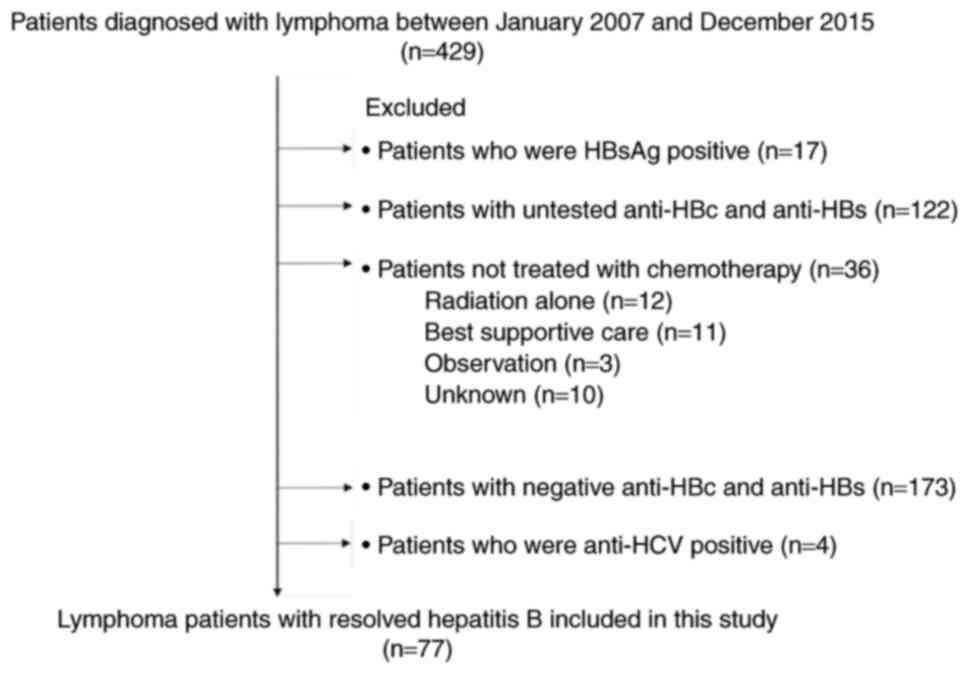
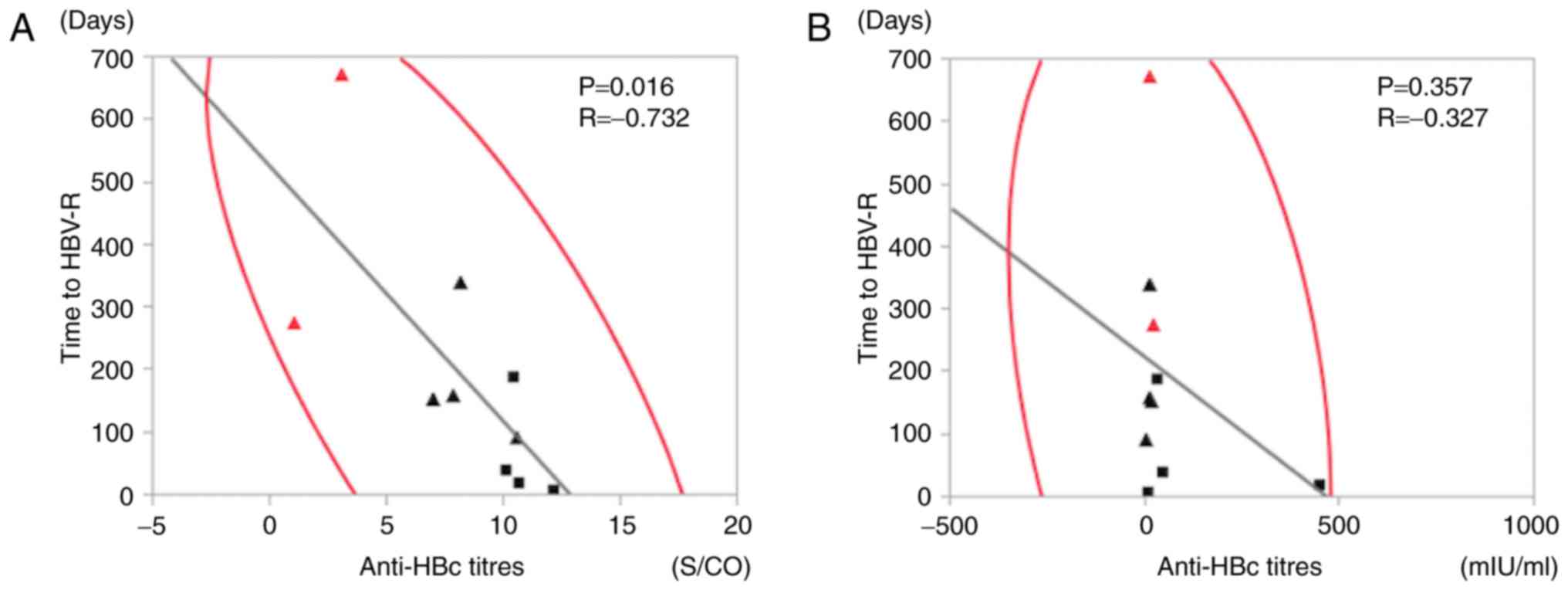
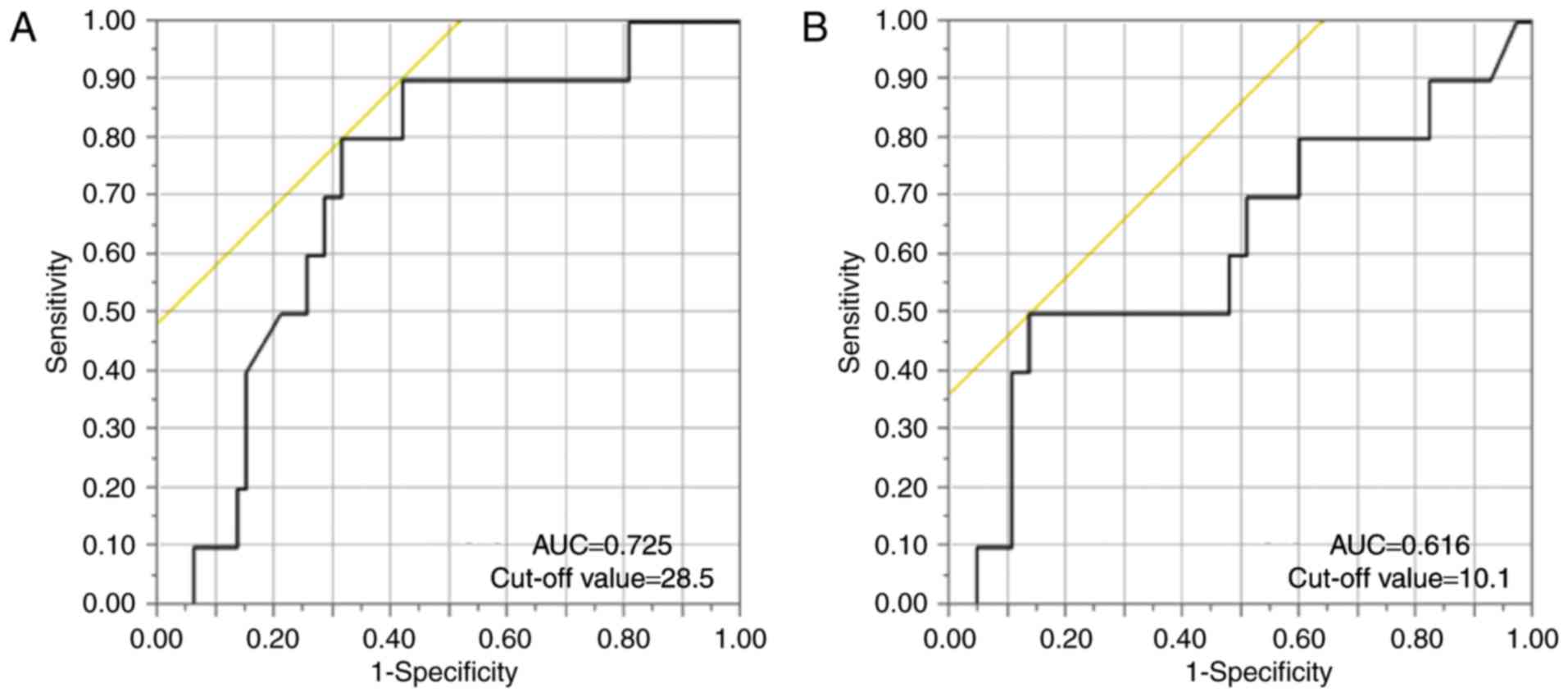
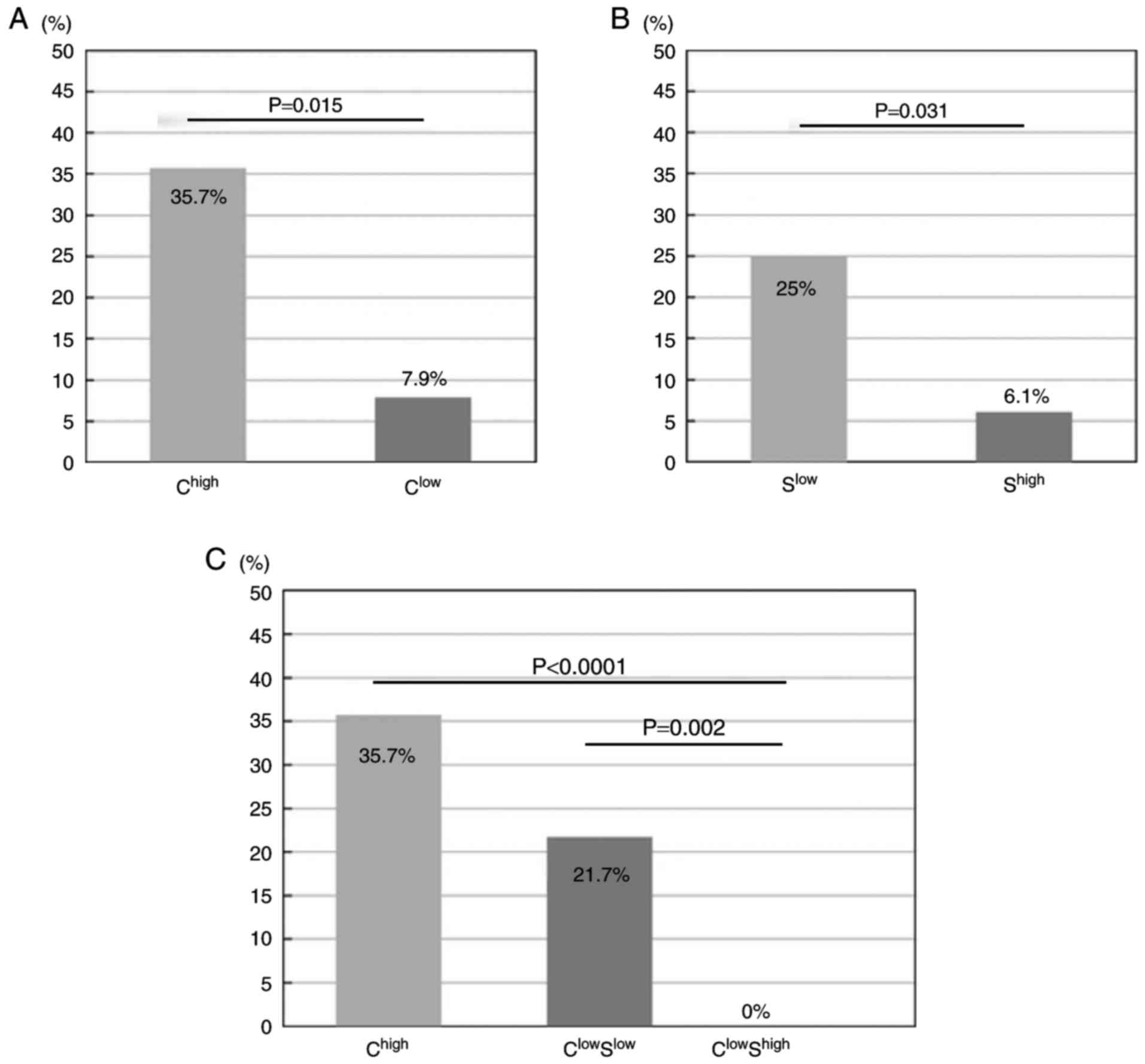
|
1
|
Huang YH, Hsiao LT, Hong YC, Chiou TJ, Yu
YB, Gau JP, Liu CY, Yang MH, Tzeng CH, Lee PC, et al: Randomized
controlled trial of entecavir prophylaxis for rituximab-associated
hepatitis B virus reactivation in patients with lymphoma and
resolved hepatitis B. J Clin Oncol. 31:2765–2772. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Matsue K, Kimura S, Takanashi Y, Iwama K,
Fujiwara H, Yamakura M and Takeuchi M: Reactivation of hepatitis B
virus after rituximab-containing treatment in patients with
CD20-positive B-cell lymphoma. Cancer. 116:4769–4776. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yeo W, Chan TC, Leung NW, Lam WY, Mo FK,
