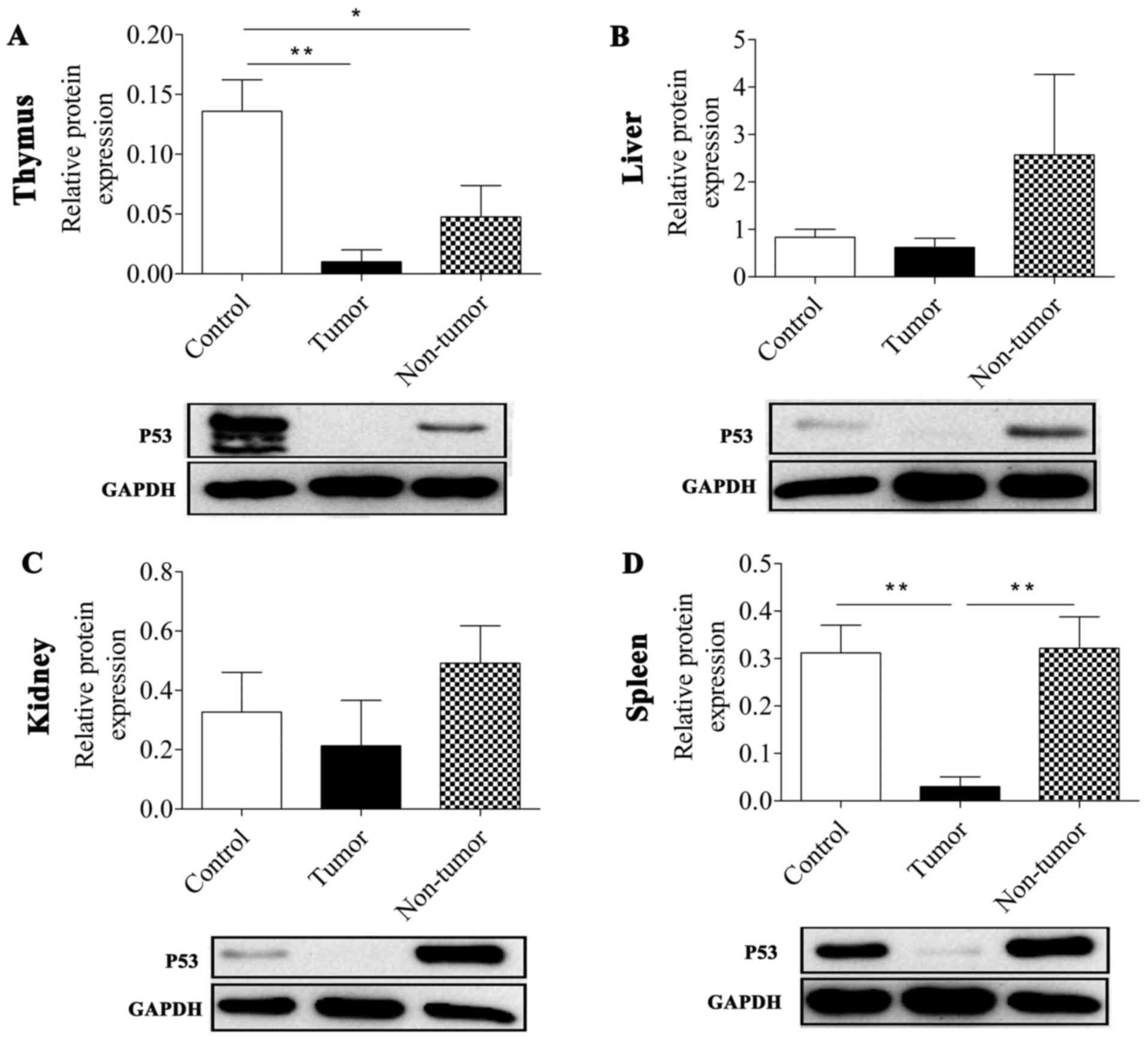
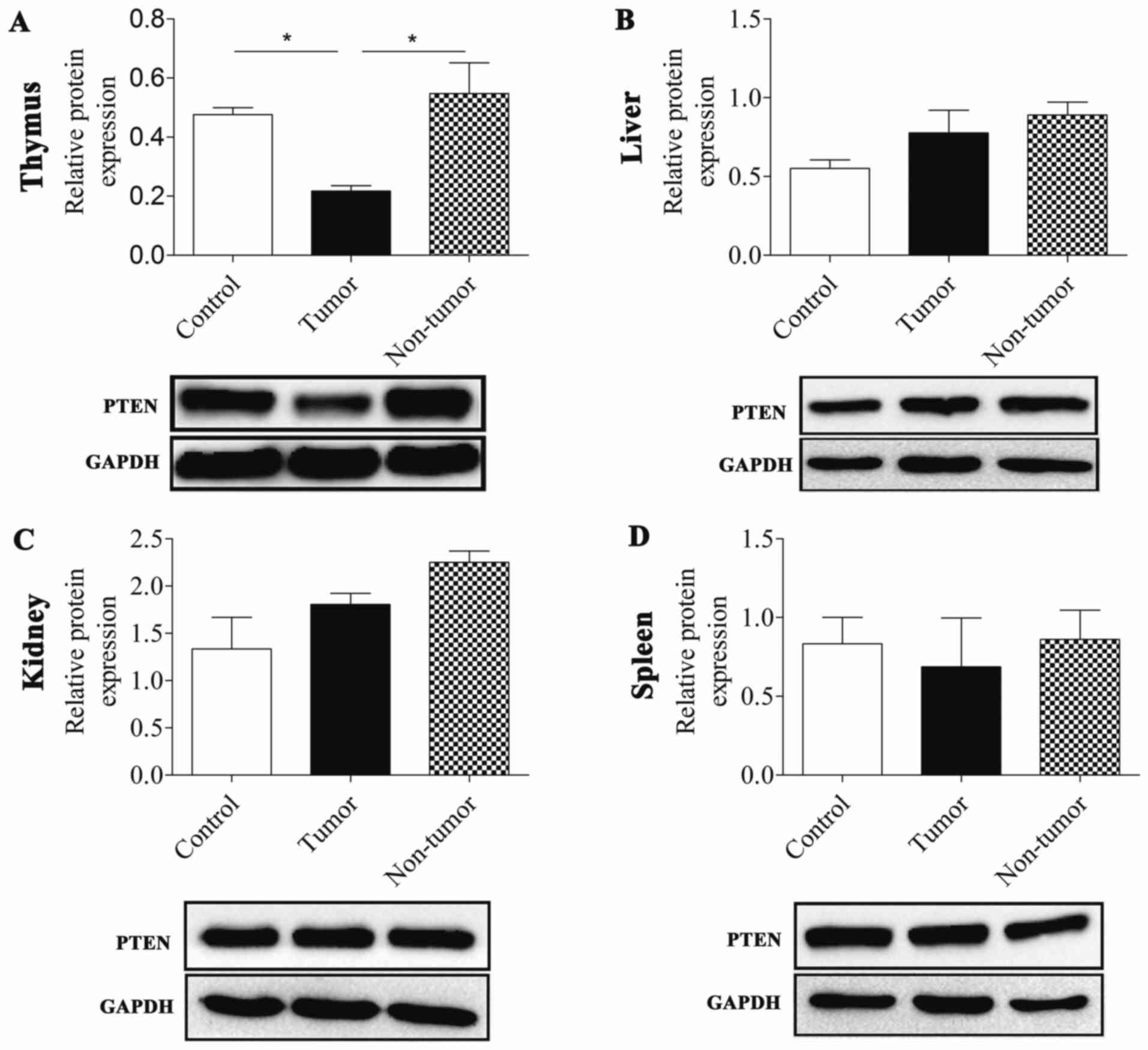
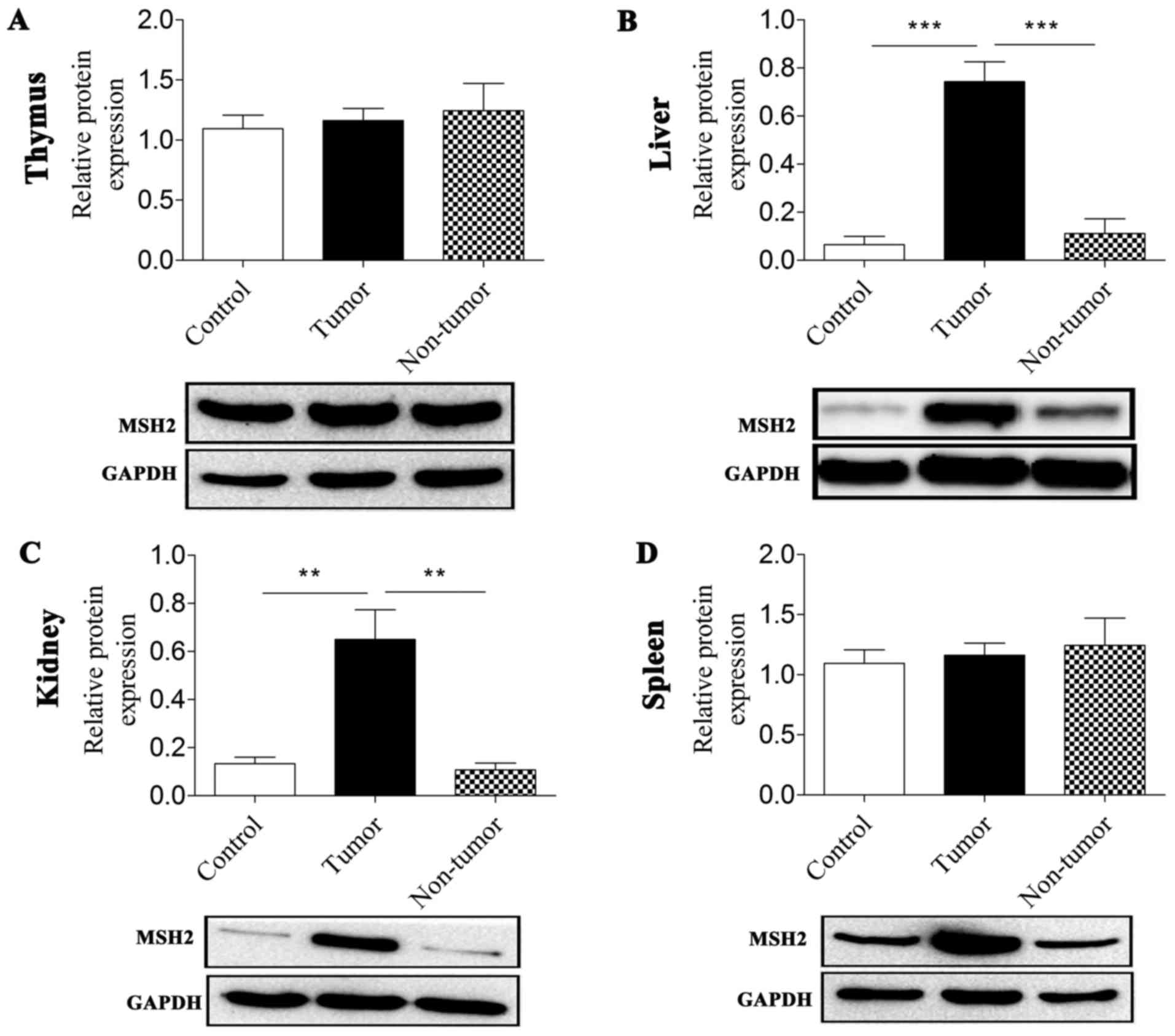
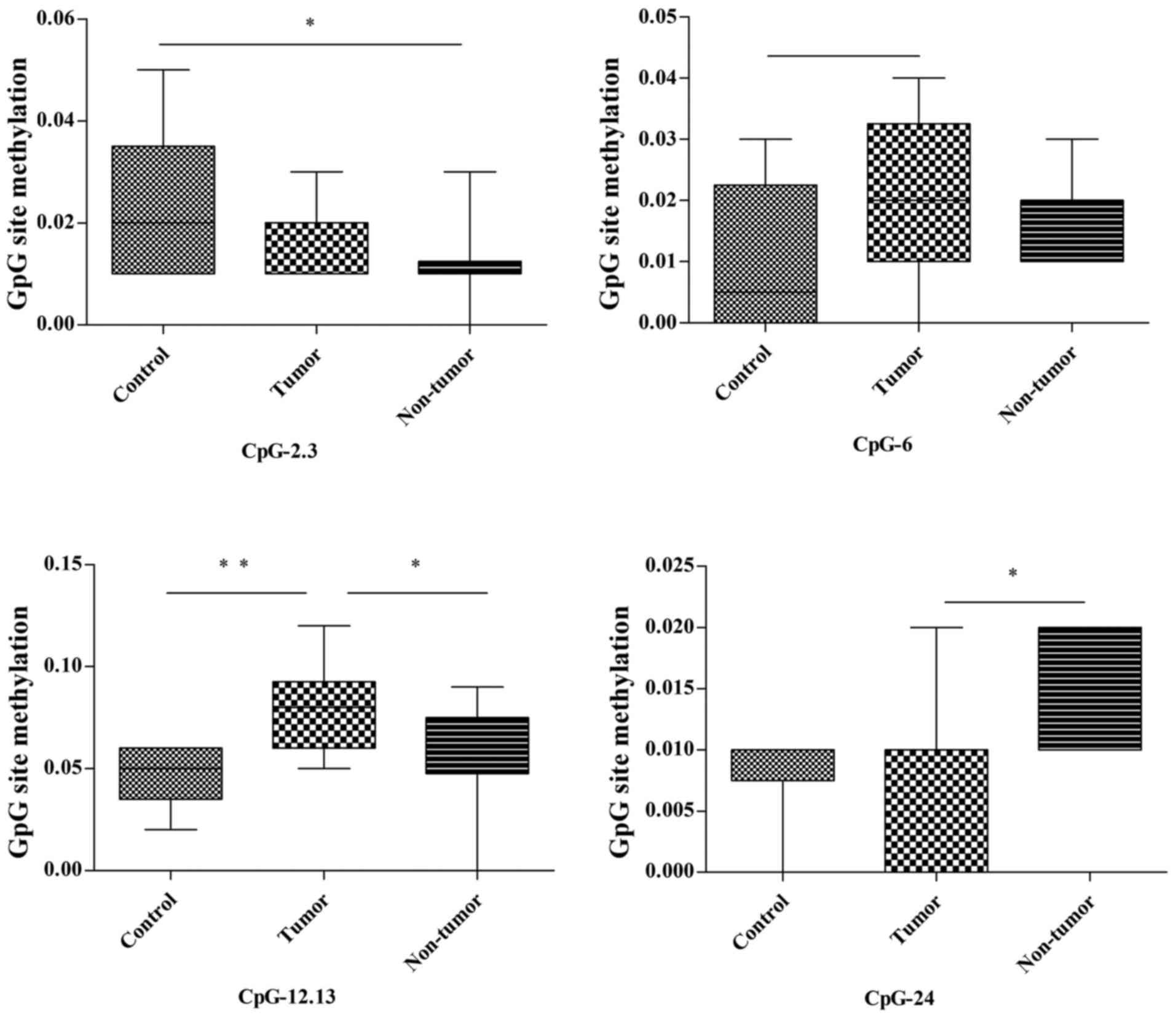
