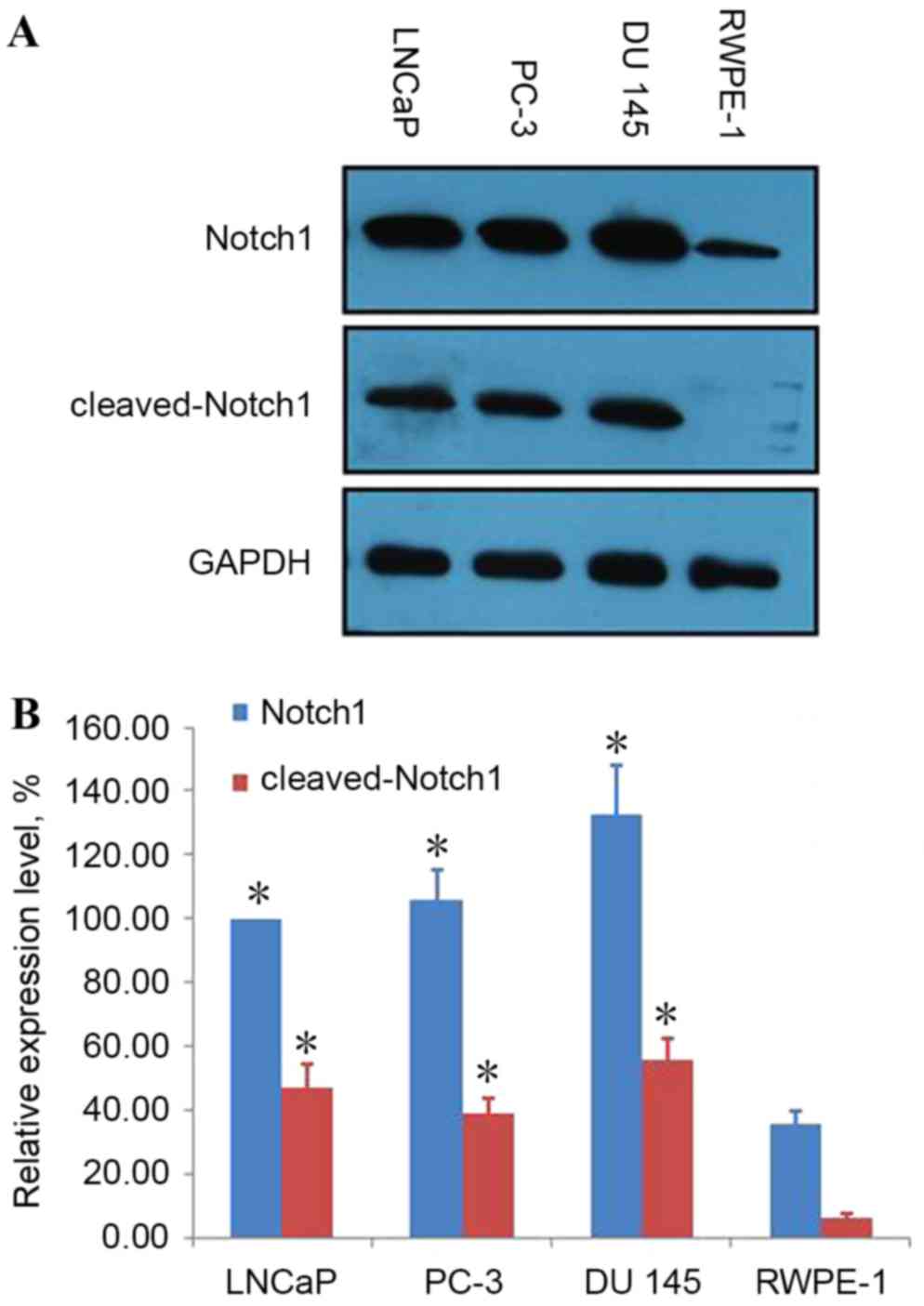
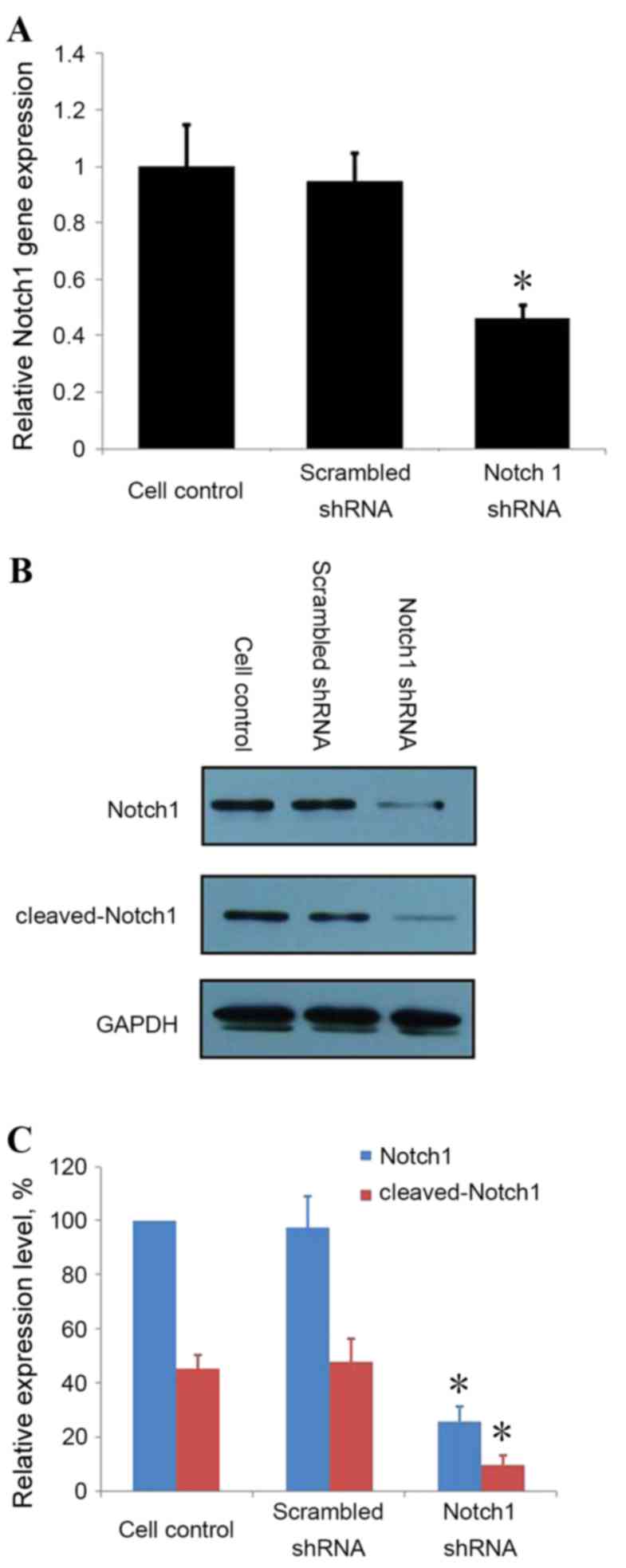
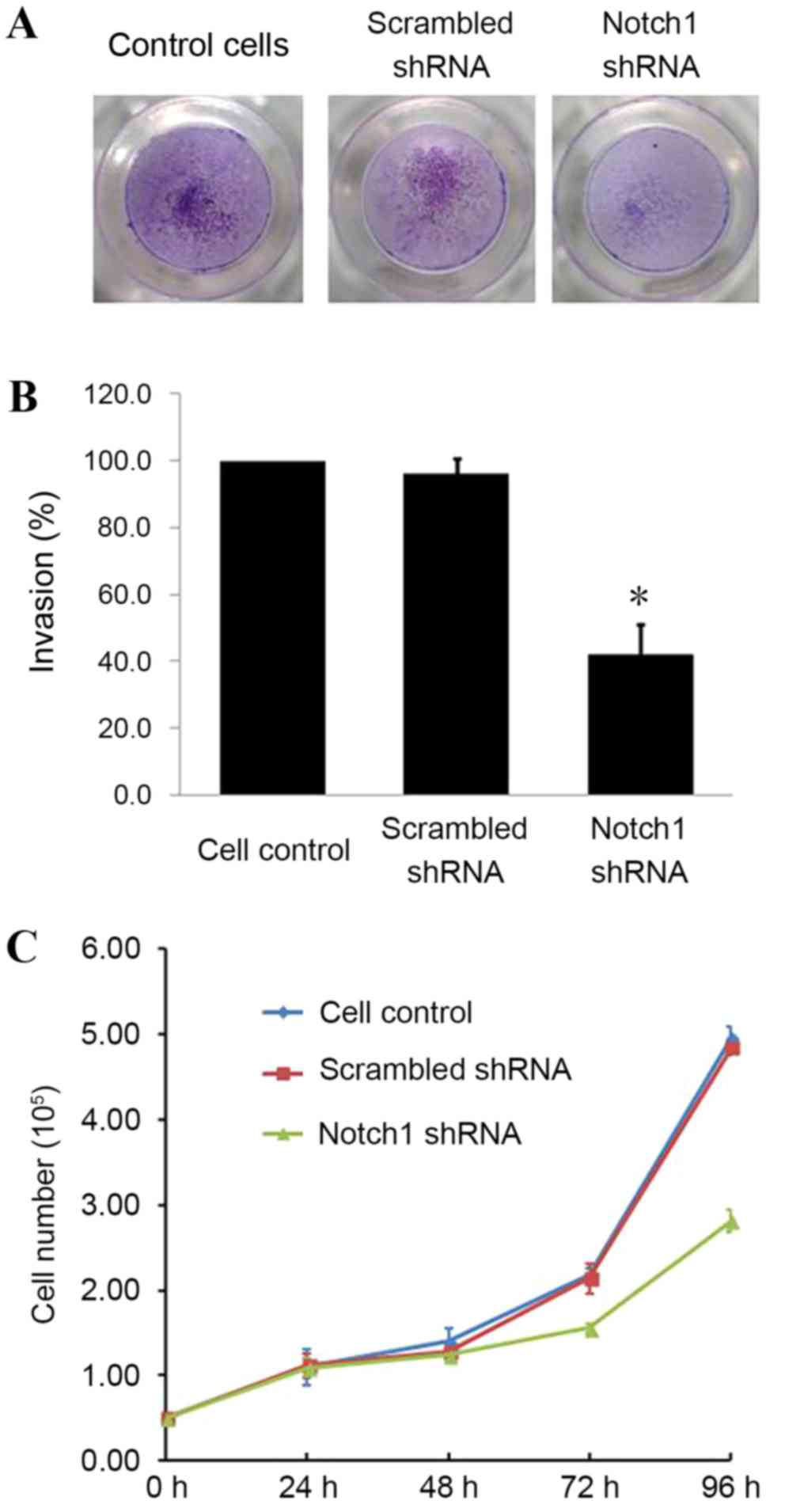
