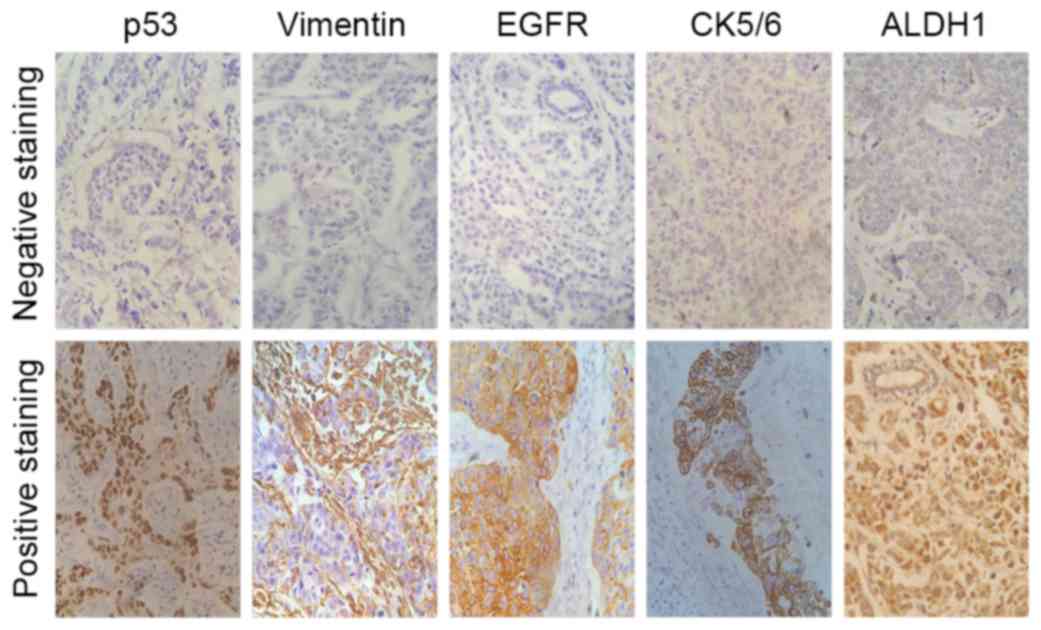
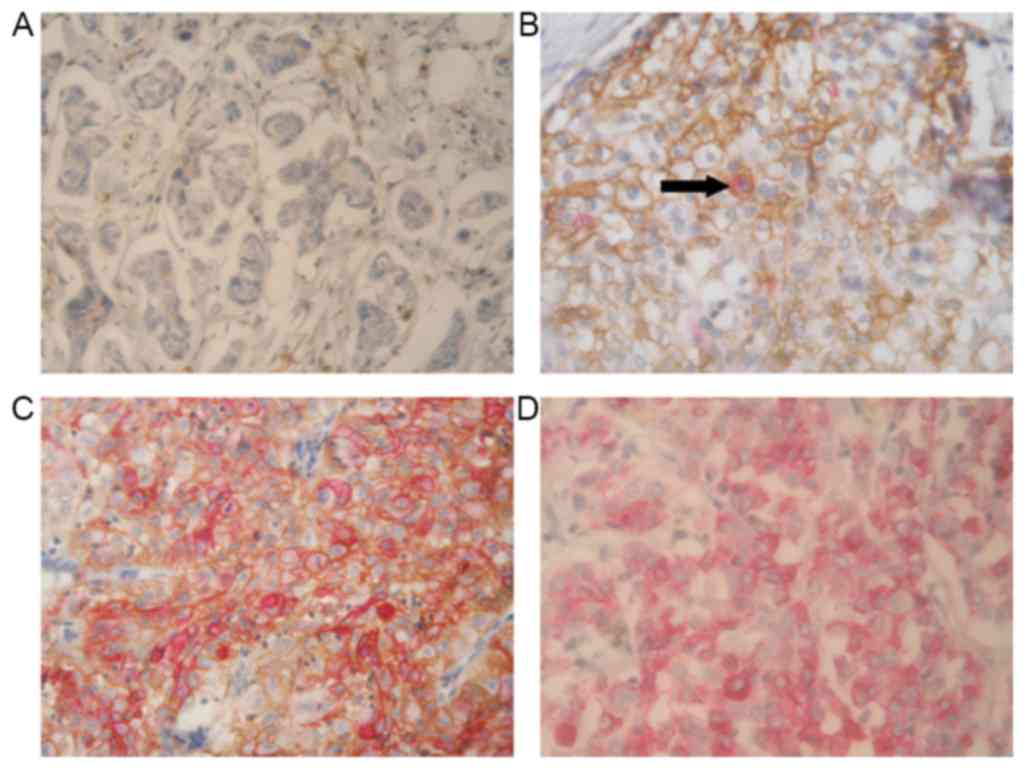
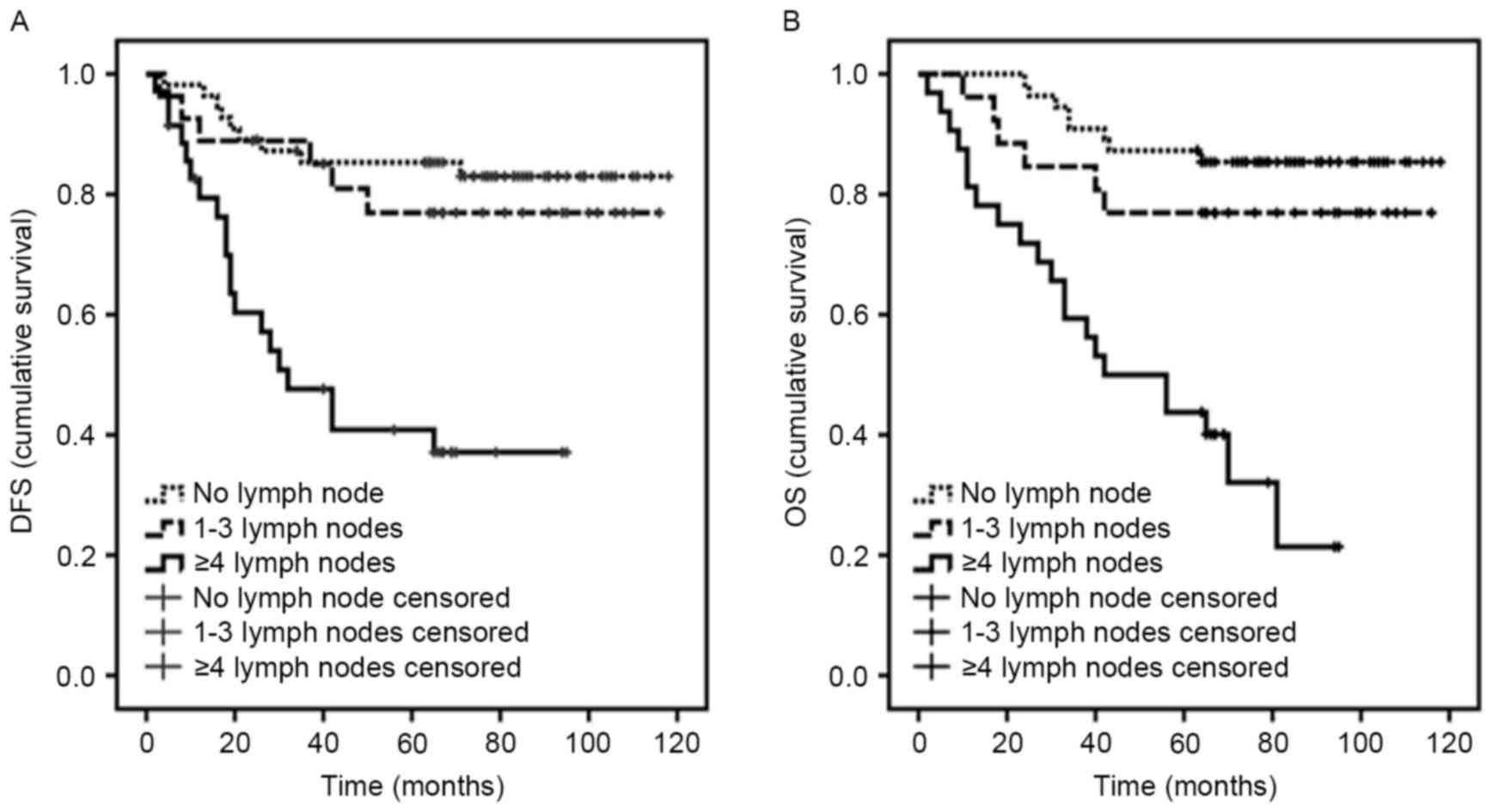
|
1
|
Sotiriou C and Pusztai L: Gene-expression
signatures in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 360:790–800. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bauer KR, Brown M, Cress RD, Parise CA and
Caggiano V: Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor
(ER)-negative, progesterone receptor (PR)-negative, and
HER2-negative invasive breast cancer, the so-called triple-negative
phenotype: A population-based study from the California Cancer
Registry. Cancer. 109:1721–1728. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Reis-Filho JS and Tutt AN: Triple negative
tumours: A critical review. Histopathology. 52:108–118. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Anders C and Carey LA: Understanding and
treating triple-negative breast cancer. Oncology (Williston Park).
