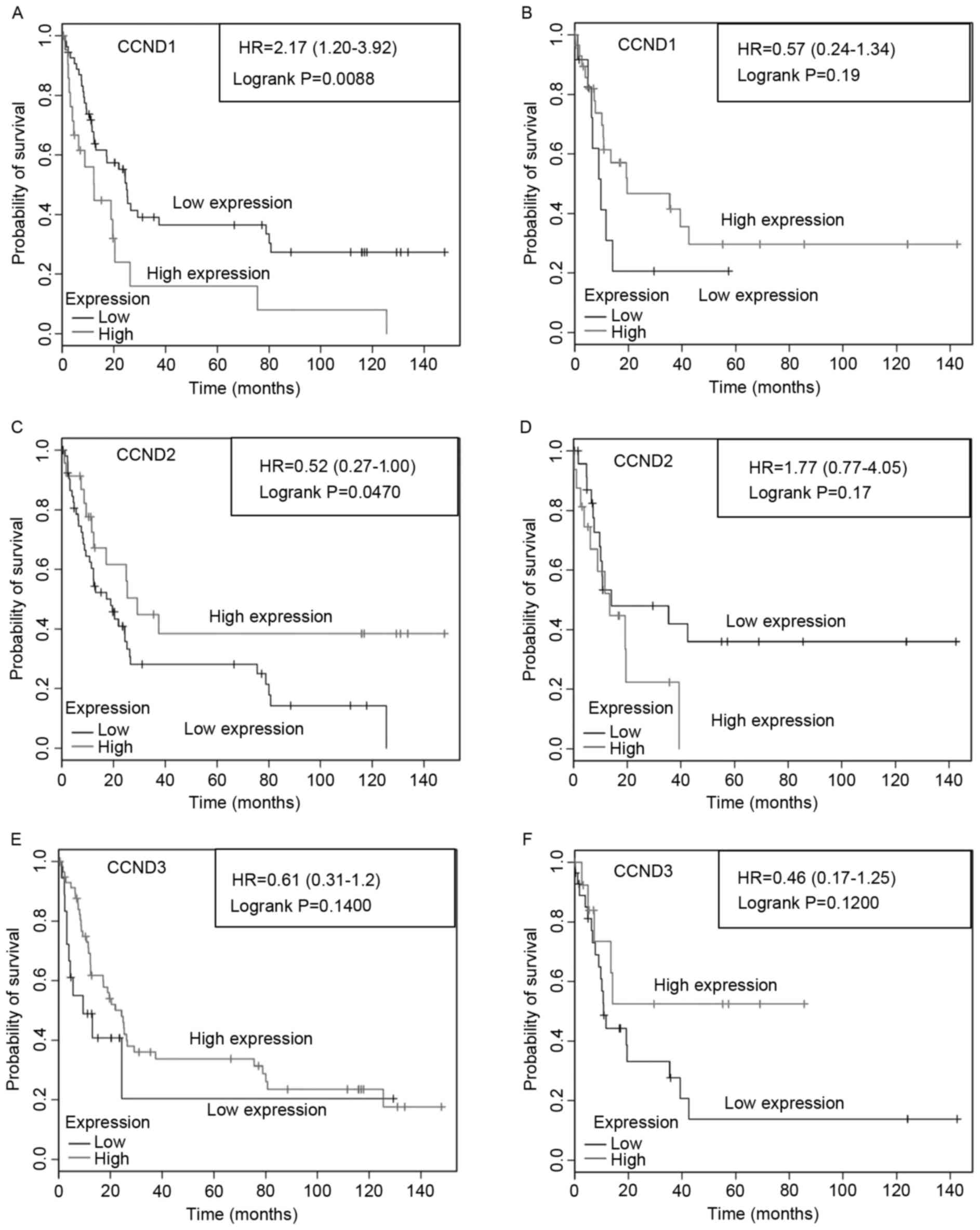
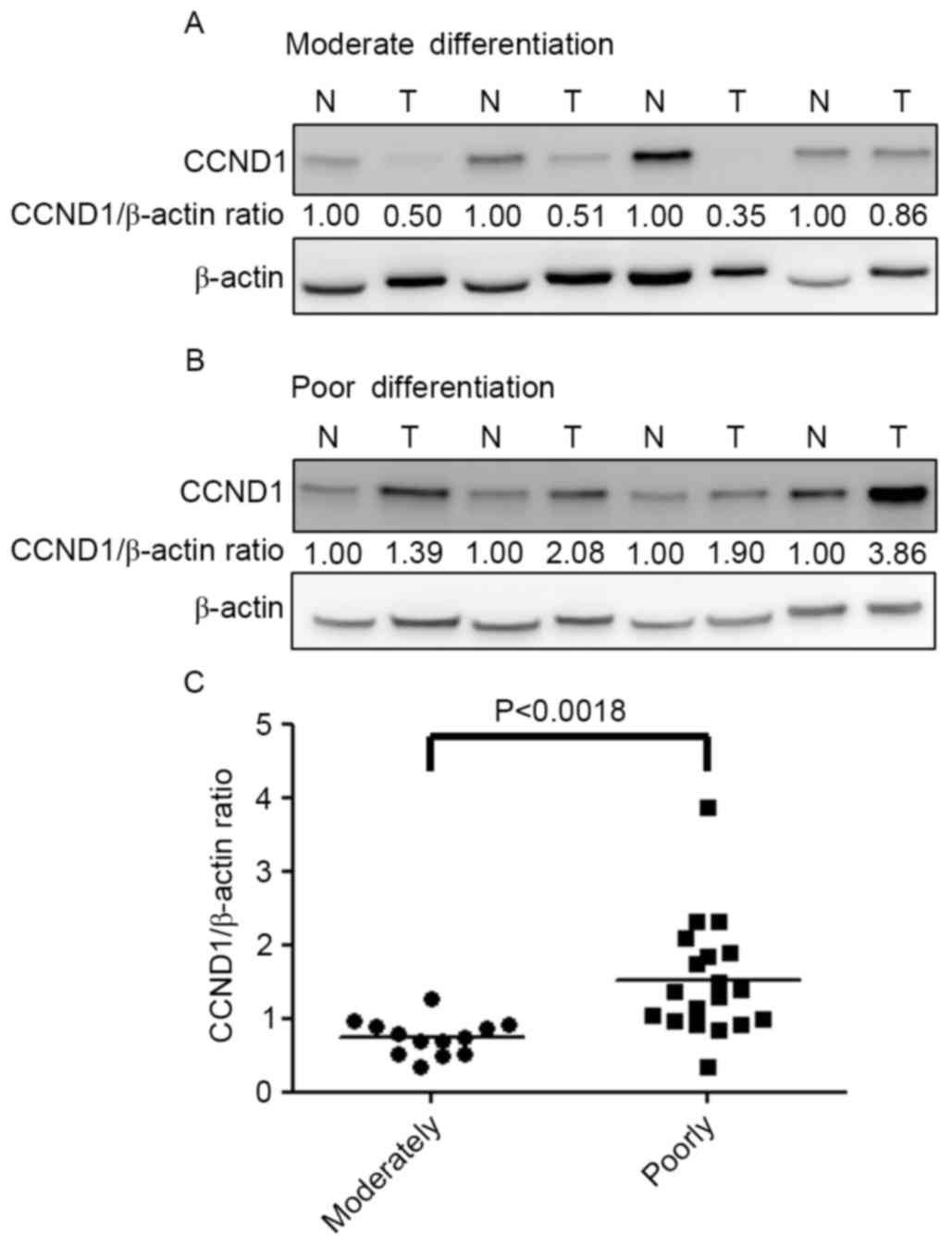
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lauren P: The two histological main types
of gastric carcinoma: Diffuse and so-called intestinal-type
carcinoma. An attempt at a histo-clinical classification. Acta
Pathol Microbiol Scand. 64:31–49. 1965. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Correa P: Human gastric carcinogenesis: A
multistep and multifactorial process-first American cancer society
award lecture on cancer epidemiology and prevention. Cancer Res.
52:6735–6740. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A,
Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A, Lordick F, Ohtsu A, Omuro Y, Satoh T,
et al: Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus
chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric
or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): A phase 3,
open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 376:687–697. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nagini S: Carcinoma of the stomach: A
review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, molecular genetics and
chemoprevention. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 4:156–169. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang W, Raufi A and Klempner SJ: Targeted
therapy for gastric cancer: Molecular pathways and ongoing
investigations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1846:232–237. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Matsuoka T and Yashiro M: The role of
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in gastric carcinoma. Cancers. 6:1441–1463.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Matsushime H, Ewen ME, Strom DK, Kato JY,
Hanks SK, Roussel MF and Sherr CJ: Identification and properties of
an atypical catalytic subunit (p34PSK-J3/cdk4) for mammalian D type
G1 cyclins. Cell. 71:323–334. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Büschges R, Weber RG, Actor B, Lichter P,
Collins VP and Reifenberger G: Amplification and expression of
cyclin D genes (CCND1, CCND2 and CCND3) in human malignant gliomas.