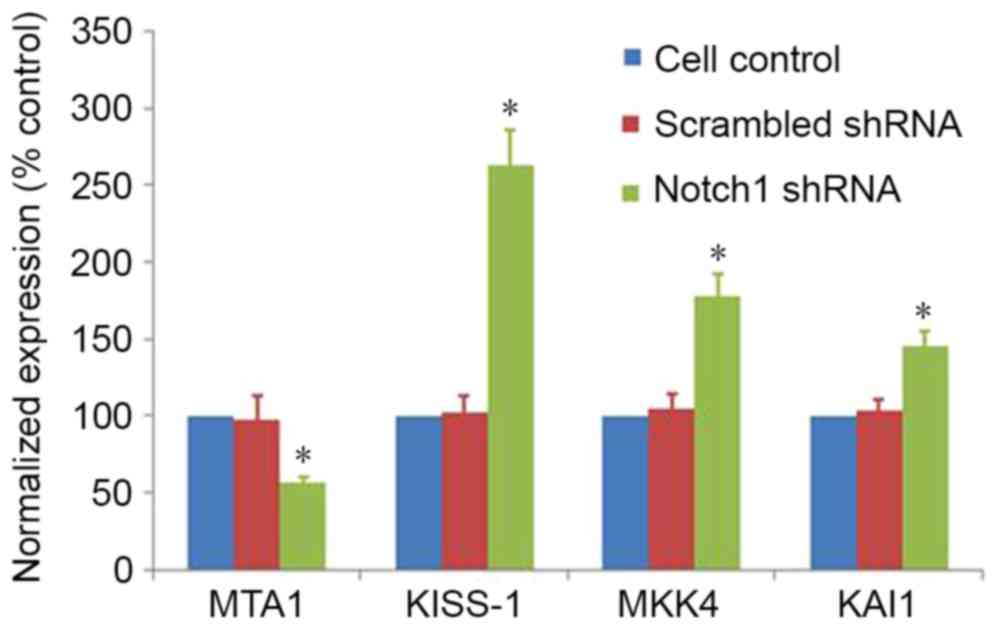
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bubendorf L, Schöpfer A, Wagner U, Sauter
G, Moch H, Willi N, Gasser TC and Mihatsch MJ: Metastatic patterns
of prostate cancer: An autopsy study of 1,589 patients. Hum Pathol.
