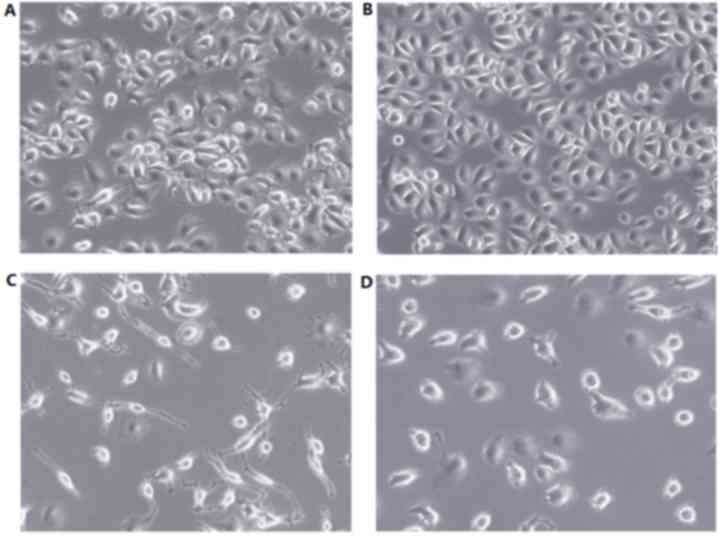
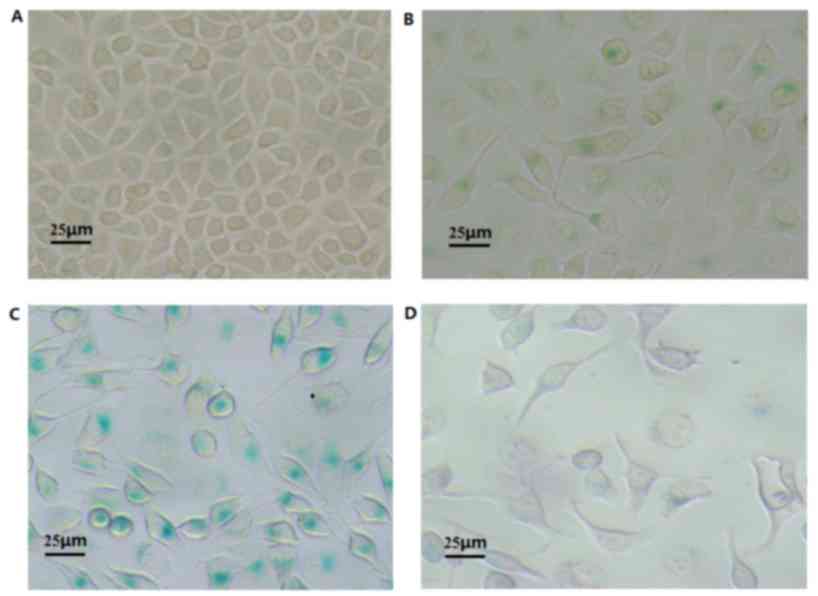
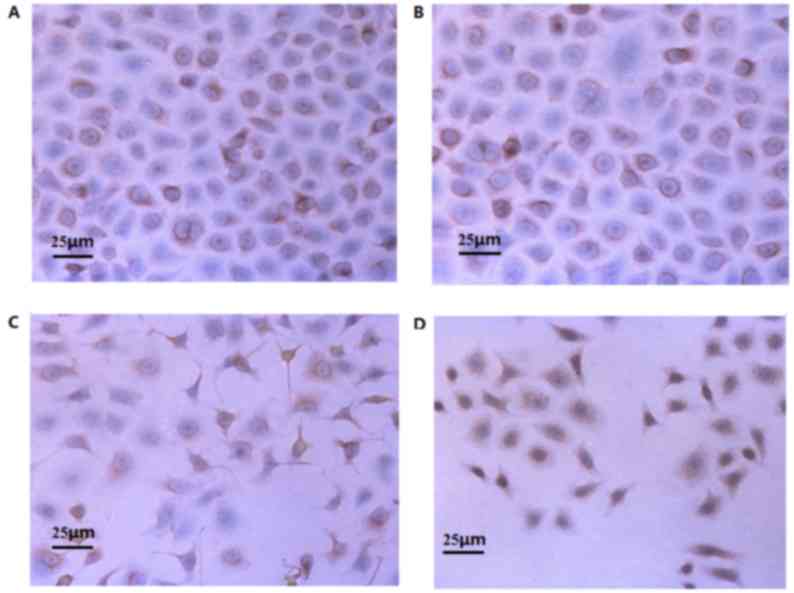
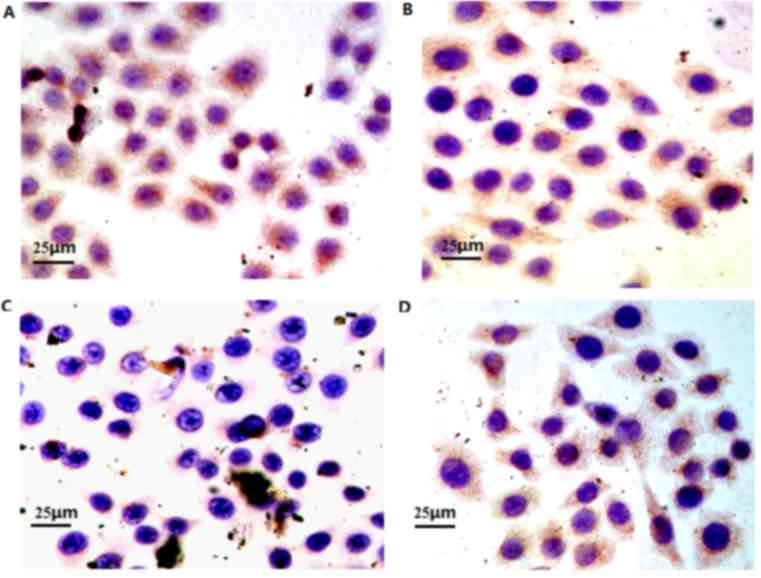
|
1
|
Torre LA, Siegel RL, Ward EM and Jemal A:
Global cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends-an update.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 25:16–27. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang J, Zhu J, Zhang YH, Chen YS, Ding LL,
Kensler TW and Chen JG: Lung cancer in a rural area of china: Rapid
rise in incidence and poor improvement in survival. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 16:7295–7302. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rosell R, Pifarré A, Monzó M, Astudillo J,
López-Cabrerizo MP, Calvo R, Moreno I, Sanchez-Céspedes M, Font A
and Navas-Palacios JJ: Reduced survival in patients with stage-I
non-small-cell lung cancer associated with DNA-replication errors.
Int J Cancer. 74:330–334. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Crane EJ and Simon G: Adjuvant
chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Curr Treat Options
Oncol. 7:51–58. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP,
Langer C, Sandler A, Krook J, Zhu J and Johnson DH: Eastern
Cooperative Oncology Group: Comparison of four chemotherapy
regimens for advanced non small-cell lung cancer. N Eng J Med.
346:92–98. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Loven D, Hasnis E, Bertolini F and Shaked
Y: Low-dose metronomic chemotherapy: From past experience to new
paradigms in the treatment of cancer. Drug Discov Today.
18:193–201. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Seng JE and Peterson BA: Low dose
