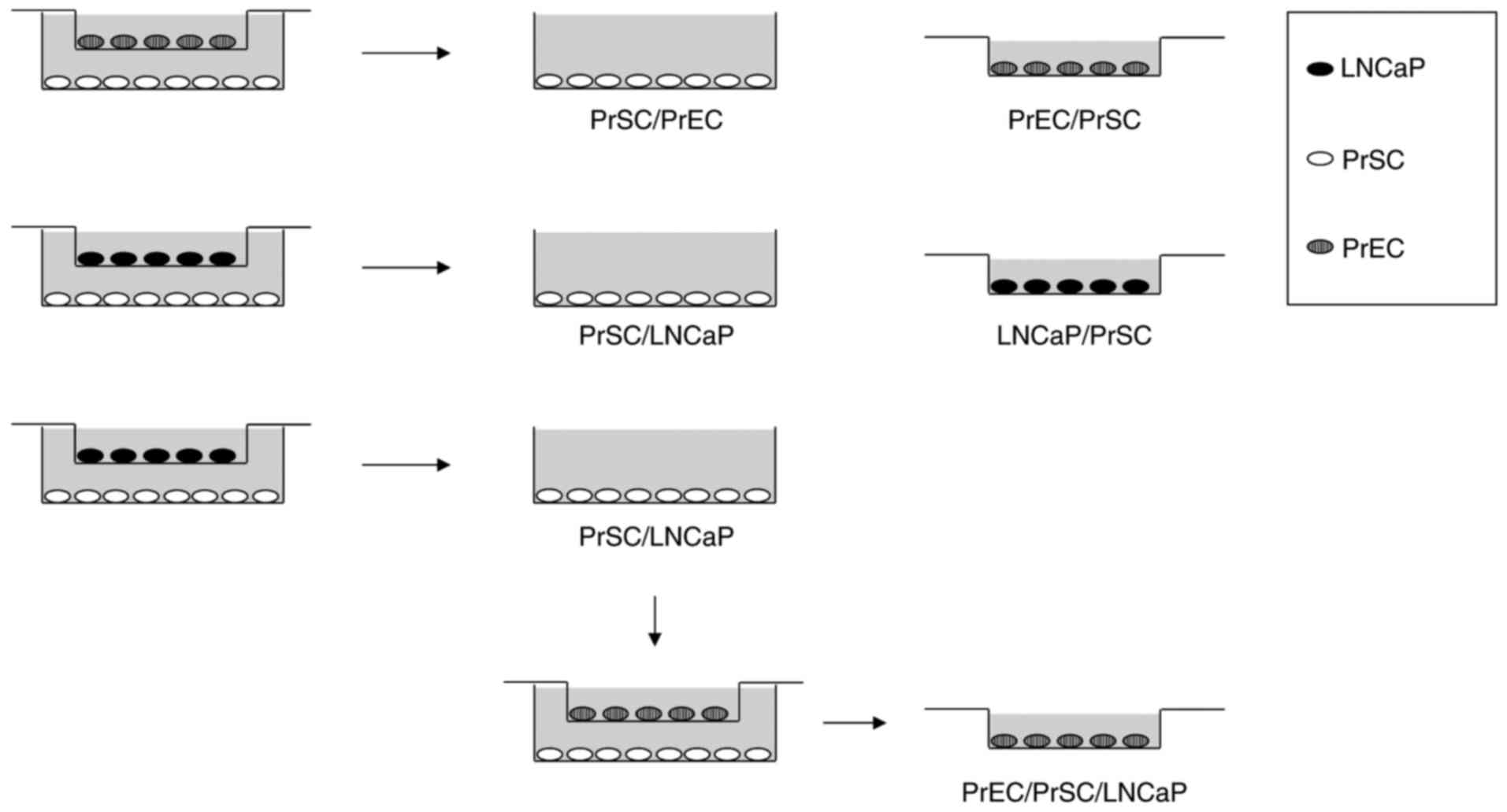
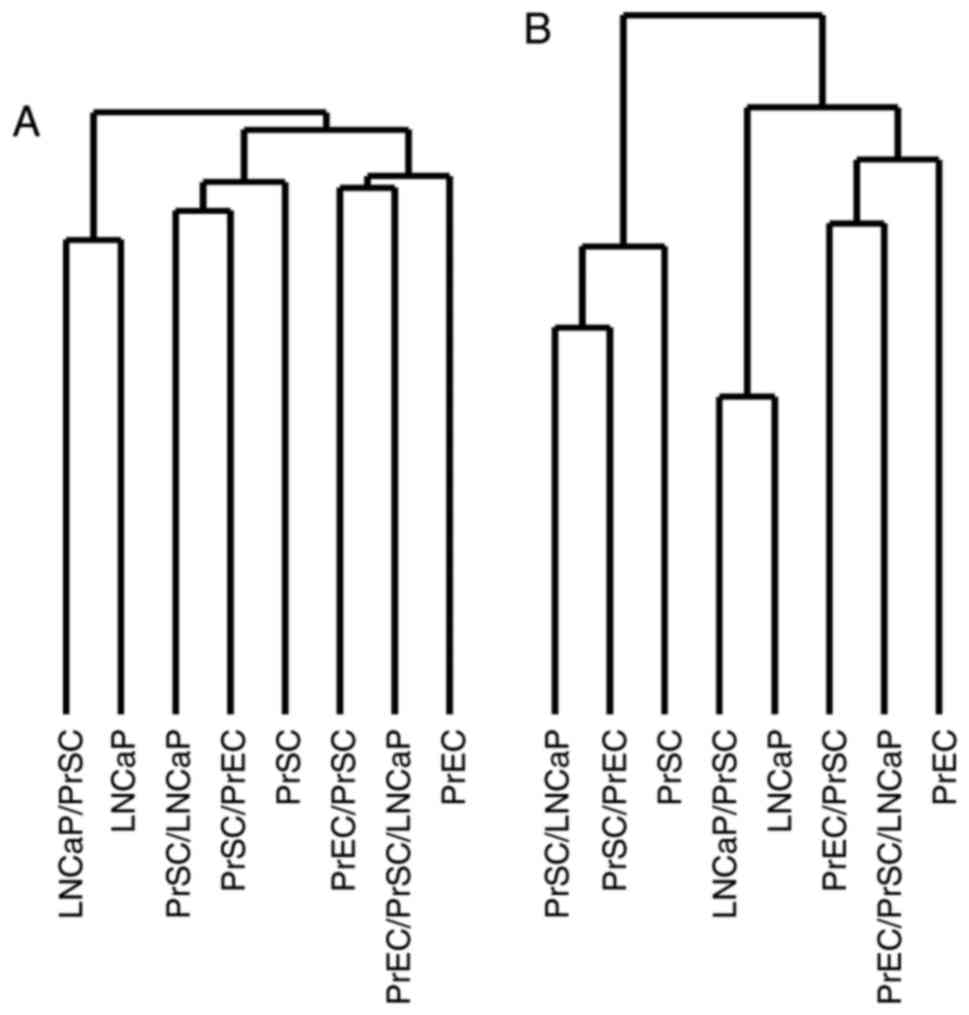
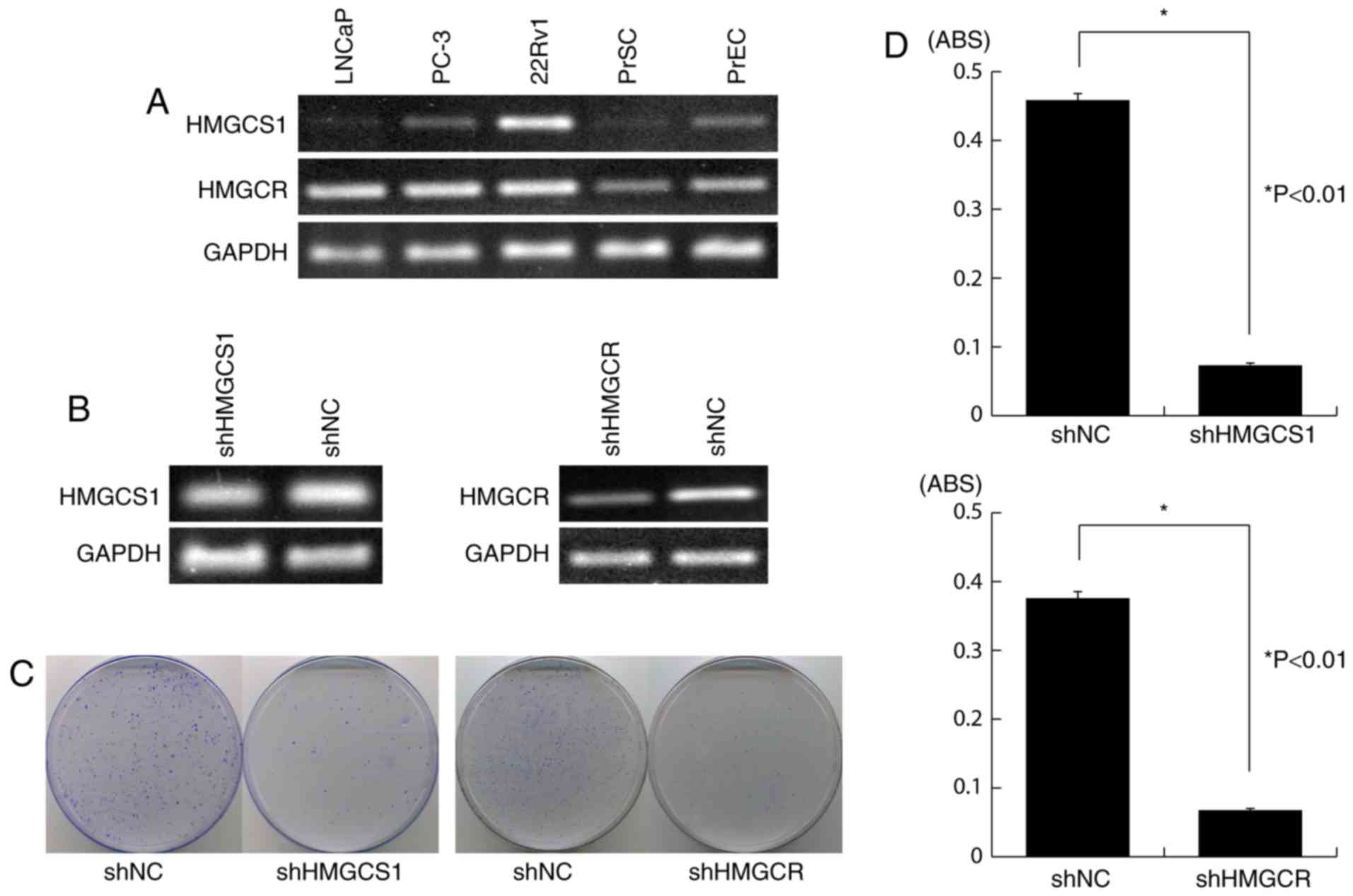