Brain Pathol. 9:435–433. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Musgrove EA, Caldon CE, Barraclough J,
Stone A and Sutherland RL: Cyclin D as a therapeutic target in
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:558–572. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jares P, Colomer D and Campo E: Genetic
and molecular pathogenesis of mantle cell lymphoma: Perspectives
for new targeted therapeutics. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:750–762. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Thomas GR, Nadiminti H and Regalado J:
Molecular predictors of clinical outcome in patients with head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Exp Pathol. 86:347–363. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
van Diest PJ, Michalides RJ, Jannink L,
van der Valk P, Peterse HL, de Jong JS, Meijer CJ and Baak JP:
Cyclin D1 expression in invasive breast cancer. Correlations and
prognostic value. Am J Pathol. 150:705–711. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jin ML, Inoue S, Umemura T, Moriya J,
Arakawa M, Nagashima K and Kato H: Cyclin D1, p16 and
retinoblastoma gene product expression as a predictor for prognosis
in non-small cell lung cancer at stages I and II. Lung Cancer.
34:207–218. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yamanouchi H, Furihata M, Fujita J,
Murakami H, Yoshinouchi T, Takahara J and Ohtsuki Y: Expression of
cyclin E and cyclin D1 in non-small cell lung cancers. Lung Cancer.
31:3–8. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ikeguchi M, Sakatani T, Ueta T and Kaibara
N: Cyclin D1 expression and retinoblastoma gene protein (pRB)
expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 127:531–536. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Izzo JG, Papadimitrakopoulou VA, Li XQ,
Ibarguen H, Lee JS, Ro JY, El-Naggar A, Hong WK and Hittelman WN:
Dysregulated cyclin D1 expression early in head and neck
tumorigenesis: In vivo evidence for an association with subsequent
gene amplification. Oncogene. 17:2313–2322. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bartkova J, Lukas J, Müller H, Strauss M,
Gusterson B and Bartek J: Abnormal patterns of D-type cyclin
expression and G1 regulation in human head and neck cancer. Cancer
Res. 55:949–956. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gansauge S, Gansauge F, Ramadani M, Stobbe
H, Rau B, Harada N and Beger HG: Overexpression of cyclin D1 in
human pancreatic carcinoma is associated with poor prognosis.
Cancer Res. 57:1634–1637. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Carthon BC, Neumann CA, Das M, Pawlyk B,
Li T, Geng Y and Sicinski P: Genetic replacement of cyclin D1
function in mouse development by cyclin D2. Mol Cell Biol.
25:1081–1088. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Choi D, Yoon S, Lee E, Hwang S, Yoon B and
Lee J: The expression of pseudogene cyclin D2 mRNA in the human
ovary may be a novel marker for decreased ovarian function
associated with the aging process. J Assist Reprod Genet.
18:110–113. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bartkova J, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Skakkebaek
NE and Bartek J: D-type cyclins in adult human testis and
testicular cancer: Relation to cell type, proliferation,
differentiation, and malignancy. J Pathol. 187:573–581. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Takano Y, Kato Y, Masuda M, Ohshima Y and
Okayasu I: Cyclin D2, but not cyclin D1, overexpression closely
correlates with gastric cancer progression and prognosis. J Pathol.
189:194–200. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu J, Leung WK, Ng EK, To KF, Ebert MP, Go
MY, Chan WY, Chan FK, Chung SC, Malfertheiner P, et al: Effect of
helicobacter pylori eradication on expression of cyclin D2
and p27 in gastric intestinal metaplasia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.
15:1505–1511. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bartkova J, Lukas J, Strauss M and Bartek
J: Cyclin D3: Requirement for G1/S transition and high abundance in
quiescent tissues suggest a dual role in proliferation and
differentiation. Oncogene. 17:1027–1037. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Flørenes VA, Faye RS, Maelandsmo GM,
Nesland JM and Holm R: Levels of cyclin D1 and D3 in malignant
melanoma: Deregulated cyclin D3 expression is associated with poor
clinical outcome in superficial melanoma. Clin Cancer Res.
6:3614–3620. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ito Y, Takeda T, Wakasa K, Tsujimoto M and
Matsuura N: Expression and possible role of cyclin D3 in human
pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Anticancer Res. 21:1043–1048.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wong SC, Chan JK, Lee KC and Hsiao WL:
Differential expression of p16/p21/p27 and cyclin D1/D3 and their
relationships to cell proliferation, apoptosis and tumour
progression in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. J Pathol.
194:35–42. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rhodes DR, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Mahavisno
V, Varambally R, Yu J, Briggs BB, Barrette TR, Anstet MJ,
Kincead-Beal C, Kulkarni P, et al: Oncomine 3.0: Genes, pathways,
and networks in a collection of 18,000 cancer gene expression
profiles. Neoplasia. 9:166–180. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shan YS, Hsu HP, Lai MD, Yen MC, Luo YP
and Chen YL: Increased expression of argininosuccinate synthetase
protein predicts poor prognosis in human gastric cancer. Oncol Rep.
