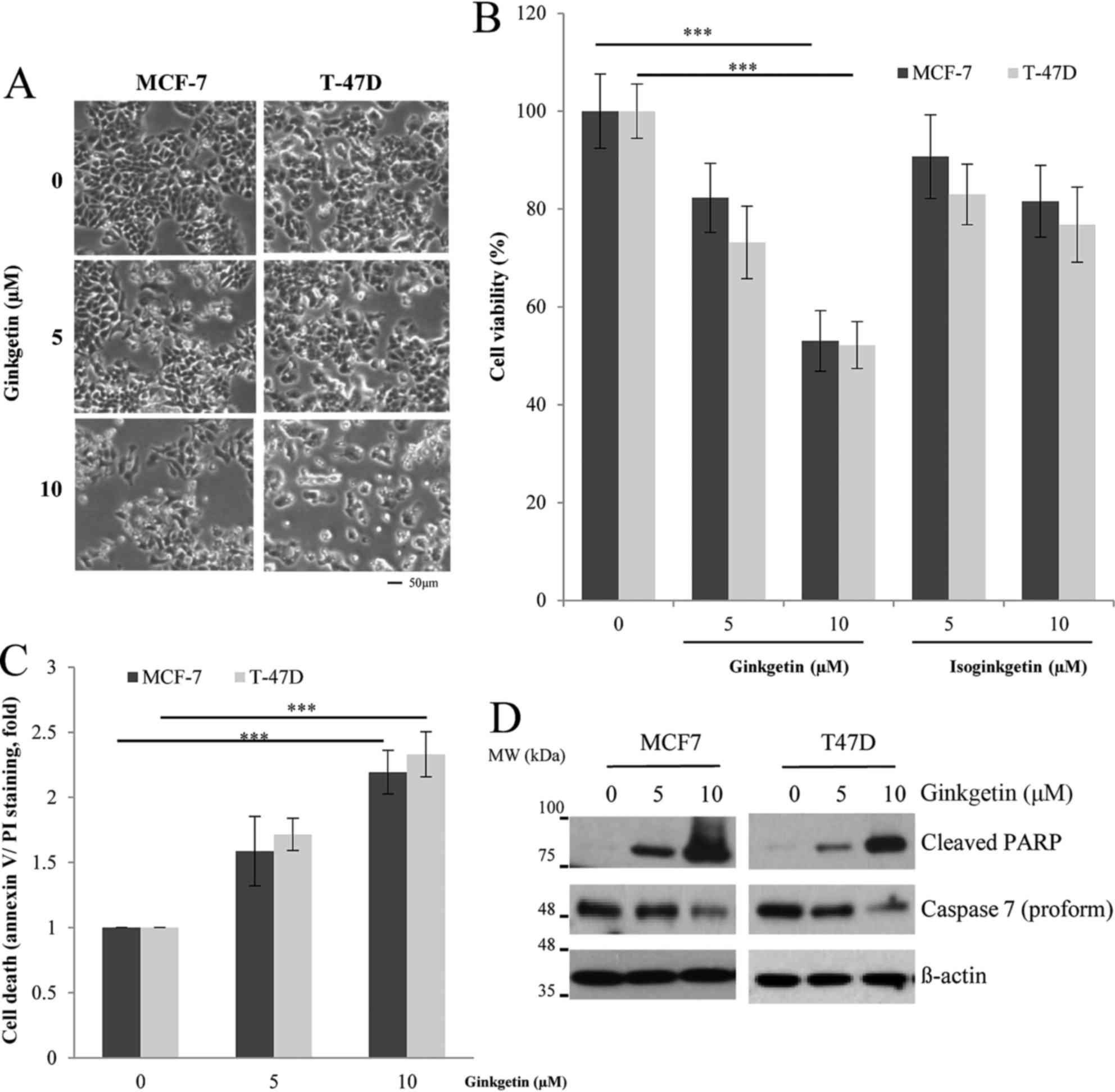
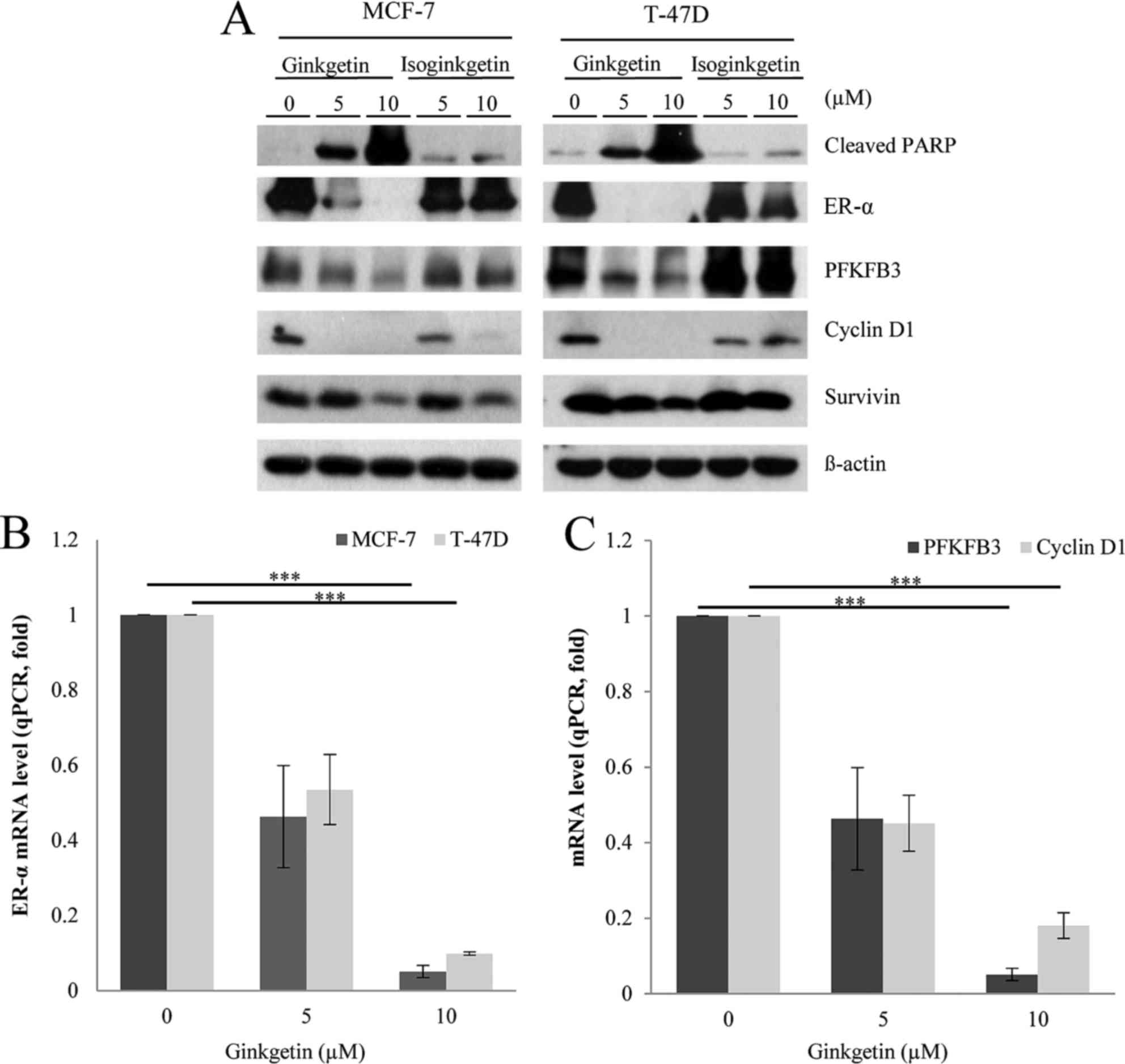
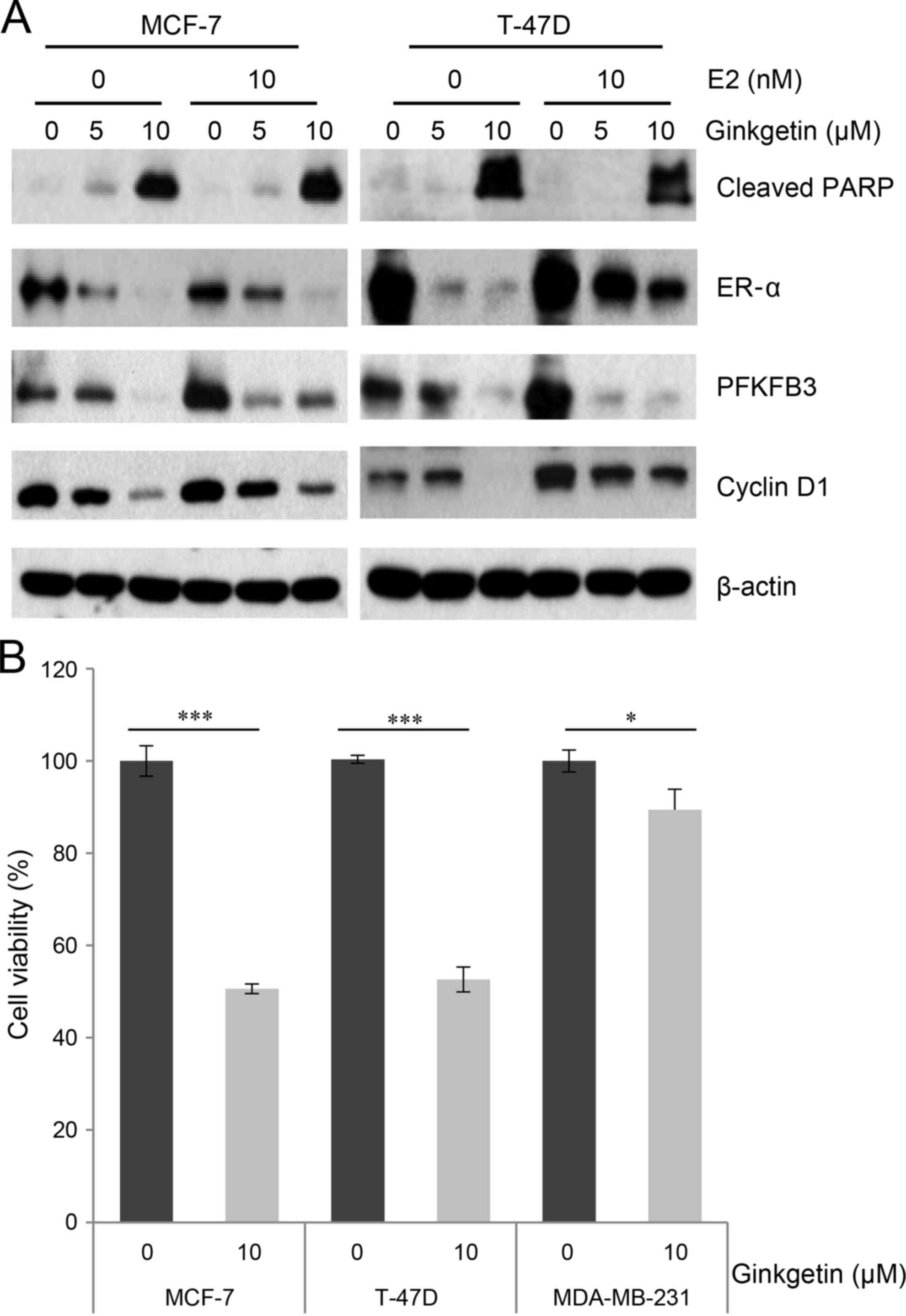
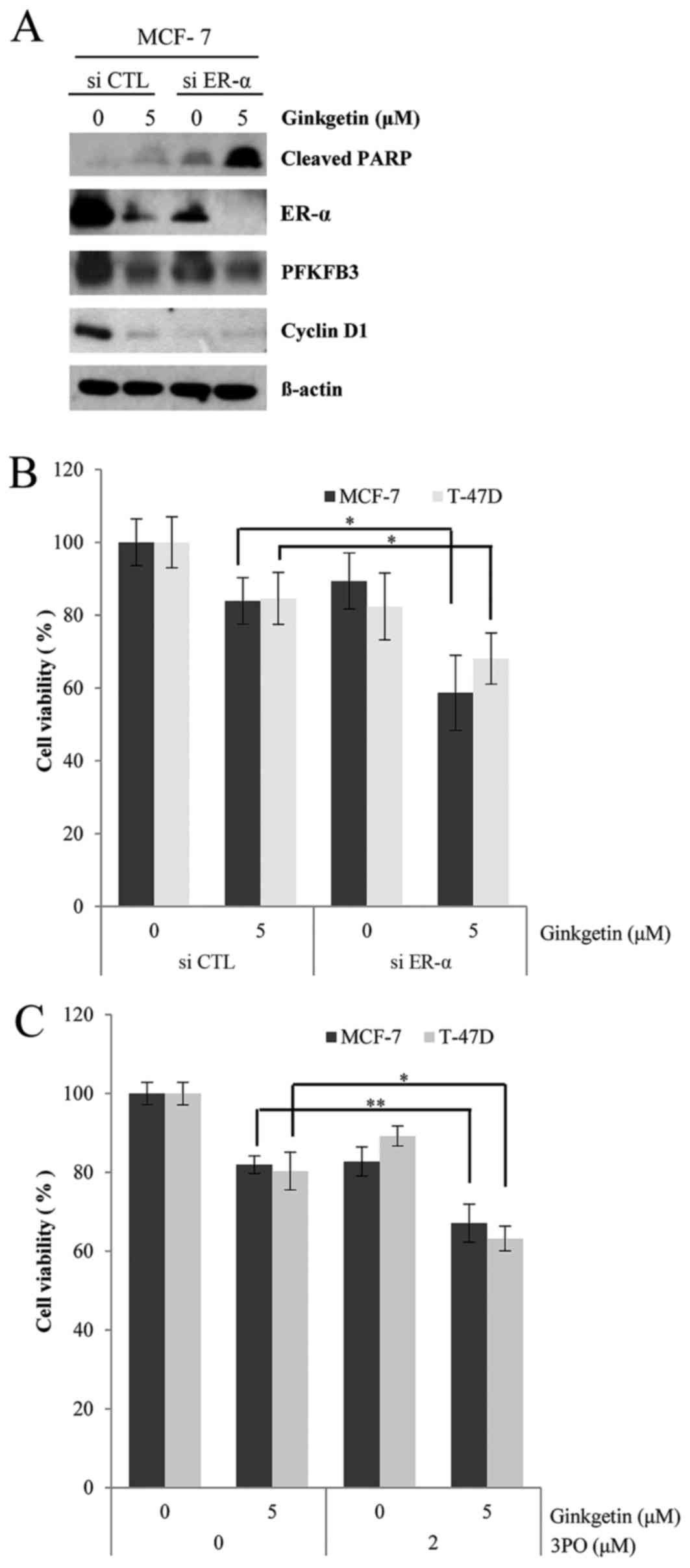
|
1
|
Weatherman RV, Fletterick RJ and Scanlan
TS: Nuclear-receptor ligands and ligand-binding domains. Annu Rev
Biochem. 68:559–581. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Acconcia F, Totta P, Ogawa S, Cardillo I,
Inoue S, Leone S, Trentalance A, Muramatsu M and Marino M: Survival
versus apoptotic 17beta-estradiol effect: Role of ER alpha and ER
beta activated non-genomic signaling. J Cell Physiol. 203:193–201.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Saji S, Okumura N, Eguchi H, Nakashima S,
Suzuki A, Toi M, Nozawa Y, Saji S and Hayashi S: MDM2 enhances the
function of estrogen receptor alpha in human breast cancer cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 281:259–265. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Smith JV and Luo Y: Studies on molecular
mechanisms of Ginkgo biloba extract. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol.
