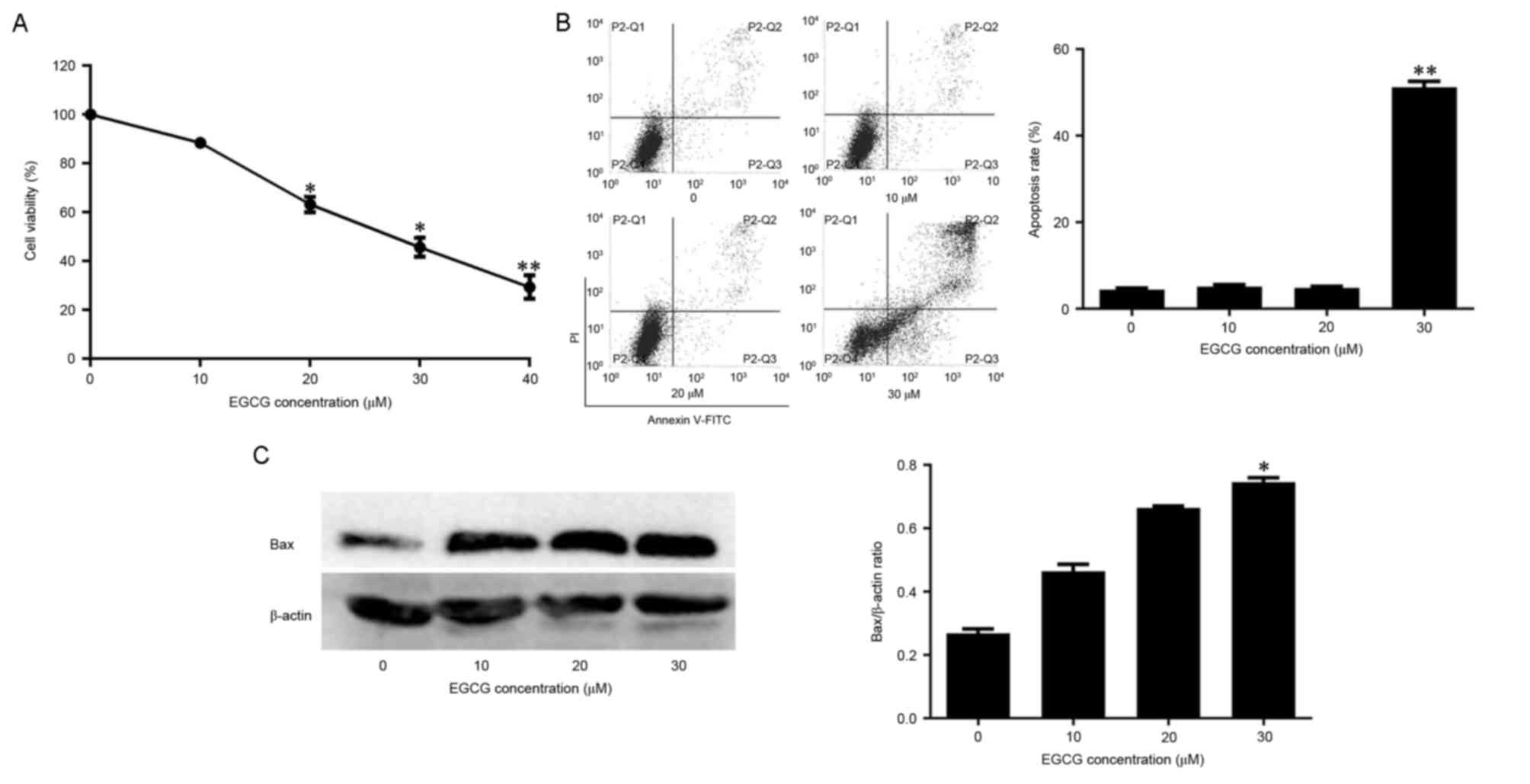
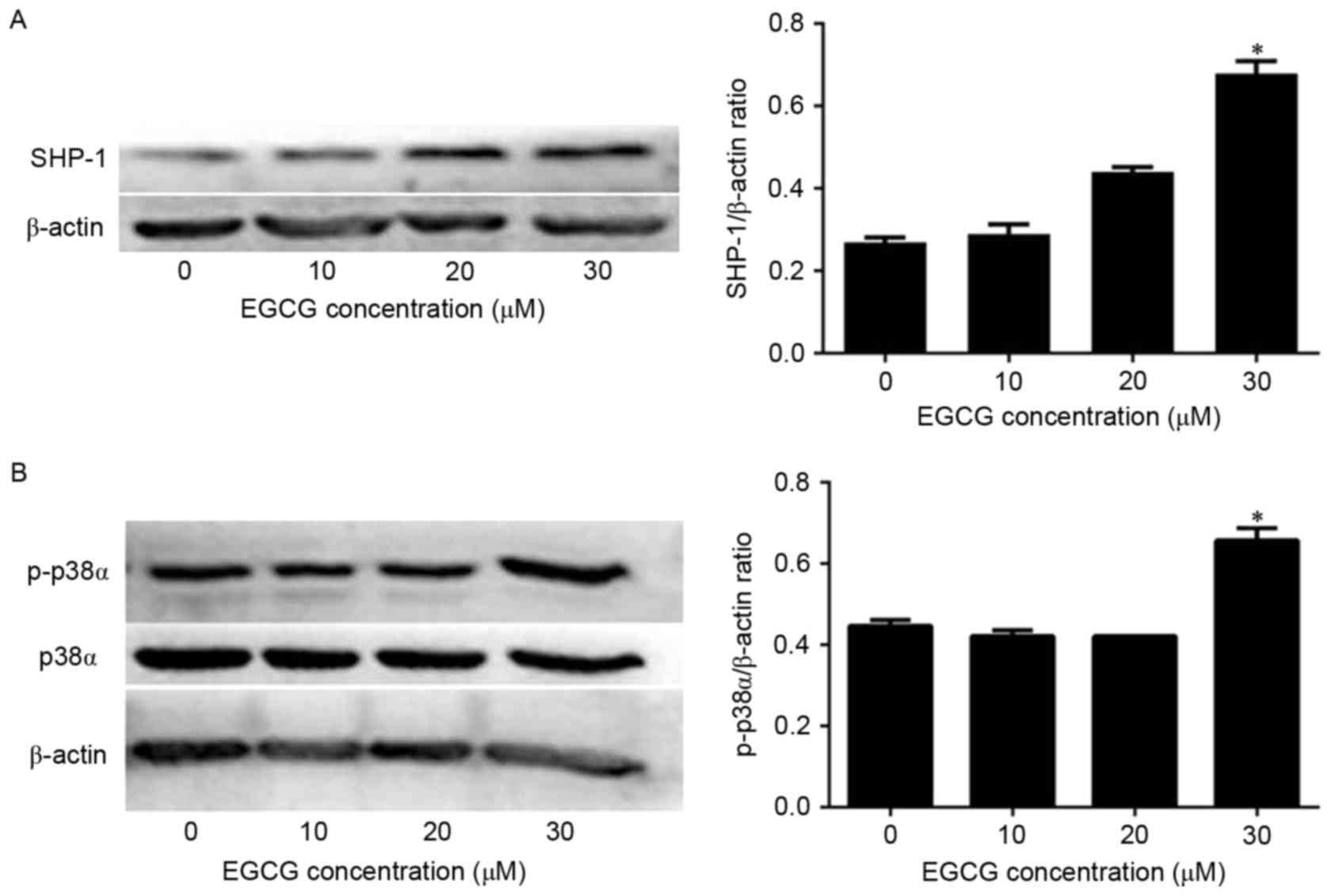
