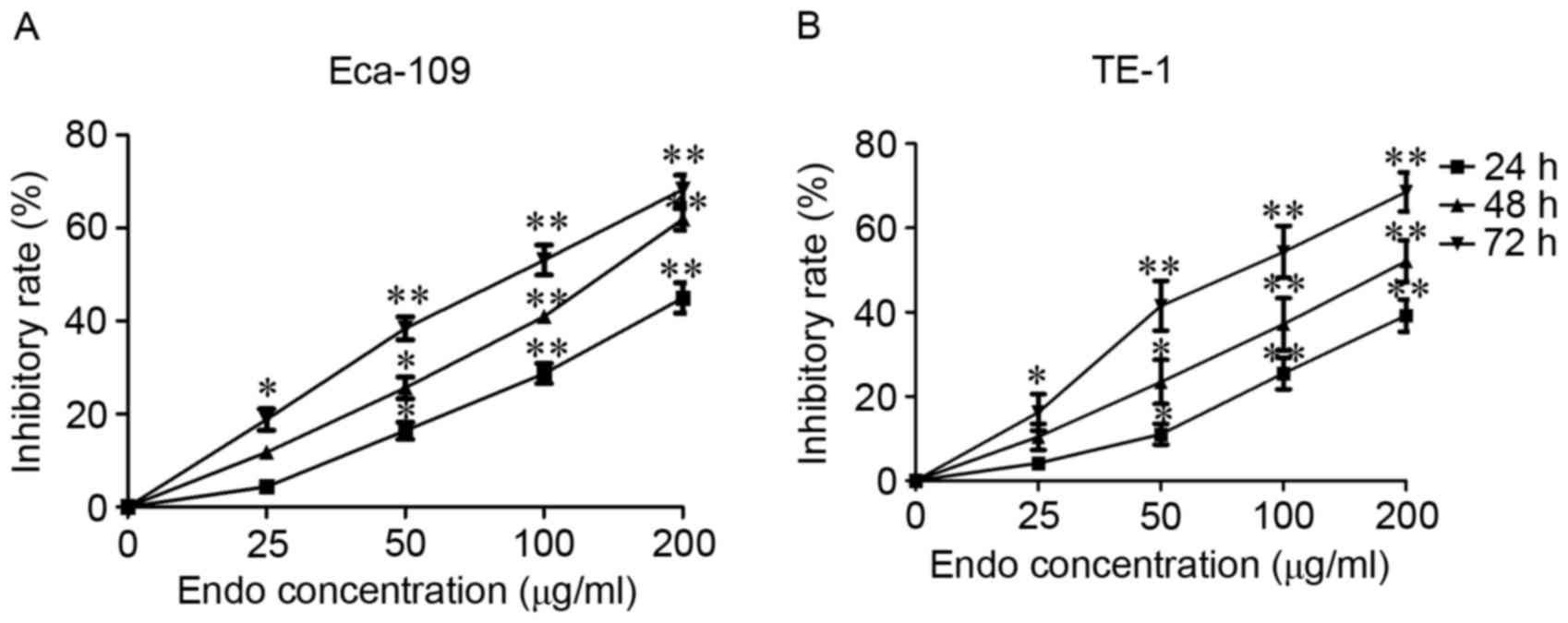
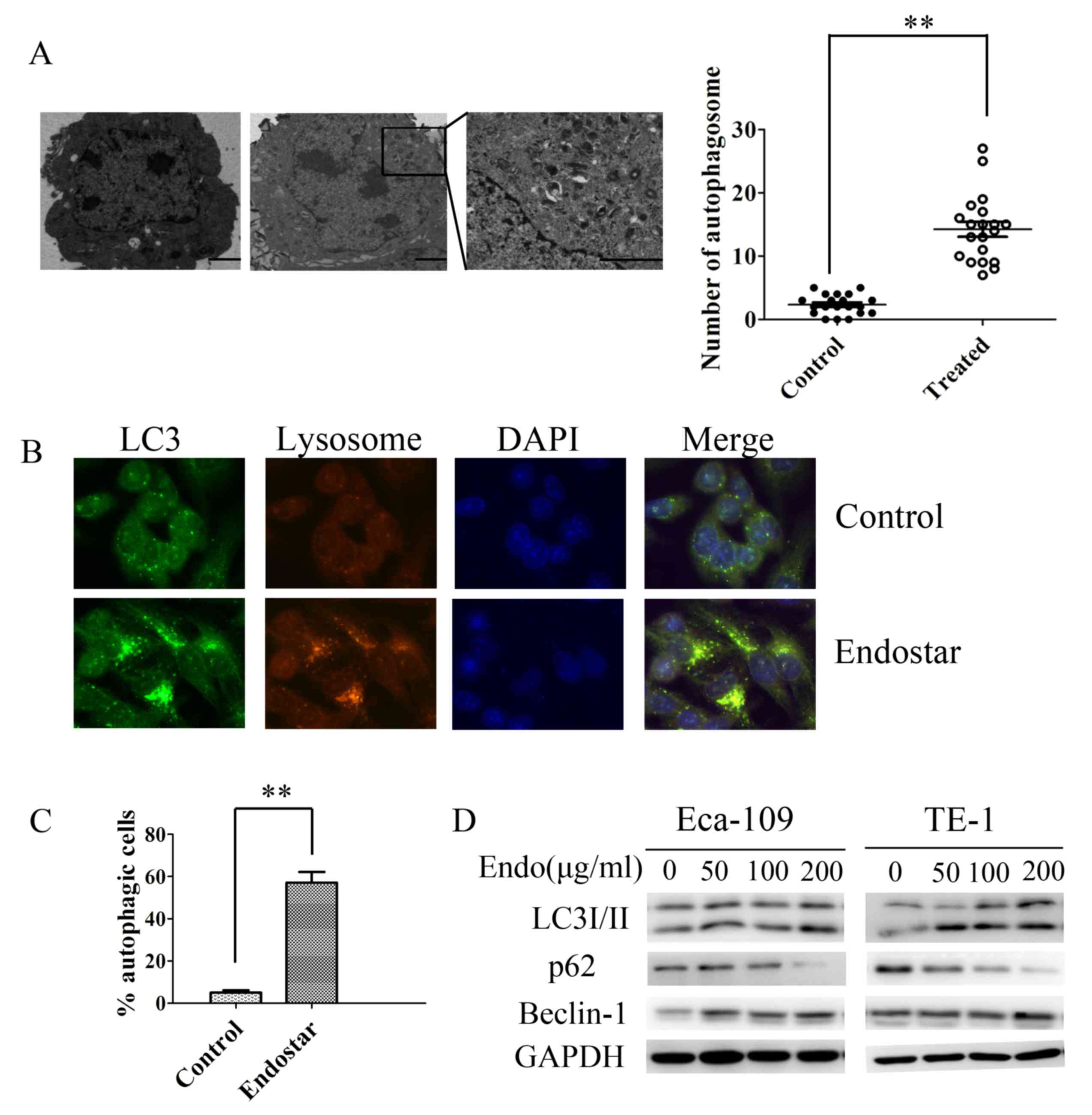
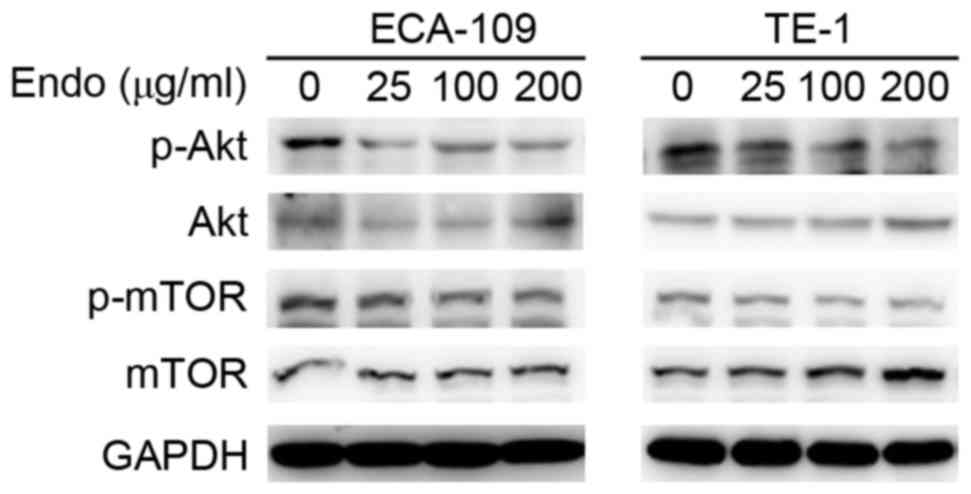
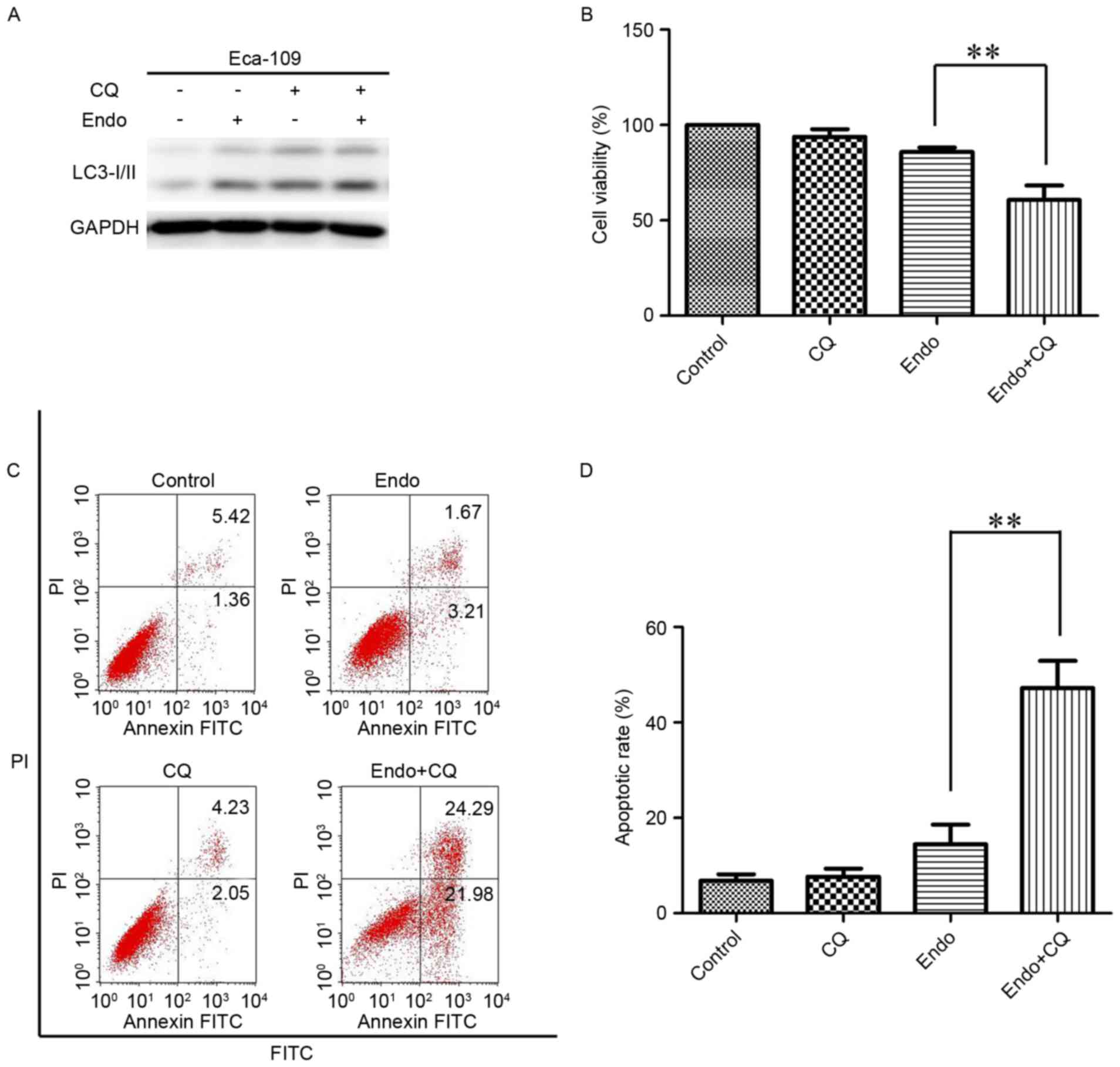
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sant M, Aareleid T, Berrino F, Lasota M
Bielska, Carli PM, Faivre J, Grosclaude P, Hedelin G, Matsuda T,
Moller H, et al: EUROCARE-3: Survival of cancer patients diagnosed
1990-94-results and commentary. Ann Oncol. 14 Suppl 5:v61–v118.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pande AU, Iyer RV, Rani A, Maddipatla S,
Yang GY, Nwogu CE, Black JD, Levea CM and Javle MM: Epidermal
