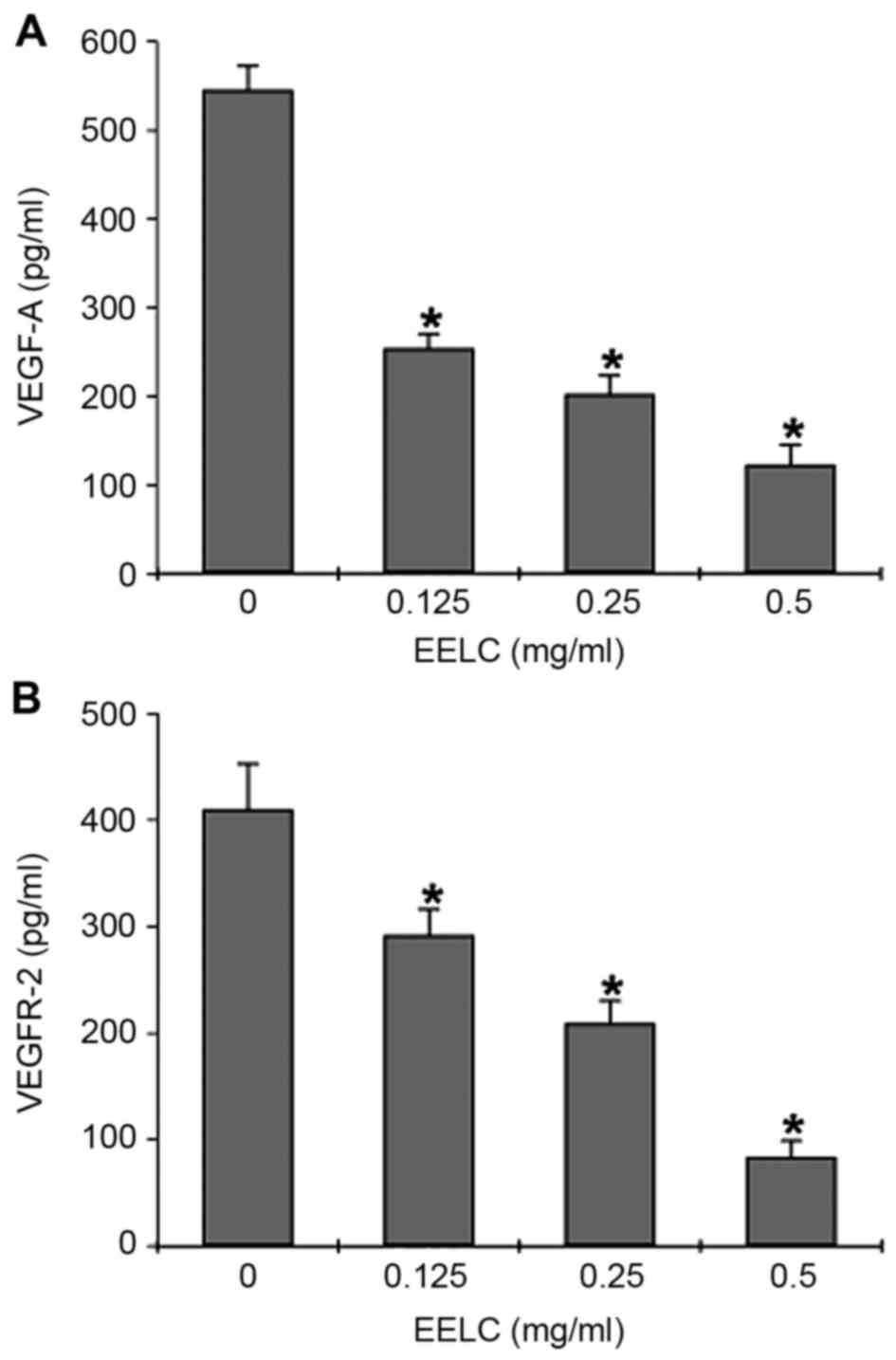
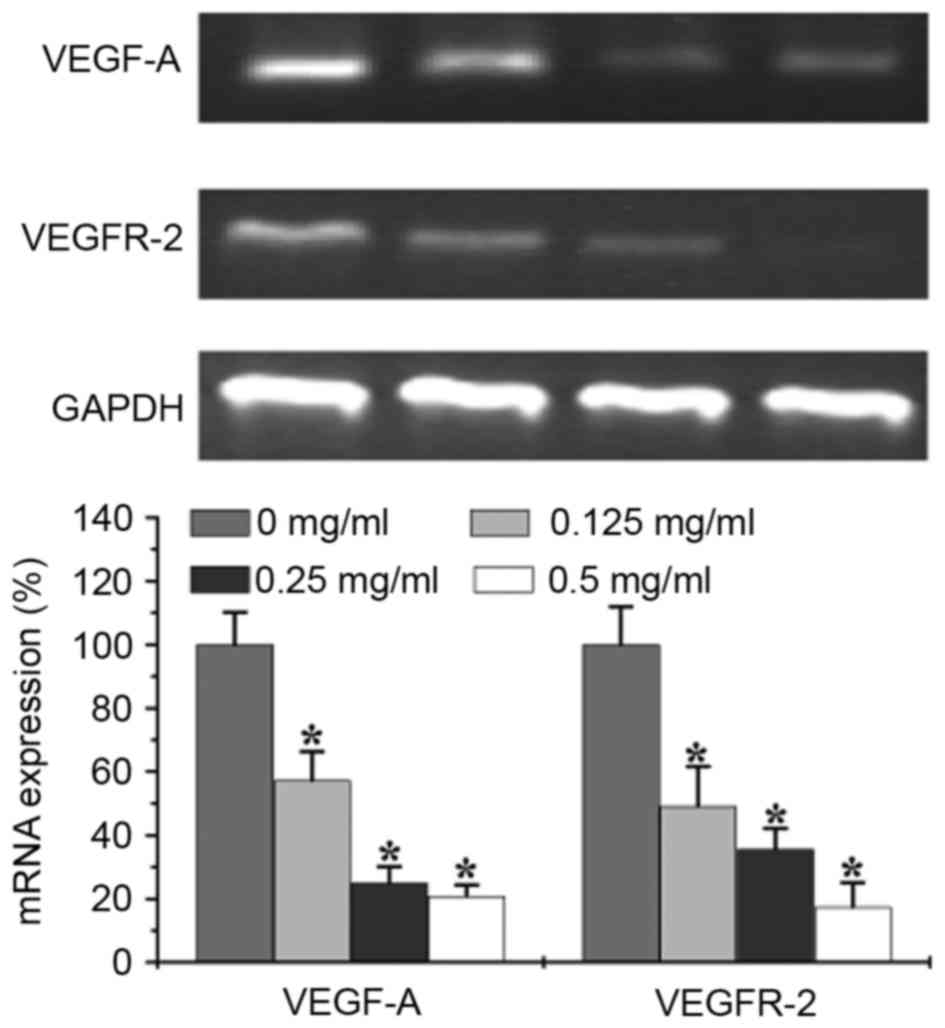
|
1
|
Chen XZ, Cao ZY, Chen TS, Zhang YQ, Liu
ZZ, Su YT, Liao LM and Du J: Water extract of Hedyotis diffusa
Willd suppresses proliferation of human HepG2 cells and potentiates
the anticancer efficacy of low-dose 5-fluorouracil by inhibitingthe
CDK2-E2F1 pathway. Oncol Rep. 28:742–748. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis: Therapeutic
implications. N Engl J Med. 285:1182–1186. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shih T and Lindley C: Bevacizumab: An
angiogenesis inhibitor for the treatment of solid malignancies.
Clin Ther. 28:1779–1802. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gotink KJ and Verheul HM: Anti-angiogenic
tyrosine kinase inhibitors: What is their mechanism of action?