chemotherapy for myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk Res. 22:481–484.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bello L, Carrabba G, Giussani C, Lucini V,
Cerutti F, Scaglione F, Landré J, Pluderi M, Tomei G, Villani R, et
al: Low-dose chemotherapy combined with an antiangiogenic drug
reduces human glioma growth in vivo. Cancer Res. 61:7501–7506.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Di Micco R, Fumagalli M, Cicalese A,
Piccinin S, Gasparini P, Luise C, Schurra C, Garre' M, Nuciforo PG,
Bensimon A, et al: Oncogene-in-duced senescence is a DNA damage
response triggered by DNA hyperreplication. Nature. 444:638–642.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Banito A and Lowe SW: A new development in
senescence. Cell. 155:977–978. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Collado M, Blasco MA and Serrano M:
Cellular senescence in cancer and aging. Cell. 130:223–233. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hornsby PJ: Senescence as an anticancer
mechanism. J Clin Oncol. 25:1852–1857. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ryan BM, Calhoun KM, Pine SR, Bowman ED,
Robles AI, Ambs S and Harris CC: MDM2 SNP285 does not antagonize
the effect of SNP309 in lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 131:2710–2716.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tang YA, Lin RK, Tsai YT, Hsu HS, Yang YC,
Chen CY and Wang YC: MDM2 overexpression deregulates the
transcriptional control of RB/E2F leading to DNA methyltransferase
3A overexpression in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 18:4325–4333.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yan J and Tang D: Prostate cancer
stem-like cells proliferate slowly and resist etoposide-induced
cytotoxicity via enhancing DNA damage response. Exp Cell Res.
