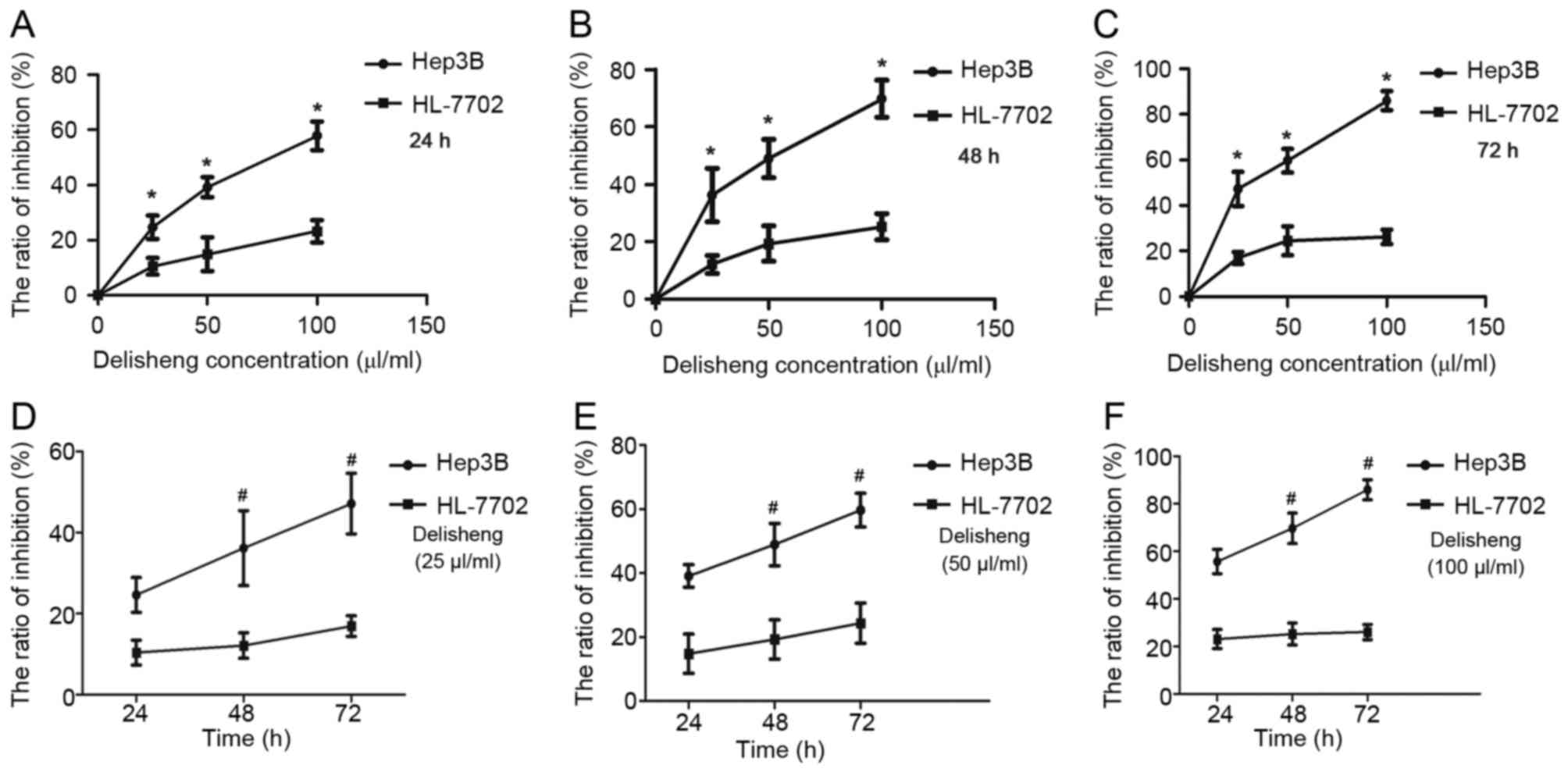
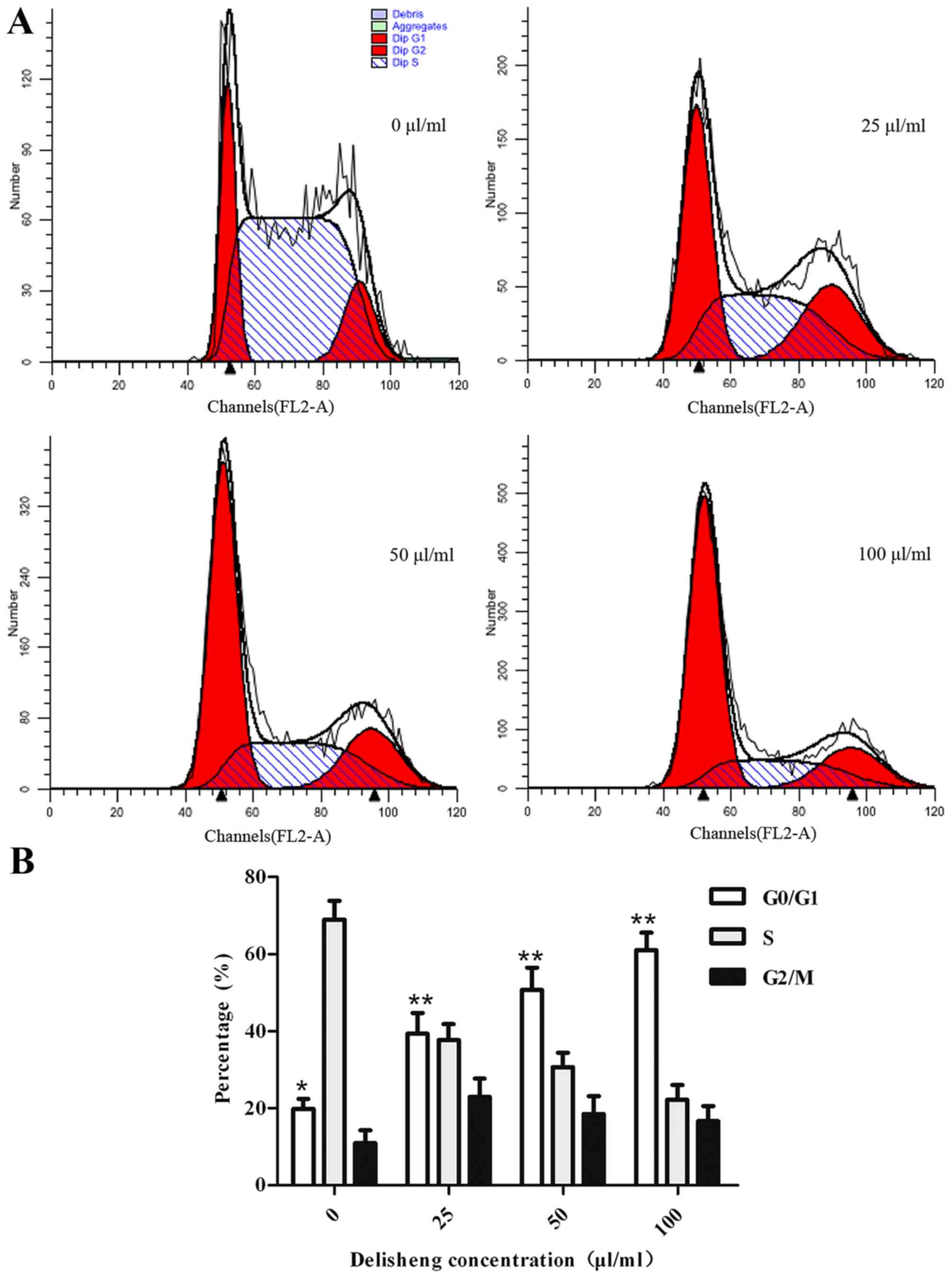
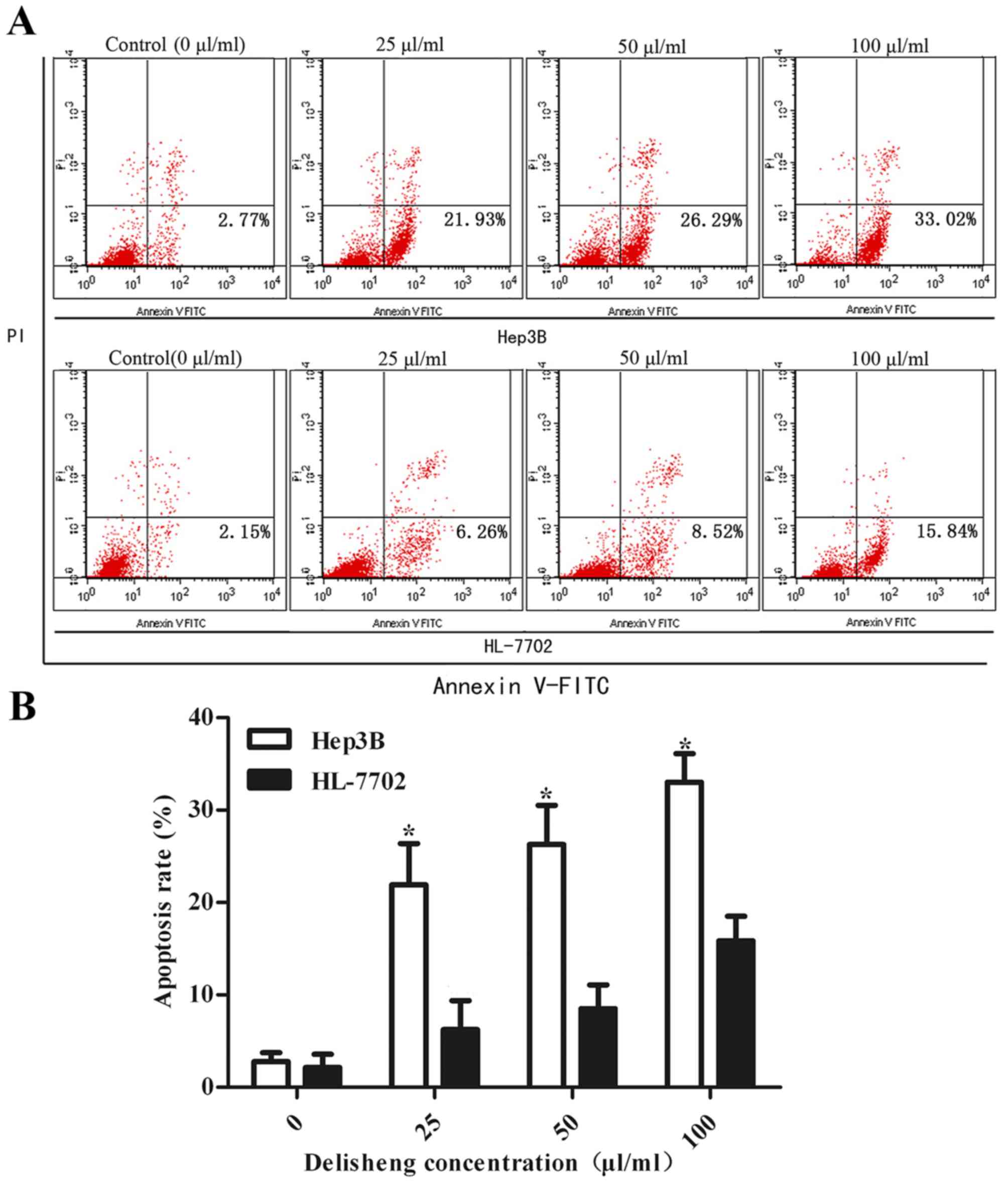
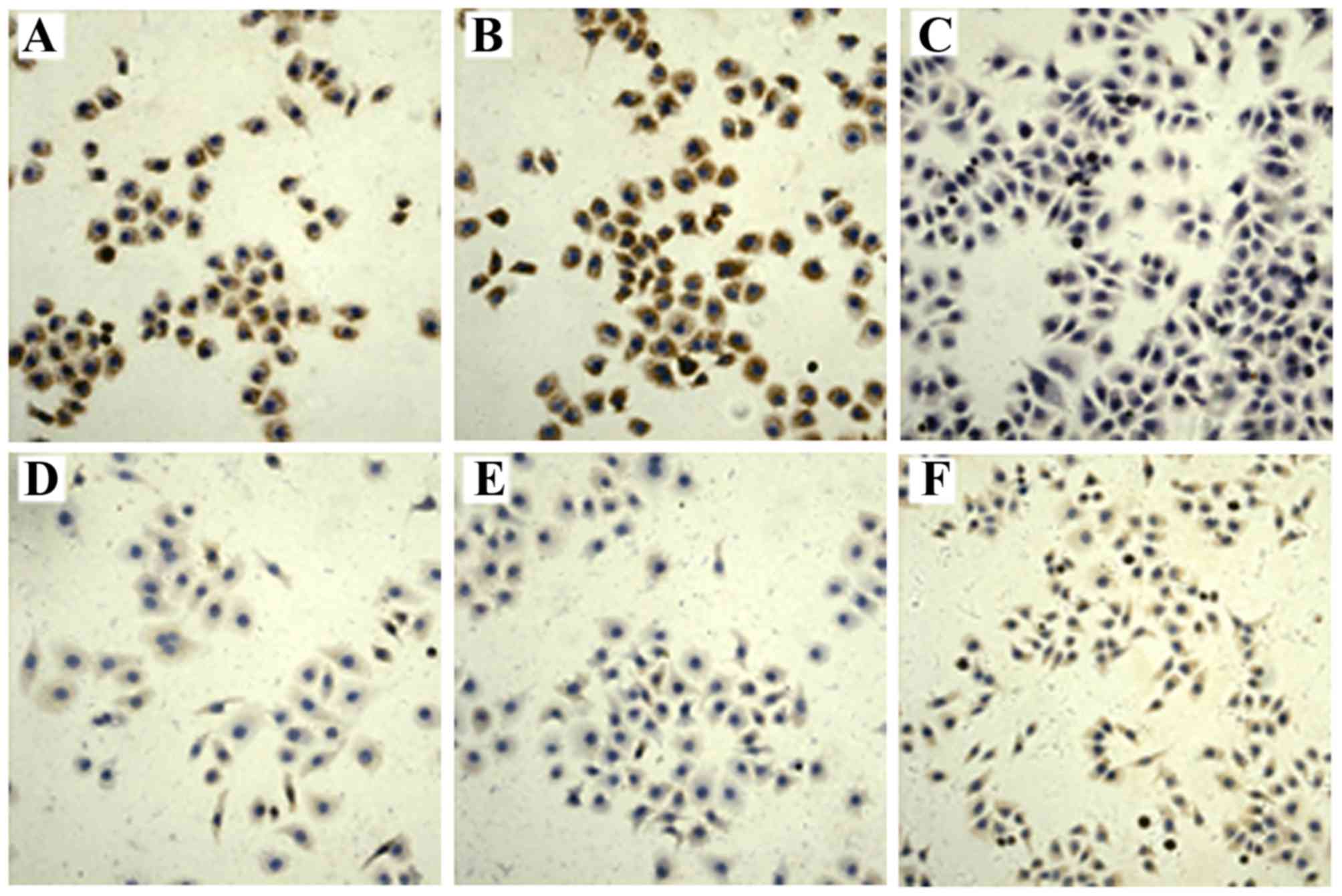
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Buell J: Hepatoma Research: The beginning
of a new forum. Hepatoma Res. 1:1–5. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
El-Serag HB, Marrero JA, Rudolph L and
Reddy KR: Diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 134:1752–1763. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Choi KJ, Baik IH, Ye SK and Lee YH:
Molecular targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Present
status and future directions. Biol Pharm Bull. 38:986–991. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu T, Jiao M, Jing L, Wang MC, Sun HF, Li
Q, Bai YY, Wei YC, Nan KJ and Guo H: Prognostic value of Notch-1
expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Onco
Targets Ther. 8:3105–3114. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang X, Wang N, Cheung F, Lao L, Li C and
Feng Y: Chinese medicines for prevention and treatment of human
hepatocellular carcinoma: Current progress on pharmacological
actions and mechanisms. J Integr Med. 13:142–164. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhai XF, Qiao CX, Liu Q, Chen Z and Ling
CQ: Quality assessment of clinical research on liver cancer treated
by intra-arterial infusion of Chinese medicine. Chin J Integr Med.