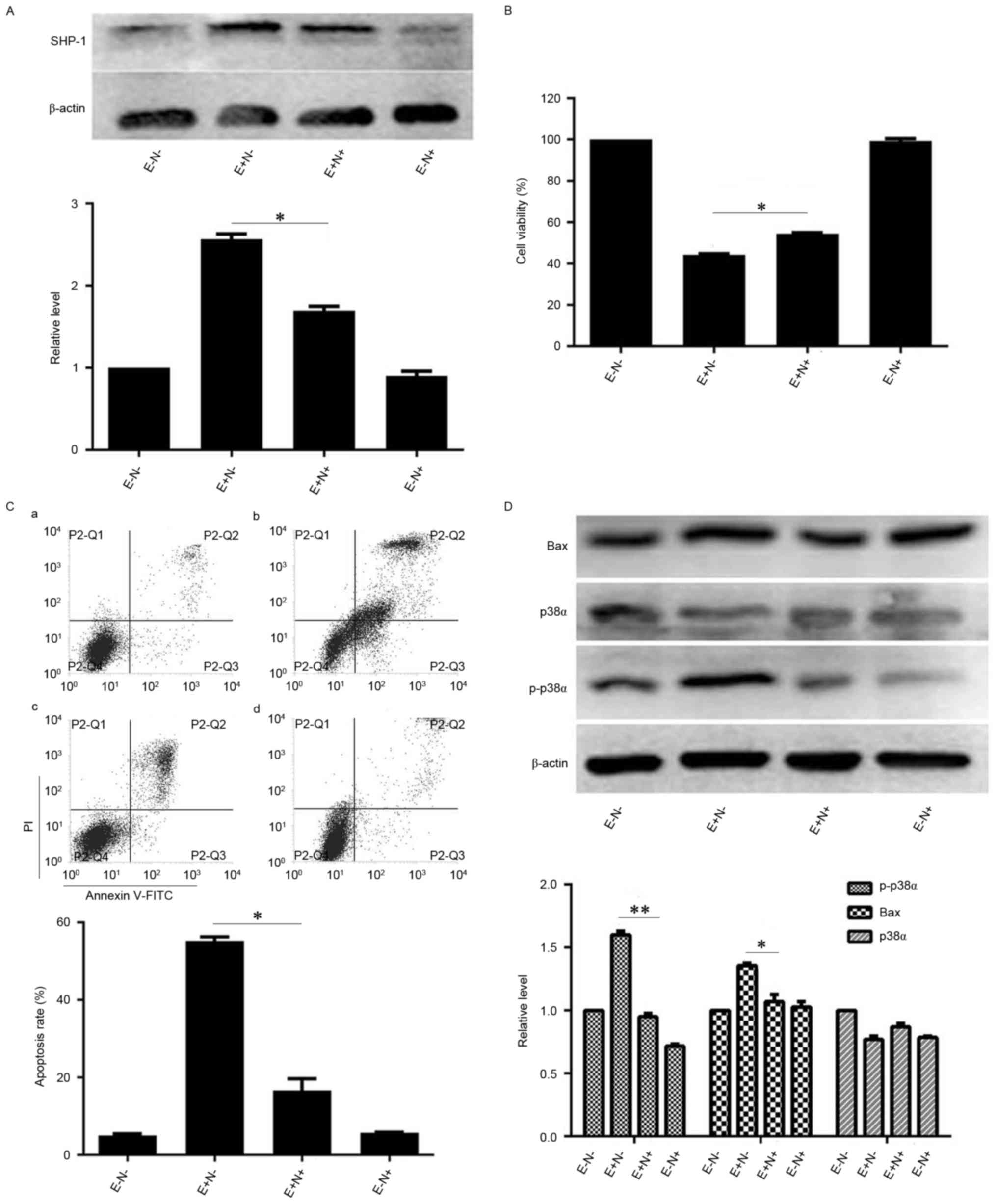
|
1
|
de Thé H, Le Bras M and
Lallemand-Breitenbach V: The cell biology of disease: Acute
promyelocytic leukemia, arrsenic, and PML bodies. J Cell Biol.
