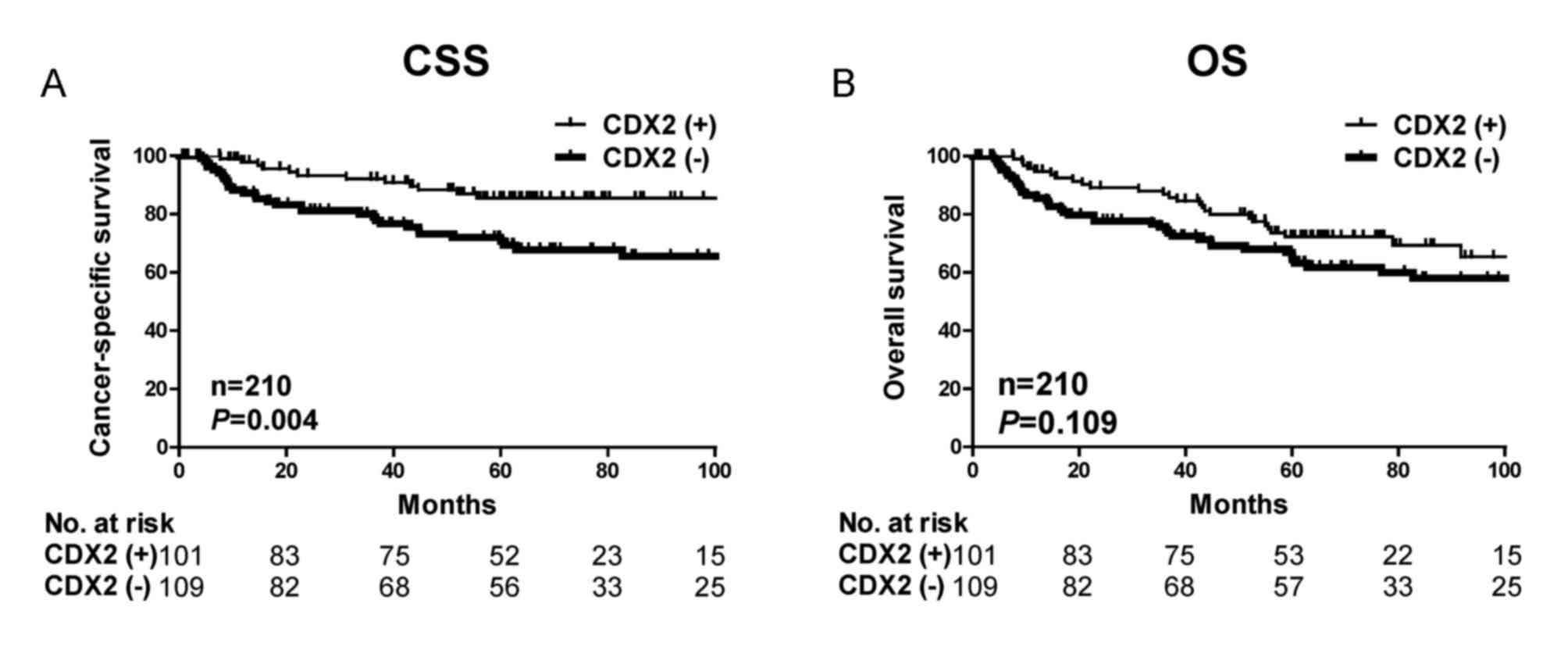
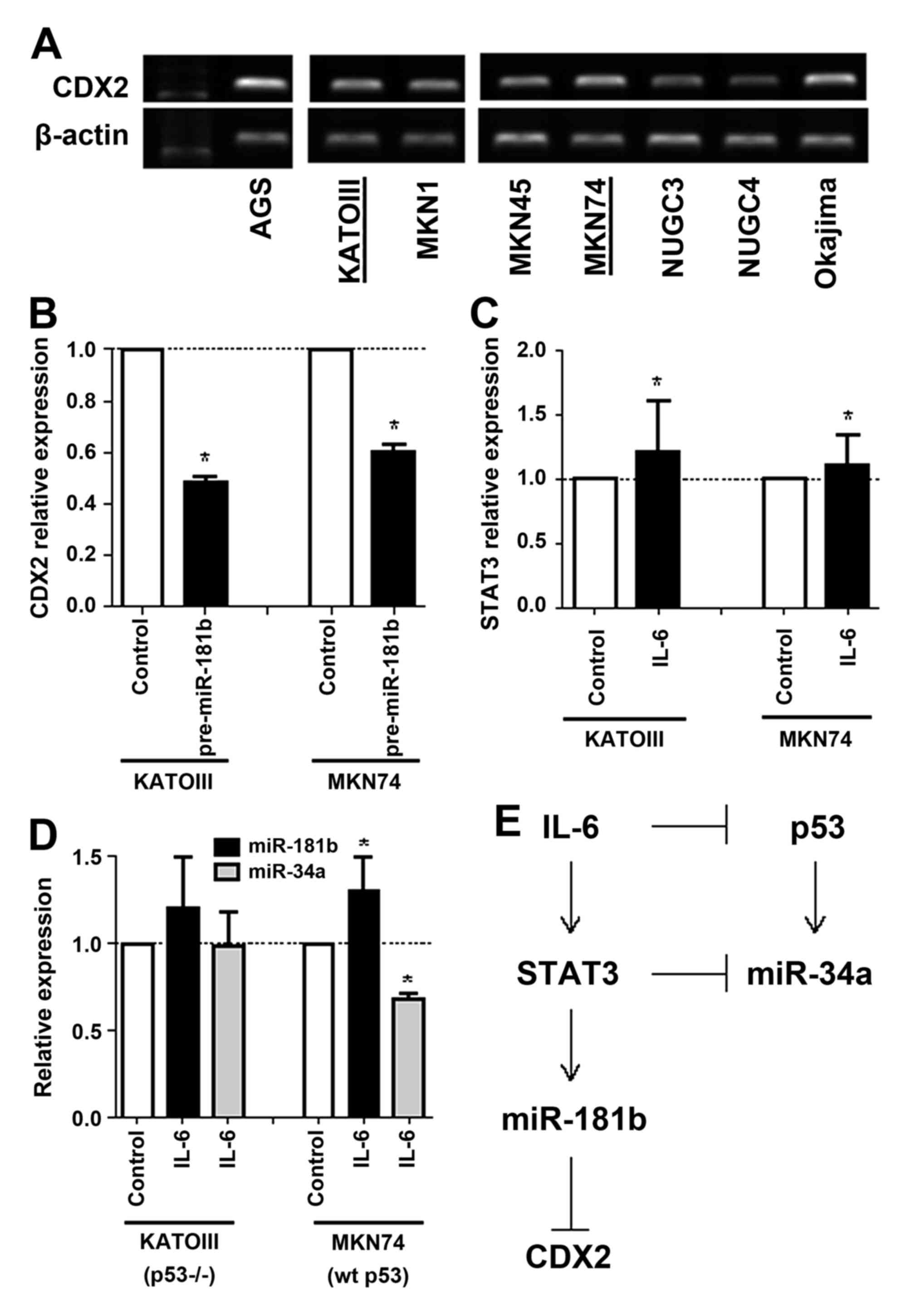
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Sauer AM, Chen MS Jr,
Kagawa-Singer M, Jemal A and Siegel RL: Cancer statistics for Asian
Americans, Native Hawaiians, and Pacific Islanders, 2016:
Converging incidence in males and females. CA Cancer J Clin.
66:182–202. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Polk DB and Peek RM Jr: Helicobacter
pylori: Gastric cancer and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:403–414.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schetter AJ, Heegaard NH and Harris CC:
Inflammation and cancer: Interweaving microRNA, free radical,
cytokine and p53 pathways. Carcinogenesis. 31:37–49. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Okayama H, Kumamoto K, Saitou K, Hayase S,
Kofunato Y, Sato Y, Miyamoto K, Nakamura I, Ohki S, Sekikawa K and
Takenoshita S: CD44v6, MMP-7 and nuclear Cdx2 are significant
biomarkers for prediction of lymph node metastasis in primary
gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 22:745–755. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu Q, Teh M, Ito K, Shah N, Ito Y and
Yeoh KG: CDX2 expression is progressively decreased in human
gastric intestinal metaplasia, dysplasia and cancer. Mod Pathol.
20:1286–1297. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bai Z, Ye Y, Chen D, Shen D, Xu F, Cui Z
and Wang S: Homeoprotein Cdx2 and nuclear PTEN expression profiles
are related to gastric cancer prognosis. APMIS. 115:1383–1390.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fan Z, Li J, Dong B and Huang X:
Expression of Cdx2 and hepatocyte antigen in gastric carcinoma:
Correlation with histologic type and implications for prognosis.
