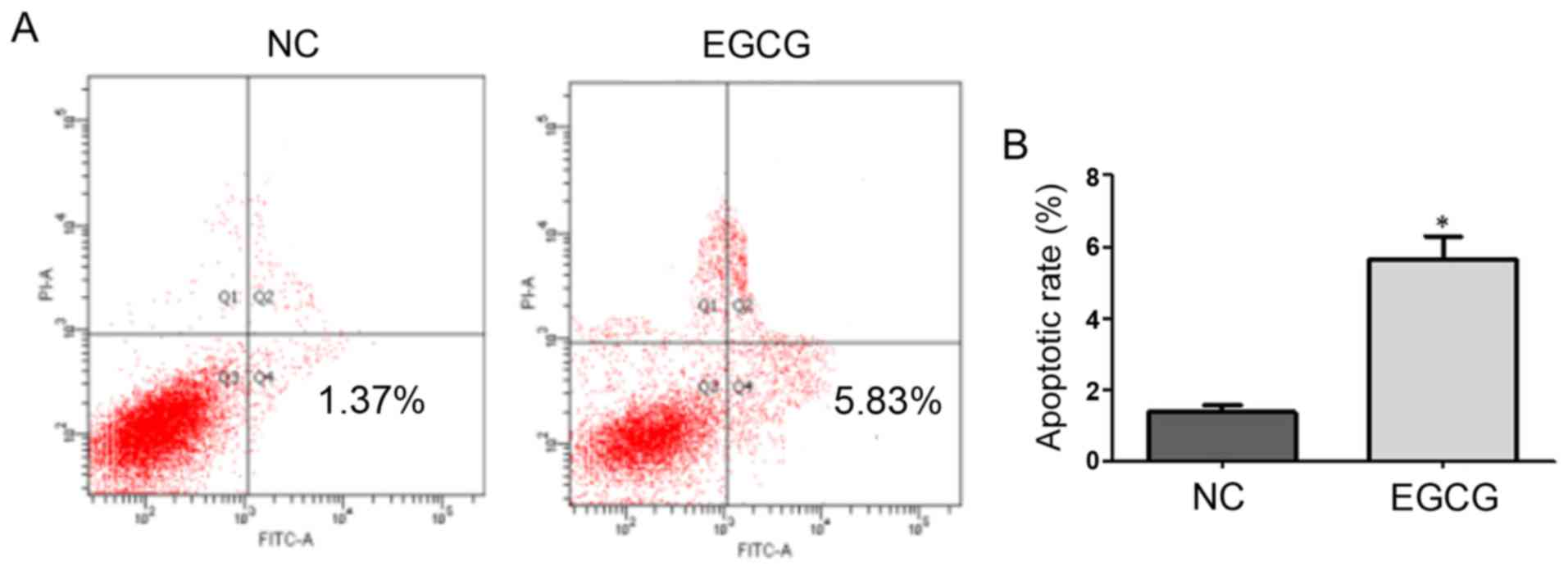
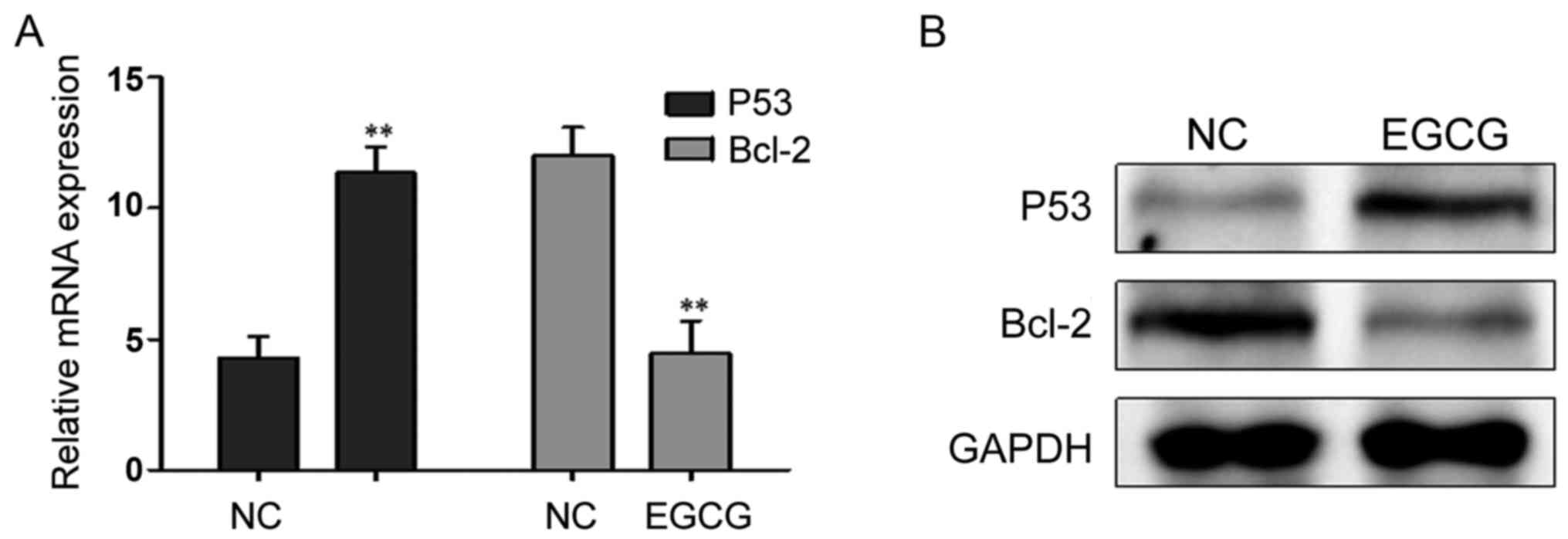
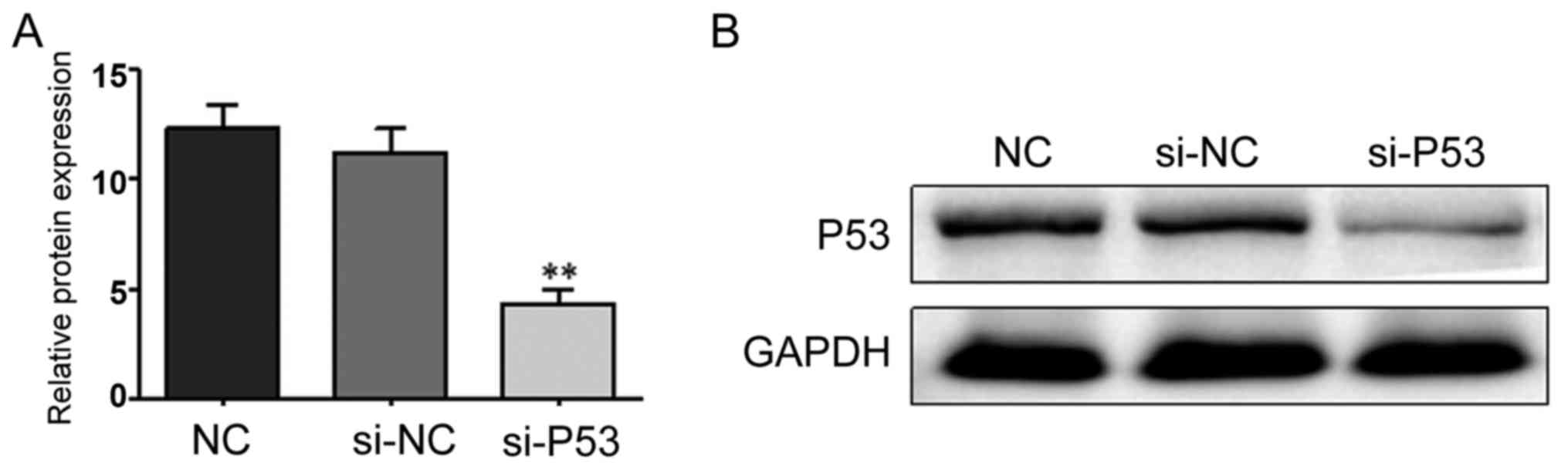
|
1
|
Yang CS and Wang ZY: Tea and cancer. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 85:1038–1049. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tan XH, Zhou DY and Zhang YL: Advances in
research on anticancer mechanism of tea. Foreign Medical Oncology.