198:11–21. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Laurenzana A, Pettersson F and Miller WH:
Role of PML/RARAα in the pathogenesis of APL. Drug Discov Today Dis
Mech. 3:499–505. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Congleton J, MacDonald R and Yen A: Src
inhibitors, PP2 and dasatinib, increase retinoic acid-induced
association of Lyn and c-Raf (S259) and enhance MAPK-dependent
differentiation of myeloid leukemia cells. Leukemia. 26:1180–1188.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liang H, Li X, Wang L, Yu S, Xu Z, Gu Y,
Pan Z, Li T, Hu M, Cui H, et al: MicroRNAs contribute to
promyelocyte apoptosis in As2O3-treated APL cells. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 32:1818–1829. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Petrie K, Zelent A and Waxman S:
Differentiation therapy of acute myeloid leukemia: Past, present
and future. Curr Opin Hematol. 16:84–91. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Neel BG, Gu H and Pao L: The “Shp”ing
news: SH2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatases in cell
signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 28:284–293. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stocco DR and Shen SH: Human protein
tyrosine phosphatase 1C (PTPN6) gene structure: Alternate promoter
usage and exon skipping generate multiple transcripts. Genomics.
27:165–173. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tseng CYLM, Su JC, Chang KC, Chu PY, Tai
WT, Shiau CW and Chen KF: Novel sorafenib analogues induces
apoptosis through SHP-1 dependent STAT3 inactivation in human
breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 15:R632013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dong G, You M, Ding L, Fan H, Liu F, Ren D
and Hou Y: STING negatively regulates Double-Stranded DNA-activated
JAK1-STAT1 signaling via SHP-1/2 in B cells. Mol Cells. 38:441–451.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Al-Jamal HA, Jusoh Mat SA, Hassan R and
Johan MF: Enhancing SHP-1 expression with 5-azacytidine may inhibit
STAT3 activation and confer sensitivity in lestaurtinib
(CEP-701)-resistant FLT3-ITD positive acute myeloid leukemia. BMC
Canner. 15:8692015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Xiong A, Yu W, Liu Y, Sanders BG and Kline
K: Elimination of ALDH+ breast tumor initiating cells by
docosahexanoic acid and/or gamma tocotrienol through SHP-1
inhibition of Stat3 signaling. Mol Carcinog. 55:420–430. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fan LC, Teng HW, Shiau CW, Lin H, Hung MH,
Chen YL, Huang JW, Tai WT, Yu HC and Chen KF: SHP-1 is a target of
regorafenib in colorectal cancer. Oncatarget. 5:6243–6251. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Nakase K, Cheng J, Zhu Q and Marasco WA:
Mechanisms of SHP-1 P2 promoter regulation in hematopoietic cells
and its silencing in HTLV-1-transformed T cells. J Leukoc Biol.
85:165–174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Delibrias CC, Floettmann JE, Rowe M and
Fearon DT: Downregulated expression of SHP-1 in Burkitt lymphomas
and germinal center B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 186:1575–1583. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Uesugi Y, Fuse I, Toba K, Kishi K,
Furukawa T, Koike T and Aizawa Y: Involvement of SHP-1, a
phosphotyrosine phosphatase, during myeloid cell differentiation in
acute promyelocytic leukemia cell lines. Eur J Haematol.
62:239–245. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Amin HM, Hoshino K, Yang H, Lin Q, Lai R
and Garcia-Manero G: Decreased expression level of SH2
domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-1 (Shp1) is
associated with progression of chronic myeloid leukaemia. J Pathol.
212:402–410. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nakazato T, Ito K, Miyakawa Y, Kinjo K,
Yamada T, Hozumi N, Ikeda Y and Kizaki M: Catechin, a green tea
component, rapidly induces apoptosis of myeloid leukemia cells via
modulation of reactive oxygen species production in vitro
andinhibits tumor growth in vivo. Haematologica. 90:317–325.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Britschgi A, Simon HU, Tobler A, Fey MF
and Tschan MP: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces cell death in
acute myeloid leukaemia cells and supports all-trans retinoic
acid-induced neutrophil differentiation via death-associated
protein kinase 2. Br J Haematol. 149:55–64. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jung JH, Yun M, Choo EJ, Kim SH, Jeong MS,
Jung DB, Lee H, Kim EO, Kato N, Kim B, et al: A derivative of
epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces apoptosis via SHP-1-mediated
suppression of BCR-ABL and STAT3 signalling in chronic myelogenous
leukaemia. Br J Pharmacol. 172:3565–3578. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Geraldes P, Hiraoka-Yamamoto J, Matsumoto
M, Clermont A, Leitges M, Marette A, Aiello LP, Kern TS and King
GL: Activation of PKC-delta and SHP-1 by hyperglycemia causes
vascular cell apoptosis and diabetic retinopathy. Nat Med.
