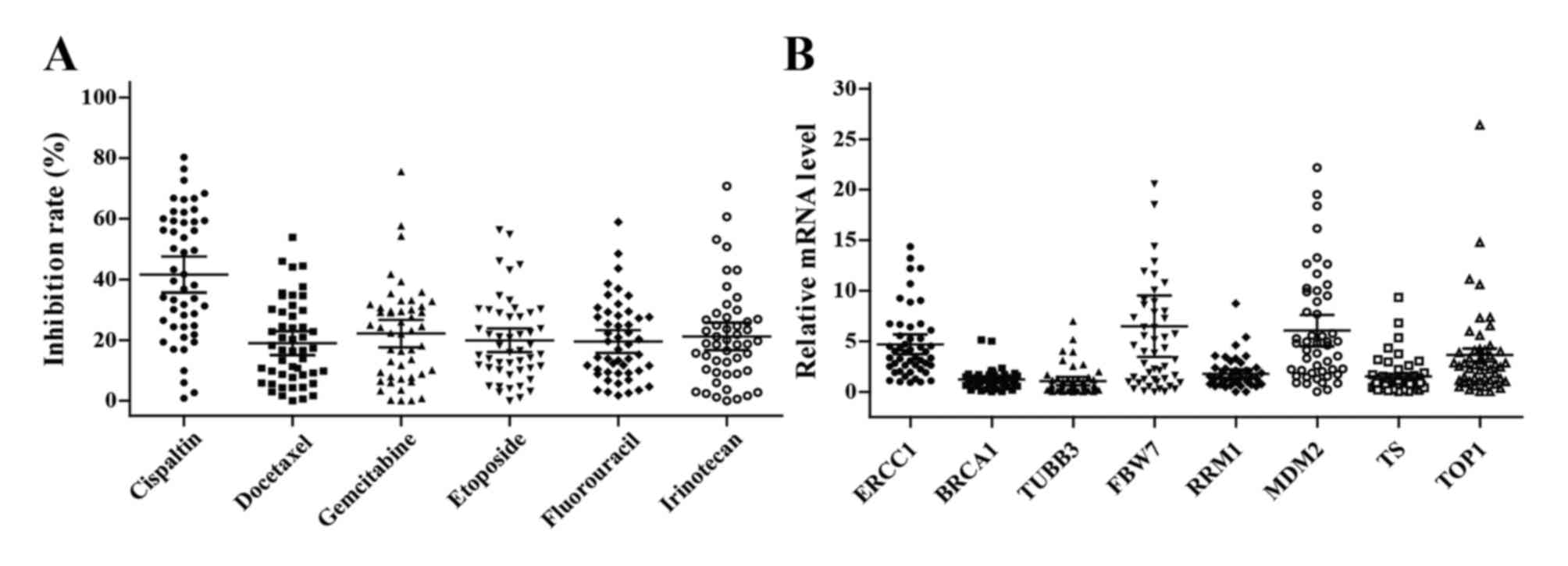
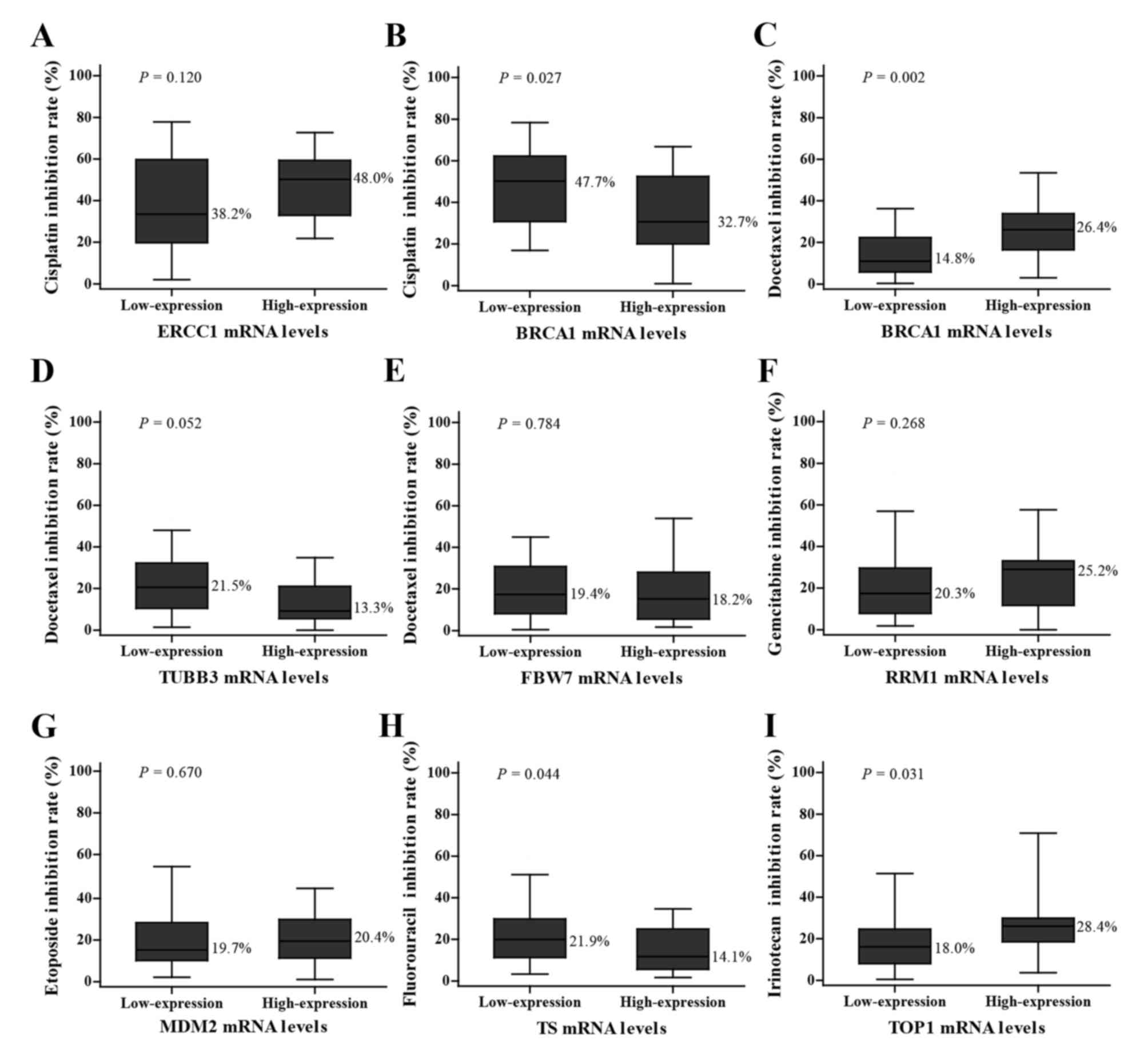
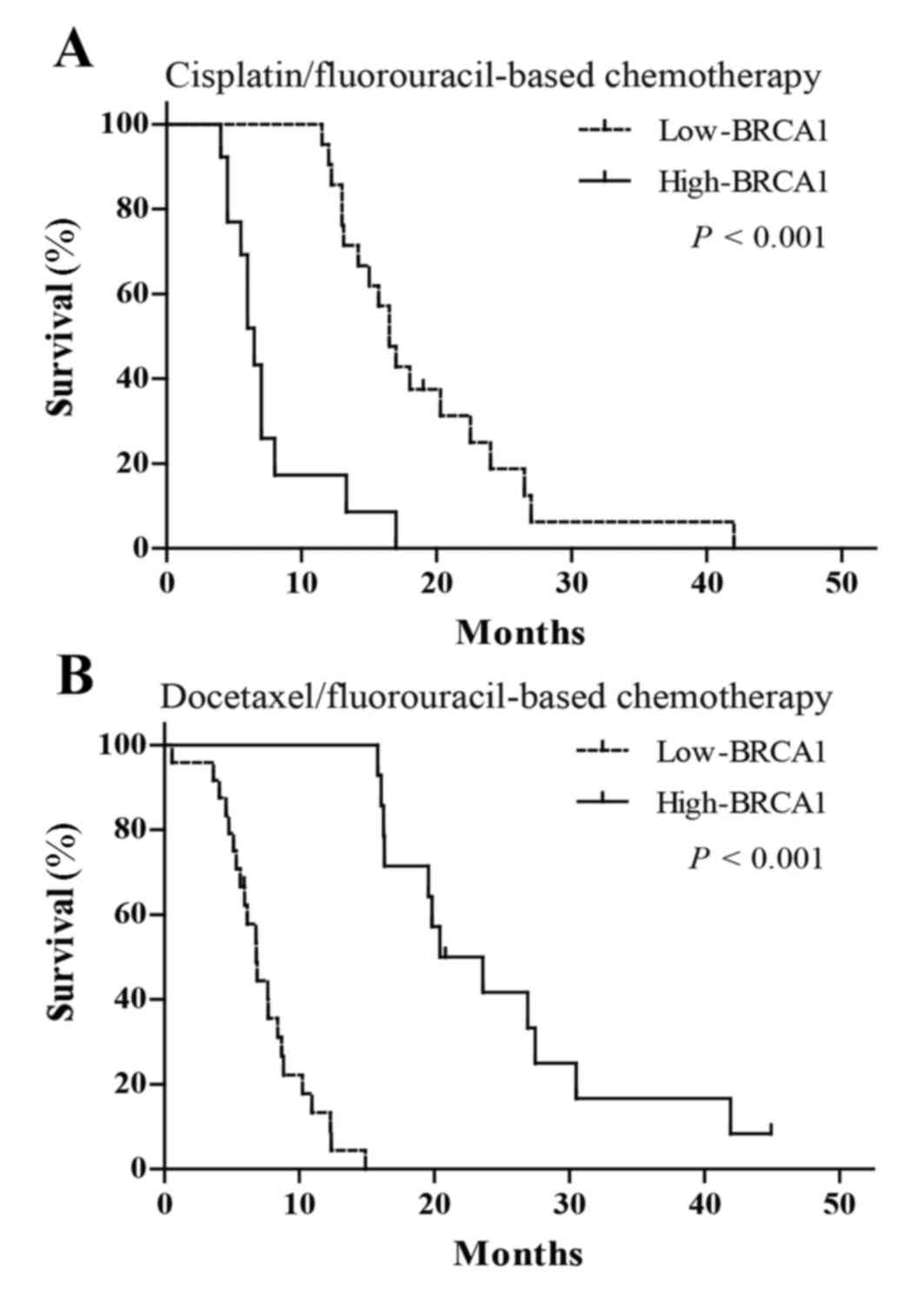
|
1
|
Zhang HZ, Jin GF and Shen HB:
Epidemiologic differences in esophageal cancer between Asian and
Western populations. Chin J Cancer. 31:281–286. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ezdinli EZ, Gelber R, Desai DV, Falkson G,
Moertel CG and Hahn RG: Chemotherapy of advanced esophageal
carcinoma: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group experience. Cancer.
46:2149–2153. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ajani JA, Ilson DH, Daugherty K, Pazdur R,
Lynch PM and Kelsen DP: Activity of taxol in patients with squamous
cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 86:1086–1091. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Millar J, Scullin P, Morrison A, McClory
B, Wall L, Cameron D, Philips H, Price A, Dunlop D and Eatock M:
