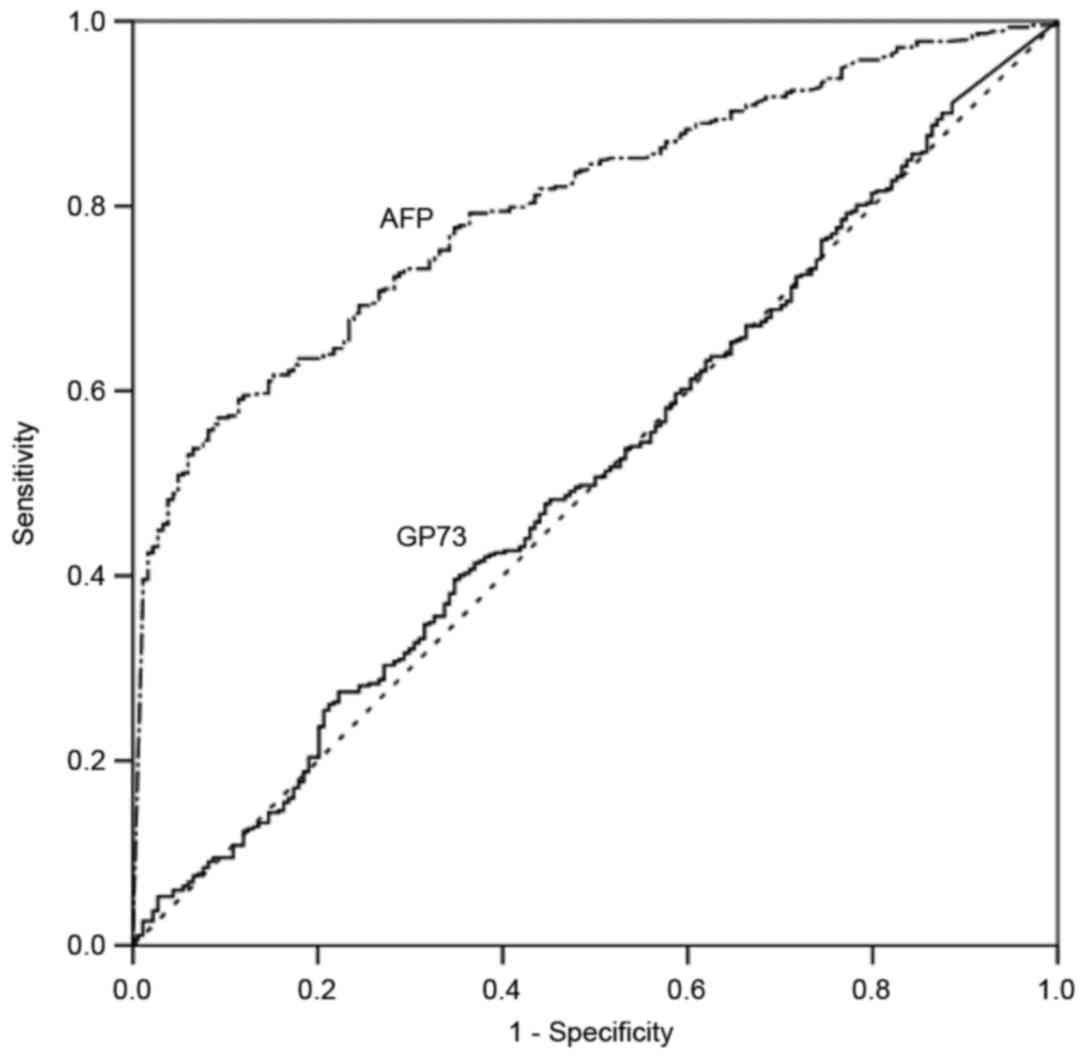
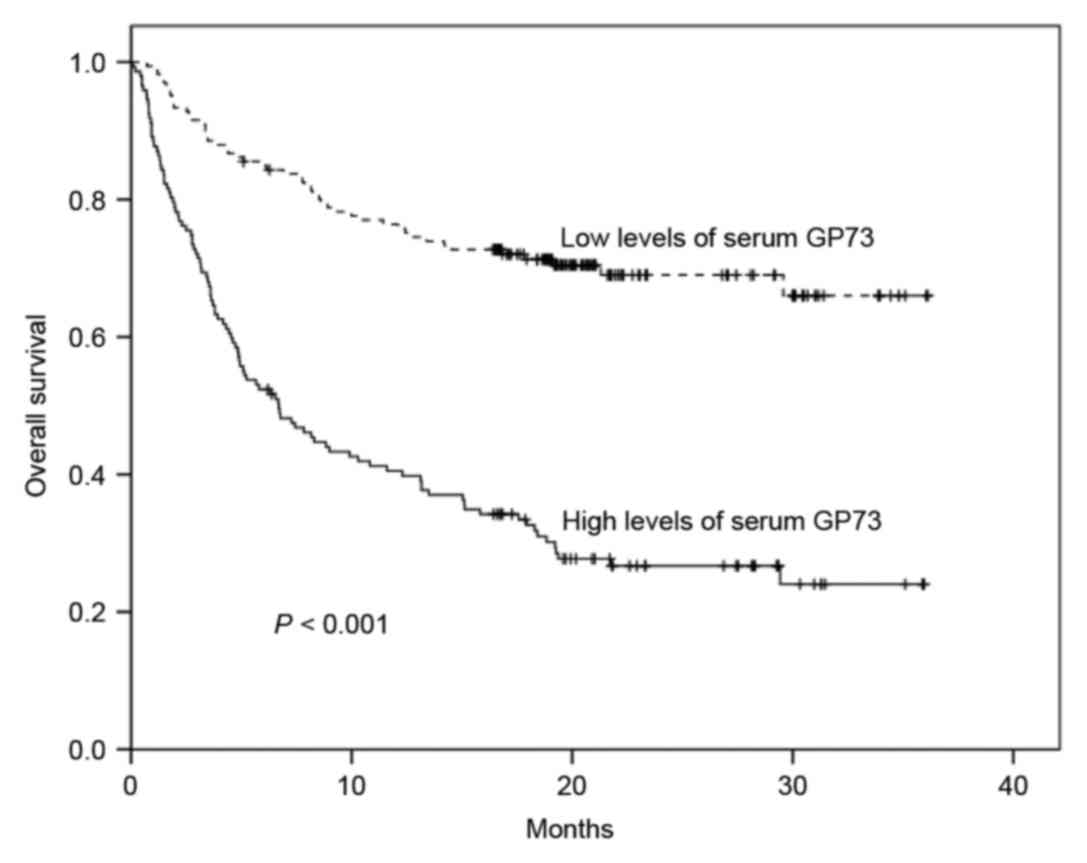
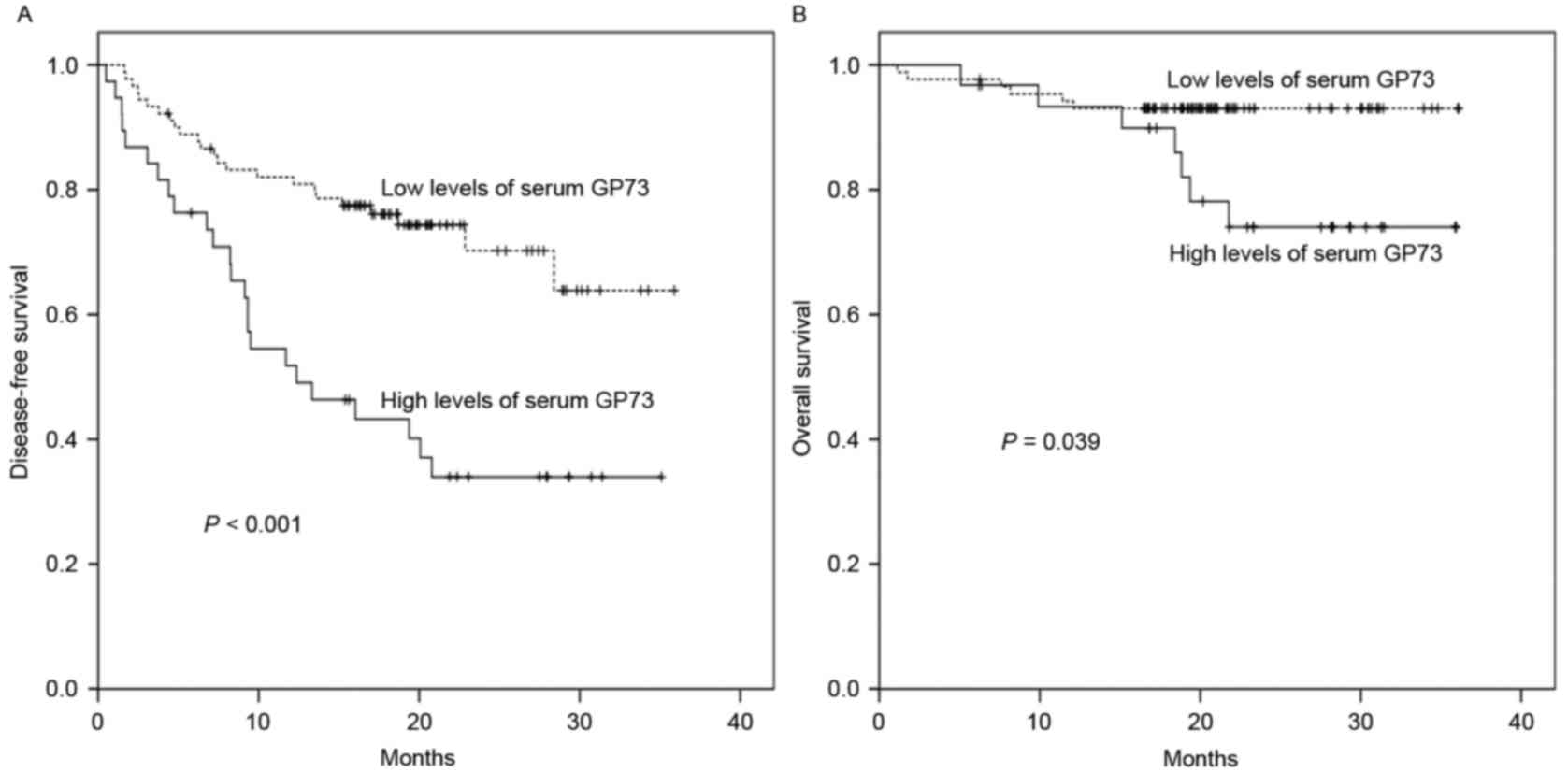
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shariff MI, Cox IJ, Gomaa AI, Khan SA,
Gedroyc W and Taylor-Robinson SD: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Current
trends in worldwide epidemiology, risk factors, diagnosis and
therapeutics. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 3:353–367. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zeng H, Zheng R, Guo Y, Zhang S, Zou X,
Wang N, Zhang L, Tang J, Chen J, Wei K, et al: Cancer survival in
China, 2003–2005: A population-based study. Int J Cancer.
136:1921–1930. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ercolani G, Grazi GL, Ravaioli M, Del
Gaudio M, Gardini A, Cescon M, Varotti G, Cetta F and Cavallari A:
Liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma on cirrhosis:
Univariate and multivariate analysis of risk factors for
