|
1
|
Wang K and Karin M: Tumor-Elicited
Inflammation and colorectal cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 128:173–196.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Berasain C, Castillo J, Perugorria MJ,
Latasa MU, Prieto J and Avila MA: Inflammation and liver cancer:
New molecular links. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1155:206–221. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kundu JK and Surh YJ: Inflammation:
Gearing the journey to cancer. Mutat Res. 659:15–30. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Umbehr MH, Gurel B, Murtola TJ, Sutcliffe
S, Peskoe SB, Tangen CM, Goodman PJ, Thompson IM, Lippman SM, Lucia
MS, et al: Intraprostatic inflammation is positively associated
with serum PSA in men with PSA <4 ng ml(−1), normal DRE and
negative for prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis.
18:264–269. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sfanos KS, Hempel HA and De Marzo AM: The
role of inflammation in prostate cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol.
816:153–181. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cheng I, Witte JS, Jacobsen SJ, Haque R,
Quinn VP, Quesenberry CP, Caan BJ and Van Den Eeden SK:
Prostatitis, sexually transmitted diseases, and prostate cancer:
The California Men's Health Study. PLoS One. 5:e87362010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Porcaro AB, Rubilotta E, Petrozziello A,
Ghimenton C, Migliorini F, Zecchini Antoniolli S, Lacola V, Monaco
C, Curti P, Cavalleri S, et al: Chronic inflammation of the
prostate type IV with respect to risk of prostate cancer. Arch Ital
Urol Androl. 86:208–211. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Adamczyk P, Wolski Z, Butkiewicz R,
Nussbeutel J and Drewa T: Inflammatory changes in biopsy specimens
from patients with suspected prostate cancer. Cent European J Urol.
66:256–262. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vandersluis AD, Guy DE, Klotz LH, Fleshner
NE, Kiss A, Parker C and Venkateswaran V: The role of lifestyle
characteristics on prostate cancer progression in two active
surveillance cohorts. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 19:305–310.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Discacciati A and Wolk A: Lifestyle and
dietary factors in prostate cancer prevention. Recent Results
Cancer Res. 202:27–37. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gonzalez CA and Riboli E: Diet and cancer
prevention: Contributions from the European Prospective
Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) study. Eur J Cancer.
46:2555–2562. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rybicki BA, Kryvenko ON, Wang Y, Jankowski
M, Trudeau S, Chitale DA, Gupta NS, Rundle A and Tang D: Racial
differences in the relationship between clinical prostatitis,
presence of inflammation in benign prostate and subsequent risk of
prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 19:145–150. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mian OY, Khattab MH, Hedayati M, Coulter
J, Abubaker-Sharif B, Schwaninger JM, Veeraswamy RK, Brooks JD,
Hopkins L, Shinohara DB, et al: GSTP1 Loss results in accumulation
of oxidative DNA base damage and promotes prostate cancer cell
survival following exposure to protracted oxidative stress.
Prostate. 76:199–206. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vasto S, Carruba G, Candore G, Italiano E,
Di Bona D and Caruso C: Inflammation and prostate cancer. Future
Oncol. 4:637–645. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nguyen DP, Li J, Yadav SS and Tewari AK:
Recent insights into NF-κB signaling pathways and the link between
inflammation and prostate cancer. BJU Int. 114:168–176. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
MacLennan GT, Eisenberg R, Fleshman RL,
Taylor JM, Fu P, Resnick MI and Gupta S: The influence of chronic
inflammation in prostatic carcinogenesis: A 5-year followup study.
J Urol. 176:1012–1016. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kulac I, Gumuskaya B, Drake CG, Gonzalez
B, Arnold KB, Goodman PJ, Kristal AR, Lucia MS, Thompson IM, Isaacs
WB, et al: Peripheral zone inflammation is not strongly associated
with lower urinary tract symptom incidence and progression in the
placebo arm of the prostate cancer prevention trial. Prostate.
76:1399–1408. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang W, Bergh A and Damber JE:
Morphological transition of proliferative inflammatory atrophy to
high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia and cancer in human prostate.
Prostate. 69:1378–1386. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Woenckhaus J and Fenic I: Proliferative
inflammatory atrophy: A background lesion of prostate cancer?
