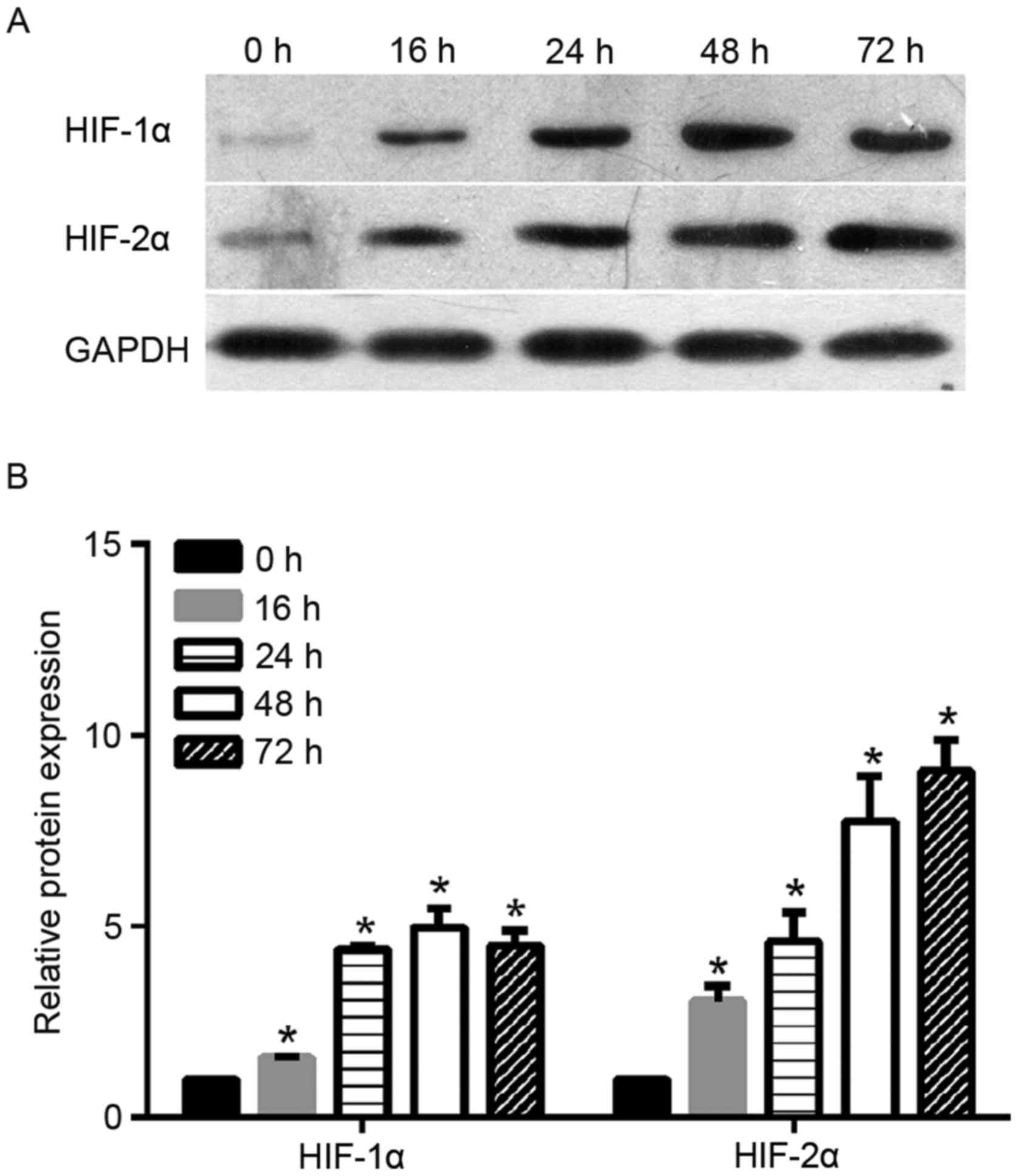
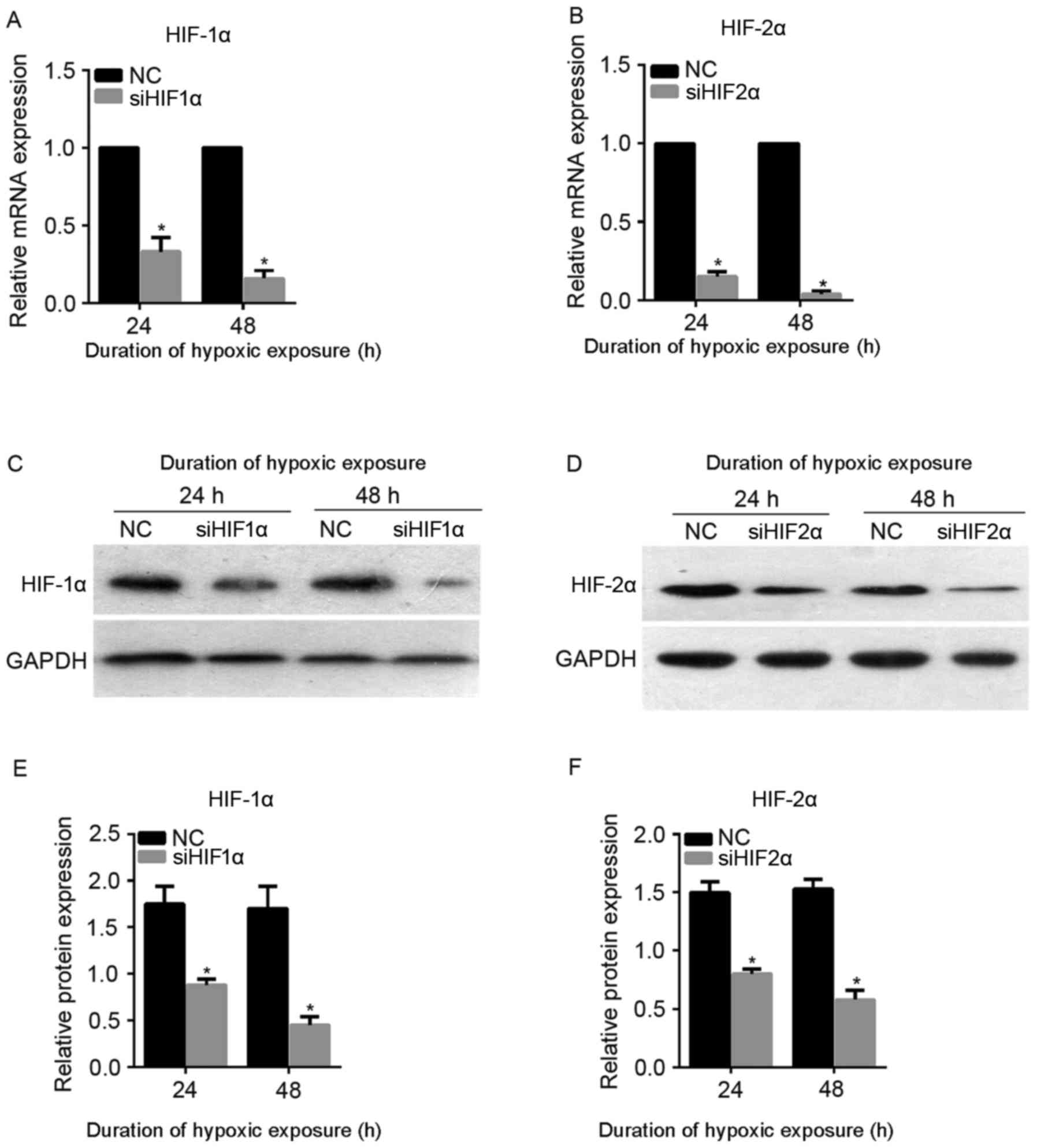
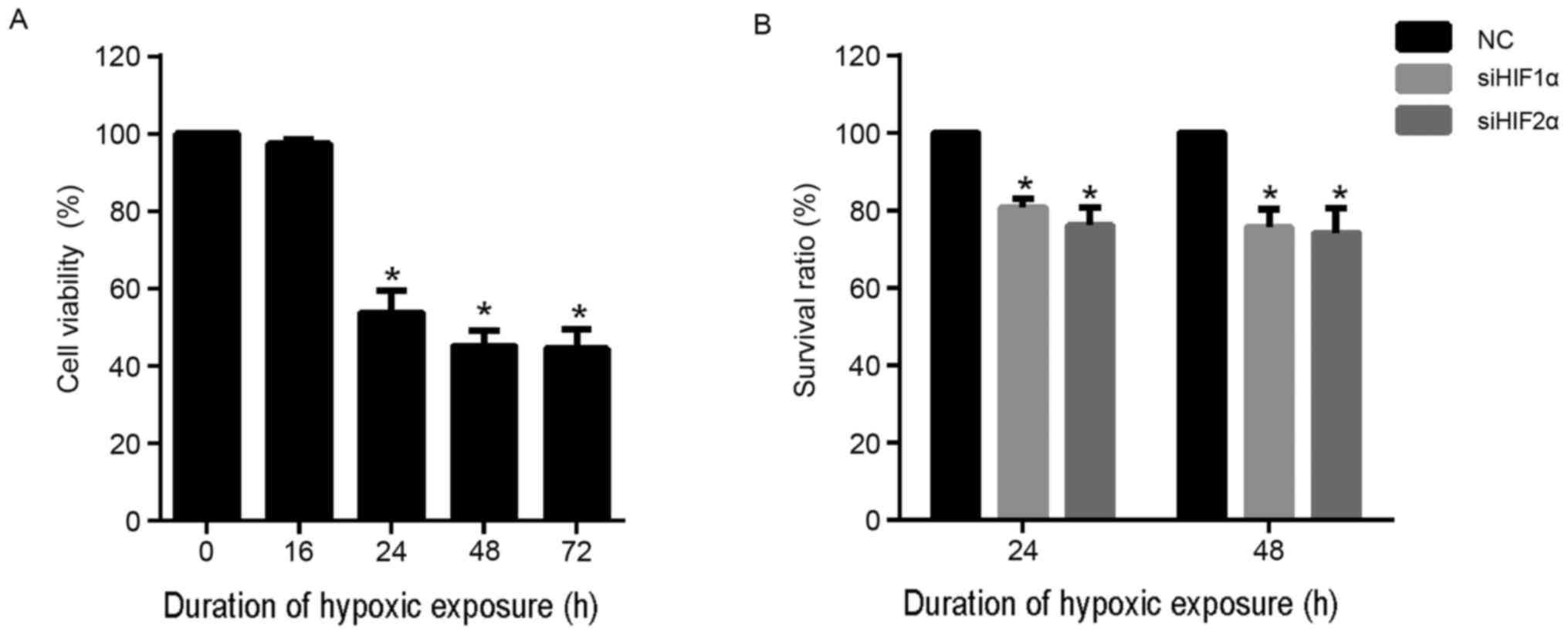
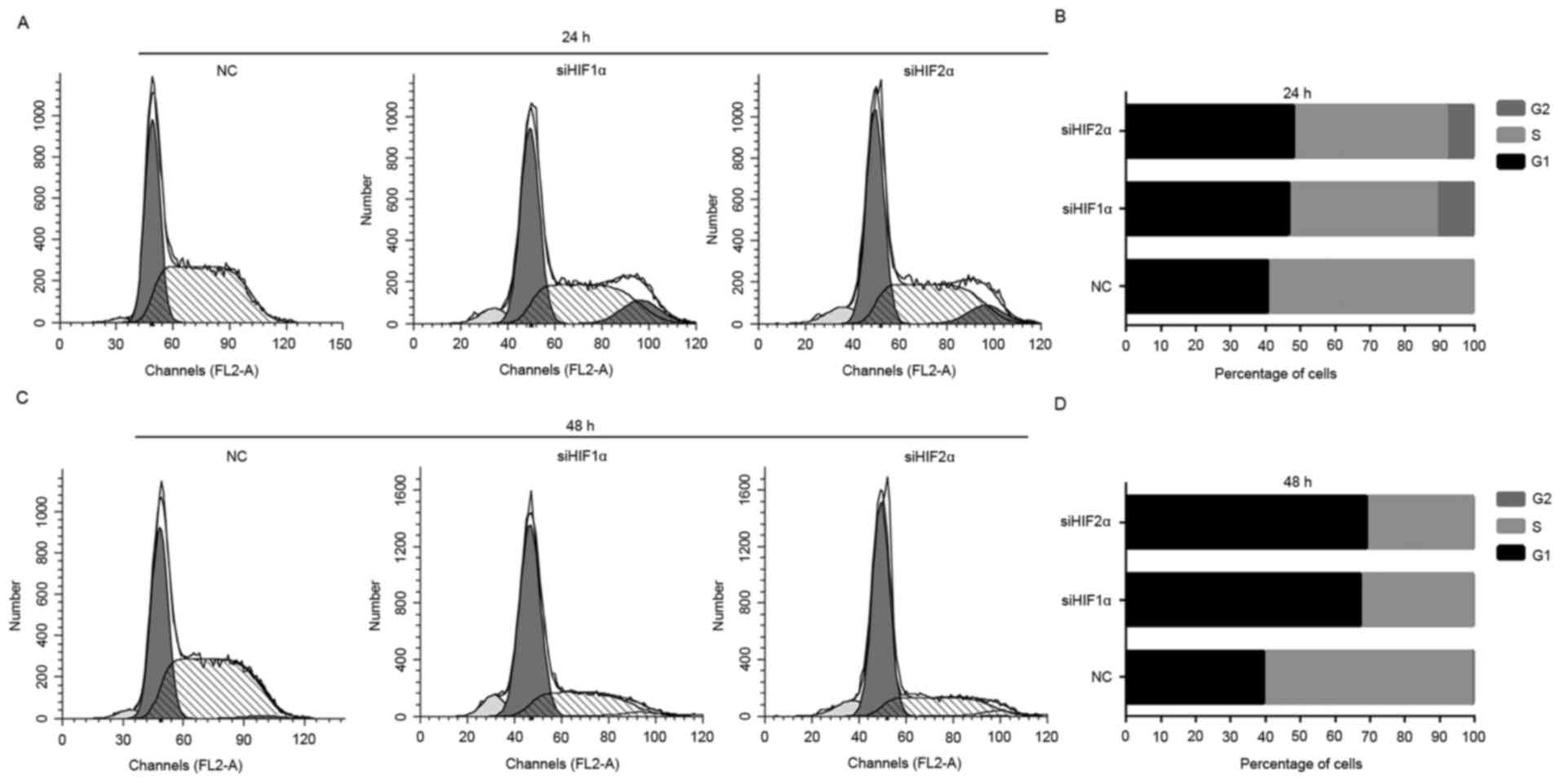
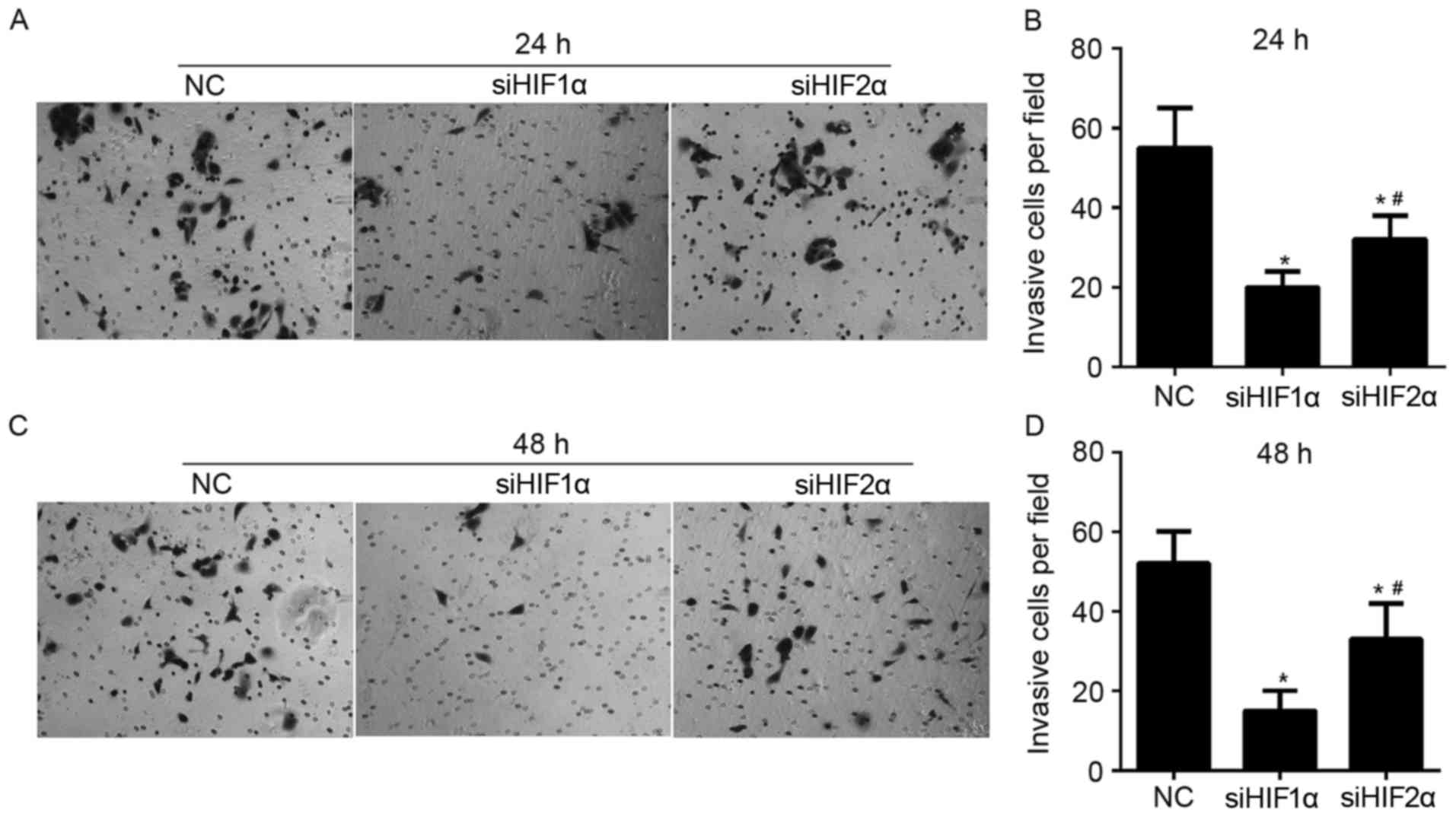
