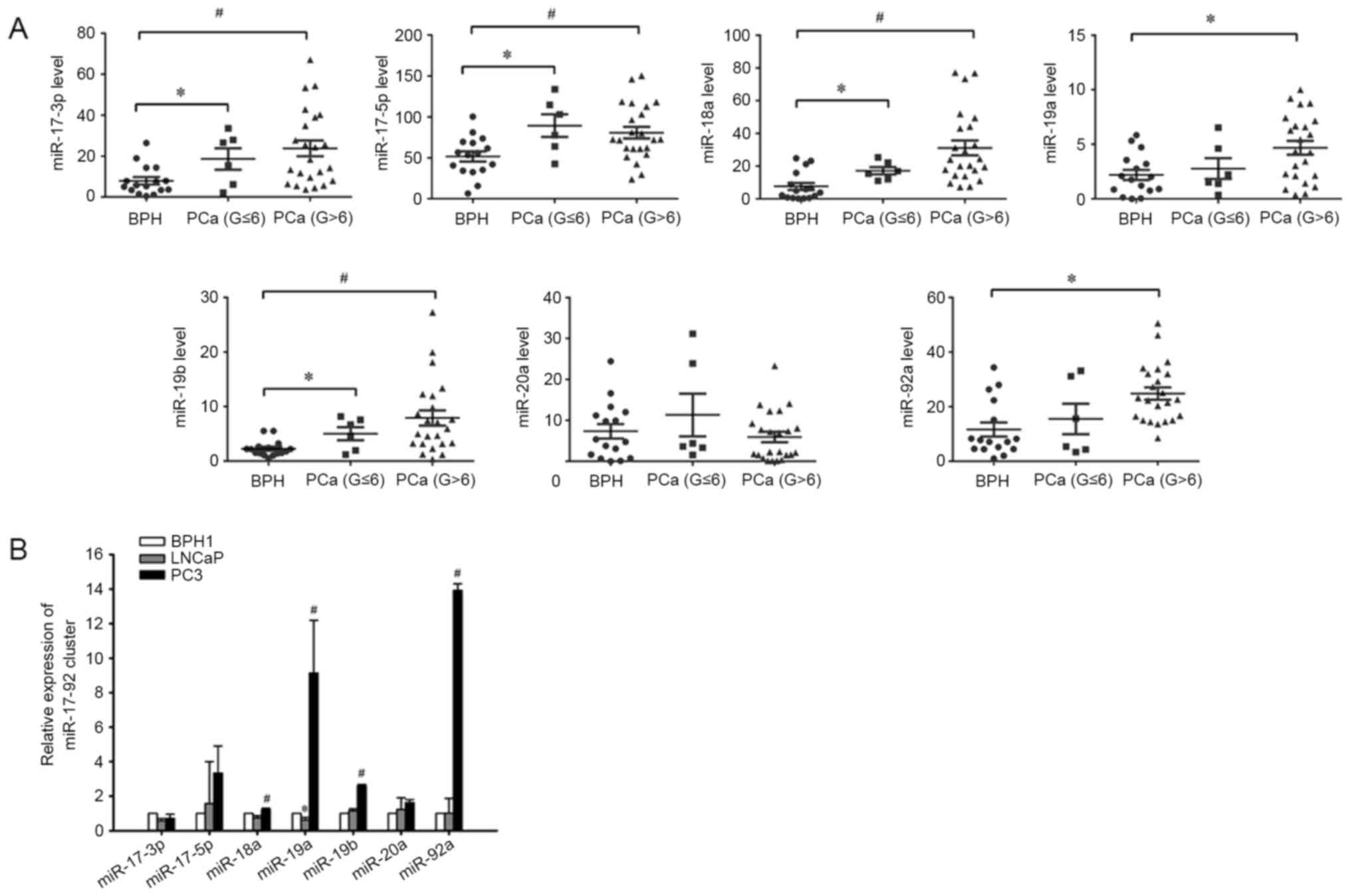
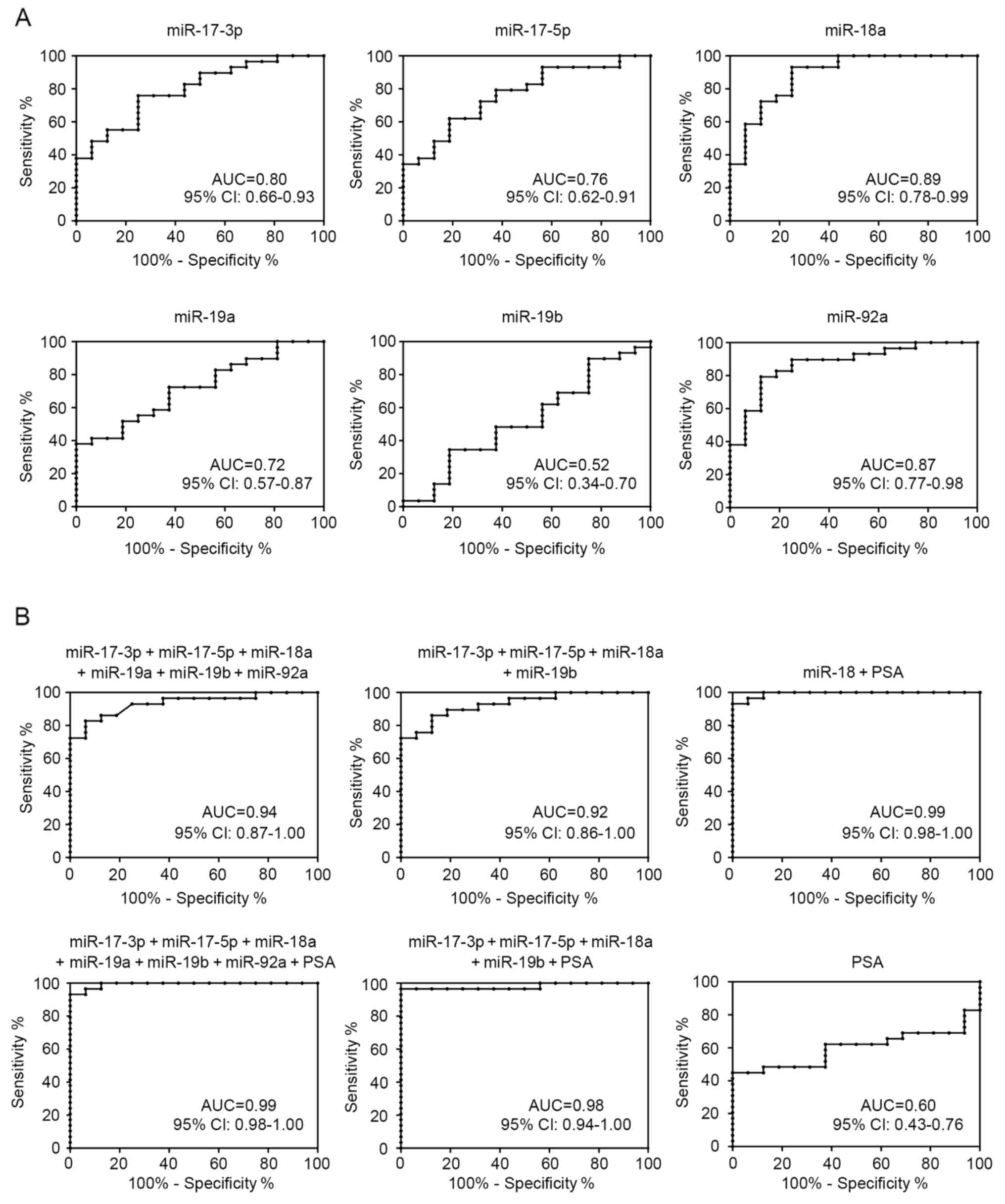
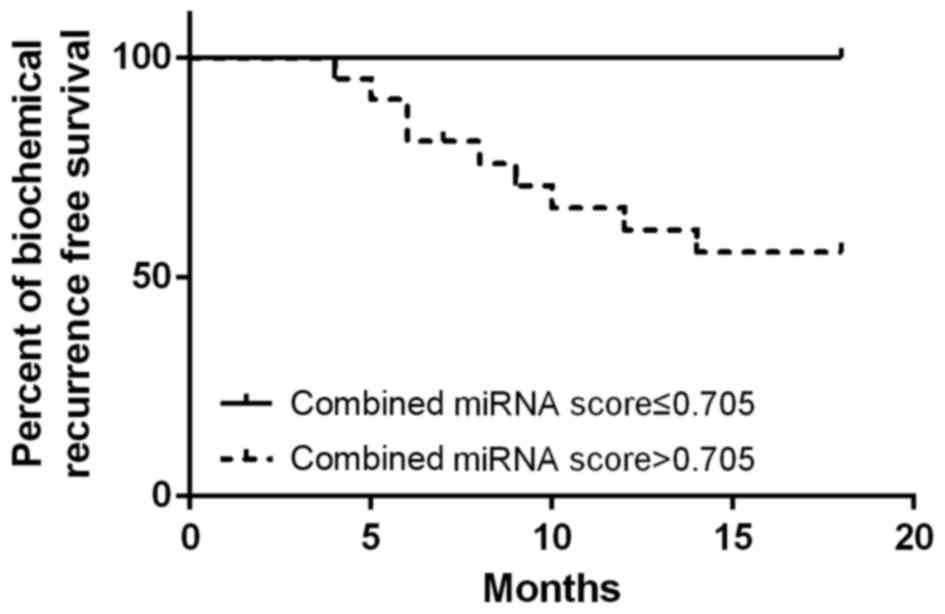
|
1
|
Torre LA, Siegel RL, Ward EM and Jemal A:
Global cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends-an update.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 25:16–27. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Saad F and Fizazi K: Androgen deprivation
therapy and secondary hormone therapy in the management of
hormone-sensitive and castration resistant prostate cancer.