20:870–875. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu P, Dugoua JJ, Eyawo O and Mills EJ:
Traditional Chinese Medicines in the treatment of hepatocellular
cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 28:1122009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qi F, Li A, Inagaki Y, Gao J, Li J, Kokudo
N, Li XK and Tang W: Chinese herbal medicines as adjuvant treatment
during chemo- or radio-therapy for cancer. Biosci Trends.
4:297–307. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qi F, Li A, Zhao L, Xu H, Inagaki Y, Wang
D, Cui X, Gao B, Kokudo N, Nakata M and Tang W: Cinobufacini, an
aqueous extract from Bufo bufo gargarizans Cantor, induces
apoptosis through a mitochondria-mediated pathway in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 128:654–661.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang SH, Wang YC, Nie YL, Hai YN, Sun HF,
Yuan ZL and Nan KJ: Antiproliferative activity of the chinese
medicinal compound, delisheng, compared with Rg3 and gemcitabine in
HepG2 Cells. Indian J Pharm Sci. 75:578–584. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sredni B: Immunomodulating tellurium
compounds as anti-cancer agents. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:60–69. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hanahan D and Folkman J: Patterns and
emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis.
Cell. 86:353–364. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Raja R, Kale S, Thorat D, Soundararajan G,
Lohite K, Mane A, Karnik S and Kundu GC: Hypoxia-driven osteopontin
contributes to breast tumor growth through modulation of
HIF1α-mediated VEGF-dependent angiogenesis. Oncogene. 33:2053–2064.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bao Y, Feng WM, Tang CW, Zheng YY, Gong HB
and Hou EG: Endostatin inhibits angiogenesis in hepatocellular
carcinoma after transarterial chemoembolization.
Hepato-gastroenterology. 59:1566–1568. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gai P, Sun H, Wang G, Xu Q, Qi X, Zhang Z
and Jiang L: miR-22 promotes apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells via
inducing cell cycle arrest. Oncol Lett. 13:2354–2358.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lu CX, Nan KJ, Nie YL, Hai YN and Jiao M:
Delisheng, a Chinese medicinal compound, exerts anti-proliferative
and pro-apoptotic effects on HepG2 cells through extrinsic and
intrinsic pathways. Mol Biol Rep. 37:3407–3412. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dong XL, Gong Y, Chen ZZ and Wang YJ:
Delisheng injection (), a Chinese medicinal compound, enhanced the
effect of cis-platinum on lung carcinoma cell line PGCL3. Chin J
Integr Med. 20:286–291. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao D, Liu XJ, Xie Q, Huang ZP, Zou BX
and Ge YB: Intensity-modulated radiation combined with Delisheng
injection for naspharyngeal carcinoma. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue
Bao. 26:874–875. 2006.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pan XY, Guo H, Han J, Hao F, An Y, Xu Y,
Xiaokaiti Y, Pan Y and Li XJ: Ginsenoside Rg3 attenuates cell
migration via inhibition of aquaporin 1 expression in PC-3M
prostate cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 683:27–34. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang SW, Zhou SY, Shao JC and Qu XW:
Primary research on Chinese medicine treatment of
androgen-independent prostate cancer. Chin J Integr Med.
15:168–169. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee HH, Lee S, Lee K, Shin YS, Kang H and
Cho H: Anti-cancer effect of Cordyceps militaris in human
colorectal carcinoma RKO cells via cell cycle arrest and
mitochondrial apoptosis. Daru. 23:352015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tsui KC, Chiang TH, Wang JS, Lin LJ, Chao
WC, Chen BH and Lu JF: Flavonoids from Gynostemma pentaphyllum
exhibit differential induction of cell cycle arrest in H460 and
A549 cancer cells. Molecules. 19:17663–17681. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee YS, Choi KM, Kim W, Jeon YS, Lee YM,
Hong JT, Yun YP and Yoo HS: Hinokitiol inhibits cell growth through
induction of S-phase arrest and apoptosis in human colon cancer
cells and suppresses tumor growth in a mouse xenograft experiment.
