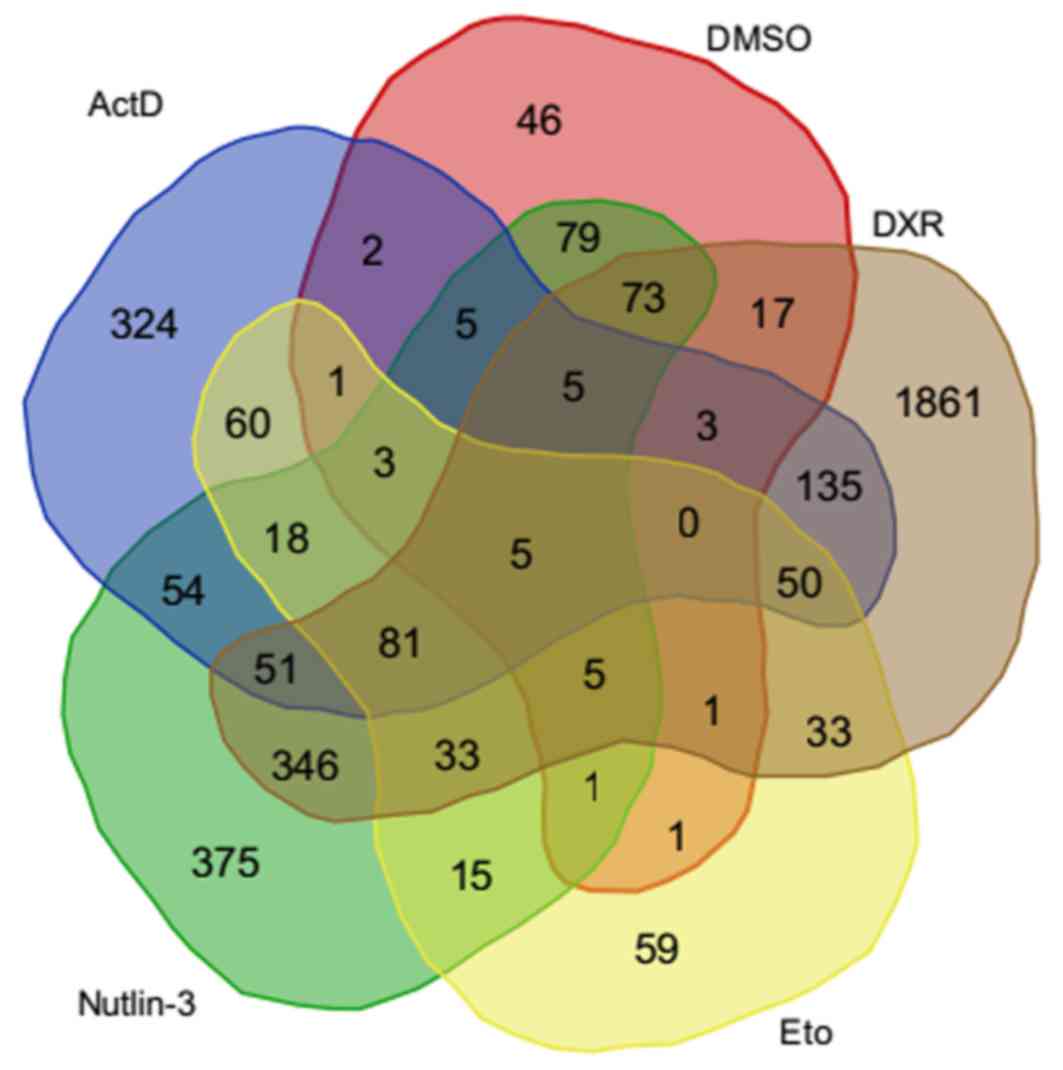
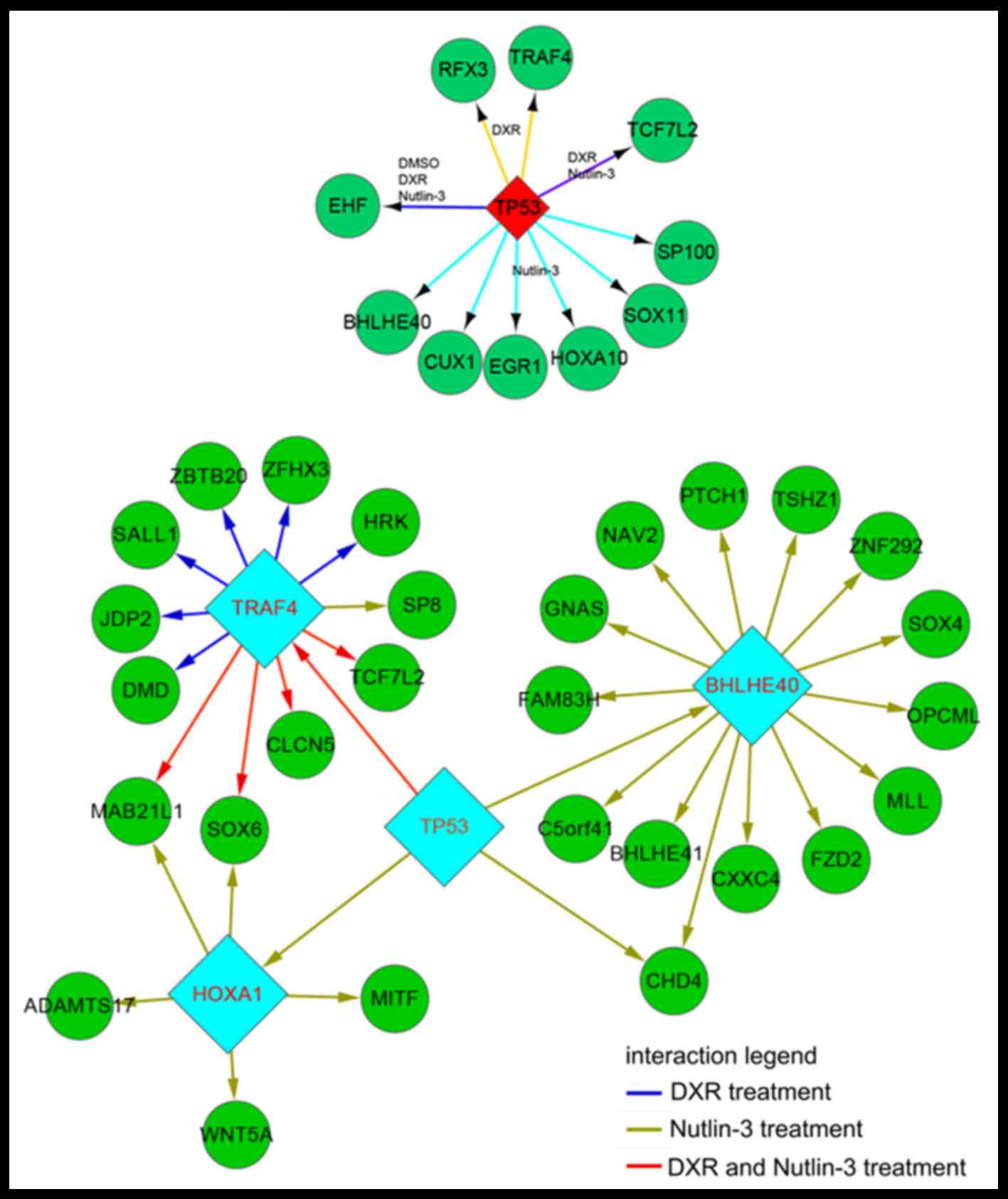
|
1
|
Burke ME, Albritton K and Marina N:
Challenges in the recruitment of adolescents and young adults to
cancer clinical trials. Cancer. 110:2385–2393. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Luetke A, Meyers PA, Lewis I and Juergens
H: Osteosarcoma treatment-where do we stand? A state of the art
review. Cancer Treat Rev. 40:523–532. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kere J: Neuropeptide S receptor 1: An
asthma susceptibility geneAllergy Frontiers: Future Perspectives.
