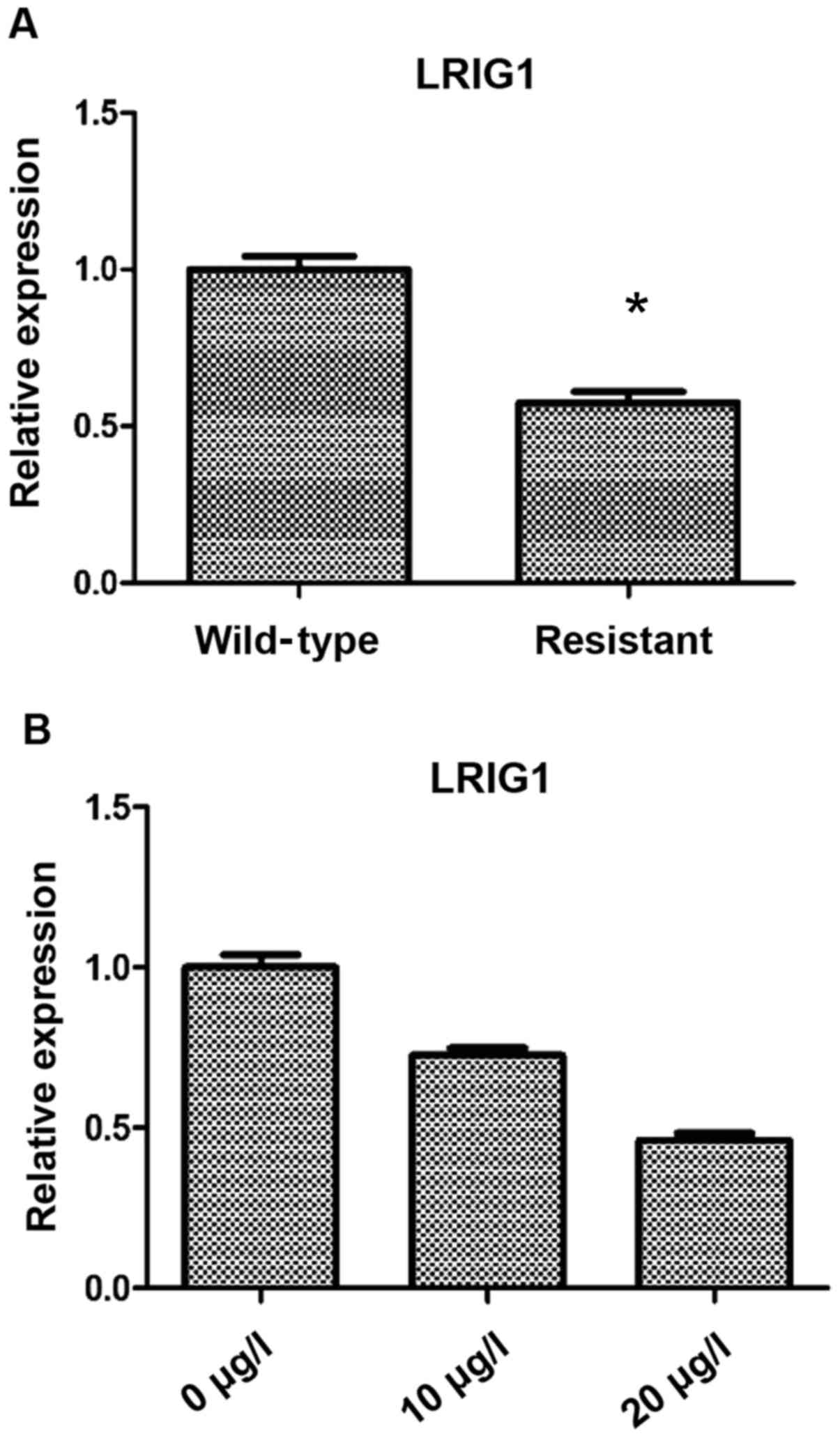
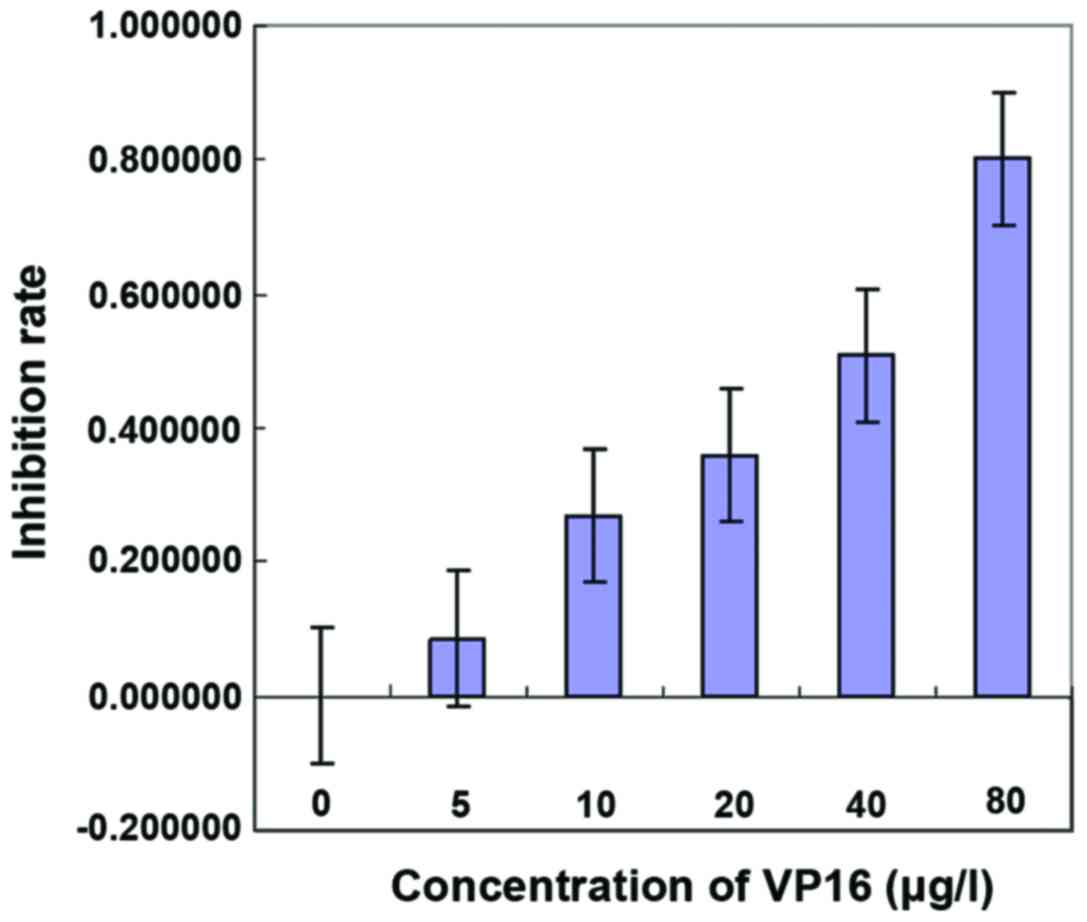
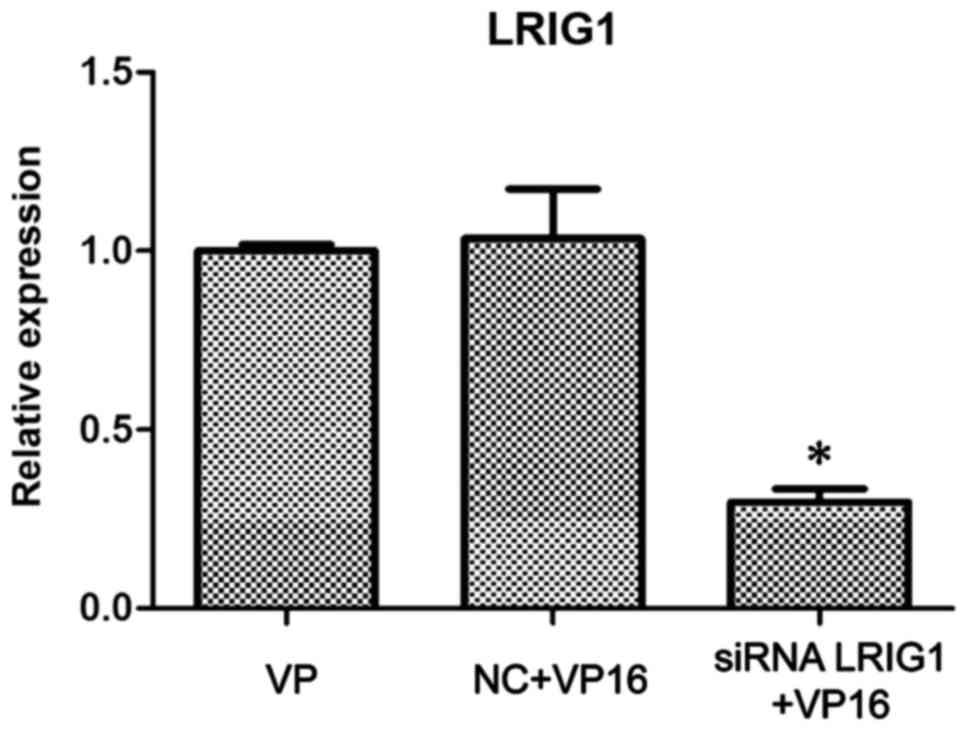
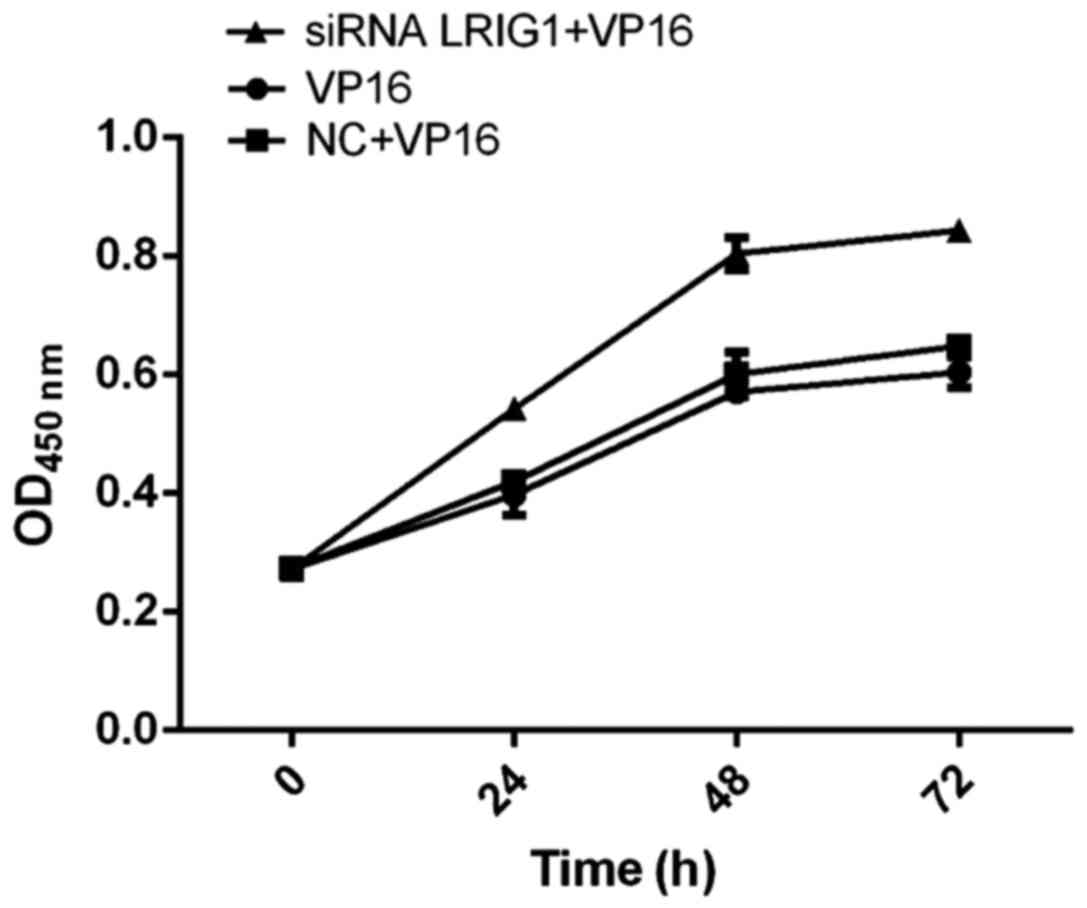
|
1
|
Krig SR, Frietze S, Simion C, Miller JK,
Fry WH, Rafidi H, Kotelawala L, Qi L, Griffith OL, Gray JW, et al:
Lrig1 is an estrogen-regulated growth suppressor and correlates
with longer relapse-free survival in ERα-positive breast cancer.
Mol Cancer Res. 9:1406–1417. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thompson PA, Ljuslinder I, Tsavachidis S,
Brewster A, Sahin A, Hedman H, Henriksson R, Bondy ML and Melin BS:
Loss of LRIG1 locus increases risk of early and late relapse of
stage I/II breast cancer. Cancer Res. 74:2928–2935. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lindström AK, Ekman K, Stendahl U, Tot T,
Henriksson R, Hedman H and Hellberg D: LRIG1 and squamous
epithelial uterine cervical cancer: Correlation to prognosis, other
tumor markers, sex steroid hormones and smoking. Int J Gynecol
Cancer. 18:312–317. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hedman H, Lindström AK, Tot T, Stendahl U,
Henriksson R and Hellberg D: LRIG2 in contrast to LRIG1 predicts
poor survival in early-stage squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine
cervix. Acta Oncol. 49:812–815. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Muller S, Lindquist D, Kanter L,
Flores-Staino C, Henriksson R, Hedman H and Andersson S: Expression
of LRIG1 and LRIG3 correlates with human papillomavirus status and
patient survival in cervical adenocarcinoma. Int J Oncol.