J Nat Prod. 76:2195–2202. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Feng R and Dong L: Knockdown of
microRNA-127 reverses adriamycin resistance via cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis sensitization in adriamycin-resistant human glioma
cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:6107–6116. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zeng Z, Huang WD, Gao Q, Su ML, Yang YF,
Liu ZC and Zhu BH: Arnebin-1 promotes angiogenesis by inducing
eNOS, VEGF and HIF-1α expression through the PI3K-dependent
pathway. Int J Mol Med. 36:685–697. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin Q, Guo L, Lin G, Chen Z, Chen T, Lin
J, Zhang B and Gu X: Clinical and prognostic significance of OPN
and VEGF expression in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer.
Cancer Epidemiol. 39:539–544. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ramchandani D and Weber GF: Interactions
between osteopontin and vascular endothelial growth factor:
Implications for cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1855:202–222.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gong X, Tong Q, Chen Z, Zhang Y, Xu C and
Jin Z: Microvascular density and vascular endothelial growth factor
and osteopontin expression during the implantation window in a
controlled ovarian hyperstimulation rat model. Exp Ther Med.
9:773–779. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ferrara N: Vascular endothelial growth
factor: Basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev.
25:581–611. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen P, Zhu J, Liu DY, Li HY, Xu N and Hou
M: Over-expression of survivin and VEGF in small-cell lung cancer
may predict the poorer prognosis. Med Oncol. 31:7752014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li C, Li R, Song H, Wang D, Feng T, Yu X,
Zhao Y, Liu J, Yu X, Wang Y and Geng J: Significance of AEG-1
expression in correlation with VEGF, microvessel density and
clinicopathological characteristics in triple-negative breast
cancer. J Surg Oncol. 103:184–192. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li J, Li L, Li Z, Gong G, Chen P, Liu H,
Wang J, Liu Y and Wu X: The role of miR-205 in the VEGF-mediated
promotion of human ovarian cancer cell invasion. Gynecol Oncol.
137:125–133. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen J, Zhu C, He Z, Geng M, Li G, Tao X
and Zhang F: Association of OPN overexpression with tumor stage,
differentiation, metastasis and tumor progression in human
laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:7116–7124.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gao P, Gao YJ and Liang HL: Effect of
NF-κB inhibitor PDTC on VEGF and endostatin expression of mice with
Lewis lung cancer. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 8:220–224. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hu Y, Hu MM, Shi GL, Han Y and Li BL:
Imbalance between vascular endothelial growth factor and endostatin
correlates with the prognosis of operable non-small cell lung
cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 40:1136–1142. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lim J, Duong T, Lee G, Seong BL, El-Rifai
W, Ruley HE and Jo D: The effect of intracellular protein delivery
on the anti-tumor activity of recombinant human endostatin.
Biomaterials. 34:6261–6271. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xu W, Ye P, Li Z, Shi J, Wang W and Yao K:
Endostar, a recently introduced recombinant human endostatin,
inhibits proliferation and migration through regulating growth
factors, adhesion factors and inflammatory mediators in
choroid-retinal endothelial cells. Mol Biol (Mosk). 44:664–670.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sund M, Hamano Y, Sugimoto H, Sudhakar A,
Soubasakos M, Yerramalla U, Benjamin LE, Lawler J, Kieran M, Shah A
and Kalluri R: Function of endogenous inhibitors of angiogenesis as
endothelium-specific tumor suppressors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:pp. 2934–2939. 2005, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee SH, Jeung IC, Park TW, Lee K, Lee DG,
Cho YL, Lee TS, Na HJ, Park YJ, Lee HG, et al: Extension of the in
vivo half-life of endostatin and its improved anti-tumor activities
upon fusion to a humanized antibody against tumor-associated
glycoprotein 72 in a mouse model of human colorectal carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 6:7182–7194. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|