Angiogenesis. 13:1–14. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cook KM and Figg WD: Angiogenesis
inhibitors: Current strategies and future prospects. CA Cancer J
Clin. 60:222–243. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang H, Li A, Dong XP and Xu XY: Screening
of anti-tumor parts from the seeds of Livistona chinensis and its
anti-angiogenesis effect. Zhong Yao Cai. 31:718–722. 2008.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cheueng S and Tai J: In vitro studies of
the dry fruit of Chinese fan palm Livistona chinensis. Oncol Rep.
5:1331–1336. 2005.
|
|
8
|
Sartippour MR, Liu C, Shao ZM, Go VL,
Heber D and Nguyen M: Livistona extract inhibits angiogenesis and
cancer growth. Oncol Rep. 6:1355–1357. 2001.
|
|
9
|
Huang WC, Hsu RM, Chi LM, Leu YL, Chang YS
and Yu JS: Selective downregulation of EGF receptor and downstream
MAPK pathway in human cancer cell lines by active components
partially purified from the seeds of Livistona chinensis R. Brown.
Cancer Lett. 248:137–146. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lin W, Zhao J, Cao Z, Zhuang Q, Zheng L,
Cai Q, Chen D, Wang L, Hong Z and Peng J: Livistona chinensis seed
suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma growth through promotion of
mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis. Oncol Rep. 29:1859–1866. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Folkman J and Shing Y: Angiogenesis. J
Biol Chem. 267:10931–10934. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Folkman J: Angiogenesis in cancer,
vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med. 1:27–31. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Folkman J: Angiogenesis. Annu Rev Med.
57:1–18. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shweiki D, Itin A, Soffer D and Keshet E:
Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate
hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature. 359:843–845. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shalaby F, Rossant J, Yamaguchi TP,
Gertsenstein M, Wu XF, Britman ML and Schuh AC: Failure of
blood-island formation and vasculogenesis in Flk-1-deficient mice.
Nature. 376:62–66. 1995. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lin W, Zhao J, Cao Z, Zhuang Q, Zheng L,
Zeng J, Hong Z and Peng J: Livistona chinensis seeds inhibit
hepatocellular carcinoma angiogenesis in vivo via suppression of
the Notch pathway. Oncol Rep. 31:1723–1728. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Siekmann AF and Lawson ND: Notch
signalling limits angiogenic cell behaviour in developing zebrafish
arteries. Nature. 445:781–784. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Suchting S, Freitas C, le Noble F,
Benedito R, Bréant C, Duarte A and Eichmann A: The Notch ligand
Delta-like 4 negatively regulates endothelial tip cell formation
and vessel branching. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:pp. 3225–3230.
2007, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ferrara N: Role of vascular endothelial
growth factor in physiologic and pathologic angiogenesis:
Therapeutic implications. Semin Oncol. 29 6 Suppl 16:S10–S14. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ferrara N, Gerber HP and LeCouter J: The
biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 9:669–676. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zachary I and Gliki G: Signaling
transduction mechanisms mediating biological actions of the
vascular endothelial growth factor family. Cardiovasc Res.
49:568–581. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Williams CK, Li JL, Murga M, Harris AL and
Tosato G: Up-regulation of the Notch ligand Delta-like 4 inhibits
VEGF-induced endothelial cell function. Blood. 107:931–939. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang G, Ye Y, Zhang X, Liu H and Song J: A
single-arm clinical study of continuous usage of bevacizumab
assecond-line chemotherapy for Chinese patients with metastatic
colorectal cancer. Med Oncol. 32:1632015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Saltz LB, Clarke S, Díaz-Rubio E,
Scheithauer W, Figer A, Wong R, Koski S, Lichinitser M, Yang TS,
Rivera F, et al: Bevacizumab in combination with oxaliplatin-based
chemotherapy as first-line therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer:
A randomized phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 26:2013–2019. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|