growth factor receptor-directed therapy in esophageal cancer.
Oncology. 73:281–289. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Folkman J: Angiogenesis: An organizing
principle for drug discovery? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 6:273–286. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang J, Sun Y, Liu Y, Yu Q, Zhang Y, Li K,
Zhu Y, Zhou Q, Hou M, Guan Z, et al: Results of randomized,
multicenter, double-blind phase III trial of rh-endostatin (YH-16)
in treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients.
Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 8:283–290. 2005.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu M, Huang H, Xiong Y, Peng B, Zhou Z,
Wang D and Yang X: Combined chemotherapy plus Endostar with
sequential stereotactic radiotherapy as salvage treatment for
recurrent esophageal cancer with severe dyspnea: A case report and
review of the literature. Oncol Lett. 8:291–294. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Deng WY, Song T, Li N, Luo SX and Li X:
Clinical observation and therapeutic evaluation of Rh-endostatin
combined with DP regimen in treating patients with advanced
esophageal cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:6565–6570. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhong Z, Gu X, Zhang Z, Wang D, Qing Y, Li
M and Dai N: Recombinant human endostatin combined with definitive
chemoradiotherapy as primary treatment for patients with
unresectable but without systemic metastatic squamous cell
carcinoma of the oesophagus. Br J Radiol. 85:e1104–e1109. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H,
Abraham RT, Acevedo-Arozena A, Adeli K, Agholme L, Agnello M,
Agostinis P, Aguirre-Ghiso JA, et al: Guidelines for the use and
interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy.