33:49–57. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American joint
committee on cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shan YS, Fang JH, Lai MD, Yen MC, Lin PW,
Hsu HP, Lin CY and Chen YL: Establishment of an orthotopic
transplantable gastric cancer animal model for studying the
immunological effects of new cancer therapeutic modules. Mol
Carcinog. 50:739–750. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shan YS, Hsu HP, Lai MD, Yen MC, Chen WC,
Fang JH, Weng TY and Chen YL: Argininosuccinate synthetase 1
suppression and arginine restriction inhibit cell migration in
gastric cancer cell lines. Sci Rep. 5:97832015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K, Deshpande N,
Varambally R, Ghosh D, Barrette T, Pandey A and Chinnaiyan AM:
ONCOMINE: A cancer microarray database and integrated data-mining
platform. Neoplasia. 6:1–6. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
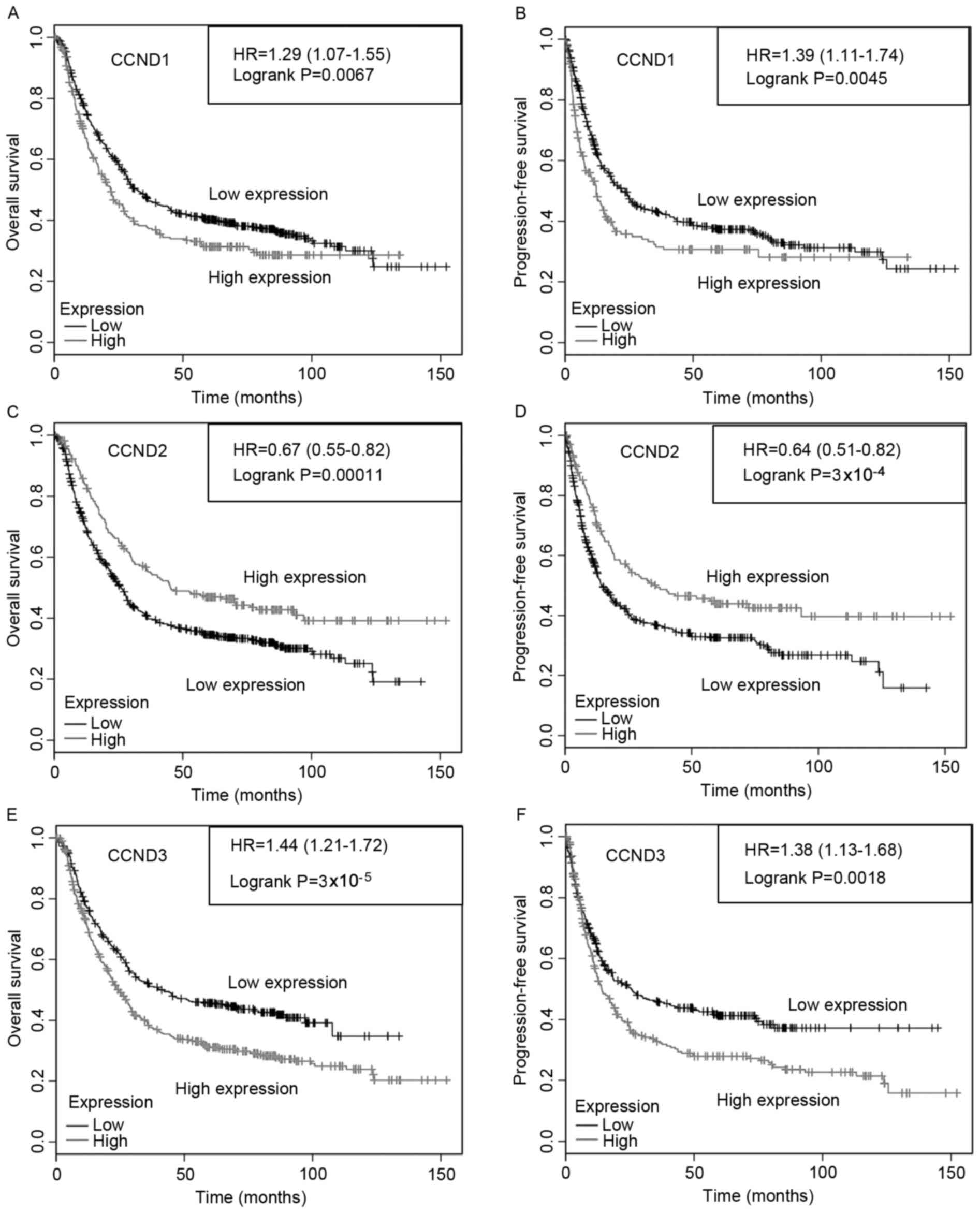
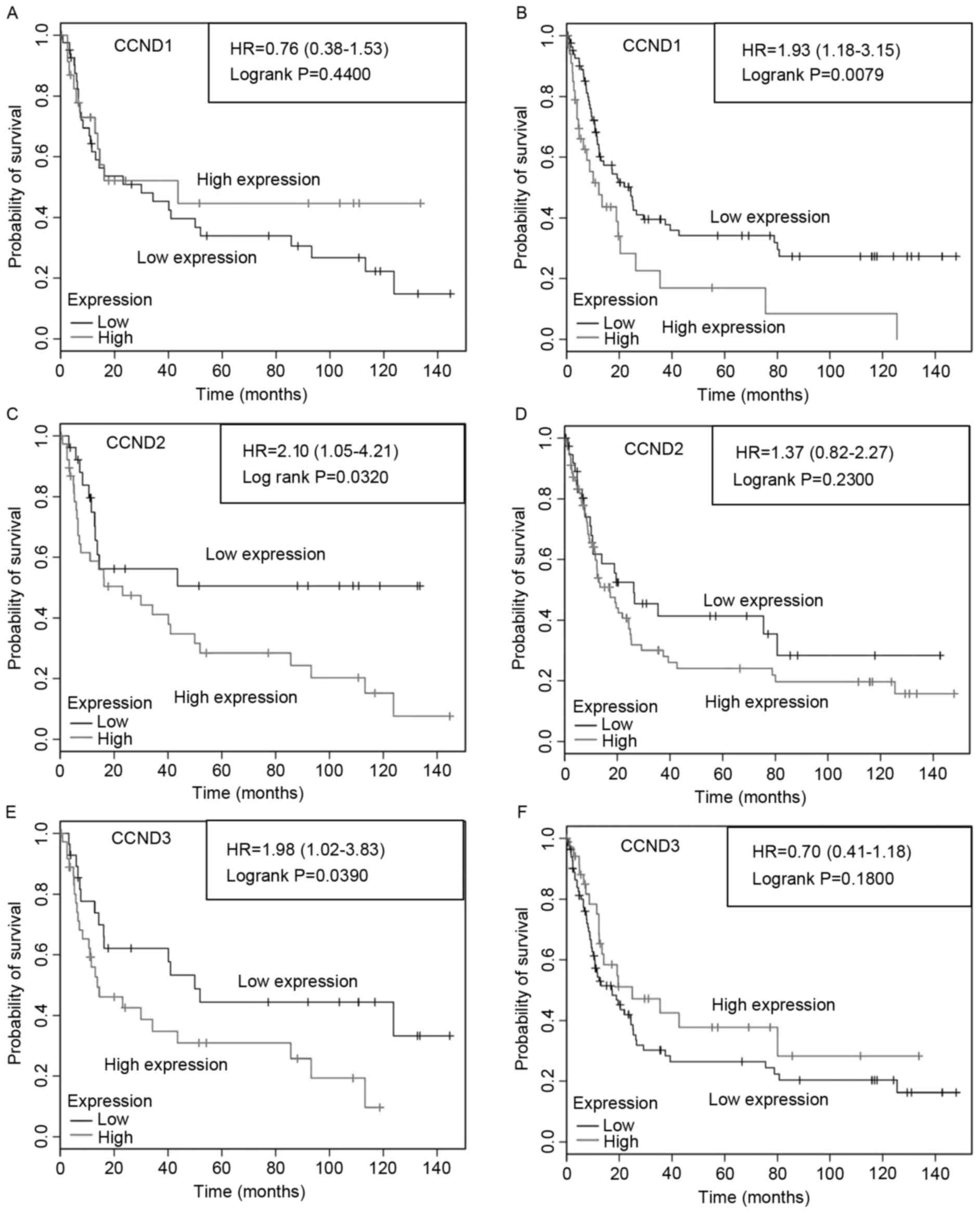
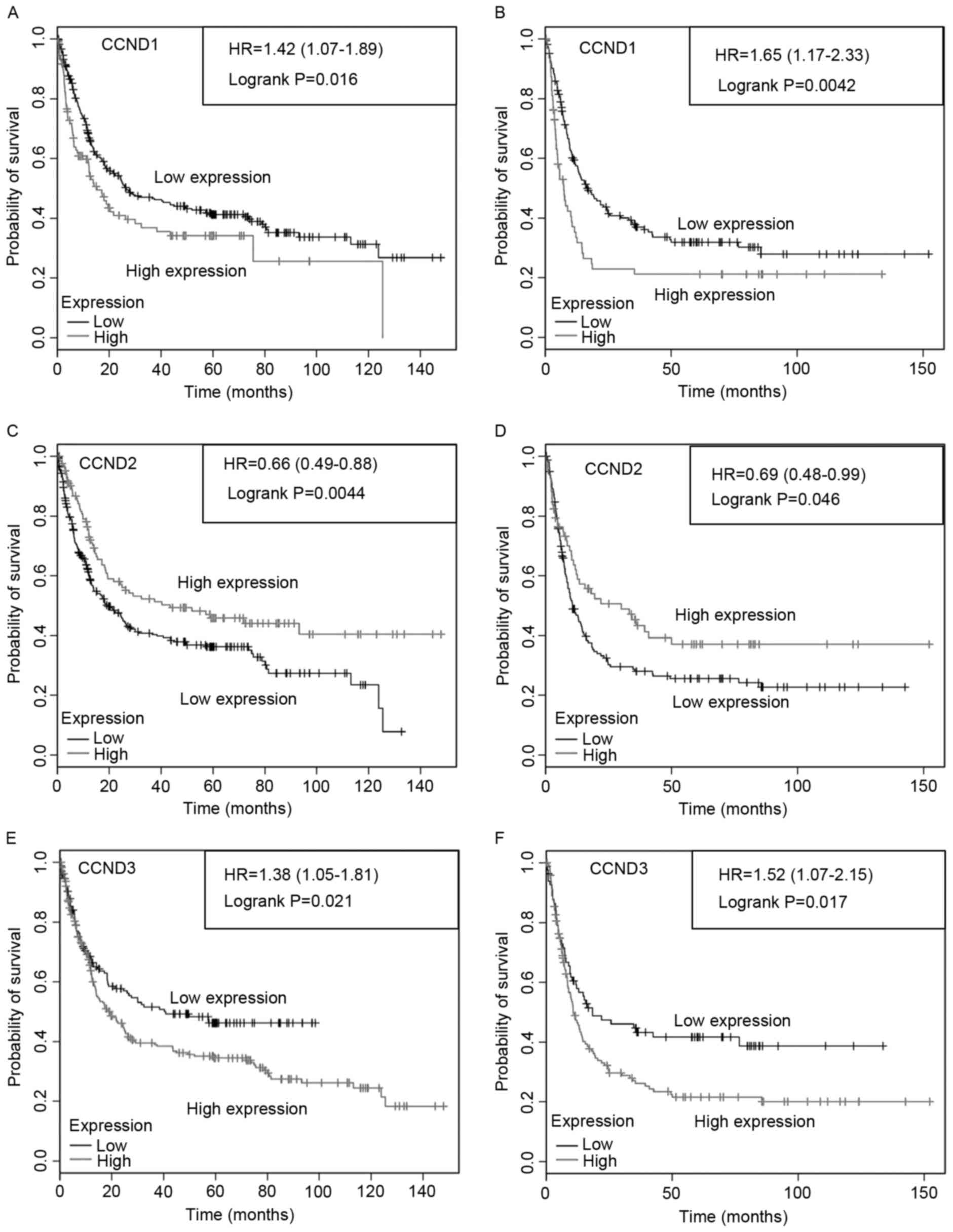
Győrffy B, Surowiak P, Budczies J and
Lànczky A: Online survival analysis software to assess the
prognostic value of biomarkers using transcriptomic data in