Chu MT, Chan HL, Hui EP, Lei KI, Mok TS and Chan PK: Hepatitis B
virus reactivation in lymphoma patients with prior resolved
hepatitis B undergoing anticancer therapy with or without
rituximab. J Clin Oncol. 27:605–611. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hui CK, Cheung WW, Zhang HY, Au WY, Yueng
YH, Leung AY, Leung N, Luk JM, Lie AK, Kwong YL, et al: Kinetics
and risk of de novo hepatitis B infection in HBsAg-negative
patients undergoing cytotoxic chemotherapy. Gastroenterology.
131:59–68. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fukushima N, Mizuta T, Tanaka M, Yokoo M,
Ide M, Hisatomi T, Kuwahara N, Tomimasu R, Tsuneyoshi N, Funai N
and Sueoka E: Retrospective and prospective studies of hepatitis B
virus reactivation in malignant lymphoma with occult HBV carrier.
Ann Oncol. 20:2013–2017. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dong HJ, Ni LN, Sheng GF, Song HL, Xu JZ
and Ling Y: Risk of hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation in
non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients receiving rituximab-chemotherapy: A
meta-analysis. J Clin Virol. 57:209–214. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cho Y, Yu SJ, Cho EJ, Lee JH, Kim TM, Heo
DS, Kim YJ and Yoon JH: High titers of anti-HBs prevent
rituximab-related viral reactivation in resolved hepatitis B
patient with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. J Med Virol. 88:1010–1017.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hayashi K, Ishigami M, Ishizu Y, Kuzuya T,
Honda T, Tachi Y, Ishikawa T, Katano Y, Yoshioka K, Toyoda H, et
al: Clinical characteristics and molecular analysis of hepatitis B
virus reactivation in hepatitis B surface antigen-negative patients
during or after immunosuppressive or cytotoxic chemotherapy. J
Gastroenterol. 51:1081–1089. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Seto WK, Chan TS, Hwang YY, Wong DK, Fung
J, Liu KS, Gill H, Lam YF, Lie AK, Lai CL, et al: Hepatitis B
reactivation in patients with previous hepatitis B virus exposure
undergoing rituximab-containing chemotherapy for lymphoma: A
prospective study. J Clin Oncol. 32:3736–3743. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kusumoto S, Tanaka Y, Suzuki R, Watanabe
T, Nakata M, Takasaki H, Fukushima N, Fukushima T, Moriuchi Y, Itoh
K, et al: Monitoring of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA and risk of HBV
reactivation in B-cell lymphoma: A prospective observational study.