8:445–544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xu Y, Yu H, Qin H, Kang J, Yu C, Zhong J,
Su J, Li H and Sun L: Inhibition of autophagy enhances cisplatin
cytotoxicity through endoplasmic reticulum stress in human cervical
cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 314:232–243. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fong MY, Jin S, Rane M, Singh RK, Gupta R
and Kakar SS: Withaferin A synergizes the therapeutic effect of
doxorubicin through ROS-mediated autophagy in ovarian cancer. PLoS
One. 7:e422652012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shimizu S, Takehara T, Hikita H, Kodama T,
Tsunematsu H, Miyagi T, Hosui A, Ishida H, Tatsumi T, Kanto T, et
al: Inhibition of autophagy potentiates the antitumor effect of the
multikinase inhibitor sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Cancer. 131:548–557. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li X and Fan Z: The epidermal growth
factor receptor antibody cetuximab induces autophagy in cancer
cells by downregulating HIF-1alpha and Bcl-2 and activating the
beclin 1/hVps34 complex. Cancer Res. 70:5942–5952. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ling Y, Yang Y, Lu N, You QD, Wang S, Gao
Y, Chen Y and Guo QL: Endostar, a novel recombinant human
endostatin, exerts antiangiogenic effect via blocking VEGF-induced
tyrosine phosphorylation of KDR/Flk-1 of endothelial cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 361:79–84. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bernatchez PN, Allen BG, Gelinas DS,
Guillemette G and Sirois MG: Regulation of VEGF-induced endothelial
cell PAF synthesis: Role of p42/44 MAPK, p38 MAPK and PI3K
pathways. Br J Pharmacol. 134:1253–1262. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li N, Fan LL, Sun GP, Wan XA, Wang ZG, Wu
Q and Wang H: Paeonol inhibits tumor growth in gastric cancer in
vitro and in vivo. World J Gastroenterol. 16:4483–4490. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pan H, Wang Z, Jiang L, Sui X, You L, Shou
J, Jing Z, Xie J, Ge W, Cai X, et al: Autophagy inhibition
sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma to the multikinase inhibitor
linifanib. Sci Rep. 4:66832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang L, Ge W, Hu K, Zhang Y, Li C, Xu X,
He D, Zhao Z, Zhang J, Jie F, et al: Endostar down-regulates HIF-1
and VEGF expression and enhances the radio response to human lung
adenocarcinoma cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep. 39:89–95. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Harris AL: Are angiostatin and endostatin
cures for cancer? Lancet. 351:1598–1599. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
O'Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, Fukai N,
Vasios G, Lane WS, Flynn E, Birkhead JR, Olsen BR and Folkman J:
Endostatin: An endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor
growth. Cell. 88:277–285. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
You ZY, Zhao Y, Liu F, Zhang YD and Wang
JJ: The radiosensitization effects of Endostar on human lung
squamous cancer cells H-520. Cancer Cell Int. 10:172010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ni Q, Ji H, Zhao Z, Fan X and Xu C:
Endostar, a modified endostatin inhibits non small cell lung cancer
cell in vitro invasion through osteopontin-related mechanism. Eur J
Pharmacol. 614:1–6. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chang L, Guo F, Lv Y, Wang Y, Huo B, Wang
L and Liu W: The inhibitory effects of Endostar combined with
chemotherapy on human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma xenograft
in mice. Mol Biol Rep. 40:669–673. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bansode RR, Ahmedna M, Svoboda KR and
Losso JN: Coupling in vitro and in vivo paradigm reveals a dose
dependent inhibition of angiogenesis followed by initiation of
autophagy by C6-ceramide. Int J Biol Sci. 7:629–644. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Selvakumaran M, Amaravadi RK, Vasilevskaya
IA and O'Dwyer PJ: Autophagy inhibition sensitizes colon cancer
cells to anti angiogenic and cytotoxic therapy. Clin Cancer Res.
19:2995–3007. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Guo XL, Li D, Sun K, Wang J, Liu Y, Song
JR, Zhao QD, Zhang SS, Deng WJ, Zhao X, et al: Inhibition of
autophagy enhances anticancer effects of bevacizumab in
hepatocarcinoma. J Mol Med (Berl). 91:473–483. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chau YP, Lin SY, Chen JH and Tai MH:
Endostatin induces autophagic cell death in EAhy926 human
endothelial cells. Histol Histopathol. 18:715–726. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Porta C, Paglino C and Mosca A: Targeting
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in cancer. Front Oncol. 4:642014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Codogno P and Meijer AJ: Autophagy and
signaling: Their role in cell survival and cell death. Cell Death
Differ. 12 Suppl 2:S1509–S1518. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Xu X, Mao W, Chen Q, Zhuang Q, Wang L, Dai
J, Wang H and Huang Z: Endostar, a modified recombinant human
endostatin, suppresses angiogenesis through inhibition of
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. PloS One. 9:e1074632014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang YB, Liu JH and Song ZM: Effects of
recombinant human endostatin on the expression of vascular
endothelial growth factor in human gastric cancer cell line
MGC-803. Biomed Rep. 1:77–79. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|