Urology. 86:852–861. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ren SC, Chen R and Sun YH: Prostate cancer
research in China. Asian J Androl. 15:350–353. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schröder FH, Hugosson J, Roobol MJ,
Tammela TL, Ciatto S, Nelen V, Kwiatkowski M, Lujan M, Lilja H,
Zappa M, et al: Screening and prostate-cancer mortality in a
randomized European study. N Engl J Med. 360:1320–1328. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Carthew RW and Sontheimer EJ: Origins and
Mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell. 136:642–655. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vanacore D, Boccellino M, Rossetti S,
Cavaliere C, D'Aniello C, Di Franco R, Romano FJ, Montanari M, La
Mantia E, Piscitelli R, et al: Micrornas in prostate cancer: An
overview. Oncotarget. 2017.[Epub ahead of print]. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Fuziwara CS and Kimura ET: Insights into
regulation of the miR-17-92 cluster of miRNAs in cancer. Front Med
(Lausanne). 2:642015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Olive V, Li Q and He L: mir-17-92: A
polycistronic oncomir with pleiotropic functions. Immunol Rev.
253:158–166. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hayashita Y, Osada H, Tatematsu Y, Yamada
H, Yanagisawa K, Tomida S, Yatabe Y, Kawahara K, Sekido Y and
Takahashi T: A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is
overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell
proliferation. Cancer Res. 65:9628–9632. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT,
Hernando-Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S, Powers S, Cordon-Cardo C, Lowe
SW, Hannon GJ and Hammond SM: A microRNA polycistron as a potential
human oncogene. Nature. 435:828–833. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Arabi L, Gsponer JR, Smida J, Nathrath M,
Perrina V, Jundt G, Ruiz C, Quagliata L and Baumhoer D:
Upregulation of the miR-17-92 cluster and its two paraloga in
osteosarcoma-reasons and consequences. Genes Cancer. 5:56–63.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
John-Aryankalayil M, Palayoor ST, Makinde
AY, Cerna D, Simone CB II, Falduto MT, Magnuson SR and Coleman CN:
Fractionated radiation alters oncomir and tumor suppressor miRNAs
in human prostate cancer cells. Radiat Res. 178:105–117. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rees MA, Resnick MI and Oesterling JE: Use
of prostate-specific antigen, Gleason score and digital rectal
examination in staging patients with newly diagnosed prostate
cancer. Urol Clin North Am. 24:379–388. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Catto JW, Alcaraz A, Bjartell AS, De Vere
White R, Evans CP, Fussel S, Hamdy FC, Kallioniemi O, Mengual L,
Schlomm T and Visakorpi T: MicroRNA in prostate, bladder and kidney
cancer: A systematic review. Eur Urol. 59:671–681. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Porkka KP, Pfeiffer MJ, Waltering KK,
Vessella RL, Tammela TL and Visakorpi T: MicroRNA expression
profiling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 67:6130–6135. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lichner Z, Fendler A, Saleh C, Nasser AN,
Boles D, Al-Haddad S, Kupchak P, Dharsee M, Nuin PS, Evans KR, et
al: MicroRNA signature helps distinguish early from late
biochemical failure in prostate cancer. Clin Chem. 59:1595–1603.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ota A, Tagawa H, Karnan S, Tsuzuki S,
Karpas A, Kira S, Yoshida Y and Seto M: Identification and
characterization of a novel gene, C13orf25, as a target for
13q31-q32 amplification in malignant lymphoma. Cancer Res.
