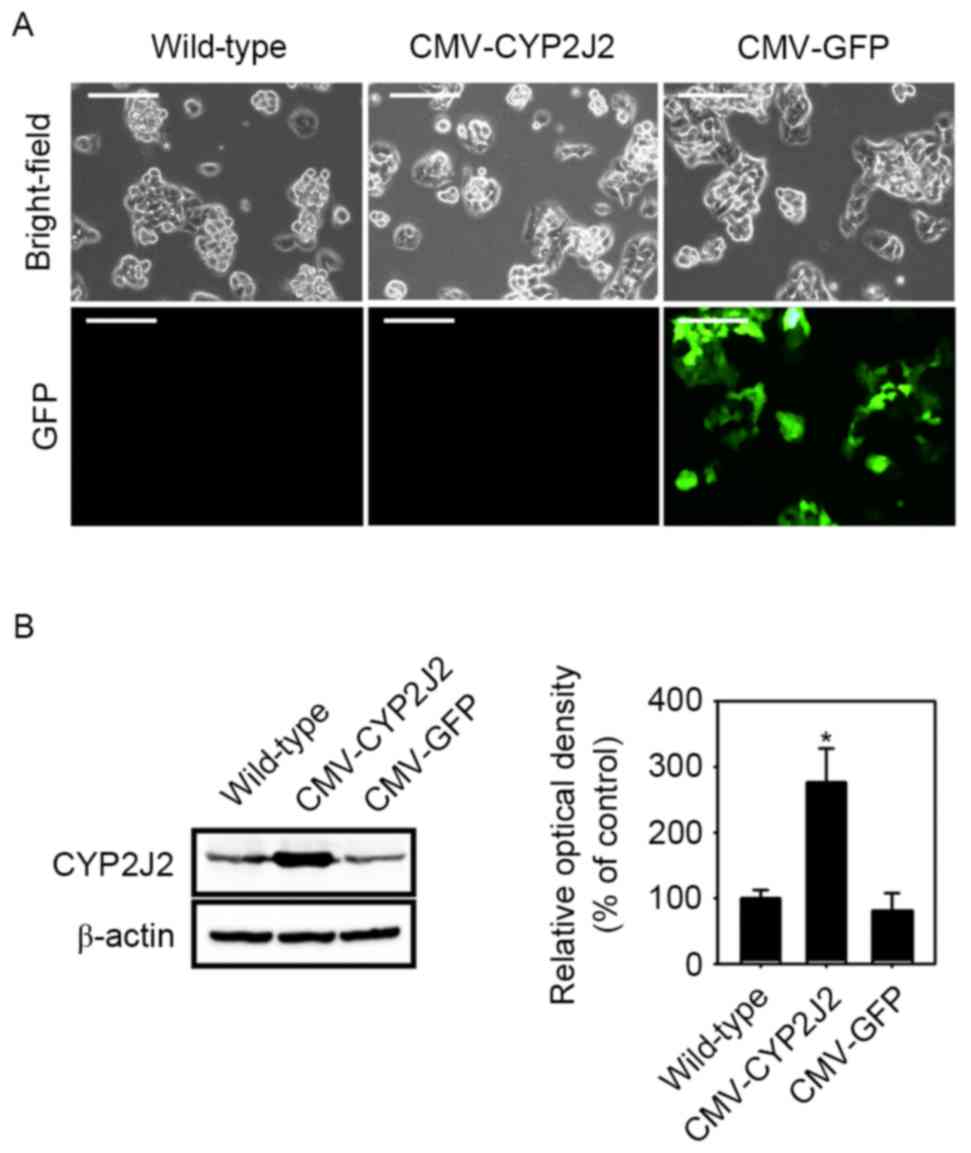
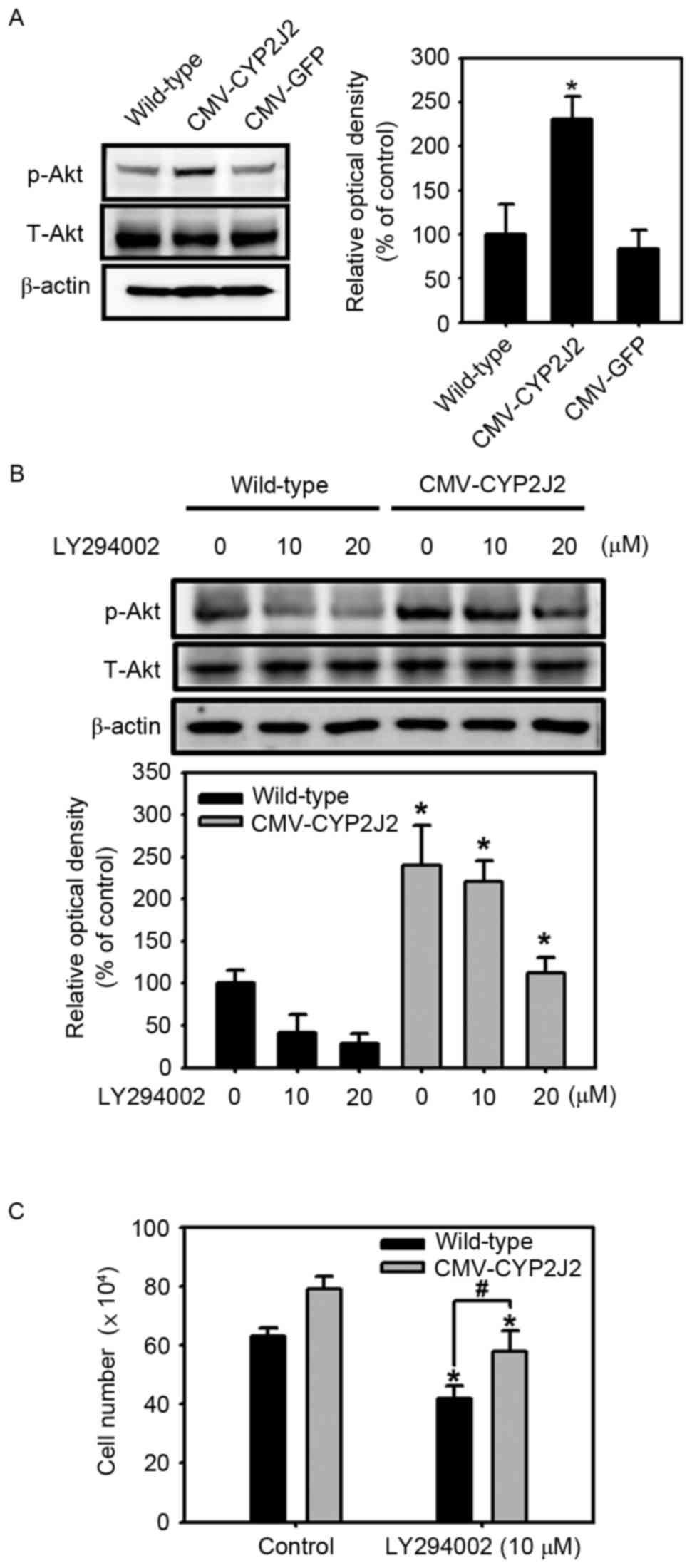
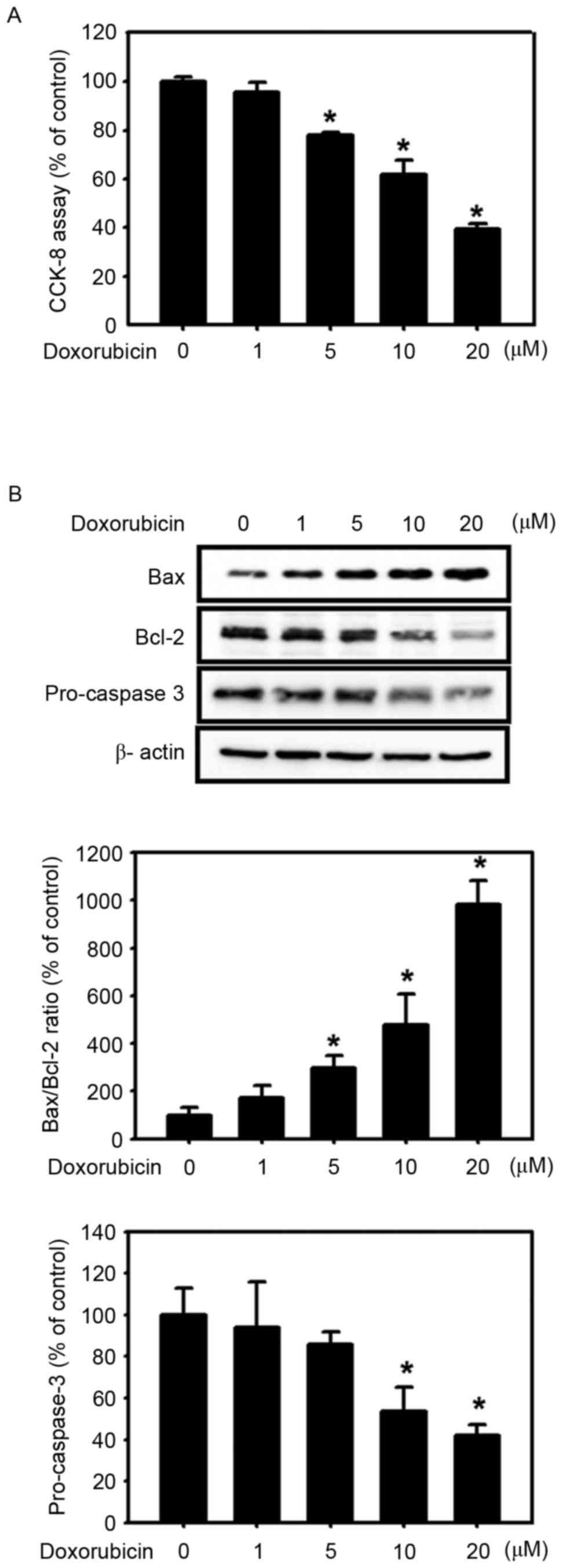
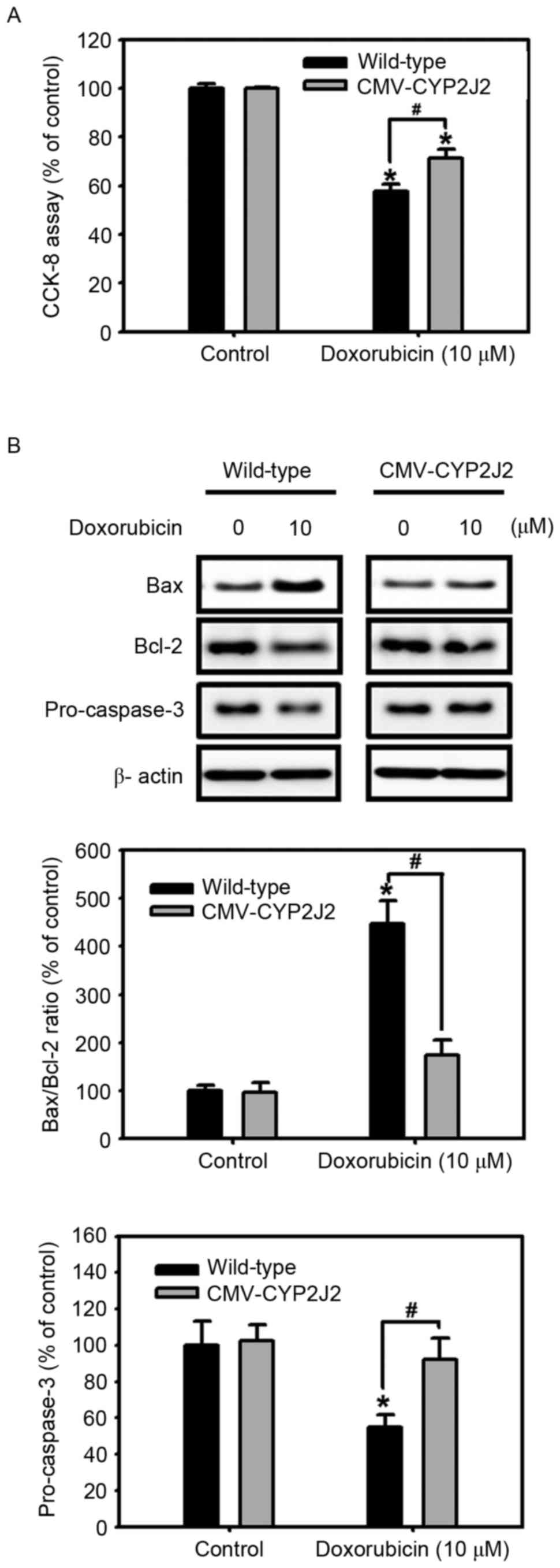
|
1
|
Capdevila JH, Falck JR and Harris RC:
Cytochrome P450 and arachidonic acid bioactivation. Molecular and
functional properties of the arachidonate monooxygenase. J Lipid
Res. 41:163–181. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Enayetallah AE, French RA, Thibodeau MS
and Grant DF: Distribution of soluble epoxide hydrolase and of
cytochrome P450 2C8, 2C9 and 2J2 in human tissues. J Histochem
Cytochem. 52:447–454. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fisslthaler B, Popp R, Kiss L, Potente M,
Harder DR, Fleming I and Busse R: Cytochrome P450 2C is an EDHF
synthase in coronary arteries. Nature. 401:493–497. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rosolowsky M and Campbell WB: Synthesis of
