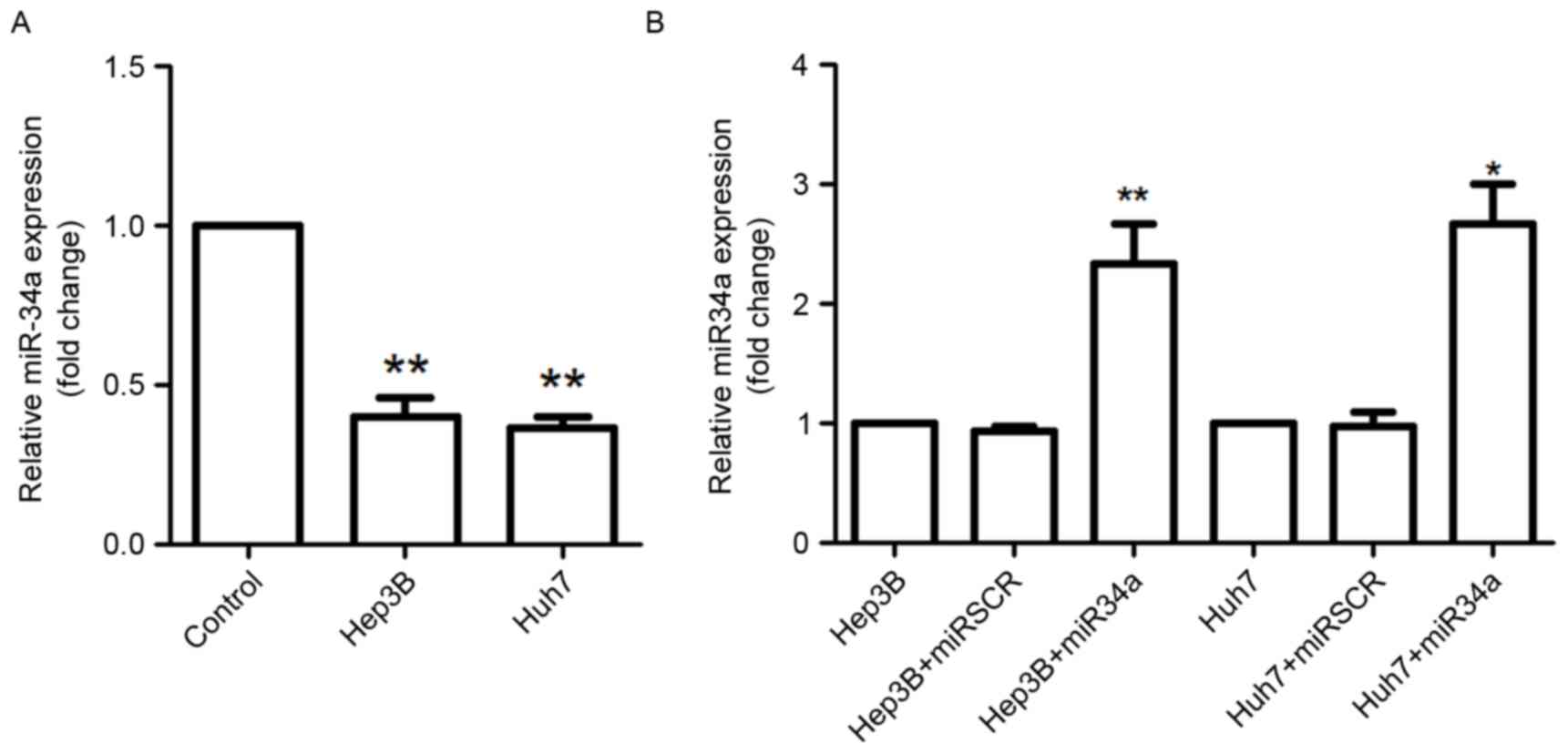
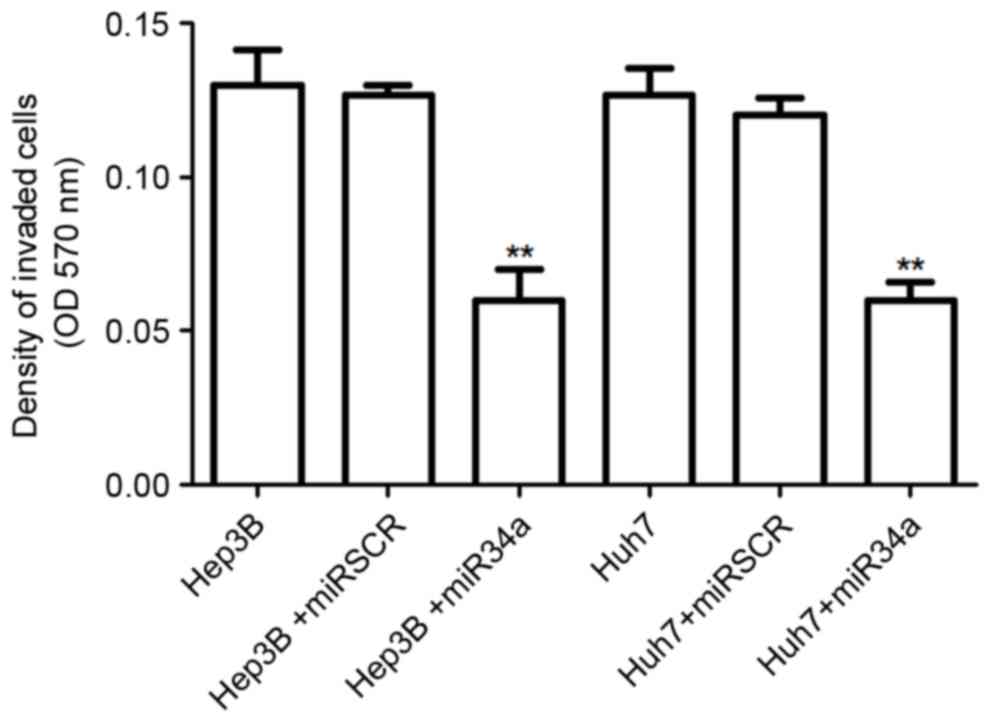
|
1
|
Utsunomiya T, Shimada M, Kudo M, Ichida T,
Matsui O, Izumi N, Matsuyama Y, Sakamoto M, Nakashima O, Ku Y, et
al: Nationwide study of 4741 patients with non-B non-C
hepatocellular carcinoma with special reference to the therapeutic
impact. Ann Surg. 259:336–345. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bruix J and Sherman M: American
Association for the Study of Liver Diseases: Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology. 53:1020–1022.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
El-Serag HB, Marrero JA, Rudolph L and
Reddy KR: Diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 134:1752–1763. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Martin RC, Scoggins CR and McMasters KM:
Safety and efficacy of microwave ablation of hepatic tumors: A
prospective review of a 5-year experience. Ann Surg Oncol.
17:171–178. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shukla GC, Singh J and Barik S: MicroRNAs:
Processing, maturation, target recognition and regulatory
functions. Mol Cell Pharmacol. 3:83–92. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ladeiro Y, Couchy G, Balabaud C,
Bioulac-Sage P, Pelletier L, Rebouissou S and Zucman-Rossi J:
MicroRNA profiling in hepatocellular tumors is associated with
clinical features and oncogene/tumor suppressor gene mutations.
Hepatology. 47:1955–1963. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Datta J, Kutay H, Nasser MW, Nuovo GJ,