Phase II study of gemcitabine and cisplatin in locally
advanced/metastatic oesophageal cancer. Br J Cancer. 93:1112–1116.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Denison TA and Bae YH: Tumor heterogeneity
and its implication for drug delivery. J Control Release.
164:187–191. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
O'Donnell PH and Dolan ME: Cancer
pharmacoethnicity: Ethnic differences in susceptibility to the
effects of chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 15:4806–4814. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Papadaki C, Sfakianaki M, Ioannidis G,
Lagoudaki E, Trypaki M, Tryfonidis K, Mavroudis D, Stathopoulos E,
Georgoulias V and Souglakos J: ERCC1 and BRAC1 mRNA expression
levels in the primary tumor could predict the effectiveness of the
second-line cisplatin-based chemotherapy in pretreated patients
with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol.
7:663–671. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wei J, Costa C, Ding Y, Zou Z, Yu L,
Sanchez JJ, Qian X, Chen H, Gimenez-Capitan A, Meng F, et al: mRNA
expression of BRCA1, PIAS1, and PIAS4 and survival after
second-line docetaxel in advanced gastric cancer. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 103:1552–1556. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wertz IE, Kusam S, Lam C, Okamoto T,
Sandoval W, Anderson DJ, Helgason E, Ernst JA, Eby M, Liu J, et al:
Sensitivity to antitubulin chemotherapeutics is regulated by MCL1
and FBW7. Nature. 471:110–114. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Urano N, Fujiwara Y, Doki Y, Kim SJ,
Miyoshi Y, Noguchi S, Miyata H, Takiguchi S, Yasuda T, Yano M and
Monden M: Clinical significance of class III beta-tubulin
expression and its predictive value for resistance to
docetaxel-based chemotherapy in gastric cancer. Int J Oncol.