non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS one. 8:e822412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Szász AM, Lánczky A, Nagy Á, Förster S,
Hark K, Green JE, Boussioutas A, Busuttil R, Szabó A and Győrffy B:
Cross-validation of survival associated biomarkers in gastric
cancer using transcriptomic data of 1,065 patients. Oncotarget.
7:49322–49333. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Győrffy B, Benke Z, Lánczky A, Balázs B,
Szállási Z, Timár J and Schäfer R: RecurrenceOnline: An online
analysis tool to determine breast cancer recurrence and hormone
receptor status using microarray data. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
132:1025–1034. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Takano Y, Kato Y, van Diest PJ, Masuda M,
Mitomi H and Okayasu I: Cyclin D2 overexpression and lack of p27
correlate positively and cyclin E inversely with a poor prognosis
in gastric cancer cases. Am J Pathol. 156:585–594. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
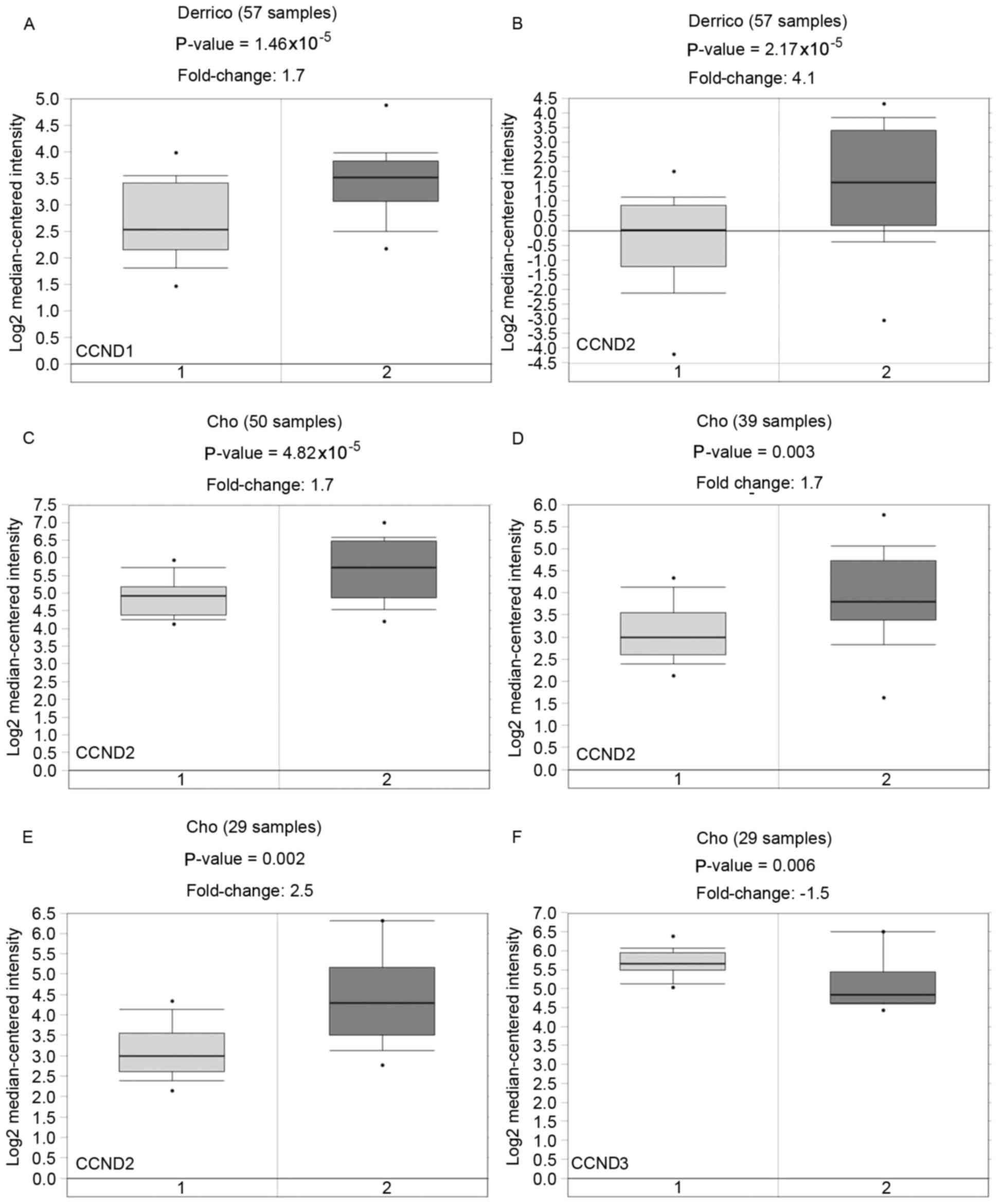
Cho JY, Lim JY, Cheong JH, Park YY, Yoon
SL, Kim SM, Kim SB, Kim H, Hong SW, Park YN, et al: Gene expression
