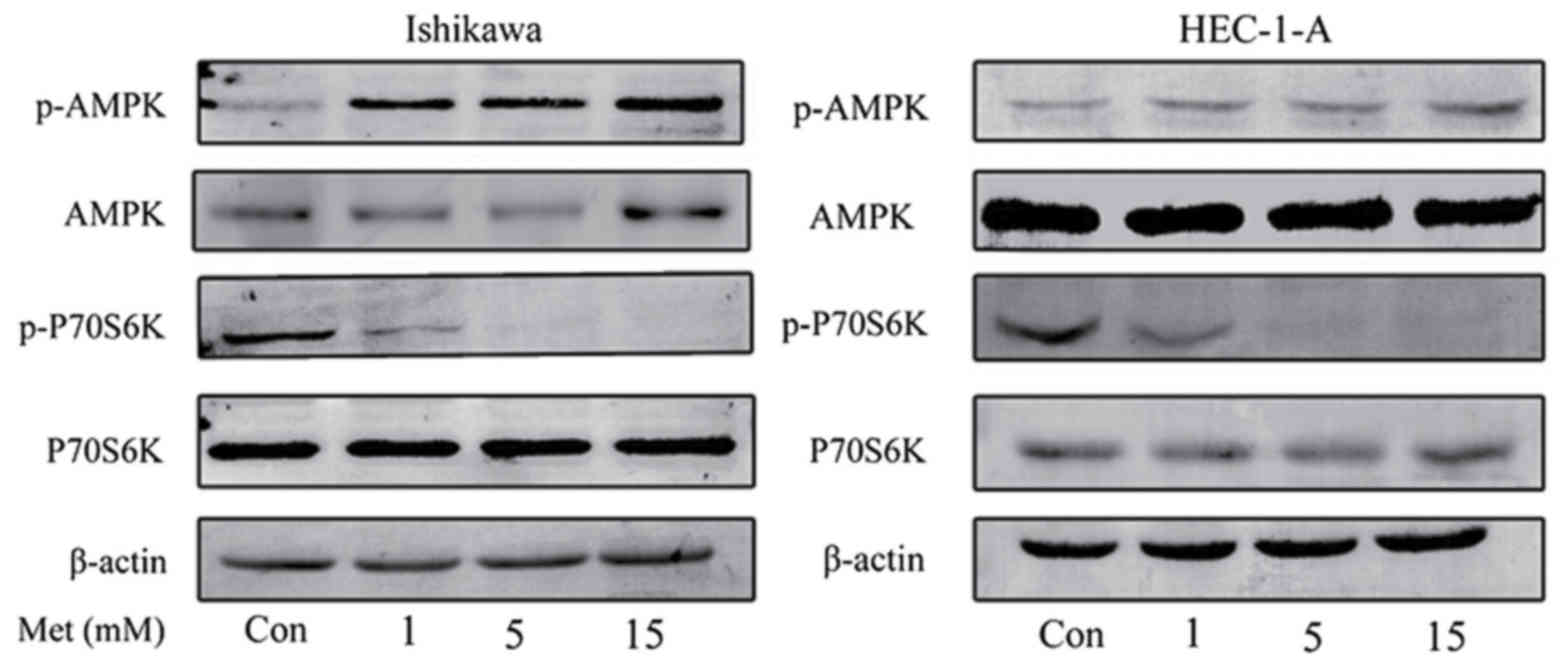
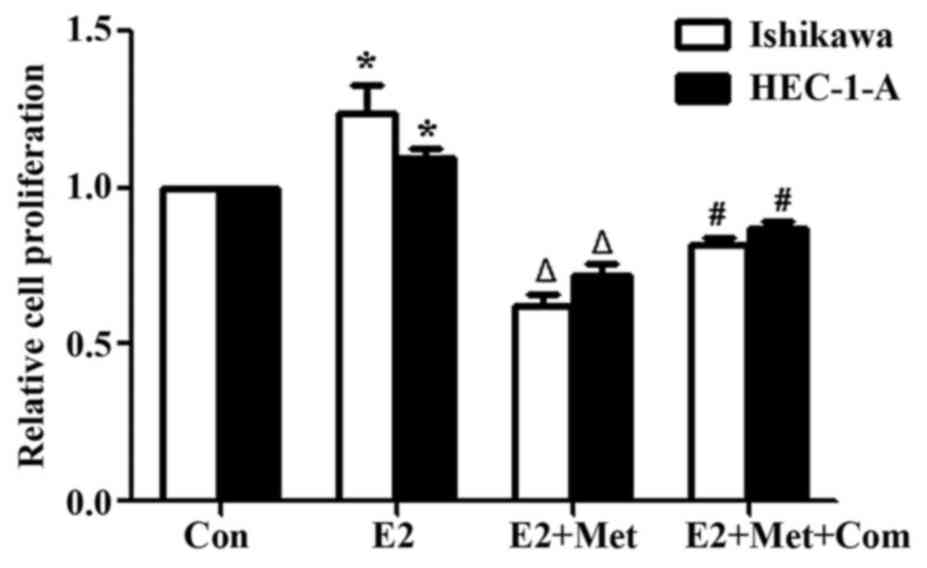
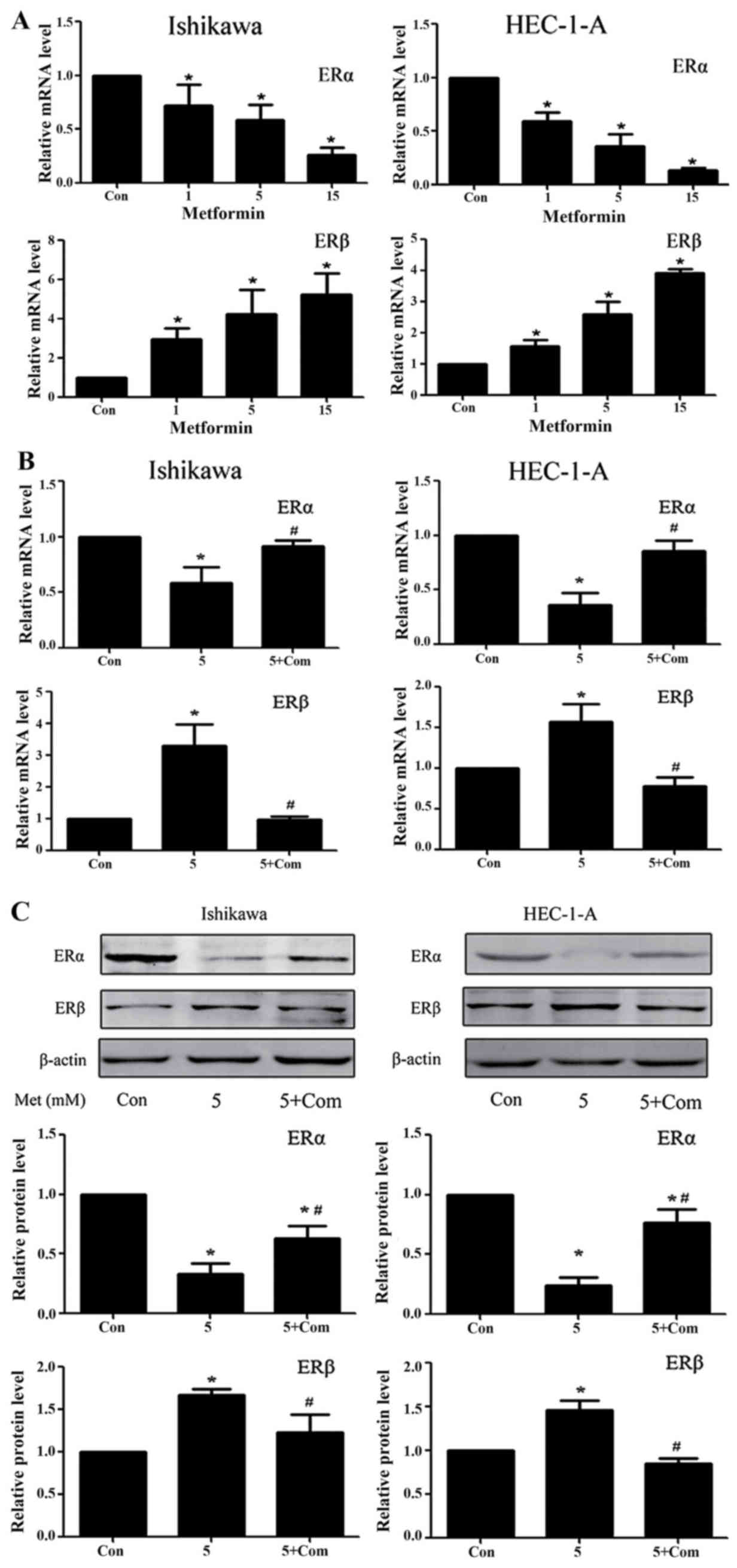
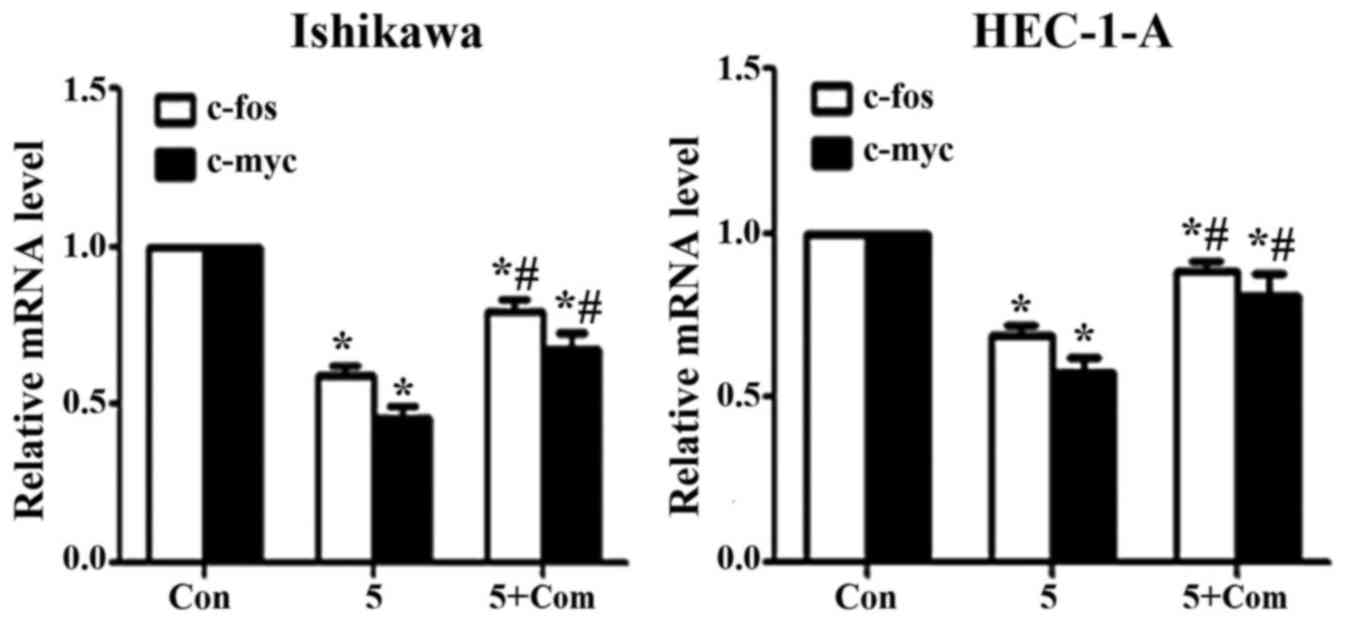
|
1
|
Fader AN, Arriba LN, Frasure HE and von
Gruenigen VE: Endometrial cancer and obesity: Epidemiology,
biomarkers, prevention and survivorship. Gynecol Oncol.
114:121–127. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rižner T: Estrogen biosynthesis, phase I
and phase II metabolism, and action in endometrial cancer. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 381:124–139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Klinge CM: Estrogen receptor interaction
with estrogen response elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 29:2905–2919.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sakaguchi H, Fujimoto J, Aoki I, Toyoki H,