64:465–472. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hayashi K, Hayashi T and Morita N:
Mechanism of action of the antiherpesvirus biflavone ginkgetin.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 36:1890–1893. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lim H, Son KH, Chang HW, Kang SS and Kim
HP: Effects of anti-inflammatory biflavonoid, ginkgetin, on chronic
skin inflammation. Biol Pharm Bull. 29:1046–1049. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Su Y, Sun CM, Chuang HH and Chang PT:
Studies on the cytotoxic mechanisms of ginkgetin in a human ovarian
adenocarcinoma cell line. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol.
362:82–90. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
You OH and Kim SH, Kim B, Sohn EJ, Lee HJ,
Shim BS, Yun M, Kwon BM and Kim SH: Ginkgetin induces apoptosis via
activation of caspase and inhibition of survival genes in PC-3
prostate cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 23:2692–2695. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jeon YJ, Jung SN, Yun J, Lee CW, Choi J,
Lee YJ, Han DC and Kwon BM: Ginkgetin inhibits the growth of DU-145
prostate cancer cells through inhibition of signal transducer and
activator of transcription 3 activity. Cancer Sci. 106:413–240.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sak K: Cytotoxicity of dietary flavonoids
on different human cancer types. Pharmacogn Rev. 8:122–146. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zheng N, Zhang P, Huang H, Liu W, Hayashi
T, Zang L, Zhang Y, Liu L, Xia M, Tashiro S, et al: ERα
down-regulation plays a key role in silibinin-induced autophagy and
apoptosis in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. J Pharmacol Sci.
128:97–107. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Altucci L, Addeo R, Cicatiello L, Dauvois
S, Parker MG, Truss M, Beato M, Sica V, Bresciani F and Weisz A:
17beta-Estradiol induces cyclin D1 gene transcription,
p36D1-p34cdk4 complex activation and p105Rb phosphorylation during
mitogenic stimulation of G(1)-arrested human breast cancer cells.
Oncogene. 12:2315–2324. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Frasor J, Danes JM, Komm B, Chang KC,
Lyttle CR and Katzenellenbogen BS: Profiling of estrogen up- and
down-regulated gene expression in human breast cancer cells:
Insights into gene networks and pathways underlying estrogenic
control of proliferation and cell phenotype. Endocrinology.
144:4562–4574. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu J, Lu X, Hua KQ, Sun H, Yu YH and Feng
YJ: Oestrogen receptor α mediates 17β-estradiol enhancement of
ovarian cancer cell motility through up-regulation of survivin
expression. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 286:729–737. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Imbert-Fernandez Y, Clem BF, O'Neal J,
Kerr DA, Spaulding R, Lanceta L, Clem AL, Telang S and Chesney J:
Estradiol stimulates glucose metabolism via
6-phosphofructo-2-kinase (PFKFB3). J Biol Chem. 289:9440–9448.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mohammed H, Russell IA, Stark R, Rueda QM,
Hickey TE, Tarulli GA, Serandour AA, Birrell SN, Bruna A, Saadi A,
et al: Progesterone receptor modulates ERα action in breast cancer.
Nature. 523:313–317. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Foster JS, Henley DC, Ahamed S and
Wimalasena J: Estrogens and cell-cycle regulation in breast cancer.
Trends Endocrinol Metab. 12:320–327. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Clark GM, Osborne CK and McGuire WL:
Correlations between estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and
patient characteristics in human breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
2:1102–1109. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ingle JN: Pharmacogenomics of endocrine
therapy in breast cancer. J Hum Genet. 58:306–312. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Iwata H, Nakayama T, Yamamoto N, Sato Y,
Tokuda Y, Aogi K, Saji S, Watanabe K, Saito T, Yoshida M, et al:
Randomized phase II study of three doses of oral TAS-108 in
postmenopausal patients with metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Sci.
103:1708–1713. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|