25:41998.
|
|
3
|
Yang GY, Liao J, Kim K, Yurkow EJ and Yang
CS: Inhibition of growth and induction of apoptosis in human cancer
cell lines by tea polyphenols. Carcinogenesis. 19:611–616. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ahmad N, Feyes DK, Nieminen AL, Agarwal R
and Mukhtar H: Green tea constituent epigallocatechin-3-gallate and
induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human carcinoma
cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 89:1881–1886. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang G, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wan X, Li J, Liu
K, Wang F, Liu K, Liu Q, Yang C, et al: Anti-cancer activities of
tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate in breast cancer patients under
radiotherapy. Curr Mol Med. 12:163–176. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liang YC, Lin-Shiau SY, Chen CF and Lin
JK: Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases 2 and 4 activities as
well as induction of Cdk inhibitors p21 and p27 during growth
arrest of human breast carcinoma cells by
(−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. J Cell Biochem. 75:1–12. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sartippour MR, Shao ZM, Heber D, Beatty P,
Zhang L, Liu C, Ellis L, Liu W, Go VL and Brooks MN: Green tea
inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induction in
human breast cancer cells. J Nutr. 132:2307–2311. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Masuda M, Suzui M, Lim JT, Deguchi A, Soh
JW and Weinstein IB: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate decreases VEGF
production in head and neck and breast carcinoma cells by
inhibiting EGFR-related pathways of signal transduction. J Exp Ther
Oncol. 2:350–359. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Farabegoli F, Papi A and Orlandi M:
(−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate down-regulates EGFR, MMP-2, MMP-9
and EMMPRIN and inhibits the invasion of MCF-7 tamoxifen-resistant
cells. Biosci Rep. 31:99–108. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Levine AJ, Momand J and Finlay CA: The p53
tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 351:453–456. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pakos EE, Kyzas PA and Ioannidis JP:
Prognostic significance for TP53 tumor suppressor gene expression
and mutations in human motations in human osteosarcoma: A
meta-analysis. Clin Cancer Res. 10:6208–6214. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Barnes DM, Dublin EA, Fisher CJ, Levison
DA and Millis RR: Immunohistochemical detection of p53 protein in
mammary carcinoma: An important new independent indicator of
prognosis? Hum Pathol. 24:469–476. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dastjerdi MN, Rarani MZ, Valiani A and
Mahmoudieh M: The effect of adenosine A1 receptor agonist and
antagonist on p53 and caspase 3, 8, and 9 expression and apoptosis
rate in MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. Res Pharm Sci. 11:303–310.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Synnott NC, Murray A, McGowan PM, Kiely M,
Kiely PA, O'Donovan N, O'Connor DP, Gallagher WM, Crown J and Duffy
MJ: Mutant p53: A novel target for the treatment of patients with
triple-negative breast cancer? Int J Cancer. 140:234–246. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Darb-Esfahani S, Denkert C, Stenzinger A,
Salat C, Sinn B, Schem C, Endris V, Klare P, Schmitt W, Blohmer JU,
et al: Role of TP53 mutations in triple negative and HER2-positive
breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant anthracycline/taxane-based
chemotherapy. Oncotarget. 7:67686–67698. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schinzel A, Kaufmann T and Borner C: Bcl-2
family members: Integrators of survival and death signals in
physiology and pathology. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1644:95–105. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mihara M, Erster S, Zaika A, Petrenko O,
Chittenden T, Pancoska P and Moll UM: p53 has a direct apoptogenic
role at the mitochondria. Mol Cell. 11:577–590. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhu BH, Zhan WH, Li ZR, Wang Z, He YL,
Peng JS, Cai SR, Ma JP and Zhang CH: (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate
inhibits growth of gastric cancer by reducing VEGF production and
angiogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 13:1162–1169. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qanungo S, Das M, Haldar S and Basu A:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces mitochondrial membrane
depolarization and caspase-dependent apoptosis in pancreatic cancer
cells. Carcinogenesis. 26:958–967. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|