intrahepatic recurrence. Ann Surg. 237:536–543. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Debruyne EN and Delanghe JR: Diagnosing
and monitoring hepatocellular carcinoma with alpha-fetoprotein: New
aspects and applications. Clin Chim Acta. 395:19–26. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Aoyagi Y, Suzuki Y, Isemura M, Nomoto M,
Sekine C, Igarashi K and Ichida F: The fucosylation index of
alpha-fetoprotein and its usefulness in the early diagnosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 61:769–774. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nakagawa T, Seki T, Shiro T, Wakabayashi
M, Imamura M, Itoh T, Tamai T, Nishimura A, Yamashiki N, Matsuzaki
K, et al: Clinicopathologic significance of protein induced vitamin
K absence or antagonist II and alpha-fetoprotein in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 14:281–286. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Giardina MG, Matarazzo M, Varriale A,
Morante R, Napoli A and Martino R: Serum alpha-L-fucosidase. A
useful marker in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer.
70:1044–1048. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu ZW, Friess H, Wang L, Abou-Shady M,
Zimmermann A, Lander AD, Korc M, Kleeff J and Büchler MW: Enhanced
glypican-3 expression differentiates the majority of hepatocellular
carcinomas from benign hepatic disorders. Gut. 48:558–564. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Giannelli G, Marinosci F, Sgarra C, Lupo
L, Dentico P and Antonaci S: Clinical role of tissue and serum
levels of SCCA antigen in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer.
116:579–583. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mao Y, Yang H, Xu H, Lu X, Sang X, Du S,
Zhao H, Chen W, Xu Y, Chi T, et al: Golgi protein 73 (GOLPH2) is a
valuable serum marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut.