Khatun S and Tamaya T: Expression of oestrogen receptor alpha and
beta in uterine endometrial and ovarian cancers. Eur J Cancer. 38
Suppl 6:S74–S75. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Utsunomiya H, Suzuki T, Harada N, Ito K,
Matsuzaki S, Konno R, Sato S, Yajima A and Sasano H: Analysis of
estrogen receptor alpha and beta in endometrial carcinomas:
Correlation with ER beta and clinicopathologic findings in 45
cases. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 19:335–341. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hu K, Zhong G and He F: Expression of
estrogen receptors ERalpha and ERbeta in endometrial hyperplasia
and adenocarcinoma. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 15:537–541. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Saegusa M and Okayasu I: Changes in
expression of estrogen receptors alpha and beta in relation to
progesterone receptor and pS2 status in normal and malignant
endometrium. Jpn J Cancer Res. 91:510–518. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bolton JL and Thatcher GR: Potential
mechanisms of estrogen quinone carcinogenesis. Chem Res Toxicol.
21:93–101. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hammes SR and Levin ER: Minireview: Recent
advances in extranuclear steroid receptor actions. Endocrinology.
152:4489–4495. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Prossnitz ER and Barton M: The
G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor GPER in health and disease. Nat
Rev Endocrinol. 7:715–726. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yamashita S, Takayanagi A and Shimizu N:
Temporal and cell-type specific expression of c-fos and c-jun
protooncogenes in the mouse uterus after estrogen stimulation.