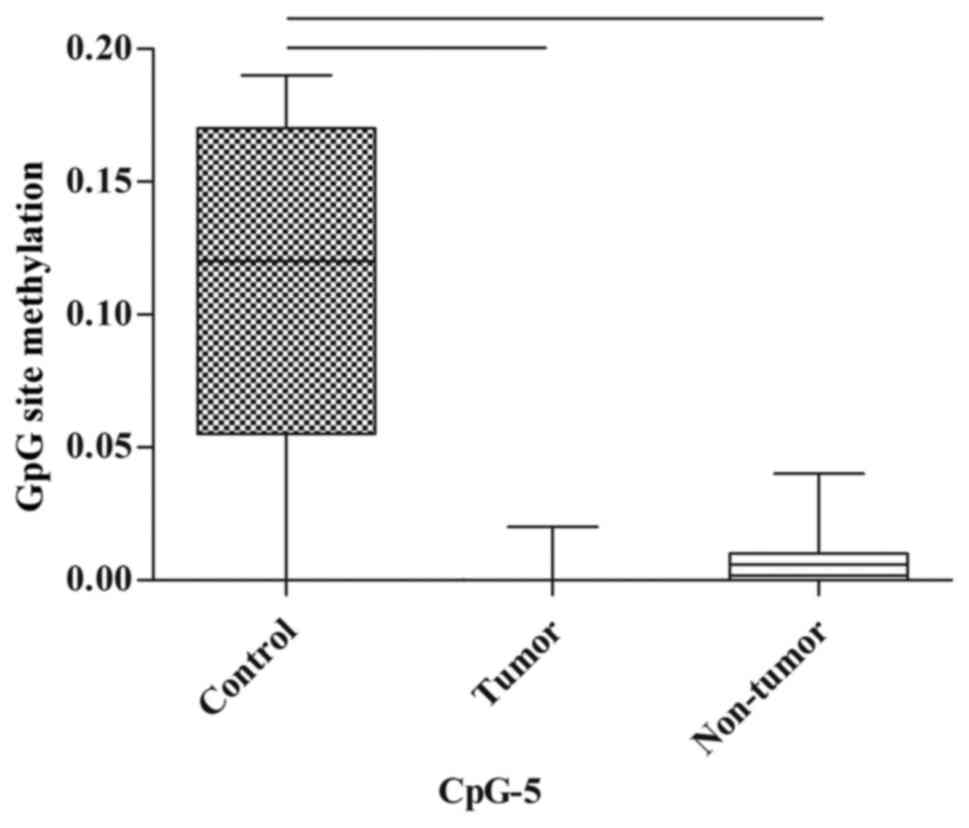
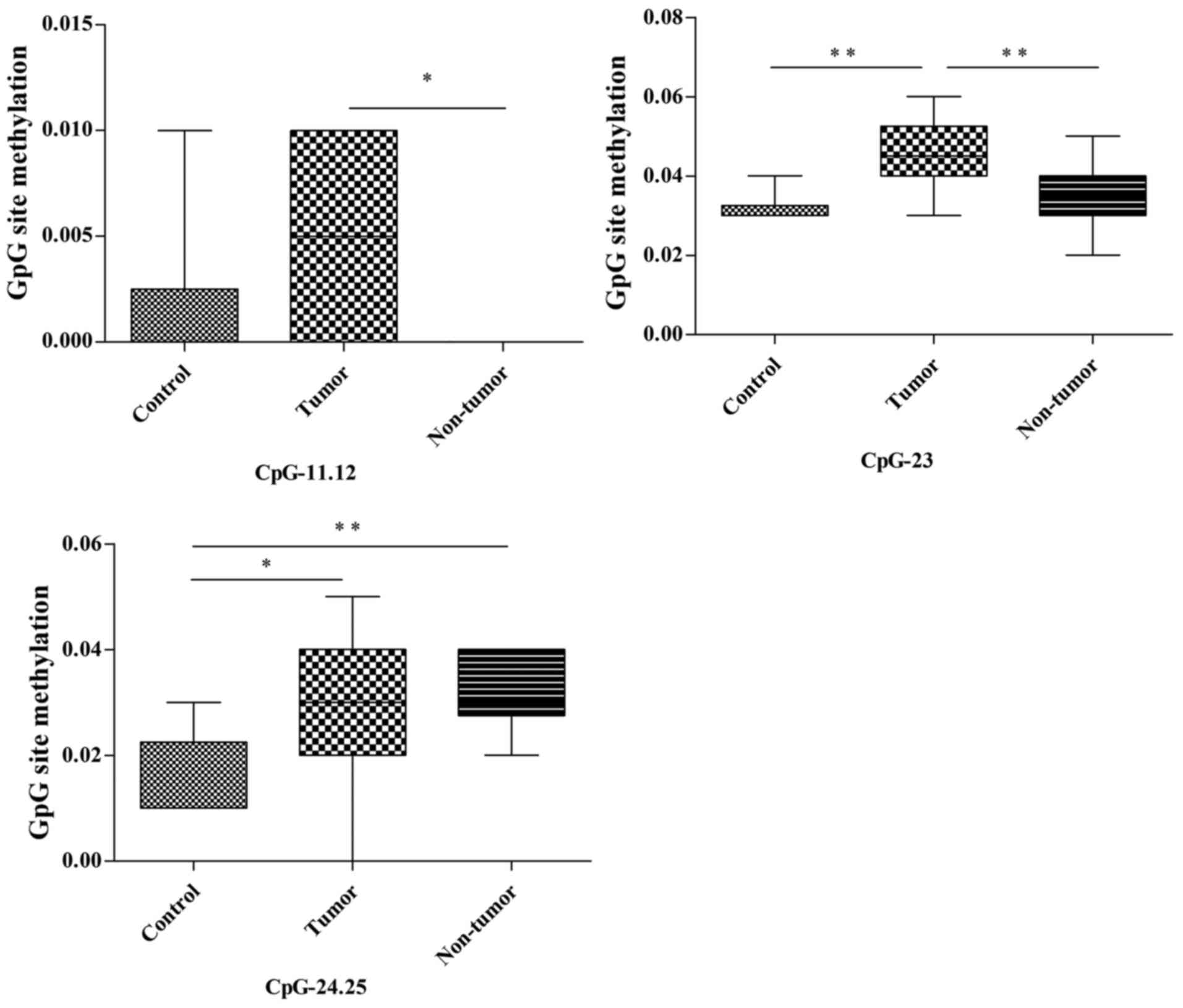
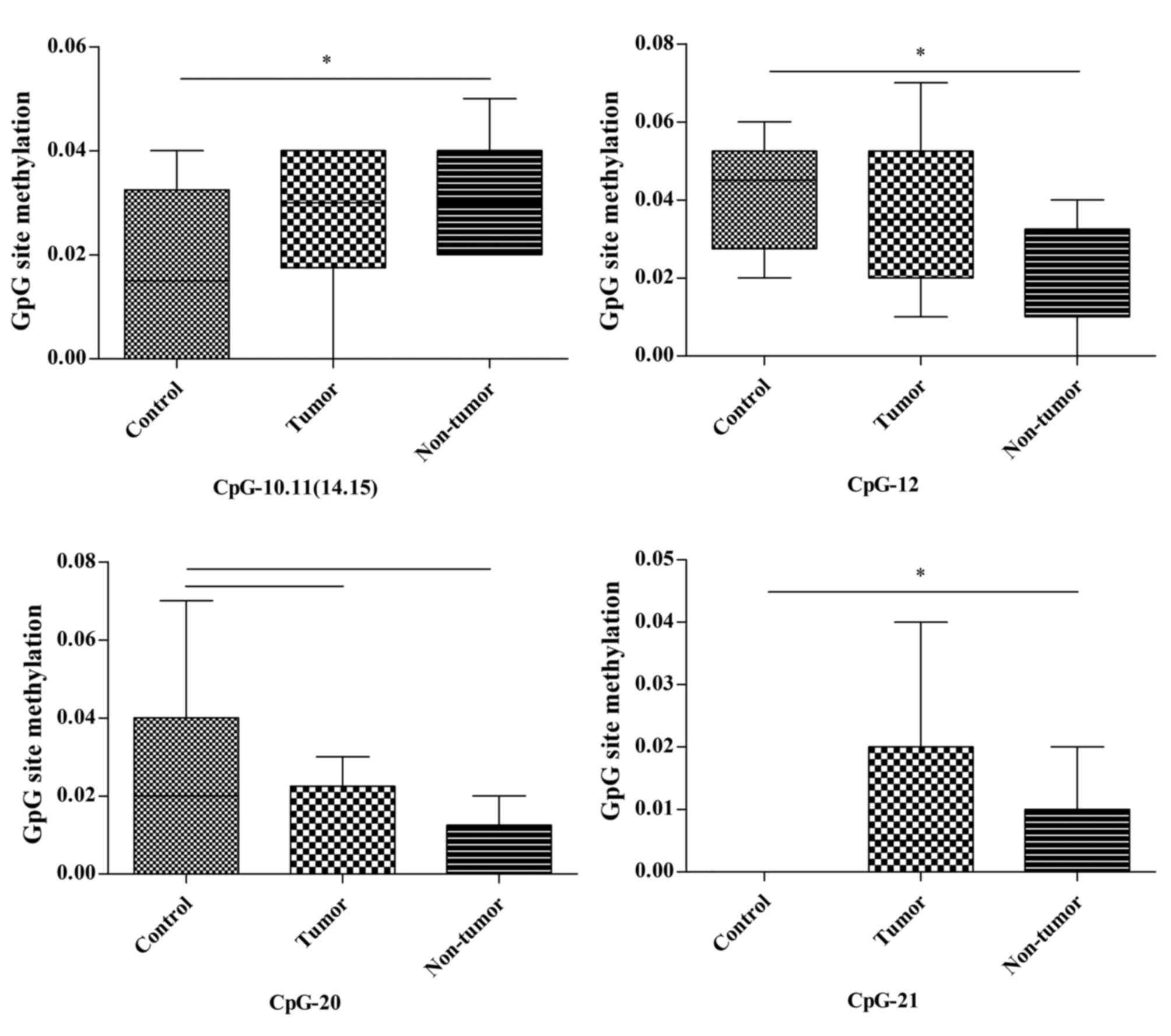
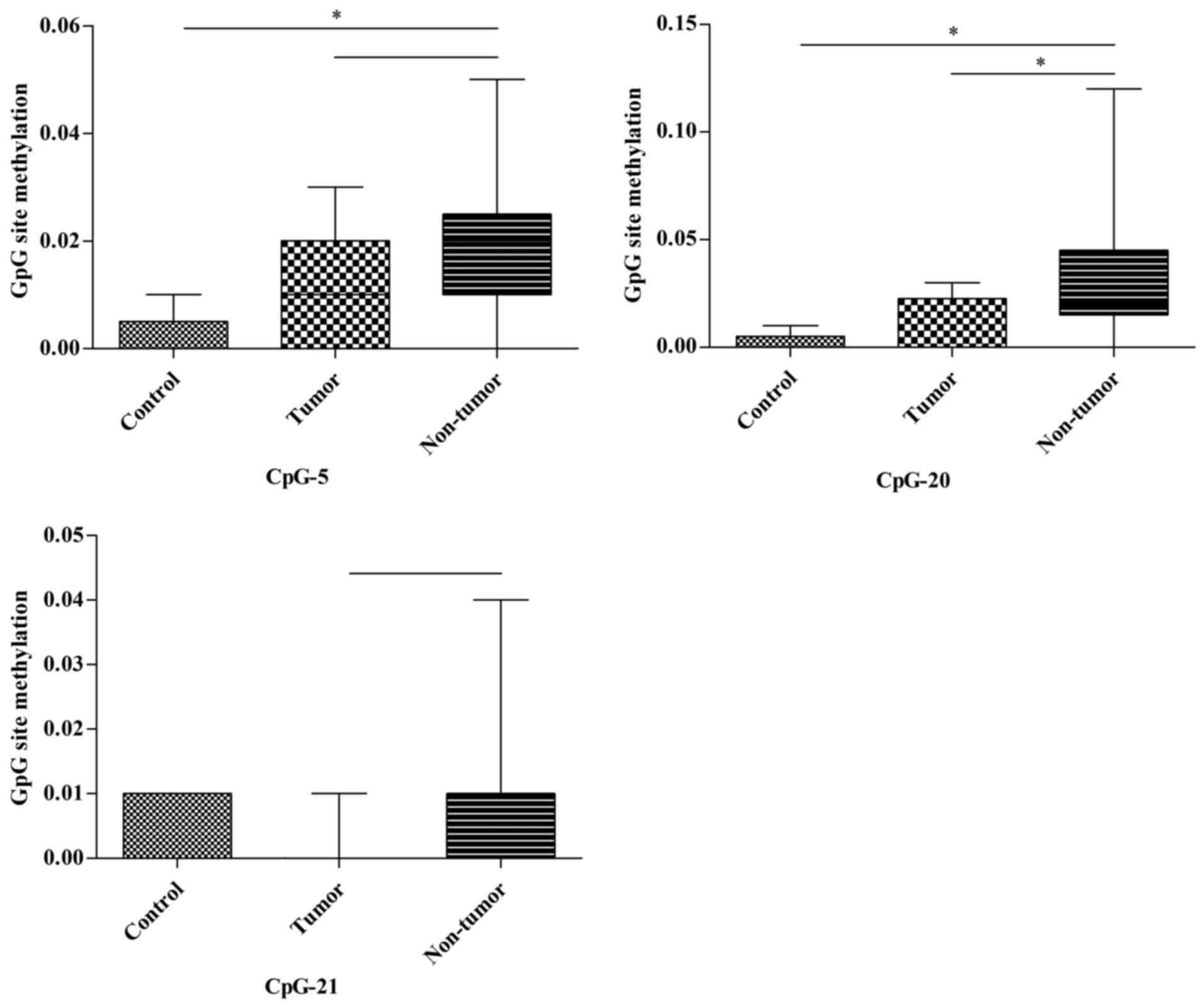
|
1
|
Han SW, Lee HJ, Bae JM, Cho NY, Lee KH,
Kim TY, Oh DY, Im SA, Bang YJ, Jeong SY, et al: Methylation and
microsatellite status and recurrence following adjuvant FOLFOX in
colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 132:2209–2216. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Salmena L, Carracedo A and Pandolfi PP:
Tenets of PTEN tumor suppression. Cell. 133:403–414. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li T, Kon N, Jiang L, Tan M, Ludwig T,
Zhao Y, Baer R and Gu W: Tumor suppression in the absence of
p53-mediated cell-cycle arrest, apoptosis, and senescence. Cell.
149:1269–1283. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vazquez F and Devreotes P: Regulation of
PTEN function as a PIP3 gatekeeper through membrane interaction.
