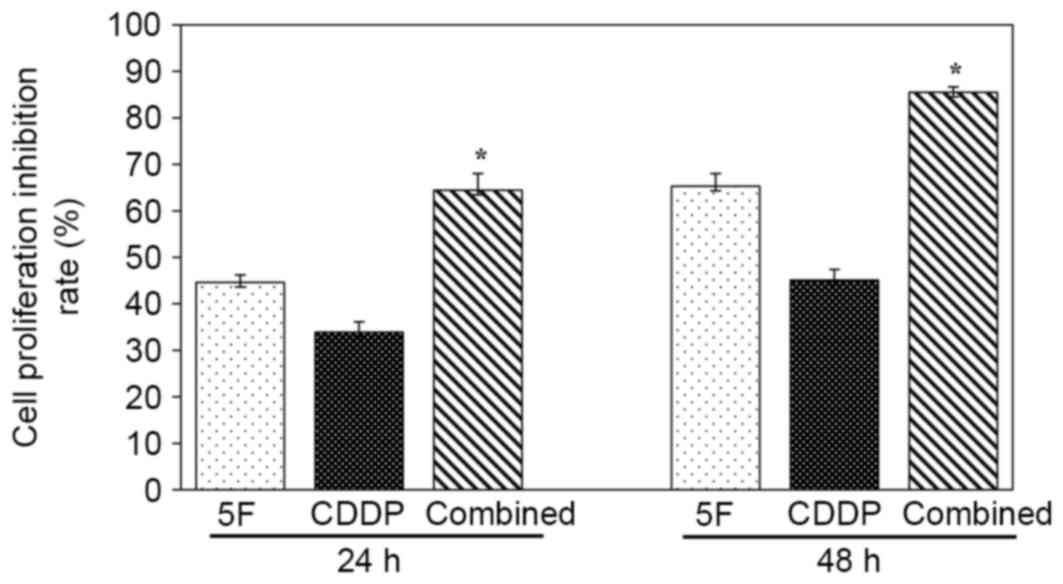
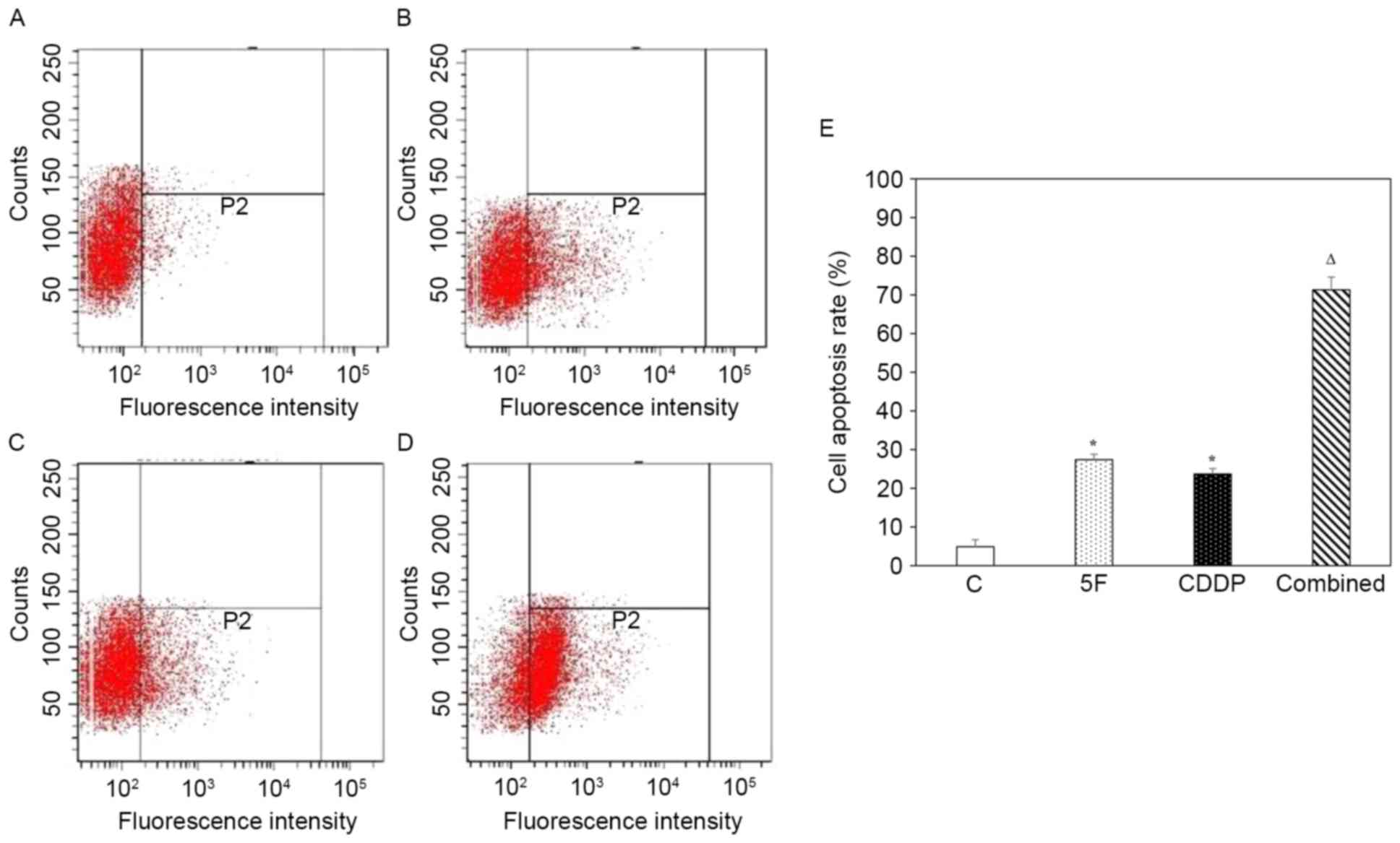
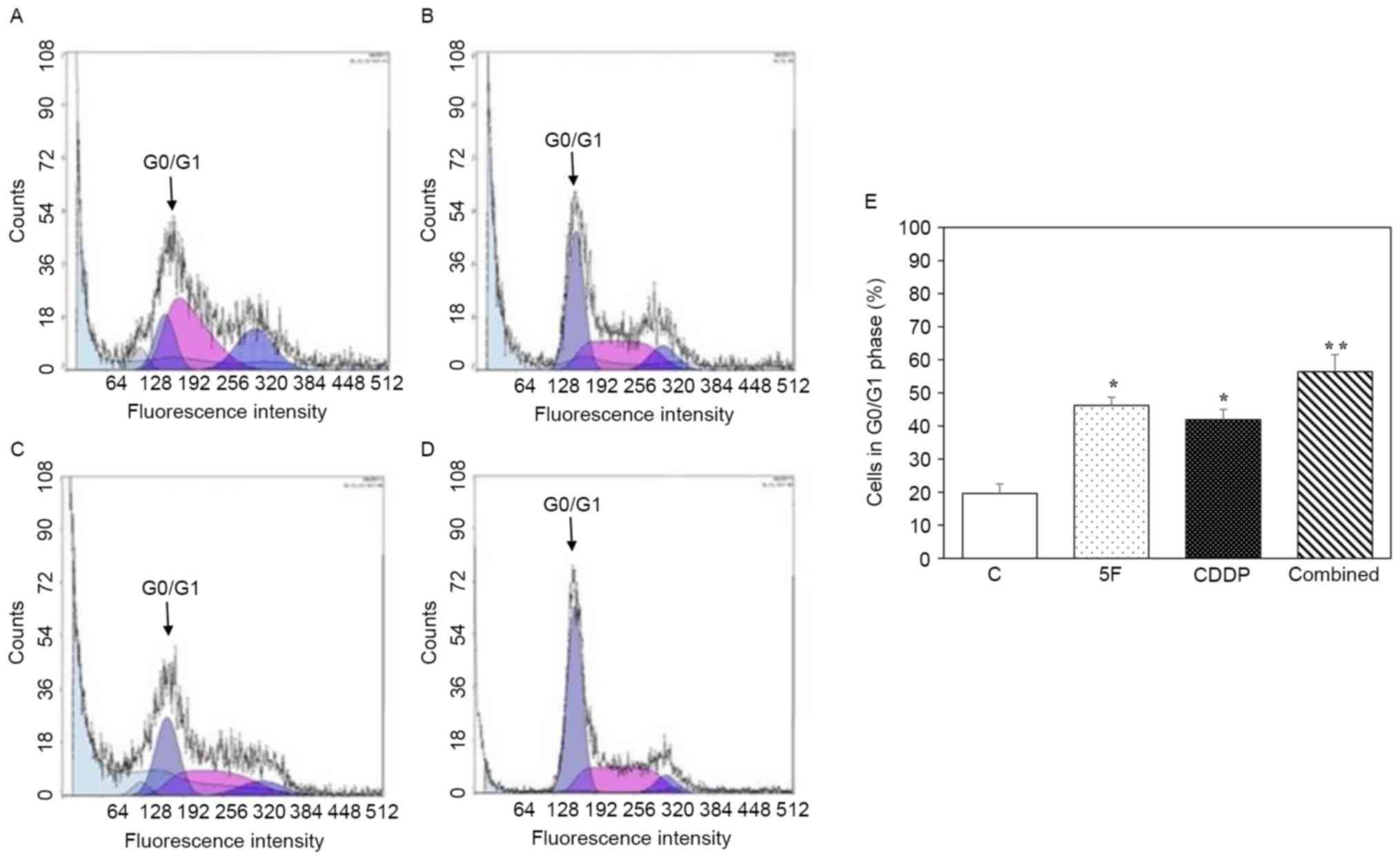
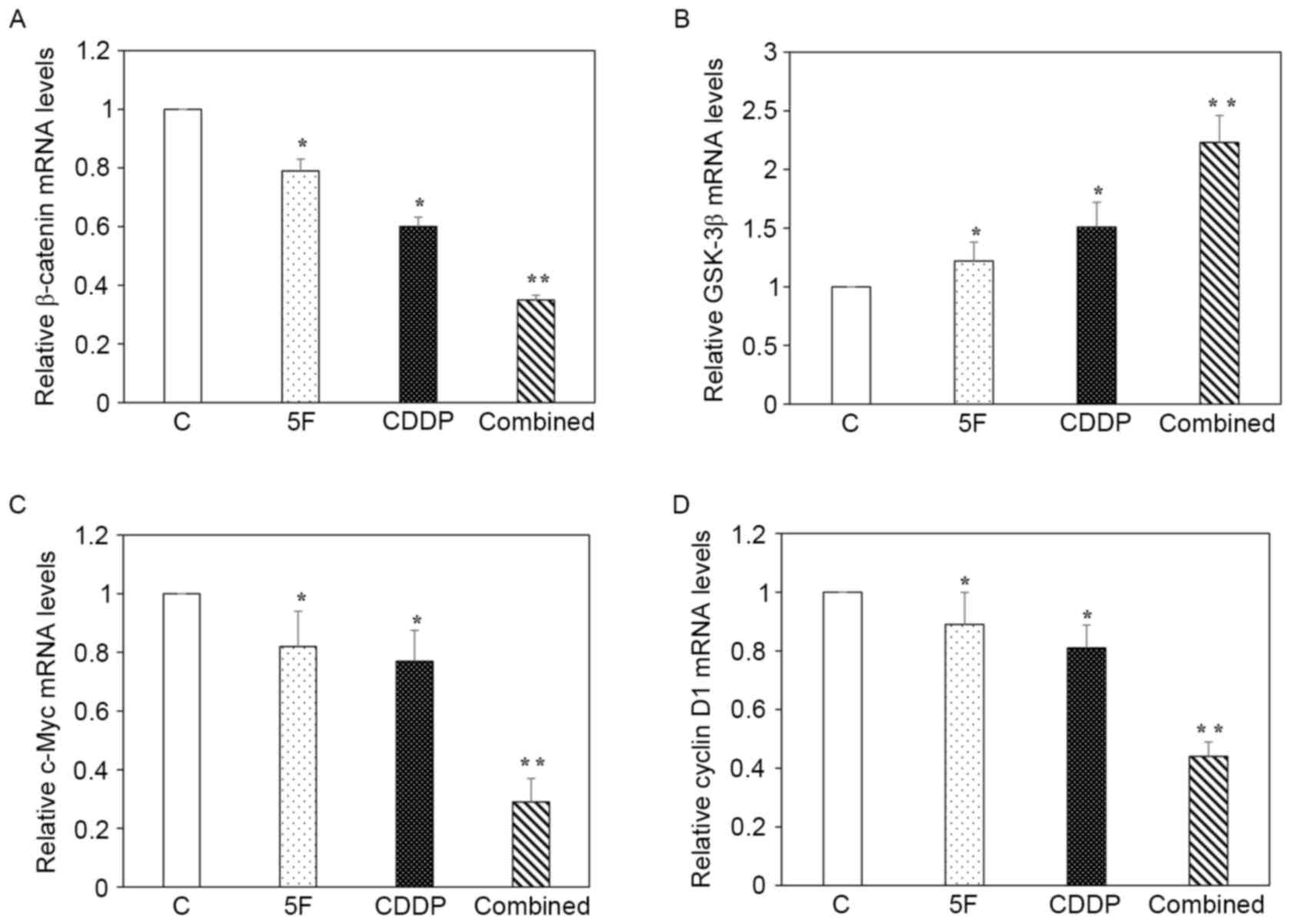
|
1
|
Boolell V, Alamgeer M, Watkins DN and
Ganju V: The evolution of therapies in non-small cell lung cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 7:1815–1846. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ramalingam S and Belani C: Systemic
chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: Recent
advances and future directions. Oncologist. 13 Suppl 1:S5–S13.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP,
Langer C, Sandler A, Krook J, Zhu J and Johnson DH: Eastern
Cooperative Oncology Group: Comparison of four chemotherapy
regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med.
346:92–98. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cullen MH, Billingham LJ, Woodroffe CM,
Chetiyawardana AD, Gower NH, Joshi R, Ferry DR, Rudd RM, Spiro SG,
Cook JE, et al: Mitomycin, ifosfamide, and cisplatin in
unresectable non-small-cell lung cancer: Effects on survival and
quality of life. J Clin Oncol. 17:3188–3194. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Billingham LJ and Cullen MH: The benefits
of chemotherapy in patient subgroups with unresectable
non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 12:1671–1675. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Creagan ET, Woods JE, Schutt AJ and
O'Fallon JR: Cyclophosphamide, adriamycin, and
cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (II) in the treatment of advanced
nonsquamous cell head and neck cancer. Cancer. 52:2007–2010. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Colombo N, Sessa C, Landoni F, Sartori E,
Pecorelli S and Mangioni C: Cisplatin, vinblastine, and bleomycin
combination chemotherapy in metastatic granulosa cell tumor of the
ovary. Obstet Gynecol. 67:265–268. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Decatris MP, Sundar S and O'Byrne KJ:
Platinum-based chemotherapy in metastatic breast cancer: Current
status. Cancer Treat Rev. 30:53–81. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dasari S and Tchounwou PB: Cisplatin in
cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol.
740:364–378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Okamoto I, Miyazaki M, Morinaga R, Kaneda
H, Ueda S, Hasegawa Y, Satoh T, Kawada A, Fukuoka M, Fukino K, et
al: Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of sorafenib in
combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel in patients with
advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Invest New Drugs. 28:844–853.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Han JY, Nam BH, Kim HY, Yoon SJ, Kim HT
and Lee JS: A randomized phase II study of irinotecan plus
cisplatin versus irinotecan plus capecitabine with or without
isosorbide-5-mononitrate in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.