Andrologia. 40:134–137. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chrisofos M, Papatsoris AG, Lazaris A and
Deliveliotis C: Precursor lesions of prostate cancer. Crit Rev Clin
Lab Sci. 44:243–270. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vral A, Magri V, Montanari E, Gazzano G,
Gourvas V, Marras E and Perletti G: Topographic and quantitative
relationship between prostate inflammation, proliferative
inflammatory atrophy and low-grade prostate intraepithelial
neoplasia: A biopsy study in chronic prostatitis patients. Int J
Oncol. 41:1950–1958. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Postma R, Schröder FH and van der Kwast
TH: Atrophy in prostate needle biopsy cores and its relationship to
prostate cancer incidence in screened men. Urology. 65:745–749.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Servian P, Celma A, Planas J, Placer J, de
Torres IM, Olivan M and Morote J: Clinical significance of
proliferative inflammatory atrophy finding in prostatic biopsies.
Prostate. 75:1669–1675. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
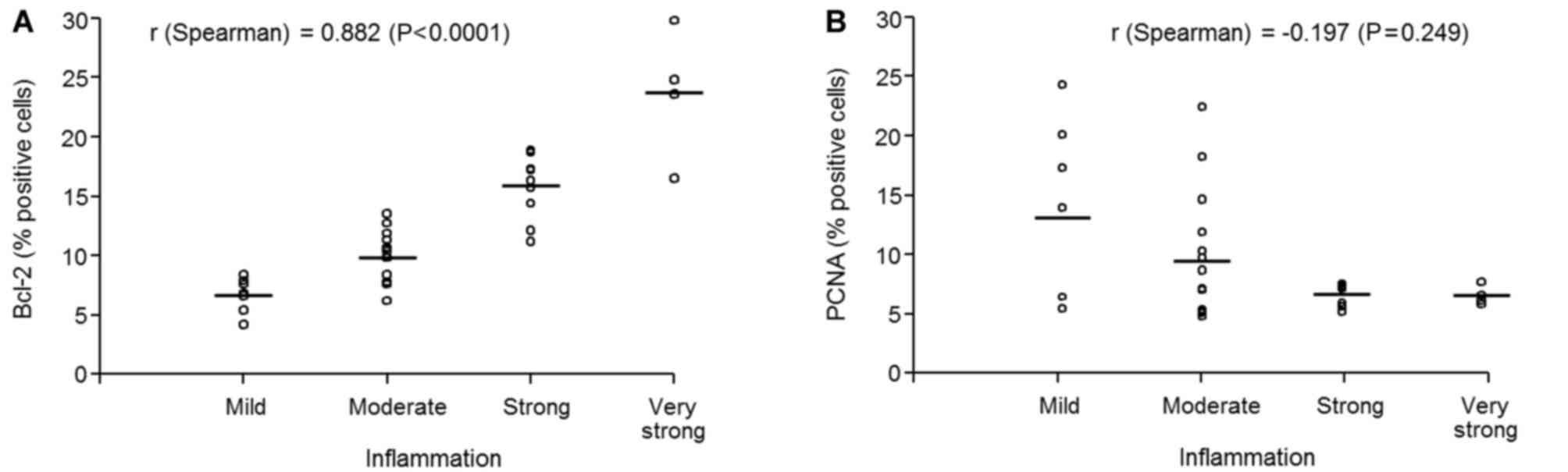
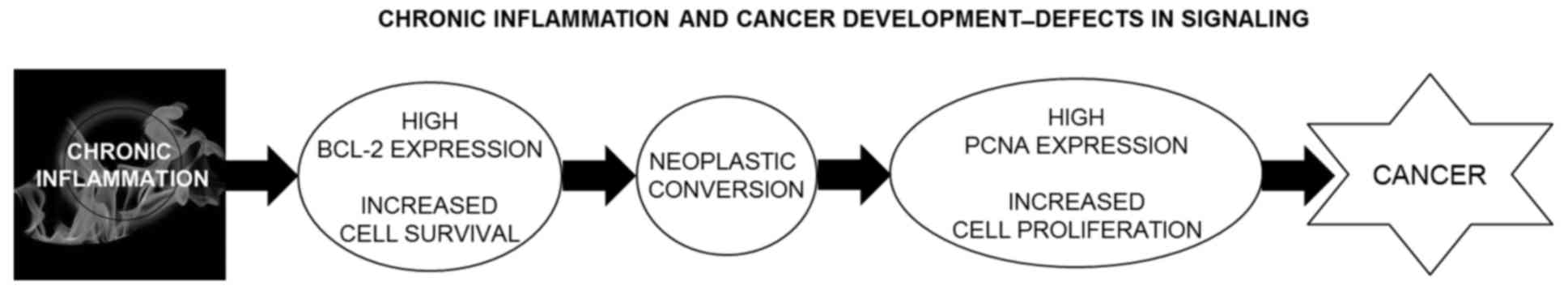
Kelly PN and Strasser A: The role of Bcl-2
and its pro-survival relatives in tumourigenesis and cancer
therapy. Cell Death Differ. 18:1414–1424. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Strzalka W and Ziemienowicz A:
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA): A key factor in DNA
replication and cell cycle regulation. Ann Bot. 107:1127–1140.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bostwick DG and Cheng L: Precursors of
prostate cancer. Histopathology. 60:4–27. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cheng L, Montironi R, Bostwick DG,
Lopez-Beltran A and Berney DM: Staging of prostate cancer.