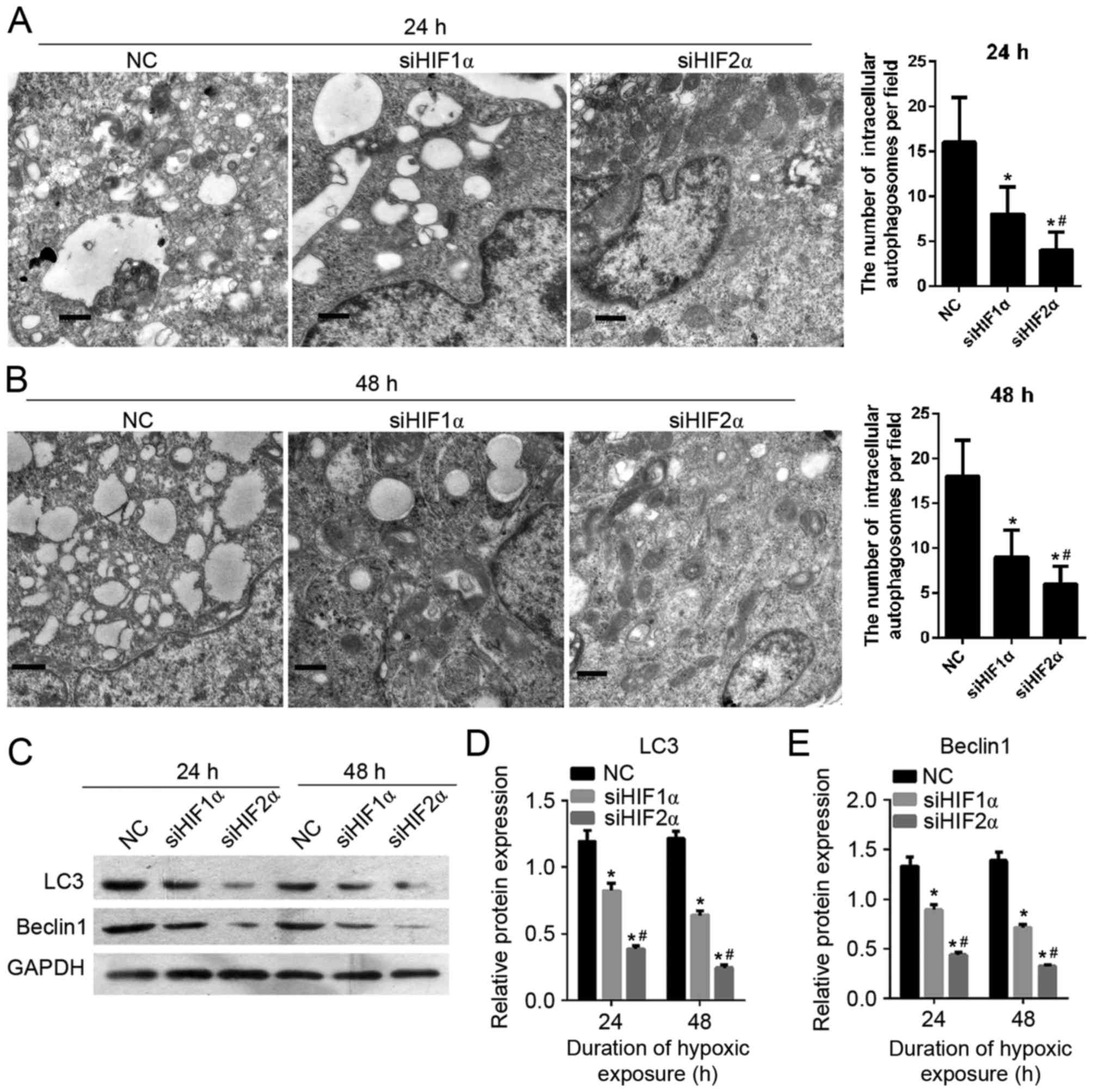
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kawano M, Mabuchi S, Matsumoto Y, Sasano
T, Takahashi R, Kuroda H, Kozasa K, Hashimoto K, Isobe A, Sawada K,
et al: The significance of G-CSF expression and myeloid-derived
suppressor cells in the chemoresistance of uterine cervical cancer.
Sci Rep. 5:182172015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Eifel PJ, Winter K, Morris M, Levenback C,
Grigsby PW, Cooper J, Rotman M, Gershenson D and Mutch DG: Pelvic
irradiation with concurrent chemotherapy versus pelvic and
para-aortic irradiation for high-risk cervical cancer: An update of
radiation therapy oncology group trial (RTOG) 90–01. J Clin Oncol.
22:872–880. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li SH, Shin DH, Chun YS, Lee MK, Kim MS
and Park JW: A novel mode of action of YC-1 in HIF inhibition:
Stimulation of FIH-dependent p300 dissociation from HIF-1{alpha}.