31:578–583. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lawton A, Sudakoff G, Dezelan LC and Davis
N: Presentation, treatment, and outcomes of dural metastases in men
with metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer: A case series.
J Palliat Med. 13:1125–1129. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
B R and C GP: Path to facilitate the
prediction of functional amino acid substitutions in red blood cell
disorders - a computational approach. PLoS One. 6:e246072011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Carvalho FL, Simons BW, Eberhart CG and
Berman DM: Notch signaling in prostate cancer: A moving target.
Prostate. 74:933–945. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vinson KE, George DC, Fender AW, Bertrand
FE and Sigounas G: The notch pathway in colorectal cancer. Int J
Cancer. 138:1835–1842. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Eliasz S, Liang S, Chen Y, De Marco MA,
Machek O, Skucha S, Miele L and Bocchetta M: Notch-1 stimulates
survival of lung adenocarcinoma cells during hypoxia by activating
the IGF-1R pathway. Oncogene. 29:2488–2498. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mumm JS and Kopan R: Notch signaling: From
the outside in. Dev Biol. 228:151–165. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Z, Li Y, Banerjee S and Sarkar FH:
Exploitation of the Notch signaling pathway as a novel target for
cancer therapy. Anticancer Res. 28:3621–3630. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Talora C, Campese AF, Bellavia D, Felli
MP, Vacca A, Gulino A and Screpanti I: Notch signaling and
diseases: An evolutionary journey from a simple beginning to
complex outcomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1782:489–497. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kopan R and Ilagan MX: The canonical Notch
signaling pathway: Unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell.
137:216–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hori K, Sen A and Artavanis-Tsakonas S:
Notch signaling at a glance. J Cell Sci. 126:2135–2140. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hudson BD, Kulp KS and Loots GG: Prostate
cancer invasion and metastasis: Insights from mining genomic data.