15:1298–1306. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Harsha Raj M, Yashaswini B, Rössler J and
Salimath BP: Combinatorial treatment with anacardic acid followed
by TRAIL augments induction of apoptosis in TRAIL resistant cancer
cells by the regulation of p53, MAPK and NFκβ pathways. Apoptosis.
21:578–593. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang JG, Yang S, Qiao J, Li T, Yang S and
Hong Y: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor regulating the
expression of VEGF-C through MAPK signal pathways in breast cancer
MCF-7 cell. World J Surg Oncol. 14:512016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rodríguez-Berriguete G, Torrealba N,
Fraile B, Paniagua R and Royuela M: Epidermal growth factor induces
p38 MAPK-dependent G0/G1-to-S transition in prostate cancer cells
upon androgen deprivation conditions. Growth Factor. 34:5–10. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Mandegary A, Hosseini R, Ghaffari SH,
Alimoghaddam K, Rostami S, Ghavamzadeh A and Ghahremani MH: The
expression of p38, ERK1 and Bax proteins has increased during the
treatment of newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia with
arsenic trioxide. Ann Oncol. 21:1884–1890. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tyurin VA, Balasubramanian K, Winnica D,
Tyurina YY, Vikulina AS, He RR, Kapralov AA, Macphee CH and Kagan
VE: Oxidatively modified phosphatidylserines om the surface of
apoptotic cells are essential phagocytic ‘eat-me’ signals: Cleavage
and inhibition of phagocytosis by Lp-PLA2. Cell Death Differ.
21:825–835. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Toden S, Tran HM, Tovar-Camargo OA,
Okugawa Y and Goel A: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate targets cancer
stem-like cells and enhances 5-fluorouracil chemosensitivity in
colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 7:16158–16171. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li M, Li JJ, Gu QH, An J, Cao LM, Yang HP
and Hu CP: EGCG induces lunch canner A549 cells apoptosis by
regulating Ku70 acetylation. Oncol Rep. 35:2339–2347. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tofolean IT, Ganea C, Ionescu D, Filippi
A, Garaiman A, Goicea A, Gaman MA, Dimancea A and Baran I: Cellular
determinants involving mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress
and apoptosis correlate with the synergic cytotoxicity of
epigallocatechin-3-gallate and menadione in human leukemia Jurkat T
cells. Pharmacol Res. 103:300–317. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vézina A, Chokor R and Annabi B: EGCG
targeting efficacy of NF-κB downstream gene products is dictated by
the monocytic/macrophagic differentiation status of promyelocytic
leukemia cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 16:2321–2331. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Elbling L, Herbacek I, Weiss RM,
Jantschitsch C, Micksche M, Gerner C, Pangratz H, Grusch M,
Knasmüller S and Berger W: Hydrogen peroxide mediates EGCG-induced
antioxidant protection in human keratinocytes. Free Radic Biol Med.
49:1444–1452. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Khan TH, Srivastava N, Srivastava A,
Sareen A, Mathur RK, Chande AG, Musti KV, Roy S, Mukhopadhyaya R
and Saha B: SHP-1 plays a crucial role in CD40 signaling
reciprocity. J Immunol. 193:3644–3653. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen YY, Hsieh CY, Jayakumar T, Lin KH,
Chou DS, Lu WJ, Hsu MJ and Sheu JR: Andrographolide induces
vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis through a
SHP-1-PP2A-p38MAPK-p53 cascade. Sci Rep. 4:56512014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|