28:375–381. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Soong R, Shah N, Salto-Tellez M, Tai BC,
Soo RA, Han HC, Ng SS, Tan WL, Zeps N, Joseph D, et al: Prognostic
significance of thymidylate synthase, dihydropyrimidine
dehydrogenase and thymidine phosphorylase protein expression in
colorectal cancer patients treated with or without
5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy. Ann Oncol. 19:915–919. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Souglakos J, Boukovinas I, Taron M, Mendez
P, Mavroudis D, Tripaki M, Hatzidaki D, Koutsopoulos A,
Stathopoulos E, Georgoulias V and Rosell R: Ribonucleotide
reductase subunits M1 and M2 mRNA expression levels and clinical
outcome of lung adenocarcinoma patients treated with
docetaxel/gemcitabine. Br J Cancer. 98:1710–1715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rodriguez-Lopez AM, Xenaki D, Eden TO,
Hickman JA and Chresta CM: MDM2 mediated nuclear exclusion of p53
attenuates etoposide-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. Mol
Pharmacol. 59:135–143. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tsurutani J, Nitta T, Hirashima T, Komiya
T, Uejima H, Tada H, Syunichi N, Tohda A, Fukuoka M and Nakagawa K:
Point mutations in the topoisomerase I gene in patients with
non-small cell lung cancer treated with irinotecan. Lung Cancer.
35:299–304. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim M, Keam B, Kim TM, Kim HG, Kim JS, Lee
SS, Shin SH, Kim MK, Park KU, Kim DW, et al: Phase II study of
irinotecan and cisplatin combination chemotherapy in metastatic,
unresectable esophageal cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 49:416–422. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Harstrick A, Bokemeyer C, Preusser P,
Köhne-Wömpner CH, Meyer HJ, Stahl M, Knipp H, Schmoll HJ and Wilke
H: Phase II study of single-agent etoposide in patients with
metastatic squamous-cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 29:321–322. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Furukawa T, Kubota T, Tanino H, Oura S,
Yuasa S, Murate H, Morita K, Kozakai K, Yano T and Hoffman RM:
Chemosensitivity of breast cancer lymph node metastasis compared to
the primary tumor from individual patients tested in the
histoculture drug response assay. Anticancer Res. 20:3657–3658.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hoffman RM: To do tissue culture in two or
three dimensions? That is the question. Stem Cells. 11:105–111.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tanino H, Oura S, Hoffman RM, Kubota T,
Furukawa T, Arimoto J, Yoshimasu T, Hirai I, Bessho T, Suzuma T, et
al: Acquisition of multidrug resistance in recurrent breast cancer
demonstrated by the histoculture drug response assay. Anticancer
Res. 21:4083–4086. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim R, Emi M, Tanabe K, Uchida Y and Toge
T: Chemosensitivity testing for gastrointestinal cancer: Survival
benefit potential and limitations. Anticancer Drugs. 14:715–723.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee SW, Kim YM, Kim MB, Kim DY, Kim JH,
Nam JH and Kim YT: In vitro chemosensitivity using the histoculture
drug response assay in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Acta Med
Okayama. 66:271–277. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rosen MA and Sullivan D: Optimal lesion
number for evaluation of tumor response in response evaluation
criteria in solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 28:e159–e161. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Goense L, van Rossum PS, Kandioler D,
Ruurda JP, Goh KL, Luyer MD, Krasna MJ and van Hillegersberg R:
Stage-directed individualized therapy in esophageal cancer. Ann N Y
Acad Sci. 1381:50–65. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu Y, Xiong Z, Beasley A, D'Amico T and
Chen XL: Personalized and targeted therapy of esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma: An update. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1381:66–73. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Furukawa T, Kubota T, Watanabe M, Takahara
T, Yamaguchi H, Takeuchi T, Kase S, Kodaira S, Ishibiki K, Kitajima
M, et al: High in vitro-in vivo correlation of drug response using
sponge-gel-supported three-dimensional histoculture and the MTT end
point. Int J Cancer. 51:489–498. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sevin BU, Peng ZL, Perras JP, Ganjei P,
Penalver M and Averette HE: Application of an ATP-bioluminescence
assay in human tumor chemosensitivity testing. Gynecol Oncol.