Springer; pp. 191–205. 2010, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ahmed H, Salama A, Salem SE and Bahnassy
AA: A case of synchronous double primary breast carcinoma and
osteosarcoma: Mismatch repair genes mutations as a possible cause
for multiple early onset malignant tumors. Am J Case Rep.
13:218–223. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vogelstein B, Lane D and Levine AJ:
Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 408:307–310. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mulligan LM, Matlashewski GJ, Scrable HJ
and Cavenee WK: Mechanisms of p53 loss in human sarcomas. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 87:5863–5867. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Toguchida J, Yamaguchi T, Dayton SH,
Beauchamp RL, Herrera GE, Ishizaki K, Yamamuro T, Meyers PA, Little
JB, Sasaki MS, et al: Prevalence and spectrum of germline mutations
of the p53 gene among patients with sarcoma. N Engl J Med.
326:1301–1308. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Luo Y, Deng Z and Chen J: Pivotal
regulatory network and genes in osteosarcoma. Arch Med Sci.
9:569–575. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sobell HM: Actinomycin and DNA
transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 82:5328–5331. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fornari FA, Randolph JK, Yalowich JC,
Ritke MK and Gewirtz DA: Interference by doxorubicin with DNA
unwinding in MCF-7 breast tumor cells. Mol Pharmacol. 45:649–656.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hande KR: Etoposide: Four decades of
development of a topoisomerase II inhibitor. Eur J Cancer.
34:1514–1521. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shinohara T and Uesugi M: In-vivo
activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of
MDM2. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 52 (13 Suppl):S1816–S1817.
2007.
|
|
13
|
Miyachi M, Kakazu N, Yagyu S, Katsumi Y,
Tsubai-Shimizu S, Kikuchi K, Tsuchiya K, Iehara T and Hosoi H:
Restoration of p53 pathway by nutlin-3 induces cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Clin Cancer Res.
15:4077–4084. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ling YH, el-Naggar AK, Priebe W and
Perez-Soler R: Cell cycle-dependent cytotoxicity, G2/M phase
arrest, and disruption of p34cdc2/cyclin B1 activity induced by
doxorubicin in synchronized P388 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 49:832–841.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu H and Krystal GW: Actinomycin D
decreases Mcl-1 expression and acts synergistically with ABT-737
against small cell lung cancer cell lines. Clin Cancer Res.
16:4392–4400. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hsiao M, Low J, Dorn E, Ku D, Pattengale
P, Yeargin J and Haas M: Gain-of-function mutations of the p53 gene
induce lymphohematopoietic metastatic potential and tissue
invasiveness. Am J Pathol. 145:7021994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Menendez D, Nguyen TA, Freudenberg JM,
Mathew VJ, Anderson CW, Jothi R and Resnick MA: Diverse stresses
dramatically alter genome-wide p53-binding and transactivation
landscape in human cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:7286–7301.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Smeenk L, van Heeringen SJ, Koeppel M,
Gilbert B, Janssen-Megens E, Stunnenberg HG and Lohrum M: Role of
p53 serine 46 in p53 target gene regulation. PLoS One.
6:e175742011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM and Irizarry
RA: affy-analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level.
Bioinformatics. 20:307–315. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Langmead B and Salzberg SL: Fast
gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods. 9:357–359. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang Y, Liu T, Meyer CA, Eeckhoute J,
Johnson DS, Bernstein BE, Nusbaum C, Myers RM, Brown M, Li W and
Liu XS: Model-based analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS). Genome Biol.
9:R1372008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ji H, Jiang H, Ma W, Johnson DS, Myers RM
and Wong WH: An integrated software system for analyzing ChIP-chip
and ChIP-seq data. Nat Biotechnol. 26:1293–1300. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Kir J, Liu D,
Bryant D, Guo Y, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki RA:
DAVID bioinformatics resources: Expanded annotation database and
novel algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists.