hydroxyeicosatetraenoic (HETEs) and epoxyeicosatrienoic acids
(EETs) by cultured bovine coronary artery endothelial cells.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1299:267–277. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee HC, Lu T, Weintraub NL, VanRollins M,
Spector AA and Shibata EF: Effects of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids on
the cardiac sodium channels in isolated rat ventricular myocytes. J
Physiol. 1:153–168. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Node K, Huo Y, Ruan X, Yang B, Spiecker M,
Ley K, Zeldin DC and Liao JK: Anti-inflammatory properties of
cytochrome P450 epoxygenase-derived eicosanoids. Science.
285:1276–1279. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen JK, Capdevila J and Harris RC:
Cytochrome p450 epoxygenase metabolism of arachidonic acid inhibits
apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 21:6322–6331. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang B, Graham L, Dikalov S, Mason RP,
Falck JR, Liao JK and Zeldin DC: Overexpression of cytochrome P450
CYP2J2 protects against hypoxia-reoxygenation injury in cultured
bovine aortic endothelial cells. Mol Pharmacol. 60:310–320.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jiang JG, Chen CL, Card JW, Yang S, Chen
JX, Fu XN, Ning YG, Xiao X, Zeldin DC and Wang DW: Cytochrome P450
2J2 promotes the neoplastic phenotype of carcinoma cells and is
up-regulated in human tumors. Cancer Res. 65:4707–4715. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang SM, Mishina YM, Liu S, Cheung A,
Stegmeier F, Michaud GA, Charlat O, Wiellette E, Zhang Y, Wiessner
S, et al: Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt
signalling. Nature. 461:614–620. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen C, Wei X, Rao X, Wu J, Yang S, Chen
F, Ma D, Zhou J, Dackor RT, Zeldin DC and Wang DW: Cytochrome P450
2J2 is highly expressed in hematologic malignant diseases and
promotes tumor cell growth. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 336:344–355.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Freedman RS, Wang E, Voiculescu S, Patenia
R, Bassett RL Jr, Deavers M, Marincola FM, Yang P and Newman RA:
Comparative analysis of peritoneum and tumor eicosanoids and
pathways in advanced ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:5736–5744.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jiang JG, Ning YG, Chen C, Ma D, Liu ZJ,
Yang S, Zhou J, Xiao X, Zhang XA, Edin ML, et al: Cytochrome p450
epoxygenase promotes human cancer metastasis. Cancer Res.