42:247–252. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sheu JJ, Lee CH, Ko JY, Tsao GS, Wu CC,
Fang CY, Tsai FJ, Hua CH, Chen CL and Chen JY: Chromosome
3p12.3-p14.2 and 3q26.2-q26.32 are genomic markers for prognosis of
advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 18:2709–2716. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sheu JJ, Lee CC, Hua CH, Li CI, Lai MT,
Lee SC, Cheng J, Chen CM, Chan C, Chao SC, et al: LRIG1 modulates
aggressiveness of head and neck cancers by regulating
EGFR-MAPK-SPHK1 signaling and extracellular matrix remodeling.
Oncogene. 33:1375–1384. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lindquist D, Näsman A, Tarján M,
Henriksson R, Tot T, Dalianis T and Hedman H: Expression of LRIG1
is associated with good prognosis and human papillomavirus status
in oropharyngeal cancer. Br J Cancer. 110:1793–1800. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guo D, Nilsson J, Haapasalo H, Raheem O,
Bergenheim T, Hedman H and Henriksson R: Perinuclear leucine-rich
repeats and immunoglobulin-like domain proteins (LRIG1-3) as
prognostic indicators in astrocytic tumors. Acta Neuropathol.
111:238–246. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Holmlund C, Haapasalo H, Yi W, Raheem O,
Brännström T, Bragge H, Henriksson R and Hedman H: Cytoplasmic
LRIG2 expression is associated with poor oligodendroglioma patient
survival. Neuropathology. 29:242–247. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Thomasson M, Wang B, Hammarsten P, Dahlman
A, Persson JL, Josefsson A, Stattin P, Granfors T, Egevad L,
Henriksson R, et al: LRIG1 and the liar paradox in prostate cancer:
A study of the expression and clinical significance of LRIG1 in
prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 128:2843–2852. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tanemura A, Nagasawa T, Inui S and Itami
S: LRIG-1 provides a novel prognostic predictor in squamous cell
carcinoma of the skin: Immunohistochemical analysis for 38 cases.
Dermatol Surg. 31:423–430. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hedman H, Nilsson J, Guo D and Henriksson
R: Is LRIG1 a tumour suppressor gene at chromosome 3p14.3? Acta
Oncol. 41:352–354. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gur G, Rubin C, Katz M, Amit I, Citri A,
Nilsson J, Amariglio N, Henriksson R, Rechavi G, Hedman H, et al:
LRIG1 restricts growth factor signaling by enhancing receptor
ubiquitylation and degradation. EMBO J. 23:3270–3281. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Laederich MB, Funes-Duran M, Yen L,
Ingalla E, Wu X, Carraway KL III and Sweeney C: The leucine-rich
repeat protein LRIG1 is a negative regulator of ErbB family
receptor tyrosine kinases. J Biol Chem. 279:47050–47056. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jensen KB and Watt FM: Single-cell
expression profiling of human epidermal stem and transit-amplifying
cells: Lrig1 is a regulator of stem cell quiescence. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 103:11958–11963. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang WM, Yan ZJ, Ye ZQ and Guo DS: LRIG1,
a candidate tumour-suppressor gene in human bladder cancer cell
line BIU87. BJU Int. 98:898–902. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shattuck DL, Miller JK, Laederich M, Funes
M, Petersen H, Carraway KL III and Sweeney C: LRIG1 is a novel
negative regulator of the Met receptor and opposes Met and Her2
synergy. Mol Cell Biol. 27:1934–1946. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Miller JK, Shattuck DL, Ingalla EQ, Yen L,
Borowsky AD, Young LJ, Cardiff RD, Carraway KL III and Sweeney C:
Suppression of the negative regulator LRIG1 contributes to ErbB2
overexpression in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 68:8286–8294. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nilsson J, Vallbo C, Guo D, Golovleva I,
Hallberg B, Henriksson R and Hedman H: Cloning, characterization,
and expression of human LIG1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
284:1155–1161. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Holmlund C, Nilsson J, Guo D, Starefeldt
A, Golovleva I, Henriksson R and Hedman H: Characterization and
tissue-specific expression of human LRIG2. Gene. 332:35–43. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Guo D, Holmlund C, Henriksson R and Hedman
H: The LRIG gene family has three vertebrate paralogs widely
expressed in human and mouse tissues and a homolog in Ascidiacea.
Genomics. 84:157–165. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nilsson J, Starefeldt A, Henriksson R and
Hedman H: LRIG1 protein in human cells and tissues. Cell Tissue
Res. 312:65–71. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ledda F, Bieraugel O, Fard SS, Vilar M and
Paratcha G: Lrig1 is an endogenous inhibitor of Ret receptor
tyrosine kinase activation, downstream signaling, and biological
responses to GDNF. J Neurosci. 28:39–49. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|