Nucleic Acids Res. 35:W169–W175. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shimizu S, Kanaseki T, Mizushima N, Mizuta
T, Arakawa-Kobayashi S, Thompson CB and Tsujimoto Y: Role of Bcl-2
family proteins in a non-apoptotic programmed cell death dependent
on autophagy genes. Nat Cell Biol. 6:1221–1228. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim Y, Starostina NG and Kipreos ET: The
CRL4Cdt2 ubiquitin ligase targets the degradation of p21Cip1 to
control replication licensing. Genes Dev. 22:2507–2519. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dujardin F, Binh MB, Bouvier C,
Gomez-Brouchet A, Larousserie F, Muret Ad, Louis-Brennetot C,
Aurias A, Coindre JM, Guillou L, et al: MDM2 and CDK4
immunohistochemistry is a valuable tool in the differential
diagnosis of low-grade osteosarcomas and other primary
fibro-osseous lesions of the bone. Mod Pathol. 24:624–637. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lukin DJ, Carvajal LA, Liu WJ,
Resnick-Silverman L and Manfredi JJ: p53 promotes cell survival due
to the reversibility of its cell cycle checkpoints. Mol Cancer Res.
13:16–28. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee YS, Oh JH, Yoon S, Kwon MS, Song CW,
Kim KH, Cho MJ, Mollah ML, Je YJ, Kim YD, et al: Differential gene
expression profiles of radioresistant non-small-cell lung cancer
cell lines established by fractionated irradiation: Tumor protein
p53-inducible protein 3 confers sensitivity to ionizing radiation.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 77:858–866. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Voltan R, Secchiero P, Corallini F and
Zauli G: Selective induction of TP53I3/p53-inducible gene 3 (PIG3)
in myeloid leukemic cells, but not in normal cells, by Nutlin-3.
Mol Carcinog. 53:498–504. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Qin X, Zhang S, Li B, Liu XD, He XP, Shang
ZF, Xu QZ, Zhao ZQ, Ye QN and Zhao PK: p53-dependent upregulation
of PIG3 transcription by γ-ray irradiation and its interaction with
KAP1 in responding to DNA damage. Chin Sci Bull. 56:3162–3171.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Bourdon A, Minai L, Serre V, Jais JP,
Sarzi E, Aubert S, Chrétien D, de Lonlay P, Paquis-Flucklinger V,
Arakawa H, et al: Mutation of RRM2B, encoding p53-controlled
ribonucleotide reductase (p53R2), causes severe mitochondrial DNA
depletion. Nat Genet. 39:776–780. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kimura T, Takeda S, Sagiya Y, Gotoh M,
Nakamura Y and Arakawa H: Impaired function of p53R2 in Rrm2b-null
mice causes severe renal failure through attenuation of dNTP pools.
Nat Genet. 34:440–445. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kas K, Finger E, Grall F, Gu X, Akbarali
Y, Boltax J, Weiss A, Oettgen P, Kapeller R and Libermann TA:
ESE-3, a novel member of an epithelium-specific ets transcription
factor subfamily, demonstrates different target gene specificity
from ESE-1. J Biol Chem. 275:2986–2998. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tugores A, Le J, Sorokina I, Snijders AJ,
Duyao M, Reddy PS, Carlee L, Ronshaugen M, Mushegian A, Watanaskul
T, et al: The epithelium-specific ETS protein EHF/ESE-3 is a
context-dependent transcriptional repressor downstream of MAPK
signaling cascades. J Biol Chem. 276:20397–20406. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jolma A, Kivioja T, Toivonen J, Cheng L,
Wei G, Enge M, Taipale M, Vaquerizas JM, Yan J, Sillanpää MJ, et
al: Multiplexed massively parallel SELEX for characterization of
human transcription factor binding specificities. Genome Res.
20:861–873. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Maijgren S, Sur I, Nilsson M and Toftgård
R: Involvement of RFX proteins in transcriptional activation from a
Ras-responsive enhancer element. Arch Dermatol Res. 295:482–489.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sengupta P, Xu Y, Wang L, Widom R and
Smith BD: Collagen alpha1(I) gene (COL1A1) is repressed by RFX
family. J Biol Chem. 280:21004–21014. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Badis G, Berger MF, Philippakis AA,
Talukder S, Gehrke AR, Jaeger SA, Chan ET, Metzler G, Vedenko A,
Chen X, et al: Diversity and complexity in DNA recognition by
transcription factors. Science. 324:1720–1723. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|