Ann Oncol. 23:2925–2930. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Paz-Ares L, Mezger J, Ciuleanu TE, Fischer
JR, von Pawel J, Provencio M, Kazarnowicz A, Losonczy G, de Castro
G Jr, Szczesna A, et al: Necitumumab plus pemetrexed and cisplatin
as first-line therapy in patients with stage IV non-squamous
non-small-cell lung cancer (INSPIRE): An open-label, randomised,
controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 16:328–337. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li MY, Leung J, Kong AW, Liang NC, Wu K,
Hsin MK, Deng YF, Gong X, Lv Y, Mok TS, et al: Anticancer efficacy
of 5F in NNK-induced lung cancer development of A/J mice and human
lung cancer cells. J Mol Med (Berl). 88:1265–1276. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li MY, Liang NC and Chen GG:
Ent-11alpha-hydroxy-15-oxo-kaur-16-en-19-oic-acid induces apoptosis
of human malignant cancer cells. Curr Drug Targets. 13:1730–1737.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu ZM, Chen GG, Vlantis AC, Liang NC,
Deng YF and van Hasselt CA: Cell death induced by
ent-11alpha-hydroxy-15-oxo-kaur-16-en-19-oic-acid in anaplastic
thyroid carcinoma cells is via a mitochondrial-mediated pathway.
Apoptosis. 10:1345–1356. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu K, Liu Y, Lv Y, Cui L, Li W, Chen J,
Liang NC and Li L: Ent-11α-hydroxy-15-oxo-kaur-16-en-19-oic-acid
induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in CNE-2Z nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 29:2101–2108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ye H, Wu Q, Guo M, Wu K, Lv Y, Yu F, Liu
Y, Gao X, Zhu Y, Cui L, et al: Growth inhibition effects of
ent-11α-hydroxy-15-oxo-kaur-16-en-19-oic-acid on colorectal
carcinoma cells and colon carcinoma-bearing mice. Mol Med Rep.
13:3525–3532. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen GG, Leung J, Liang NC, Li L, Wu K,
Chan UP, Leung BC, Li M, Du J, Deng YF, et al:
Ent-11α-hydroxy-15-oxo-kaur-16-en-19-oic-acid inhibits
hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo via stabilizing IkBα.
Invest New Drugs. 30:2210–2218. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lu Y, Wu K, Liang N and Chen GG: LC method
for quantification of ent-11α-Hydroxy-15-oxo-kaur-16-en-19-oic acid
in rabbit plasma: Validation and application to a pharmacokinetic
study. Chromatographia. 70:15992009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Alamgeer M, Ganju V and Watkins DN: Novel
therapeutic targets in non-small cell lung cancer. Curr Opin
Pharmacol. 13:394–401. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Akiri G, Cherian MM, Vijayakumar S, Liu G,
Bafico A and Aaronson SA: Wnt pathway aberrations including
autocrine Wnt activation occur at high frequency in human
non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Oncogene. 28:2163–2172. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
de Castria TB, da Silva EM, Gois AF and
Riera R: Cisplatin versus carboplatin in combination with
third-generation drugs for advanced non-small cell lung cancer.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev: CD009256. 2013.doi:
10.1002/14651858.CD009256.pub2. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Byun JM, Jeong DH, Lee DS, Kim JR, Park
SG, Kang MS, Kim YN, Lee KB, Sung MS and Kim KT: Tetraarsenic oxide
and cisplatin induce apoptotic synergism in cervical cancer. Oncol
Rep. 29:1540–1546. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nusse R and Varmus HE: Wnt genes. Cell.
69:1073–1087. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gao C and Chen YG: Dishevelled: The hub of
Wnt signaling. Cell Signal. 22:717–727. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wong HC, Bourdelas A, Krauss A, Lee HJ,
Shao Y, Wu D, Mlodzik M, Shi DL and Zheng J: Direct binding of the
PDZ domain of Dishevelled to a conserved internal sequence in the
C-terminal region of Frizzled. Mol Cell. 12:1251–1260. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gordon MD and Nusse R: Wnt signaling:
Multiple pathways, multiple receptors, and multiple transcription
factors. J Biol Chem. 281:22429–22433. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
MacDonald BT, Tamai K and He X:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases.
Dev Cell. 17:9–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Alao JP: The regulation of cyclin D1
degradation: Roles in cancer development and the potential for
therapeutic invention. Mol Cancer. 6:242007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Diehl JA: Cycling to cancer with cyclin
D1. Cancer Biol Ther. 1:226–231. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Meyer N and Penn LZ: Reflecting on 25
years with MYC. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:976–990. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nesbit CE, Tersak JM and Prochownik EV:
MYC oncogenes and human neoplastic disease. Oncogene. 18:3004–3016.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|