328:132–142. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Itahana K, Itahana Y and Dimri GP:
Colorimetric detection of senescence-associated β galactosidase.
Methods Mol Biol. 965:143–156. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hayflick L and Moorhead PS: The serial
cultivation of human diploid cell strains. Exp Cell Res.
25:585–621. 1961. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tchkonia T, Zhu Y, van Deursen J, Campisi
J and Kirkland JL: Cellular senescence and the senescent secretory
phenotype: Therapeutic opportunities. J Clin Invest. 123:966–972.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mao Z, Ke Z, Gorbunova V and Seluanov A:
Replicatively senescent cells are arrested in G1 and G2 phases.
Aging (Albany NY). 4:431–435. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huna A, Salmina K, Erenpreisa J,
Vazquez-Martin A, Krigerts J, Inashkina I, Gerashchenko BI,
Townsend PA, Cragg MS and Jackson TR: Role of stress-activated
OCT4A in the cell fate decisions of embryonal carcinoma cells
treated with etoposide. Cell Cycle. 14:2969–2984. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yap DB, Hsieh JK, Chan FS and Lu X: Mdm2:
A bridge over the two tumour suppressors, p53 and Rb. Oncogene.
18:7681–7689. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Seviour EG, Sehgal V, Lu Y, Luo Z, Moss T,
Zhang F, Hill SM, Liu W, Maiti SN, Cooper L, et al: Functional
proteomics identifies miRNAs to target a p27/Myc/phospho-Rb
signature in breast and ovarian cancer. Oncogene. 35:691–701. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Carrillo AM, Hicks M, Khabele D and
Eischen CM: Pharmacologically increasing Mdm2 inhibits DNA repair
and cooperates with genotoxic agents to Kill p53-inactivated
ovarian cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 13:1197–1205. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dimri GP, Lee X, Basile G, Acosta M, Scott
G, Roskelley C, Medrano EE, Linskens M, Rubelj I, Pereira-Smith O,
et al: A biomarker that identifies senescent human cells in culture
and in aging skin in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:9363–9367.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schmitt CA: In vivo Complexities of
Cellular Senescence in Tumor Development and Therapy. AACR
Education Book. 499–504. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Roninson IB: Tumor cellular senescence in
cancer treatment. Cancer Res. 63:2705–2715. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Erdmann J: Cancer's big sleep: Senescence
may be potential target for cancer therapies. J Natl Cancer Inst.
97:89–91. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cristofalo VJ and Pignolo RJ: Molecular
markers of senescence in fibroblast-like cultures. Exp Gerontol.
31:111–123. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Herbig U, Jobling WA, Chen BP, Chen DJ and
Sedivy JM: Telomere shortening triggers seneseence of human ceils
through a pathway involving ATM, p53, and p21(CIPI), but not
p16(INK4a). Mol Cell. 14:501–513. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Serrano M, Lin AW, McCurrach ME, Beach D
and Lowe SW: Oncogenic ras provokes premature cell senescence
associated with accumulation of p53 and p16INK4a. Cell. 88:593–602.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sharpless NE and DePinho RA: Cancer: Crime
and punishment. Nature. 436:636–637. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Collado M, Gil J, Efeyan A, Guerra C,
Schuhmacher AJ, Barradas M, Benguría A, Zaballos A, Flores JM,
Barbacid M, et al: Tumour biology: Senescence in premalignant
turnouts. Nature. 436:6422005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Elmore LW, Rehder CW, Di X, McChesney PA,
Jackson-Cook CK, Gewirtz DA and Holt SE: Adriamycin-induced
senescence in breast tumor cells involves functional p53 and
telomere dysfunction. J Biol Chem. 277:35509–35515. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fujiwara-Igarashi A, Goto-Koshino Y,
Mochizuki H, Sato M, Fujino Y, Ohno K and Tsujimoto H: Inhibition
of p16 tumor suppressor gene expression via promoter
hypermethylation in canine lymphoid tumor cells. Res Vet Sci.
97:60–63. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kamesaki S, Kamesaki H, Jorgensen TJ,
Tanizawa A, Pommier Y and Cossman J: Bcl-2 protein inhibits
etoposide-induced apoptosis through its effects on events
subsequent to topoisomerase II-induced DNA strand breaks and their
repair. Cancer Res. 53:4251–4256. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|