Mol Cancer Ther. 7:3729–3738. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lou JJ, Chua YL, Chew EH, Gao J, Bushell M
and Hagen T: Inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha
(HIF-1alpha) protein synthesis by DNA damage inducing agents. PLoS
One. 5:00105222010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhang J, Cao J, Weng Q, Wu R, Yan Y, Jing
H, Zhu H, He Q and Yang B: Suppression of hypoxia-inducible factor
1α (HIF-1α) by tirapazamine is dependent on eIF2α phosphorylation
rather than the mTORC1/4E-BP1 pathway. PLoS One. 5:00139102010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Rankin EB and Giaccia AJ: The role of
hypoxia-inducible factors in tumorigenesis. Cell Death Differ.
15:678–685. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hu CJ, Sataur A, Wang L, Chen H and Simon
MC: The N-terminal transactivation domain confers target gene
specificity of hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha.
Mol Biol Cell. 18:4528–4542. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tian H, McKnight SL and Russell DW:
Endothelial PAS domain protein 1 (EPAS1), a transcription factor
selectively expressed in endothelial cells. Genes Dev. 11:72–82.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shah T, Krishnamachary B, Wildes F,
Mironchik Y, Kakkad SM, Jacob D, Artemov D and Bhujwalla ZM: HIF
isoforms have divergent effects on invasion, metastasis, metabolism
and formation of lipid droplets. Oncotarget. 6:28104–28119. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang M, Chen Q, Xiao J, Yao T, Bian L,
Liu C and Lin Z: Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α is a
predictor of poor prognosis in cervical cancer: A clinicopathologic
study and a meta-analysis. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 24:1054–1064.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ellingsen C, Andersen LM, Galappathi K and
Rofstad EK: Hypoxia biomarkers in squamous cell carcinoma of the
uterine cervix. BMC Cancer. 15:8052015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim NS, Kang YJ, Jo JO, Kim HY, Oh YR, Kim
YO, Jung MH, Ock MS and Cha HJ: Elevated expression of thymosin β4,
vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and hypoxia inducible
factor (HIF)-1α in early-stage cervical cancers. Pathol Oncol Res.
17:493–502. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tang B, Qu Y, Zhao F, Mao M, Tang J, Li X,
Ferriero D and Mu D: In vitro effects of hypoxia-inducible factor
1alpha on the biological characteristics of the SiHa uterine cervix
cancer cell line. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 19:898–904. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schwock J, Geddie WR and Hedley DW:
Analysis of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha accumulation and cell
cycle in geldanamycin-treated human cervical carcinoma cells by
laser scanning cytometry. Cytometry A. 68:59–70. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim MK, Kim TJ, Sung CO, Choi CH, Lee JW,
Bae DS and Kim BG: Clinical significance of HIF-2α immunostaining
area in radioresistant cervical cancer. J Gynecol Oncol. 22:44–48.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kawanaka T, Kubo A, Ikushima H, Sano T,
Takegawa Y and Nishitani H: Prognostic significance of HIF-2alpha
expression on tumor infiltrating macrophages in patients with
uterine cervical cancer undergoing radiotherapy. J Med Invest.
55:78–86. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lin Q, Wang Y, Chen D, Sheng X, Liu J and
Xiong H: Cisplatin regulates cell autophagy in endometrial cancer
cells via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway. Oncol Lett.
13:3567–3571. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lin D and Wu J: Hypoxia inducible factor
in hepatocellular carcinoma: A therapeutic target. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:12171–12178. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Masoud GN and Li W: HIF-1alpha pathway:
Role, regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm
Sin B. 5:378–389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Imamura T, Kikuchi H, Herraiz MT, Park DY,
Mizukami Y, Mino-Kenduson M, Lynch MP, Rueda BR, Benita Y, Xavier
RJ and Chung DC: HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha have divergent roles in
colon cancer. Int J Cancer. 124:763–771. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Menrad H, Werno C, Schmid T, Copanaki E,
Deller T, Dehne N and Brüne B: Roles of hypoxia-inducible
factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) versus HIF-2alpha in the survival of
hepatocellular tumor spheroids. Hepatology. 51:2183–2192. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|