Endocrinology. 137:5468–5475. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bjørge T, Lukanova A, Jonsson H, Tretli S,
Ulmer H, Manjer J, Stocks T, Selmer R, Nagel G, Almquist M, et al:
Metabolic syndrome and breast cancer in the me-can (metabolic
syndrome and cancer) project. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
19:1737–1745. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Del Barco S, Vazquez-Martin A, Cufi S,
Oliveras-Ferraros C, Bosch-Barrera J, Joven J, Martin-Castillo B
and Menendez JA: Metformin: Multi-faceted protection against
cancer. Oncotarget. 2:896–917. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dowling RJ, Goodwin PJ and Stambolic V:
Understanding the benefit of metformin use in cancer treatment. BMC
Med. 9:332011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rocha GZ, Dias MM, Ropelle ER,
Osório-Costa F, Rossato FA, Vercesi AE, Saad MJ and Carvalheira JB:
Metformin amplifies chemotherapy-induced AMPK activation and
antitumoral growth. Clin Cancer Res. 17:3993–4005. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cantrell LA, Zhou C, Mendivil A, Malloy
KM, Gehrig PA and Bae-Jump VL: Metformin is a potent inhibitor of
endometrial cancer cell proliferation-implications for a novel
treatment strategy. Gynecol Oncol. 116:92–98. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang Q, Celestino J, Schmandt R,
McCampbell AS, Urbauer DL, Meyer LA, Burzawa JK, Huang M, Yates MS,
Iglesias D, et al: Chemopreventive effects of metformin on
obesity-associated endometrial proliferation. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
209:24.e1–24.e12. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Dowling RJ, Zakikhani M, Fantus IG, Pollak
M and Sonenberg N: Metformin inhibits mammalian target of
rapamycin-dependent translation initiation in breast cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 67:10804–10812. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Viollet B, Guigas B, Garcia Sanz N,
Leclerc J, Foretz M and Andreelli F: Cellular and molecular
mechanisms of metformin: An overview. Clin Sci (Lond). 122:253–270.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Esteva FJ, Moulder SL, Gonzalez-Angulo AM,
Ensor J, Murray JL, Green MC, Koenig KB, Lee MH, Hortobagyi GN and
Yeung SC: Phase I trial of exemestane in combination with metformin
and rosiglitazone in nondiabetic obese postmenopausal women with
hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 71:63–72. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Campagnoli C, Berrino F, Venturelli E,
Abbà C, Biglia N, Brucato T, Cogliati P, Danese S, Donadio M, Zito
G and Pasanisi P: Metformin decreases circulating androgen and
estrogen levels in nondiabetic women with breast cancer. Clin
Breast Cancer. 13:433–438. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Markowska A, Pawałowska M, Filas V, Korski
K, Gryboś M, Sajdak S, Olejek A, Bednarek W, Spiewankiewicz B,
Lubin J and Markowska J: Does Metformin affect ER, PR, IGF-1R,
β-catenin and PAX-2 expression in women with diabetes mellitus and
endometrial cancer? Diabetol Metab Syndr. 5:762013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xie Y, Wang YL, Yu L, Hu Q, Ji L, Zhang Y
and Liao QP: Metformin promotes progesterone receptor expression
via inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in
endometrial cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 126:113–120.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang J, Zhang B, Yin Z, Chen F, Liu T, Xu
H, Liu Y and Zhou X: Effects of metformin on the estrogen-induced
proliferation and the expression of ER in human endometrial cancer
cells. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 49:932–937. 2014.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Emerling BM, Viollet B, Tormos KV and
Chandel NS: Compound C inhibits hypoxic activation of HIF-1
independent of AMPK. FEBS Lett. 581:5727–5731. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jefferies HB, Fumagalli S, Dennis PB,
Reinhard C, Pearson RB and Thomas G: Rapamycin suppresses 5′TOP
mRNA translation through inhibition of p70s6k. EMBO J.
16:3693–3704. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ellenson LH and Wu TC: Focus on
endometrial and cervical cancer. Cancer Cell. 5:533–538. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Farnell YZ and Ing NH: The effects of
estradiol and selective estrogen receptor modulators on gene
expression and messenger RNA stability in immortalized sheep
endometrial stromal cells and human endometrial adenocarcinoma
cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 84:453–461. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Soliman PT, Wu D, Tortolero-Luna G,
Schmeler KM, Slomovitz BM, Bray MS, Gershenson DM and Lu KH:
Association between adiponectin, insulin resistance, and
endometrial cancer. Cancer. 106:2376–2381. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zakikhani M, Dowling RJ, Sonenberg N and
Pollak MN: The effects of adiponectin and metformin on prostate and
colon neoplasia involve activation of AMP-activated protein kinase.
Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 1:369–375. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gotlieb WH, Saumet J, Beauchamp MC, Gu J,
Lau S, Pollak MN and Bruchim I: In vitro metformin anti-neoplastic
activity in epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 110:246–250.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Terry KL and Missmer SA: Epidemiology of
ovarian and endometrial cancers. Pathol Epidemiol Cancer. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhao H, Jiang Y, Liu Y, Yun C and Li L:
Endogenous estrogen metabolites as biomarkers for endometrial
cancer via a novel method of liquid chromatography-mass
spectrometry with hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction. Horm
Metab Res. 47:158–164. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Patel SM, Iqbal N, Kaul S, Ratcliffe SJ,
Rickels MR, Reilly MP, Scattergood T, Basu A, Fuller C and Cappola
AR: The effects of metformin and leuprolide acetate on insulin
resistance and testosterone levels in non-diabetic postmenopausal
women: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Fertil Steril.
94:2161–2166. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Brown KA, Hunger NI, Docanto M and Simpson
ER: Metformin inhibits aromatase expression in human breast adipose
stromal cells via stimulation of AMP-activated protein kinase.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 123:591–596. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Erdemoglu E, Güney M, Giray SG, Take G and
Mungan T: Effects of metformin on mammalian target of rapamycin in
a mouse model of endometrial hyperplasia. Eur J Obstet Gynecol
Reprod Biol. 145:195–199. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Burns KA and Korach KS: Estrogen receptors
and human disease: An update. Arch Toxicol. 86:1491–1504. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ström A, Hartman J, Foster JS, Kietz S,
Wimalasena J and Gustafsson JA: Estrogen receptor beta inhibits
17beta-estradiol-stimulated proliferation of the breast cancer cell
line T47D. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:1566–1571. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Helguero LA, Faulds MH, Gustafsson JA and
Haldosén LA: Estrogen receptors alfa (ERalpha) and beta (ERbeta)
differentially regulate proliferation and apoptosis of the normal
murine mammary epithelial cell line HC11. Oncogene. 24:6605–6616.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Paruthiyil S, Parmar H, Kerekatte V, Cunha
GR, Firestone GL and Leitman DC: Estrogen receptor beta inhibits
human breast cancer cell proliferation and tumor formation by
causing a G2 cell cycle arrest. Cancer Res. 64:423–428. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Grober OM, Mutarelli M, Giurato G, Ravo M,
Cicatiello L, De Filippo MR, Ferraro L, Nassa G, Papa MF, Paris O,
et al: Global analysis of estrogen receptor beta binding to breast
cancer cell genome reveals an extensive interplay with estrogen
receptor alpha for target gene regulation. BMC Genomics. 12:362011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Matthews J and Gustafsson JA: Estrogen
signaling: A subtle balance between ER alpha and ER beta. Mol
Interv. 3:281–292. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ali SH, O'Donnell AL, Balu D, Pohl MB,
Seyler MJ, Mohamed S, Mousa S and Dandona P: Estrogen
receptor-alpha in the inhibition of cancer growth and angiogenesis.
Cancer Res. 60:7094–7098. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ali SH, O'Donnell AL, Balu D, Pohl MB,
Seyler MJ, Mohamed S, Mousa S and Dandona P: High levels of
oestrogen receptor-alpha in tumorigenesis: Inhibition of cell
growth and angiogenic factors. Cell Prolif. 34:223–231. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Loose-Mitchell DS, Chiappetta C and
Stancel GM: Estrogen regulation of c-fos messenger ribonucleic
acid. Mol Endocrinol. 2:946–951. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Murphy LJ, Murphy LC and Friesen HG:
Estrogen induction of N-myc and c-myc proto-oncogene expression in
the rat uterus. Endocrinology. 120:1882–1888. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Weisz A, Cicatiello L, Persico E, Scalona
M and Bresciani F: Estrogen stimulates transcription of c-jun
protooncogene. Mol Endocrinol. 4:1041–1050. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Akinyeke T, Matsumura S, Wang X, Wu Y,
Schalfer ED, Saxena A, Yan W, Logan SK and Li X: Metformin targets
c-MYC oncogene to prevent prostate cancer. Carcinogenesis.
34:2823–2832. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Blandino G, Valerio M, Cioce M, Mori F,
Casadei L, Pulito C, Sacconi A, Biagioni F, Cortese G, Galanti S,
et al: Metformin elicits anticancer effects through the sequential
modulation of DICER and c-MYC. Nat Commun. 3:8652012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Dang CV: MYC on the path to cancer. Cell.
149:22–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|