Brief Funct Genomics. 12:397–410. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Balint K, Xiao M, Pinnix CC, Soma A, Veres
I, Juhasz I, Brown EJ, Capobianco AJ, Herlyn M and Liu ZJ:
Activation of Notch1 signaling is required for
beta-catenin-mediated human primary melanoma progression. J Clin
Invest. 115:3166–3176. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yeh TS, Wu CW, Hsu KW, Liao WJ, Yang MC,
Li AF, Wang AM, Kuo ML and Chi CW: The activated Notch1 signal
pathway is associated with gastric cancer progression through
cyclooxygenase-2. Cancer Res. 69:5039–5048. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Negri FV, Crafa P, Pedrazzi G, Bozzetti C,
Lagrasta C, Gardini G, Tamagnini I, Bisagni A, Azzoni C, Bottarelli
L, et al: Strong Notch activation hinders bevacizumab efficacy in
advanced colorectal cancer. Future Oncol. 11:3167–3174. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ponnurangam S, Dandawate PR, Dhar A,
Tawfik OW, Parab RR, Mishra PD, Ranadive P, Sharma R, Mahajan G,
Umar S, et al: Quinomycin A targets Notch signaling pathway in
pancreatic cancer stem cells. Oncotarget. 7:3217–3232. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lefort K, Ostano P, Mello-Grand M, Calpini
V, Scatolini M, Farsetti A, Dotto GP and Chiorino G: Dual tumor
suppressing and promoting function of Notch1 signaling in human
prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 7:48011–48026. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Stylianou S, Clarke RB and Brennan K:
Aberrant activation of notch signaling in human breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 66:1517–1525. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Agrawal N, Frederick MJ, Pickering CR,
Bettegowda C, Chang K, Li RJ, Fakhry C, Xie TX, Zhang J, Wang J, et
al: Exome sequencing of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
reveals inactivating mutations in NOTCH1. Science. 333:1154–1157.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Leong KG, Niessen K, Kulic I, Raouf A,
Eaves C, Pollet I and Karsan A: Jagged1-mediated Notch activation
induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through Slug-induced
repression of E-cadherin. J Exp Med. 204:2935–2948. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen J, Imanaka N, Chen J and Griffin JD:
Hypoxia potentiates Notch signaling in breast cancer leading to
decreased E-cadherin expression and increased cell migration and
invasion. Br J Cancer. 102:351–360. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Santagata S, Demichelis F, Riva A,
Varambally S, Hofer MD, Kutok JL, Kim R, Tang J, Montie JE,
Chinnaiyan AM, et al: JAGGED1 expression is associated with
prostate cancer metastasis and recurrence. Cancer Res.
64:6854–6857. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bin Hafeez B, Adhami VM, Asim M, Siddiqui
IA, Bhat KM, Zhong W, Saleem M, Din M, Setaluri V and Mukhtar H:
Targeted knockdown of Notch1 inhibits invasion of human prostate
cancer cells concomitant with inhibition of matrix
metalloproteinase-9 and urokinase plasminogen activator. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:452–459. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang Y, Wang Z, Ahmed F, Banerjee S, Li Y
and Sarkar FH: Down-regulation of Jagged-1 induces cell growth
inhibition and S phase arrest in prostate cancer cells. Int J
Cancer. 119:2071–2077. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shou J, Ross S, Koeppen H, de Sauvage FJ
and Gao WQ: Dynamics of notch expression during murine prostate
development and tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 61:7291–7297.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Toh Y, Pencil SD and Nicolson GL: A novel
candidate metastasis-associated gene, mta1, differentially
expressed in highly metastatic mammary adenocarcinoma cell lines.
cDNA cloning, expression, and protein analyses. J Biol Chem.
269:22958–22963. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Toh Y and Nicolson GL: The role of the MTA
family and their encoded proteins in human cancers: Molecular
functions and clinical implications. Clin Exp Metastasis.
26:215–227. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu J, Xu D, Wang H, Zhang Y, Chang Y,
Zhang J, Wang J, Li C, Liu H, Zhao M, et al: The subcellular
distribution and function of MTA1 in cancer differentiation.
Oncotarget. 5:5153–5164. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xue Y, Wong J, Moreno GT, Young MK, Côté J
and Wang W: NURD, a novel complex with both ATP-dependent
chromatin-remodeling and histone deacetylase activities. Mol Cell.
2:851–861. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li J, Ye L, Sun PH, Satherley L, Hargest
R, Zhang Z and Jiang WG: MTA1 Is Up-regulated in colorectal cancer
and is inversely correlated with lymphatic metastasis. Cancer
Genomics Proteomics. 12:339–345. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kang HJ, Lee MH, Kang HL, Kim SH, Ahn JR,
Na H, Na TY, Kim YN, Seong JK and Lee MO: Differential regulation
of estrogen receptor α expression in breast cancer cells by
metastasis-associated protein 1. Cancer Res. 74:1484–1494. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang RA: MTA1-a stress response protein: A
master regulator of gene expression and cancer cell behavior.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 33:1001–1009. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Luo H, Li H, Yao N, Hu L and He T:
Metastasis-associated protein 1 as a new prognostic marker for
solid tumors: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Tumour Biol.
35:5823–5832. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|