Histopathology. 60:87–117. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shukla S, MacLennan GT, Fu P, Patel J,
Marengo SR, Resnick MI and Gupta S: Nuclear factor-kappaB/p65 (Rel
A) is constitutively activated in human prostate adenocarcinoma and
correlates with disease progression. Neoplasia. 6:390–400. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Henrique R, Jerónimo C, Teixeira MR, Hoque
MO, Carvalho AL, Pais I, Ribeiro FR, Oliveira J, Lopes C and
Sidransky D: Epigenetic heterogeneity of high-grade prostatic
intraepithelial neoplasia: Clues for clonal progression in prostate
carcinogenesis. Mol Cancer Res. 4:1–8. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nguyen DP, Li J and Tewari AK:
Inflammation and prostate cancer: The role of interleukin 6 (IL-6).
BJU Int. 113:986–992. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Taverna G, Pedretti E, Di Caro G, Borroni
EM, Marchesi F and Grizzi F: Inflammation and prostate cancer:
Friends or foe? Inflamm Res. 64:275–86. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang W, Bergh A and Damber JE: Chronic
inflammation in benign prostate hyperplasia is associated with
focal upregulation of cyclooxygenase-2, Bcl-2 and cell
proliferation in the glandular epithelium. Prostate. 61:60–72.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gerstenbluth RE, Seftel AD, MacLennan GT,
Rao RN, Corty EW, Ferguson K and Resnick MI: Distribution of
chronic prostatitis in radical prostatectomy specimens with
up-regulation of bcl-2 in areas of inflammation. J Urol.
167:2267–2270. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Azad N, Iyer A, Vallyathan V, Wang L,
Castranova V, Stehlik C and Rojanasakul Y: Role of
oxidative/nitrosative stress-mediated Bcl-2 regulation in apoptosis
and malignant transformation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1203:1–6. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Medan D, Luanpitpong S, Azad N, Wang L,
Jiang BH, Davis ME, Barnett JB, Guo L and Rojanasakul Y:
Multifunctional role of Bcl-2 in malignant transformation and
tumorigenesis of Cr(VI)-transformed lung cells. PLoS One.
7:e370452012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
van Soest RJ, van Royen ME, de Morrée ES,
Moll JM, Teubel W, Wiemer EA, Mathijssen RH, de Wit R and van
Weerden WM: Cross-resistance between taxanes and new hormonal
agents abiraterone and enzalutamide may affect drug sequence
choices in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur J
Cancer. 49:3821–3830. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
De Marzo AM, Marchi VL, Epstein JI and
Nelson WG: Proliferative inflammatory atrophy of the prostate:
Implications for prostatic carcinogenesis. Am J Pathol.
155:1985–1992. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kanwal R, Pandey M, Bhaskaran N, Maclennan
GT, Fu P, Ponsky LE and Gupta S: Protection against oxidative DNA
damage and stress in human prostate by glutathione S-transferase
P1. Mol Carcinog. 53:8–18. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Schnekenburger M, Karius T and Diederich
M: Regulation of epigenetic traits of the glutathione S-transferase
P1 gene: From detoxification toward cancer prevention and
diagnosis. Front Pharmacol. 5:1702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Crundwell MC, Chughtai S, Knowles M, Takle
L, Luscombe M, Neoptolemos JP, Morton DG and Phillips SM: Allelic
loss on chromosomes 8p, 22q and 18q (DCC) in human prostate cancer.
Int J Cancer. 69:295–300. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tapia-Laliena MA, Korzeniewski N,
Hohenfellner M and Duensing S: High-risk prostate cancer: A disease
of genomic instability. Urol Oncol. 32:1101–1107. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Schrecengost R and Knudsen KE: Molecular
pathogenesis and progression of prostate cancer. Semin Oncol.
40:244–258. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|