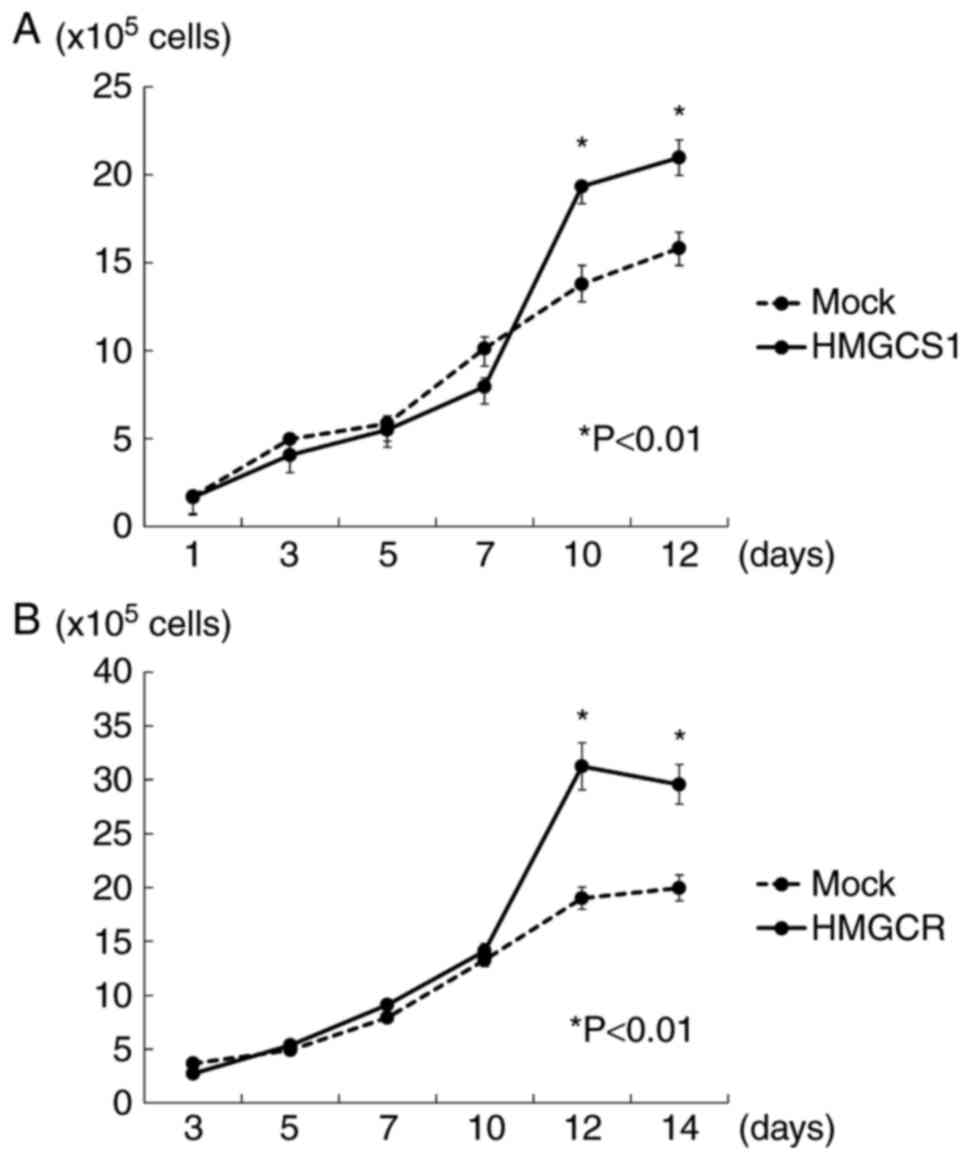
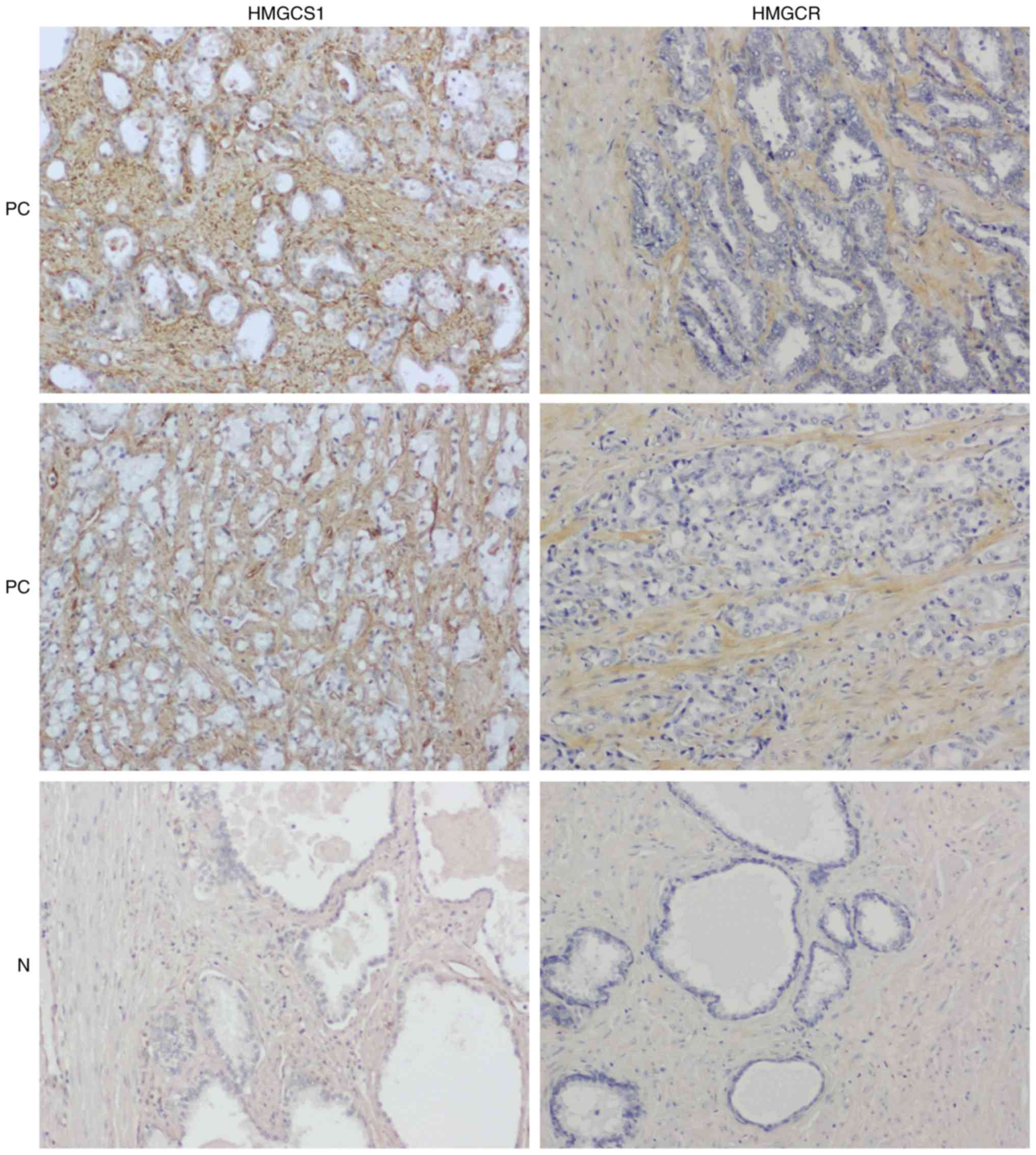
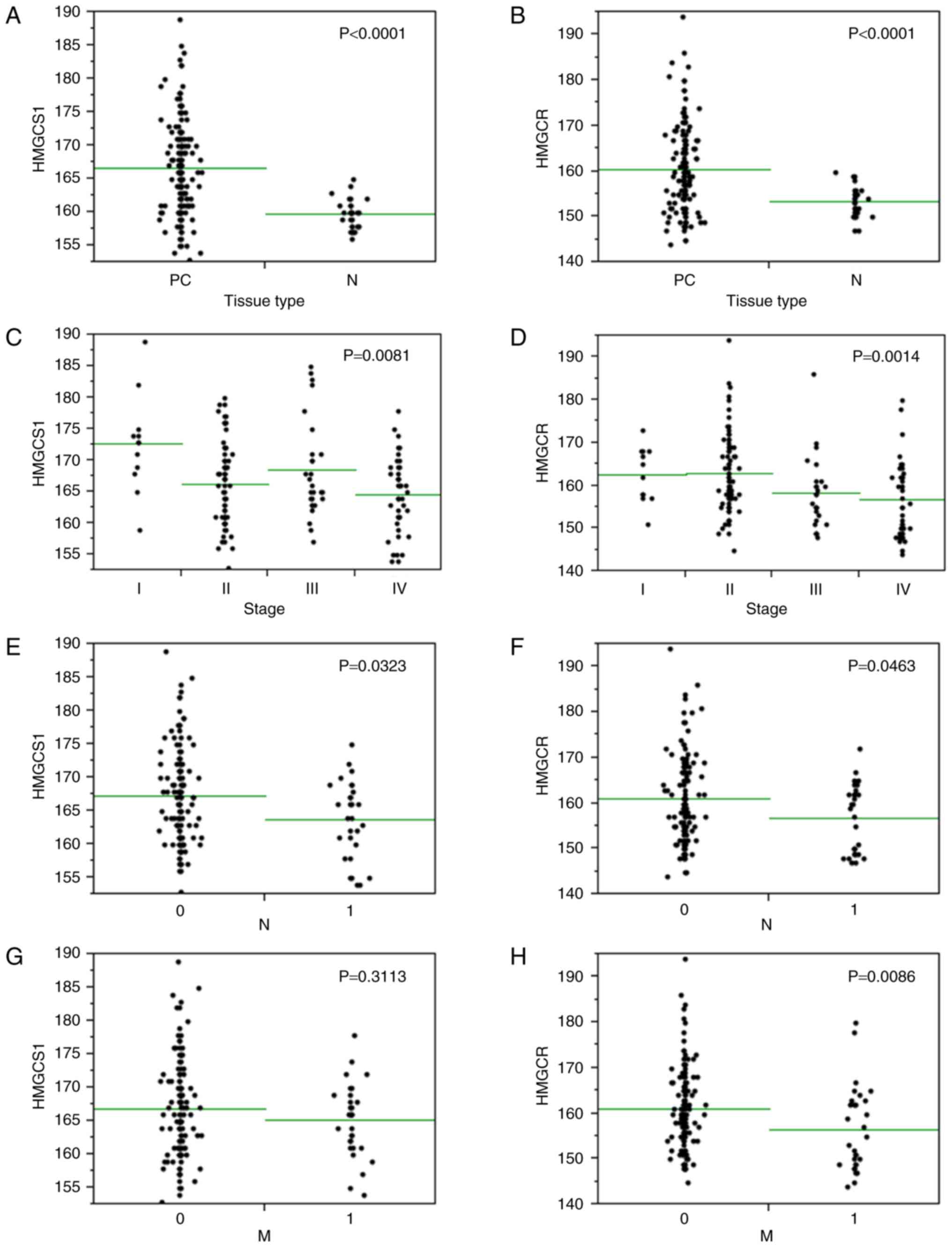
|
1
|
Chung LW, Baseman A, Assikis V and Zhau
HE: Molecular insights into prostate cancer progression: The
missing link of tumor microenvironment. J Urol. 173:10–20. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sung SY, Hsieh CL, Law A, Zhau HE, Pathak
S, Multani AS, Lim S, Coleman IM, Wu LC, Figg WD, et al:
Coevolution of prostate cancer and bone stroma in three-dimensional
coculture: Implications for cancer growth and metastasis. Cancer
Res. 68:9996–10003. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tuxhorn JA, Ayala GE and Rowley DR:
Reactive stroma in prostate cancer progression. J Urol.