signature-based prognostic risk score in gastric cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 17:1850–1857. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
D'Errico M, de Rinaldis E, Blasi MF, Viti
V, Falchetti M, Calcagnile A, Sera F, Saieva C, Ottini L, Palli D,
et al: Genome-wide expression profile of sporadic gastric cancers
with microsatellite instability. Eur J Cancer. 45:461–469. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Kaptain S, Tan LK and Chen B: Her-2/neu
and breast cancer. Diagn Mol Pathol. 10:139–152. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gravalos C and Jimeno A: HER2 in gastric
cancer: A new prognostic factor and a novel therapeutic target. Ann
Oncol. 19:1523–1529. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yu J, Leung WK, Ebert MP, Leong RW, Tse
PC, Chan MW, Bai AH, To KF, Malfertheiner P and Sung JJ: Absence of
cyclin D2 expression is associated with promoter hypermethylation
in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 88:1560–1565. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Evron E, Umbricht CB, Korz D, Raman V,
Loeb DM, Niranjan B, Buluwela L, Weitzman SA, Marks J and Sukumar
S: Loss of cyclin D2 expression in the majority of breast cancers
is associated with promoter hypermethylation. Cancer Res.
61:2782–2787. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Padar A, Sathyanarayana UG, Suzuki M,
Maruyama R, Hsieh JT, Frenkel EP, Minna JD and Gazdar AF:
Inactivation of cyclin D2 gene in prostate cancers by aberrant
promoter methylation. Clin Cancer Res. 9:4730–4734. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Mermelshtein A, Gerson A, Walfisch S,
Delgado B, Shechter-Maor G, Delgado J, Fich A and Gheber L:
Expression of D-type cyclins in colon cancer and in cell lines from
colon carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 93:338–345. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bartkova J, Thullberg M, Slezak P,
Jaramillo E, Rubio C, Thomassen LH and Bartek J: Aberrant
expression of G1-phase cell cycle regulators in flat and exophytic
adenomas of the human colon. Gastroenterology. 120:1680–1688. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cunningham D, Allum WH, Stenning SP,
Thompson JN, Van de Velde CJ, Nicolson M, Scarffe JH, Lofts FJ,
Falk SJ, Iveson TJ, et al: Perioperative chemotherapy versus
surgery alone for resectable gastroesophageal cancer. N Engl J Med.