Clin Infect Dis. 61:719–729. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nishida T, Hiramatsu N, Mizuki M, Nagatomo
I, Kida H, Tazumi K, Shinzaki S, Miyazaki M, Yakushijin T, Tatsumi
T, et al: Managing hepatitis B virus carriers with systemic
chemotherapy or biologic therapy in the outpatient clinic. Hepatol
Res. 43:339–346. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Drafting Committee for Hepatitis
Management Guidelines and the Japan Society of Hepatology, . JSH
Guidelines for the Management of Hepatitis B Virus infection.
Hepatol Res. 44 Suppl:S1–S58. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Umemura T, Tanaka E, Kiyosawa K and Kumada
H; Japan de novo Hepatitis B Research Group, : Mortality secondary
to fulminant hepatic failure in patients with prior resolution of
hepatitis B virus infection in Japan. Clin Infect Dis. 47:e52–e56.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pei SN, Ma MC, Wang MC, Kuo CY, Rau KM, Su
CY and Chen CH: Analysis of hepatitis B surface antibody titers in
B cell lymphoma patients after rituximab therapy. Ann Hematol.
91:1007–1012. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Han JW, Yang H, Lee HL, Bae SH, Choi JY,
Lee JW, Kim HJ, Lee S, Cho SG, Min CK, et al: Risk factors and
outcomes of hepatitis B virus reactivation in hepatitis B surface
antigen negative patients with hematological malignancies. Hepatol
Res. 46:657–668. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang X, Lu W, Zheng Y, Wang W, Bai L,
Chen L, Feng Y, Zhang Z and Yuan Z: In situ analysis of
intrahepatic virological events in chronic hepatitis B virus
infection. J Clin Invest. 126:1079–1092. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rehermann B, Ferrari C, Pasquinelli C and
Chisari FV: The hepatitis B virus persists for decades after
patients' recovery from acute viral hepatitis despite active
maintenance of a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response. Nat Med.
2:1104–1108. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yuki N, Nagaoka T, Yamashiro M, Mochizuki
K, Kaneko A, Yamamoto K, Omura M, Hikiji K and Kato M: Long-term
histologic and virologic outcomes of acute self-limited hepatitis
B. Hepatology. 37:1172–1179. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Uemoto S, Sugiyama K, Marusawa H, Inomata
Y, Asonuma K, Egawa H, Kiuchi T, Miyake Y, Tanaka K and Chiba T:
Transmission of hepatitis B virus from hepatitis B core
antibody-positive donors in living related liver transplants.
Transplantation. 65:494–499. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Akahane Y, Okada S, Sakamoto M, Wakamiya
M, Kitamura T, Tawara A, Naitoh S, Tsuda F and Okamoto H:
Persistence of hepatitis B viremia after recovery from acute
hepatitis B: Correlation between anti-HBc titer and HBV DNA in
serum. Hepatol Res. 24:82002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kobyashi M, Chayama K, Arase Y, Tsubota A,
Saitoh S, Suzuki Y, Kobayashi M, Murashima N, Ikeda K, Hagiwara M,
et al: Progressive and sufficient decrease of hepatitis B core
antibody can predict the disappearance of hepatitis B virus DNA in
Japanese patients with hepatitis B surface antigen clearance. J
Gastroenterol. 35:753–757. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Takahashi H, Ikeda M, Kumada T, Osaki Y,
Kondo S, Kusumoto S, Ohkawa K, Nadano S, Furuse J, Kudo M, et al:
Multicenter cooperative case survey of hepatitis B virus
reactivation by chemotherapeutic agents. Hepatol Res. 45:1220–1227.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|