166:2472–2483. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ashida S, Orloff MS, Bebek G, Zhang L,
Zheng P, Peehl DM and Eng C: Integrated analysis reveals critical
genomic regions in prostate tumor microenvironment associated with
clinicopathologic phenotypes. Clin Cancer Res. 18:1578–1587. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nauseef JT and Henry MD:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer: Paradigm
or puzzle? Nat Rev Urol. 8:428–439. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vaarala MH, Hirvikoski P, Kauppila S and
Paavonen TK: Identification of androgen-regulated genes in human
prostate. Mol Med Rep. 6:466–472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kestens C, Siersema PD, Offerhaus GJ and
van Baal JW: BMP4 signaling is able to induce an
epithelial-mesenchymal transition-like phenotype in barrett's
esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma through induction of
SNAIL2. PLoS One. 11:e01557542016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee WJ, Kim SC, Yoon JH, Yoon SJ, Lim J,
Kim YS, Kwon SW and Park JH: Meta-analysis of tumor stem-like
breast cancer cells using gene set and network analysis. PLoS One.
11:e01488182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Meerzaman DM, Yan C, Chen QR, Edmonson MN,
Schaefer CF, Clifford RJ, Dunn BK, Dong L, Finney RP, Cultraro CM,
et al: Genome-wide transcriptional sequencing identifies novel
mutations in metabolic genes in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 11:1–12. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pandyra A, Mullen PJ, Kalkat M, Yu R, Pong
JT, Li Z, Trudel S, Lang KS, Minden MD, Schimmer AD and Penn LZ:
Immediate utility of two approved agents to target both the
metabolic mevalonate pathway and its restorative feedback loop.
Cancer Res. 74:4772–4782. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pandyra AA, Mullen PJ, Goard CA, Ericson
E, Sharma P, Kalkat M, Yu R, Pong JT, Brown KR, Hart T, et al:
Genome-wide RNAi analysis reveals that simultaneous inhibition of
specific mevalonate pathway genes potentiates tumor cell death.
Oncotarget. 6:26909–26921. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Van der Meer DL, Degenhardt T, Väisänen S,
de Groot PJ, Heinäniemi M, de Vries SC, Müller M, Carlberg C and
Kersten S: Profiling of promoter occupancy by PPARalpha in human
hepatoma cells via ChIP-chip analysis. Nucleic Acids Res.
38:2839–2850. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wali VB, Haskins JW, Gilmore-Hebert M,
Platt JT, Liu Z and Stern DF: Convergent and divergent cellular
responses by ErbB4 isoforms in mammary epithelial cells. Mol Cancer
Res. 12:1140–1155. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao M, Li H, Bu X, Lei C, Fang Q and Hu
Z: Quantitative proteomic analysis of cellular resistance to the
nanoparticle abraxane. ACS Nano. 9:10099–10112. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rokosz LL, Boulton DA, Butkiewicz EA,
Sanyal G, Cueto MA, Lachance PA and Hermes JD: Human cytoplasmic
3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A synthase: Expression,
purification, and characterization of recombinant wild-type and
Cys129 mutant enzymes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 312:1–13. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bull CJ, Bonilla C, Holly JM, Perks CM,
Davies N, Haycock P, Yu OH, Richards JB, Eeles R, Easton D, et al:
Blood lipids and prostate cancer: A Mendelian randomization
analysis. Cancer Med. 5:1125–1136. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim JH, Cox ME and Wasan KM: Effect of
simvastatin on castration-resistant prostate cancer cells. Lipids
Health Dis. 13:562014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li X, Chen YT, Josson S, Mukhopadhyay NK,
Kim J, Freeman MR and Huang WC: MicroRNA-185 and 342 inhibit
tumorigenicity and induce apoptosis through blockade of the SREBP
metabolic pathway in prostate cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e709872013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Menter DG, Ramsauer VP, Harirforoosh S,