355:11–20. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lim L, Michael M, Mann GB and Leong T:
Adjuvant therapy in gastric cancer. J Clin Oncol. 23:6220–6232.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Matsuura Y, Saito R, Kawagoe T, Toki N,
Sugihara K and Kashimura M: Cytologic analysis of primary stomach
adenocarcinoma metastatic to the uterine cervix. Acta Cytol.
41:291–294. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Pèrez-Montiel D, Serrano-Olvera A, Salazar
LC, Cetina-Pèrez L, Candelaria M, Coronel J, Montalvo LA and de
Leon DC: Adenocarcinoma metastatic to the uterine cervix: A case
series. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 38:541–549. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jares P, Colomer D and Campo E: Genetic
and molecular pathogenesis of mantle cell lymphoma: Perspectives
for new targeted therapeutics. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:750–762. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Nakagawa H, Zukerberg L, Togawa K, Meltzer
SJ, Nishihara T and Rustgi AK: Human cyclin D1 oncogene and
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer. 76:541–549. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chen B, Zhang XY, Zhang YJ, Zhou P, Gu Y
and Fan DM: Antisense to cyclin D1 reverses the transformed
phenotype of human gastric cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol.
5:18–21. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhou P, Jiang W, Zhang YJ, Kahn SM,
Schieren I, Santella RM and Weinstein IB: Antisense to cyclin D1
inhibits growth and reverses the transformed phenotype of human
esophageal cancer cells. Oncogene. 11:571–580. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Seo JH, Jeong ES and Choi YK: Therapeutic
effects of lentivirus-mediated shRNA targeting of cyclin D1 in
human gastric cancer. BMC cancer. 14:1752014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Jiang W, Kahn SM, Zhou P, Zhang YJ, Cacace
AM, Infante AS, Doi S, Santella RM and Weinstein IB: Overexpression
of cyclin D1 in rat fibroblasts causes abnormalities in growth
control, cell cycle progression and gene expression. Oncogene.
8:3447–3457. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Baldin V, Lukas J, Marcote MJ, Pagano M
and Draetta G: Cyclin D1 is a nuclear protein required for cell
cycle progression in G1. Genes Dev. 7:812–821. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ma L, Wang X, Lan F, Yu Y, Ouyang X, Liu
W, Xie F and Huang Q: Prognostic value of differential CCND1
expression in patients with resected gastric adenocarcinoma. Med
Oncol. 32:3382015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Stahl P, Seeschaaf C, Lebok P, Kutup A,
Bockhorn M, Izbicki JR, Bokemeyer C, Simon R, Sauter G and Marx AH:
Heterogeneity of amplification of HER2, EGFR, CCND1 and MYC in
gastric cancer. BMC Gastroenterol. 15:72015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Liu SC, Bassi DE, Zhang SY, Holoran D,
Conti CJ and Klein-Szanto AJ: Overexpression of cyclin D2 is
associated with increased in vivo invasiveness of human squamous
carcinoma cells. Mol Carcinog. 34:131–139. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wang W, Zhao LJ, Tan YX, Ren H and Qi ZT:
MiR-138 induces cell cycle arrest by targeting cyclin D3 in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 33:1113–1120. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kalish LH, Kwong RA, Cole IE, Gallagher
RM, Sutherland RL and Musgrove EA: Deregulated cyclin D1 expression
is associated with decreased efficacy of the selective epidermal
growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib in head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Clin Cancer Res.
10:7764–7774. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Stendahl M, Kronblad A, Rydén L, Emdin S,
Bengtsson NO and Landberg G: Cyclin D1 overexpression is a negative
predictive factor for tamoxifen response in postmenopausal breast
cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 90:1942–1948. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lundgren K, Brown M, Pineda S, Cuzick J,
Salter J, Zabaglo L, Howell A, Dowsett M and Landberg G: TransATAC
investigators: Effects of cyclin D1 gene amplification and protein
expression on time to recurrence in postmenopausal breast cancer
patients treated with anastrozole or tamoxifen: A TransATAC study.
Breast Cancer Res. 14:R572012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Boku N: HER2-positive gastric cancer.
Gastric Cancer. 17:1–12. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Deng NT, Goh LK, Wang HN, Das K, Tao J,
Tan IB, Zhang SL, Lee MH, Wu JN, Lim KH, et al: A comprehensive
survey of genomic alterations in gastric cancer reveals systematic
patterns of molecular exclusivity and co-occurrence among distinct
therapeutic targets. Gut. 61:673–684. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|