67:6665–6674. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
El-Serag HB: Hepatocellular carcinoma. N
Engl J Med. 365:1118–1127. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Critelli RM, De Maria N and Villa E:
Biology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Dig Dis. 33:635–641. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kroetz DL and Zeldin DC: Cytochrome P450
pathways of arachidonic acid metabolism. Curr Opin Lipidol.
13:273–283. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Manchado E, Guillamot M and Malumbres M:
Killing cells by targeting mitosis. Cell Death Differ. 19:369–377.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Williams GH and Stoeber K: The cell cycle
and cancer. J Pathol. 226:352–364. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Holohan C, Van Schaeybroeck S, Longley DB
and Johnston PG: Cancer drug resistance: An evolving paradigm. Nat
Rev Cancer. 13:714–726. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gruh I, Wunderlich S, Winkler M, Schwanke
K, Heinke J, Blömer U, Ruhparwar A, Rohde B, Li RK, Haverich A and
Martin U: Human CMV immediate-early enhancer: A useful tool to
enhance cell-type-specific expression from lentiviral vectors. J
Gene Med. 10:21–32. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stead E, White J, Faast R, Conn S,
Goldstone S, Rathjen J, Dhingra U, Rathjen P, Walker D and Dalton
S: Pluripotent cell division cycles are driven by ectopic Cdk2,
cyclin A/E and E2F activities. Oncogene. 21:8320–8333. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee MY, Lim HW, Lee SH and Han HJ: Smad,
PI3K/Akt and Wnt-dependent signaling pathways are involved in
BMP-4-induced ESC self-renewal. Stem Cells. 27:1858–1868. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Altomare DA and Testa JR: Perturbations of
the AKT signaling pathway in human cancer. Oncogene. 24:7455–7464.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades N and Koutsilieris
M: The Akt pathway: Molecular targets for anti-cancer drug
development. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 4:235–256. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Joh EH, Hollenbaugh JA, Kim B and Kim DH:
Pleckstrin homology domain of Akt kinase: A proof of principle for
highly specific and effective non-enzymatic anti-cancer target.
PLoS One. 7:e504242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Milburn CC, Deak M, Kelly SM, Price NC,
Alessi DR and Van Aalten DM: Binding of phosphatidylinositol
3,4,5-trisphosphate to the pleckstrin homology domain of protein
kinase B induces a conformational change. Biochem J. 375:531–538.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Song G, Ouyang G and Bao S: The activation
of Akt/PKB signaling pathway and cell survival. J Cell Mol Med.
9:59–71. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yeo W, Mok TS, Zee B, Leung TW, Lai PB,
Lau WY, Koh J, Mo FK, Yu SC, Chan AT, et al: A randomized phase III
study of doxorubicin versus cisplatin/interferon
alpha-2b/doxorubicin/fluorouracil (PIAF) combination chemotherapy
for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst.
97:1532–1538. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rebbaa A, Zheng X, Chou PM and Mirkin BL:
Caspase inhibition switches doxorubicin-induced apoptosis to
senescence. Oncogene. 22:2805–2811. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Evan GI and Vousden KH: Proliferation,
cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature. 411:342–348. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Takasaki C, Kobayashi M, Ishibashi H,
Akashi T and Okubo K: Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
affects tumor proliferation and antiapoptosis in surgically
resected lung cancer. Mol Clin Oncol. 5:295–300. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guo Y, Wang J, Zhang L, Shen S, Guo R,
Yang Y, Chen W, Wang Y, Chen G and Shuai X: Theranostical
nanosystem-mediated identification of an oncogene and highly
effective therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
63:1240–1255. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ye YW, Zhou Y, Yuan L, Wang CM, Du CY,
Zhou XY, Zheng BQ, Cao X, Sun MH, Fu H and Shi YQ: Fibroblast
growth factor receptor 4 regulates proliferation and antiapoptosis
during gastric cancer progression. Cancer. 117:5304–5313. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|