Cell Cycle. 5:1523–1527. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vousden KH and Prives C: P53 and
prognosis: New insights and further complexity. Cell. 120:7–10.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Soria JC, Lee HY, Lee JI, Wang L, Issa JP,
Kemp BL, Liu DD, Kurie JM, Mao L and Khuri FR: Lack of PTEN
expression in non-small cell lung cancer could be related to
promoter methylation. Clin Cancer Res. 8:1178–1184. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jesionek-Kupnicka D, Szybka M, Malachowska
B, Fendler W, Potemski P, Piaskowski S, Jaskolski D, Papierz W,
Skowronski W, Och W, et al: TP53 promoter methylation in primary
glioblastoma: Relationship with TP53 mRNA and protein expression
and mutation status. Dna Cell BioL. 33:217–226. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zeng X and Kinsella TJ: A novel role for
DNA mismatch repair and the autophagic processing of chemotherapy
drugs in human tumor cells. Autophagy. 3:368–370. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Harfe BD and Jinks-Robertson S: Sequence
composition and context effects on the generation and repair of
frameshift intermediates in mononucleotide runs in Saccharomyces
cerevisiae. Genetics. 156:571–578. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Campbell MR, Wang Y, Andrew SE and Liu Y:
Msh2 deficiency leads to chromosomal abnormalities, centrosome
amplification, and telomere capping defect. Oncogene. 25:2531–2536.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Song W, Liu Y, Liu Y, Zhang C, Yuan B,
Zhang L and Sun S: Increased P16 DNA methylation in mouse thymic
lymphoma induced by irradiation. PLoS One. 9:e938502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Douet V, Heller MB and Le Saux O: DNA
methylation and Sp1 binding determine the tissue-specific
transcriptional activity of the mouse Abcc6 promoter. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 354:66–71. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Suzuki MM and Bird A: DNA methylation
landscapes: Provocative insights from epigenomics. Nat Rev Genet.
9:465–476. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nishida N and Kudo M: Alteration of
epigenetic profile in human hepatocellular carcinoma and its
clinical implications. Liver Cancer. 3:417–427. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Singla N and Dhawan DK: N-methyl
N-nitrosourea induced functional and structural alterations in mice
brain-role of curcumin. Neurotox Res. 22:115–126. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chang YC, Hsu JD, Lin WL, Lee YJ and Wang
CJ: High incidence of acute promyelocytic leukemia specifically
induced by N-nitroso-N-methylurea (NMU) in Sprague-Dawley rats.
Arch Toxicol. 86:315–327. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huo X, Zhang S, Li Z, Gao J, Wang C, Li C,
Guo M, Du X and Chen Z: Analysis of the relationship between
microsatellite instability and thymic lymphoma induced by
N-methyl-N-nitrosourea in C57BL/6J mice. Mutat Res. 771:21–28.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Coolen MW, Statham AL, Gardiner-Garden M
and Clark SJ: Genomic profiling of CpG methylation and allelic
specificity using quantitative high-throughput mass spectrometry:
Critical evaluation and improvements. Nucleic Acids Res.
35:e1192007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Otozai S, Ishikawa-Fujiwara T, Oda S,
Kamei Y, Ryo H, Sato A, Nomura T, Mitani H, Tsujimura T, Inohara H
and Todo T: p53-Dependent suppression of genome instability in germ
cells. Mutat Res. 760:24–32. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kamimura K, Ohi H, Kubota T, Okazuka K,
Yoshikai Y, Wakabayashi Y, Aoyagi Y, Mishima Y and Kominami R:
Haploinsufficiency of Bcl11b for suppression of lymphomagenesis and
thymocyte development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 355:538–542.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guo W, Schubbert S, Chen JY, Valamehr B,
Mosessian S, Shi H, Dang NH, Garcia C, Theodoro MF, Varella-Garcia
M and Wu H: Suppression of leukemia development caused by PTEN
loss. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:1409–1414. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Buckler JL, Walsh PT, Porrett PM, Choi Y
and Turka LA: Cutting edge: T cell requirement for CD28
costimulation is due to negative regulation of TCR signals by PTEN.
J Immunol. 177:4262–4266. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hagenbeek TJ and Spits H: T-cell lymphomas
in T-cell-specific Pten-deficient mice originate in the thymus.
Leukemia. 22:608–619. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Suzuki A, Yamaguchi MT, Ohteki T, Sasaki
T, Kaisho T, Kimura Y, Yoshida R, Wakeham A, Higuchi T, Fukumoto M,
et al: T cell-specific loss of Pten leads to defects in central and
peripheral tolerance. Immunity. 14:523–534. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xue L, Nolla H, Suzuki A, Mak TW and
Winoto A: Normal development is an integral part of tumorigenesis
in T cell-specific PTEN-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:2022–2027. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|