22:1233–1239. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee E, McKean-Cowdin R, Ma H, Spicer DV,
Van Den Berg D, Bernstein L and Ursin G: Characteristics of
triple-negative breast cancer in patients with a BRCA1 mutation:
Results from a population-based study of young women. J Clin Oncol.
29:4373–4380. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF and
Weissman IL: Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature.
414:105–111. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Clarke MF, Dick JE, Dirks PB, Eaves CJ,
Jamieson CH, Jones DL, Visvader J, Weissman IL and Wahl GM: Cancer
stem cells-perspectives on current status and future directions:
AACR workshop on cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 66:9339–9344. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,
Morrison SJ and Clarke MF: Prospective identification of
tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:3983–3988. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ginestier C, Hur MH, Charafe-Jauffret E,
Monville F, Dutcher J, Brown M, Jacquemier J, Viens P, Kleer CG,
Liu S, et al: ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human
mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell
Stem Cell. 1:555–567. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang J, Niu C, Ye L, Huang H, He X, Tong
WG, Ross J, Haug J, Johnson T, Feng JQ, et al: Identification of
the haematopoietic stem cell niche and control of the niche size.
Nature. 425:836–841. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Patrawala L, Calhoun T,
Schneider-Broussard R, Zhou J, Claypool K and Tang DG: Side
population is enriched in tumorigenic, stem-like cancer cells,
whereas ABCG2+ and ABCG2− cancer cells are
similarly tumorigenic. Cancer Res. 65:6207–6219. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin L, Hutzen B, Lee HF, Peng Z, Wang W,
Zhao C, Lin HJ, Sun D, Li PK, Li C, et al: Evaluation of STAT3
signaling in ALDH+ and
ALDH+/CD44+/CD24− subpopulations
of breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e828212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Honeth G, Bendahl PO, Ringnér M, Saal LH,
Gruvberger-Saal SK, Lövgren K, Grabau D, Fernö M, Borg A and
Hegardt C: The CD44+/CD24− phenotype is
enriched in basal-like breast tumors. Breast Cancer Res.
10:R532008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ricardo S, Vieira AF, Gerhard R, Leitão D,
Pinto R, Cameselle-Teijeiro JF, Milanezi F, Schmitt F and Paredes
J: Breast cancer stem cell markers CD44, CD24 and ALDH1: Expression
distribution within intrinsic molecular subtype. J Clin Pathol.
64:937–946. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sinn HP, Helmchen B and Wittekind CH: TNM
classification of breast cancer: Changes and comments on the 7th
edition. Pathologe. 31:361–366. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hernandez-Aya LF, Chavez-Macgregor M, Lei
X, Meric-Bernstam F, Buchholz TA, Hsu L, Sahin AA, Do KA, Valero V,
Hortobagyi GN and Gonzalez-Angulo AM: Nodal status and clinical
outcomes in a large cohort of patients with triple-negative breast
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 29:2628–2634. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nielsen TO, Hsu FD, Jensen K, Cheang M,
Karaca G, Hu Z, Hernandez-Boussard T, Livasy C, Cowan D, Dressler
L, et al: Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the
basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
10:5367–5374. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Resetkova E, Reis-Filho JS, Jain RK, Mehta
R, Thorat MA, Nakshatri H and Badve S: Prognostic impact of ALDH1
in breast cancer: A story of stem cells and tumor microenvironment.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 123:97–108. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Abdel-Fatah TM, Arora A, Alsubhi N,
Agarwal D, Moseley PM, Perry C, Doherty R, Chan SY, Green AR, Rakha
E, et al: Clinicopathological significance of ATM-Chk2 expression
in sporadic breast cancers: A comprehensive analysis in large
cohorts. Neoplasia. 16:982–991. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee JG and Wu R: Erlotinib-cisplatin
combination inhibits growth and angiogenesis through c-MYC and
HIF-1α in EGFR-mutated lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. Neoplasia.