Wang B, Majumder S, Liu CG, Volinia S, Croce CM, Schmittgen TD, et
al: Methylation mediated silencing of MicroRNA-1 gene and its role
in hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 68:5049–5058. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tsai WC, Hsu PW, Lai TC, Chau GY, Lin CW,
Chen CM, Lin CD, Liao YL, Wang JL, Chau YP, et al: MicroRNA-122, a
tumor suppressor microRNA that regulates intrahepatic metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 49:1571–1582. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tazawa H, Tsuchiya N, Izumiya M and
Nakagama H: Tumor-suppressive miR-34a induces senescence-like
growth arrest through modulation of the E2F pathway in human colon
cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:pp. 15472–15477. 2007,
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lodygin D, Tarasov V, Epanchintsev A,
Berking C, Knyazeva T, Körner H, Knyazev P, Diebold J and Hermeking
H: Inactivation of miR-34a by aberrant CpG methylation in multiple
types of cancer. Cell Cycle. 7:2591–2600. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu C, Kelnar K, Liu B, Chen X,
Calhoun-Davis T, Li H, Patrawala L, Yan H, Jeter C, Honorio S, et
al: The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and
metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat Med. 17:211–215. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ji Q, Hao X, Zhang M, Tang W, Yang M, Li
L, Xiang D, Desano JT, Bommer GT, Fan D, et al: MicroRNA miR-34
inhibits human pancreatic cancer tumor-initiating cells. PLoS One.