59:1687–1693. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kladney RD, Cui X, Bulla GA, Brunt EM and
Fimmel CJ: Expression of GP73, a resident Golgi membrane protein,
in viral and nonviral liver disease. Hepatology. 35:1431–1440.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Iftikhar R, Kladney RD, Havlioglu N,
Schmitt-Gräff A, Gusmirovic I, Solomon H, Luxon BA, Bacon BR and
Fimmel CJ: Disease- and cell-specific expression of GP73 in human
liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 99:1087–1095. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bao YX, Cao Q, Yang Y, Mao R, Xiao L,
Zhang H, Zhao HR and Wen H: Expression and prognostic significance
of golgiglycoprotein 73 (GP73) with epithelial-mesenchymal
transition (EMT) related molecules in hepatocellular carcinoma
(HCC). Diagn Pathol. 8:1972013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shan SG, Gao YT, Xu YJ, Huang Y, Zhang Q,
Zhai DK, Li JB, Wang FM, Jing X, Du Z and Wang YJ: Gradually
increased Golgi protein 73 expression in the progression of benign
liver diseases to precancerous lesions and hepatocellular carcinoma
correlates with prognosis of patients. Hepatol Res. 43:1199–1210.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bachert C, Fimmel C and Linstedt AD:
Endosomal trafficking and proprotein convertase cleavage of cis
Golgi protein GP73 produces marker for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Traffic. 8:1415–1423. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Block TM, Comunale MA, Lowman M, Steel LF,
Romano PR, Fimmel C, Tennant BC, London WT, Evans AA, Blumberg BS,
et al: Use of targeted glycoproteomics to identify serum
glycoproteins that correlate with liver cancer in woodchucks and
humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:779–784. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Marrero JA, Romano PR, Nikolaeva O, Steel
L, Mehta A, Fimmel CJ, Comunale MA, D'Amelio A, Lok AS and Block
TM: GP73, a resident Golgi glycoprotein, is a novel serum marker
for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 43:1007–1012. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shi Y, Chen J, Li L, Sun Z, Zen L, Xu S,
Zhang Y and Zhang L: A study of diagnostic value of golgi protein
GP73 and its genetic assay in primary hepatic carcinoma. Technol
Cancer Res Treat. 10:287–294. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu WJ, Guo BL, Han YG, Shi L and Ma WS:
Diagnostic value of alpha-fetoprotein-L3 and Golgi protein 73 in
hepatocellular carcinomas with low AFP levels. Tumour Biol.
35:12069–12074. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hou SC, Xiao MB, Ni RZ, Ni WK, Jiang F, Li
XY, Lu CH and Chen BY: Serum GP73 is complementary to AFP and
GGT-II for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett.
6:1152–1158. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gu Y, Chen W, Zhao Y, Chen L and Peng T:
Quantitative analysis of elevated serum Golgi protein-73 expression
in patients with liver diseases. Ann Clin Biochem. 46:38–43. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Riener MO, Stenner F, Liewen H, Soll C,
Breitenstein S, Pestalozzi BC, Samaras P, Probst-Hensch N,
Hellerbrand C, Müllhaupt B, et al: Golgi phosphoprotein 2 (GOLPH2)
expression in liver tumors and its value as a serum marker in
hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatology. 49:1602–1609. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bröker ME, Ijzermans JN, Witjes CD, van
Vuuren HJ and de Man RA: The predictive value of Golgi protein 73
in differentiating benign from malignant liver tumors. PLoS One.
9:e1001872014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tian L, Wang Y, Xu D, Gui J, Jia X, Tong
H, Wen X, Dong Z and Tian Y: Serological AFP/Golgi protein 73 could
be a new diagnostic parameter of hepatic diseases. Int J Cancer.
129:1923–1931. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kristiansen G, Fritzsche FR, Wassermann K,
Jäger C, Tölls A, Lein M, Stephan C, Jung K, Pilarsky C, Dietel M
and Moch H: GOLPH2 protein expression as a novel tissue biomarker
for prostate cancer: Implications for tissue-based diagnostics. Br
J Cancer. 99:939–948. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xu Z, Liu L, Pan X, Wei K, Wei M, Liu L,
Yang H and Liu Q: Serum Golgi protein 73 (GP73) is a diagnostic and
prognostic marker of chronic HBV liver disease. Medicine
(Baltimore). 94:e6592015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen X, Wang Y, Tao J, Shi Y, Gai X, Huang
F, Ma Q, Zhou Z, Chen H, Zhang H, et al: mTORC1 Up-Regulates GP73
to promote proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma
cells and growth of xenograft tumors in mice. Gastroenterology.
149:741–52.e14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jin D, Tao J, Li D, Wang Y, Li L, Hu Z,
Zhou Z, Chang X, Qu C and Zhang H: Golgi protein 73 activation of
MMP-13 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion. Oncotarget.
6:33523–33533. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|