Chakraborty K, Yang P, Hsi L, Newman RA and Krishnan K:
Differential effects of pravastatin and simvastatin on the growth
of tumor cells from different organ sites. PLoS One. 6:e288132011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Murtola TJ, Syvälä H, Pennanen P, Bläuer
M, Solakivi T, Ylikomi T and Tammela TL: The importance of LDL and
cholesterol metabolism for prostate epithelial cell growth. PLoS
One. 7:e394452012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sakai M, Martinez-Arguelles DB, Aprikian
AG, Magliocco AM and Papadopoulos V: De novo steroid biosynthesis
in human prostate cell lines and biopsies. Prostate. 76:575–587.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bengtsson E, Nerjovaj P, Wangefjord S,
Nodin B, Eberhard J, Uhlén M, Borgquist S and Jirström K: HMG-CoA
reductase expression in primary colorectal cancer correlates with
favourable clinicopathological characteristics and an improved
clinical outcome. Diagn Pathol. 9:782014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Borgquist S, Djerbi S, Pontén F,
Anagnostaki L, Goldman M, Gaber A, Manjer J, Landberg G and
Jirström K: HMG-CoA reductase expression in breast cancer is
associated with a less aggressive phenotype and influenced by
anthropometric factors. Int J Cancer. 123:1146–1153. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Borgquist S, Jögi A, Pontén F, Rydén L,
Brennan DJ and Jirström K: Prognostic impact of tumour-specific
HMG-CoA reductase expression in primary breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res. 10:R792008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Brennan DJ, Laursen H, O'Connor DP,
Borgquist S, Uhlen M, Gallagher WM, Pontén F, Millikan RC, Rydén L
and Jirström K: Tumor-specific HMG-CoA reductase expression in
primary premenopausal breast cancer predicts response to tamoxifen.
Breast Cancer Res. 13:R122011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gustbée E, Tryggvadottir H, Markkula A,
Simonsson M, Nodin B, Jirström K, Rose C, Ingvar C, Borgquist S and
Jernström H: Tumor-specific expression of HMG-CoA reductase in a
population-based cohort of breast cancer patients. BMC Clin Pathol.
15:82015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Anazawa Y, Nakagawa H, Furihara M, Ashida
S, Tamura K, Yoshioka H, Shuin T, Fujioka T, Katagiri T and
Nakamura Y: PCOTH, a novel gene overexpressed in prostate cancers,
promotes prostate cancer cell growth through phosphorylation of
oncoprotein TAF-Ibeta/SET. Cancer Res. 65:4578–4586. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Anchi T, Tamura K, Furihata M, Satake H,
Sakoda H, Kawada C, Kamei M, Shimamoto T, Fukuhara H, Fukata S, et
al: SNRPE is involved in cell proliferation and progression of
high-grade prostate cancer through the regulation of androgen
receptor expression. Oncol Lett. 3:264–268. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ashida S, Furihata M, Katagiri T, Tamura
K, Anazawa Y, Yoshioka H, Miki T, Fujioka T, Shuin T, Nakamura Y
and Nakagawa H: Expression of novel molecules, MICAL2-PV (MICAL2
prostate cancer variants), increases with high Gleason score and
prostate cancer progression. Clin Cancer Res. 12:2767–2773. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Satake H, Tamura K, Furihata M, Anchi T,
Sakoda H, Kawada C, Iiyama T, Ashida S and Shuin T: The
ubiquitin-like molecule interferon-stimulated gene 15 is
overexpressed in human prostate cancer. Oncol Rep. 23:11–16.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tamura K, Makino A, Hullin-Matsuda F,
Kobayashi T, Furihata M, Chung S, Ashida S, Miki T, Fujioka T,
Shuin T, et al: Novel lipogenic enzyme ELOVL7 is involved in
prostate cancer growth through saturated long-chain fatty acid
metabolism. Cancer Res. 69:8133–8140. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Togashi A, Katagiri T, Ashida S, Fujioka
T, Maruyama O, Wakumoto Y, Sakamoto Y, Fujime M, Kawachi Y, Shuin T
and Nakamura Y: Hypoxia-inducible protein 2 (HIG2), a novel
diagnostic marker for renal cell carcinoma and potential target for
molecular therapy. Cancer Res. 65:4817–4826. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|