31:191–204. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bogden AE, Cobb WR, Lepage DJ, Haskell PM,
Gulkin TA, Ward A, Kelton DE and Esber HJ: Chemotherapy
responsiveness of human tumors as first transplant generation
xenografts in the normal mouse: Six-day subrenal capsule assay.
Cancer. 48:10–20. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shen J, Wei J, Wang H, Yue G, Yu L, Yang
Y, Xie L, Zou Z, Qian X, Ding Y, et al: A three-gene signature as
potential predictive biomarker for irinotecan sensitivity in
gastric cancer. J Transl Med. 11:732013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Furukawa T, Kubota T and Hoffman RM:
Clinical applications of the histoculture drug response assay. Clin
Cancer Res. 1:305–311. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yoshimasu T, Oura S, Hirai I, Tamaki T,
Kokawa Y, Hata K, Ohta F, Nakamura R, Kawago M, Tanino H, et al:
Data acquisition for the histoculture drug response assay in lung
cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 133:303–308. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang Q, Shen J, Wang H, Hu J, Yu L, Xie
L, Wei J, Liu B, Guan W and Qian X: TS mRNA levels can predict
pemetrexed and raltitrexed sensitivity in colorectal cancer. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 73:325–333. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yue G, Wei J, Qian X, Yu L, Zou Z, Guan W,
Wang H, Shen J and Liu B: Synergistic anticancer effects of
polyphyllin I and evodiamine on freshly-removed human gastric
tumors. PLoS One. 8:e651642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kinoshita M, Kodera Y, Hibi K, Nakayama G,
Inoue T, Ohashi N, Ito Y, Koike M, Fujiwara M and Nakao A: Gene
expression profile of 5-fluorouracil metabolic enzymes in primary
colorectal cancer: Potential as predictive parameters for response
to fluorouracil-based chemotherapy. Anticancer Res. 27:851–856.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fakhrejahani E, Miyamoto A and Tanigawa N:
Correlation between thymidylate synthase and dihydropyrimidine
dehydrogenase mRNA level and in vitro chemosensitivity to
5-fluorouracil, in relation to differentiation in gastric cancer.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 60:437–446. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shen J, Wei J, Wang H, Yang Y, Yue G, Wang
L, Yu L, Xie L, Sun X, Bian X, et al: SULF2 methylation is
associated with in vitro cisplatin sensitivity and clinical
efficacy for gastric cancer patients treated with a modified FOLFOX
regimen. PLoS One. 8:e755642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ohashi T, Yoshimasu T, Oura S, Kokawa Y,
Kawago M, Hirai Y, Miyasaka M, Aoishi Y, Kiyoi M, Nishiguchi H, et
al: Class III beta-tubulin expression in non-small cell lung
cancer: A predictive factor for paclitaxel response. Anticancer
Res. 35:2669–2674. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xie L, Wei J, Qian X, Chen G, Yu L, Ding Y
and Liu B: CXCR4, a potential predictive marker for docetaxel
sensitivity in gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 30:2209–2216.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yang Y, Wu N, Shen J, Teixido C, Sun X,
Lin Z, Qian X, Zou Z, Guan W, Yu L, et al: MET overexpression and
amplification define a distinct molecular subgroup for targeted
therapies in gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 19:778–788. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gao Y, Zhu J, Zhang X, Wu Q, Jiang S, Liu
Y, Hu Z, Liu B and Chen X: BRCA1 mRNA expression as a predictive
and prognostic marker in advanced esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma treated with cisplatin- or docetaxel-based
chemotherapy/chemoradiotherapy. PLoS One. 8:e525892013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wei B, Han Q, Xu L, Zhang X, Zhu J, Wan L,
Jin Y, Qian Z, Wu J, Gao Y, et al: Effects of JWA, XRCC1 and BRCA1
mRNA expression on molecular staging for personalized therapy in
patients with advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC
Cancer. 15:3312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|