64:3087–3095. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mendell JT: miRiad roles for the miR-17-92
cluster in development and disease. Cell. 133:217–222. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mogilyansky E and Rigoutsos I: The
miR-17/92 cluster: A comprehensive update on its genomics,
genetics, functions and increasingly important and numerous roles
in health and disease. Cell Death Differ. 20:1603–1614. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhu H, Han C and Wu T: MiR-17-92 cluster
promotes hepatocarcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 36:1213–1222. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Go H, Jang JY, Kim PJ, Kim YG, Nam SJ,
Paik JH, Kim TM, Heo DS, Kim CW and Jeon YK: MicroRNA-21 plays an
oncogenic role by targeting FOXO1 and activating the PI3K/AKT
pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget.
6:15035–15049. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Saki N, Abroun S, Soleimani M, Hajizamani
S, Shahjahani M, Kast RE and Mortazavi Y: Involvement of microRNA
in T-cell differentiation and malignancy. Int J Hematol Oncol Stem
Cell Res. 9:33–49. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Osada H and Takahashi T: let-7 and
miR-17-92: Small-sized major players in lung cancer development.
Cancer Sci. 102:9–17. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jin L, Lim M, Zhao S, Sano Y, Simone BA,
Savage JE, Wickstrom E, Camphausen K, Pestell RG and Simone NL: The
metastatic potential of triple-negative breast cancer is decreased
via caloric restriction-mediated reduction of the miR-17~92
cluster. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 146:41–50. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Servín-González LS, Granados-López AJ and
López JA: Families of microRNAs expressed in clusters regulate cell
signaling in cervical cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 16:12773–12790. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sylvestre Y, De Guire V, Querido E,
Mukhopadhyay UK, Bourdeau V, Major F, Ferbeyre G and Chartrand P:
An E2F/miR-20a autoregulatory feedback loop. J Biol Chem.
282:2135–2143. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pasqualini L, Bu H, Puhr M, Narisu N,
Rainer J, Schlick B, Schäfer G, Angelova M, Trajanoski Z, Börno ST,
et al: miR-22 and miR-29a are members of the androgen receptor
cistrome modulating LAMC1 and Mcl-1 in prostate cancer. Mol
Endocrinol. 29:1037–1054. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang X, Du WW, Li H, Liu F, Khorshidi A,
Rutnam ZJ and Yang BB: Both mature miR-17-5p and passenger strand
miR-17-3p target TIMP3 and induce prostate tumor growth and
invasion. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:9688–9704. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang SY, Shiboski S, Belair CD, Cooperberg
MR, Simko JP, Stoppler H, Cowan J, Carroll PR and Blelloch R:
miR-19, miR-345, miR-519c-5p serum levels predict adverse pathology
in prostate cancer patients eligible for active surveillance. PLoS
One. 9:e985972014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pesta M, Klecka J, Kulda V, Topolcan O,
Hora M, Eret V, Ludvikova M, Babjuk M, Novak K, Stolz J and Holubec
L: Importance of miR-20a expression in prostate cancer tissue.
Anticancer Res. 30:3579–3583. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Takeshita H,
Morimura R, Hirajima S, Tsujiura M, Kawaguchi T, Miyamae M, Nagata
H, Konishi H, et al: Circulating miR-18a: A sensitive cancer
screening biomarker in human cancer. In Vivo. 28:293–297.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shen Z, Wu X, Wang Z, Li B and Zhu X:
Effect of miR-18a overexpression on the radiosensitivity of
non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:643–648.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Su ZX, Zhao J, Rong ZH, Wu YG, Geng WM and
Qin CK: Diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating miR-18a in
the plasma of patients with gastric cancer. Tumour Biol.
35:12119–12125. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li T, Li RS, Li YH, Zhong S, Chen YY,
Zhang CM, Hu MM and Shen ZJ: miR-21 as an independent biochemical
recurrence predictor and potential therapeutic target for prostate
cancer. J Urol. 187:1466–1472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kobayashi N, Uemura H, Nagahama K, Okudela
K, Furuya M, Ino Y, Ito Y, Hirano H, Inayama Y, Aoki I, et al:
Identification of miR-30d as a novel prognostic maker of prostate
cancer. Oncotarget. 3:1455–1471. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Barron N, Keenan J, Gammell P, Martinez
VG, Freeman A, Masters JR and Clynes M: Biochemical relapse
following radical prostatectomy and miR-200a levels in prostate
cancer. Prostate. 72:1193–1199. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Goto Y, Kojima S, Nishikawa R, Enokida H,
Chiyomaru T, Kinoshita T, Nakagawa M, Naya Y, Ichikawa T and Seki
N: The microRNA-23b/27b/24-1 cluster is a disease progression
marker and tumor suppressor in prostate cancer. Oncotarget.
5:7748–7759. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|