Clin Cancer Res. 11:6162–6170. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ge J and Chen Z, Wu S, Yuan W, Hu B and
Chen Z: A clinicopathological study on the expression of
cadherin-17 and caudal-related homeobox transcription factor (CDX2)
in human gastric carcinoma. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 20:275–283.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang X, Tsukamoto T, Mizoshita T, Ban H,
Suzuki H, Toyoda T and Tatematsu M: Expression of osteopontin and
CDX2: Indications of phenotypes and prognosis in advanced gastric
cancer. Oncol Rep. 21:609–613. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Silberg DG, Sullivan J, Kang E, Swain GP,
Moffett J, Sund NJ, Sackett SD and Kaestner KH: Cdx2 ectopic
expression induces gastric intestinal metaplasia in transgenic
mice. Gastroenterology. 122:689–696. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mutoh H, Sakurai S, Satoh K, Tamada K,
Kita H, Osawa H, Tomiyama T, Sato Y, Yamamoto H, Isoda N, et al:
Development of gastric carcinoma from intestinal metaplasia in
Cdx2-transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 64:7740–7747. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huntzinger E and Izaurralde E: Gene
silencing by microRNAs: Contributions of translational repression
and mRNA decay. Nat Rev Genet. 12:99–110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Iliopoulos D, Jaeger SA, Hirsch HA, Bulyk
ML and Struhl K: STAT3 activation of miR-21 and miR-181b-1 via PTEN
and CYLD are part of the epigenetic switch linking inflammation to
cancer. Mol Cell. 39:493–506. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ji J, Yamashita T, Budhu A, Forgues M, Jia
HL, Li C, Deng C, Wauthier E, Reid LM, Ye QH, et al: Identification
of microRNA-181 by genome-wide screening as a critical player in
EpCAM-positive hepatic cancer stem cells. Hepatology. 50:472–480.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rokavec M, Öner MG, Li H, Jackstadt R,
Jiang L, Lodygin D, Kaller M, Horst D, Ziegler PK, Schwitalla S, et
al: IL-6R/STAT3/miR-34a feedback loop promotes EMT-mediated
colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis. J Clin Invest.
124:1853–1867. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sobin LH and Compton CC: TNM seventh
edition: What's new, what's changed: Communication from the
international union against cancer and the american joint committee
on cancer. Cancer. 116:5336–5339. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
CH: International Union against Cancer(UICC): TNM Classification of
Malignant Tumors 7th edition. Oxford, UK: Wiley-Blackwell; 2009
|
|
19
|
Tachibana K, Saito M, Imai JI, Ito E,
Yanagisawa Y, Honma R, Saito K, Ando J, Momma T, Ohki S, et al:
Clinicopathological examination of dipeptidase 1 expression in
colorectal cancer. Biomed Rep. 6:423–428. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bai Y, Akiyama Y, Nagasaki H, Yagi OK,
Kikuchi Y, Saito N, Takeshita K, Iwai T and Yuasa Y: Distinct
expression of CDX2 and GATA4/5, development-related genes, in human
gastric cancer cell lines. Mol Carcinog. 28:184–188. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Saito M, Schetter AJ, Mollerup S, Kohno T,
Skaug V, Bowman ED, Mathé EA, Takenoshita S, Yokota J, Haugen A and
Harris CC: The association of microRNA expression with prognosis
and progression in early-stage, non-small cell lung adenocarcinoma:
A retrospective analysis of three cohorts. Clin Cancer Res.
17:1875–1882. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Saito M, Shiraishi K, Matsumoto K,
Schetter AJ, Ogata-Kawata H, Tsuchiya N, Kunitoh H, Nokihara H,
Watanabe S, Tsuta K, et al: A three-microRNA signature predicts
responses to platinum-based doublet chemotherapy in patients with
lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 20:4784–4793. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dweep H and Gretz N: miRWalk2.0: A
comprehensive atlas of microRNA-target interactions. Nat Methods.
12:6972015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang XT, Wei WY, Kong FB, Lian C, Luo W,
Xiao Q and Xie YB: Prognostic significance of Cdx2
immunohistochemical expression in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis
of published literatures. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 31:982012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang J, Sai K, Chen FR and Chen ZP:
miR-181b modulates glioma cell sensitivity to temozolomide by
targeting MEK1. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 72:147–158. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang B, Hsu SH, Majumder S, Kutay H, Huang
W, Jacob ST and Ghoshal K: TGFbeta-mediated upregulation of hepatic
miR-181b promotes hepatocarcinogenesis by targeting TIMP3.
Oncogene. 29:1787–1797. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhao Y, Schetter AJ, Yang GB, Nguyen G,
Mathé EA, Li P, Cai H, Yu L, Liu F, Hang D, et al: microRNA and
inflammatory gene expression as prognostic marker for overall
survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer.
132:2901–2909. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et
al: A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines
cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guo JX, Tao QS, Lou PR, Chen XC, Chen J
and Yuan GB: miR-181b as a potential molecular target for
anticancer therapy of gastric neoplasms. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
13:2263–2267. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Brighenti E, Calabrese C, Liguori G,
Giannone FA, Trerè D, Montanaro L and Derenzini M: Interleukin 6
downregulates p53 expression and activity by stimulating ribosome
biogenesis: A new pathway connecting inflammation to cancer.
Oncogene. 33:4396–4406. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Giraud AS, Menheniott TR and Judd LM:
Targeting STAT3 in gastric cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
16:889–901. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|