17:190–200. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bane A, Viloria-Petit A, Pinnaduwage D,
Mulligan AM, O'Malley FP and Andrulis IL: Clinical-pathologic
significance of cancer stem cell marker expression in familial
breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 140:195–205. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jacquemier J, Ginestier C, Rougemont J,
Bardou VJ, Charafe-Jauffret E, Geneix J, Adélaïde J, Koki A,
Houvenaeghel G, Hassoun J, et al: Protein expression profiling
identifies subclasses of breast cancer and predicts prognosis.
Cancer Res. 65:767–779. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Fiska A and
Koukourakis MI: The CD44+/CD24− phenotype
relates to ‘triple-negative’ state and unfavorable prognosis in
breast cancer patients. Med Oncol. 28:745–752. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Idowu MO, Kmieciak M, Dumur C, Burton RS,
Grimes MM, Powers CN and Manjili MH: CD44(+)/CD24(−/low) cancer
stem/progenitor cells are more abundant in triple-negative invasive
breast carcinoma phenotype and are associated with poor outcome.
Hum Pathol. 43:364–373. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nalwoga H, Arnes JB, Wabinga H and Akslen
LA: Expression of aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 (ALDH1) is associated
with basal-like markers and features of aggressive tumours in
African breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 102:369–375. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang D, Lu P, Zhang H, Luo M, Zhang X, Wei
X, Gao J, Zhao Z and Liu C: Oct-4 and Nanog promote the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer stem cells and
are associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients.
Oncotarget. 5:10803–10815. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pandit TS, Kennette W, Mackenzie L, Zhang
G, Al-Katib W, Andrews J, Vantyghem SA, Ormond DG, Allan AL,
Rodenhiser DI, et al: Lymphatic metastasis of breast cancer cells
is associated with differential gene expression profiles that
predict cancer stem cell-like properties and the ability to
survive, establish and grow in a foreign environment. Int J Oncol.
35:297–308. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Meyer MJ, Fleming JM, Ali MA, Pesesky MW,
Ginsburg E and Vonderhaar BK: Dynamic regulation of CD24 and the
invasive, CD44posCD24neg phenotype in breast cancer cell lines.
Breast Cancer Res. 11:R822009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ma L and Jiang T: Clinical implications of
Ezrin and CD44 co-expression in breast cancer. Oncol Rep.
30:1899–1905. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ahmed MA, Aleskandarany MA, Rakha EA,
Moustafa RZ, Benhasouna A, Nolan C, Green AR, Ilyas M and Ellis IO:
A CD44−/CD24+ phenotype is a poor prognostic
marker in early invasive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
133:979–995. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mylona E, Giannopoulou I, Fasomytakis E,
Nomikos A, Magkou C, Bakarakos P and Nakopoulou L: The
clinicopathologic and prognostic significance of
CD44+/CD24 (−/low) and CD44−/CD24+
tumor cells in invasive breast carcinomas. Hum Pathol.
39:1096–1102. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Charafe-Jauffret E, Ginestier C, Iovino F,
Tarpin C, Diebel M, Esterni B, Houvenaeghel G, Extra JM, Bertucci
F, Jacquemier J, et al: Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1-positive cancer
stem cells mediate metastasis and poor clinical outcome in
inflammatory breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 16:45–55. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Moestue SA, Dam CG, Gorad SS, Kristian A,
Bofin A, Mælandsmo GM, Engebråten O, Gribbestad IS and Bjørkøy G:
Metabolic biomarkers for response to PI3K inhibition in basal-like
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 15:R162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|