4:e68162009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li N, Fu H, Tie Y, Hu Z, Kong W, Wu Y and
Zheng X: miR-34a inhibits migration and invasion by down-regulation
of c-Met expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer
Lett. 275:44–53. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Adini A, Fainaru O, Udagawa T, Connor KM,
Folkman J and D'Amato RJ: Matrigel cytometry: A novel method for
quantifying angiogenesis in vivo. J Immunol Methods. 342:78–81.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li Q, Ding C, Chen C, Zhang Z, Xiao H, Xie
F, Lei L, Chen Y, Mao B, Jiang M, et al: miR-224 promotion of cell
migration and invasion by targeting Homeobox D 10 gene in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 29:835–842.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hummon AB, Lim SR, Difilippantonio MJ and
Ried T: Isolation and solubilization of proteins after TRIzol
extraction of RNA and DNA from patient material following prolonged
storage. Biotechniques. 42(467–470): 4722007.
|
|
17
|
Ish-Shalom S and Lichter A: Analysis of
fungal gene expression by real time quantitative PCR. Methods Mol
Biol. 638:103–114. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang Y, Kuramitsu Y, Takashima M, Yokoyama
Y, Iizuka N, Tamesa T, Sakaida I, Oka M and Nakamura K:
Identification of four isoforms of aldolase B down-regulated in
hepatocellular carcinoma tissues by means of two-dimensional
Western blotting. In Vivo. 25:881–886. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li N, Fu H, Tie Y, Hu Z, Kong W, Wu Y and
Zheng X: miR-34a inhibits migration and invasion by down-regulation
of c-Met expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer
Lett. 275:44–53. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pogribny IP, Starlard-Davenport A,
Tryndyak VP, Han T, Ross SA, Rusyn I and Beland FA: Difference in
expression of hepatic microRNAs miR-29c, miR34a, miR-155, and
miR-200b is associated with strain-specific susceptibility to
dietary nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Lab Invest.
90:1437–1446. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Condeelis J and Pollard JW: Macrophages:
Obligate partners for tumor cell migration, invasion, and
metastasis. Cell. 124:263–266. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Welch C, Chen Y and Stallings RL:
MicroRNA-34a functions as a potential tumor suppressor by inducing
apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. Oncogene. 26:5017–5022. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang P, Li QJ, Feng Y, Zhang Y, Markowitz
GJ, Ning S, Deng Y, Zhao J, Jiang S, Yuan Y, et al:
TGF-β-miR-34a-CCL22 signaling-induced Treg cell recruitment
promotes venous metastases of HBV-positive hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 22:291–303. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Peng L, Yuan Z, Li Y, Ling H, Izumi V,
Fang B, Fukasawa K, Koomen J, Chen J and Seto E: Ubiquitinated
sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) function is modulated during DNA damage-induced
cell death and survival. J Biol Chem. 290:8904–8912. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chung YR, Kim H, Park SY, Park IA, Jang
JJ, Choe JY, Jung YY, Im SA, Moon HG, Lee KH, et al: Distinctive
role of SIRT1 expression on tumor invasion and metastasis in breast
cancer by molecular subtype. Hum Pathol. 46:1027–1035. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hao C, Zhu PX, Yang X, Han ZP, Jiang JH,
Zong C, Zhang XG, Liu WT, Zhao QD, Fan TT, et al: Overexpression of
SIRT1 promotes metastasis through epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 14:9782014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Levine AJ, Bargonetti J, Bond GL, Hoh J,
Onel K, Overholtzer M, Stoffel AK, Walsh CA and Jin S: The p53
network. Protein Rev. 2:1–23. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Prives C and Manley JL: Why is p53
acetylated? Cell. 107:815–818. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Singh K, Mogare D, Giridharagopalan RO,
Gogiraju R, Pande G and Chattopadhyay S: p53 target gene SMAR1 is
dysregulated in breast cancer: Its role in cancer cell migration
and invasion. PLoS One. 2:e6602007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|