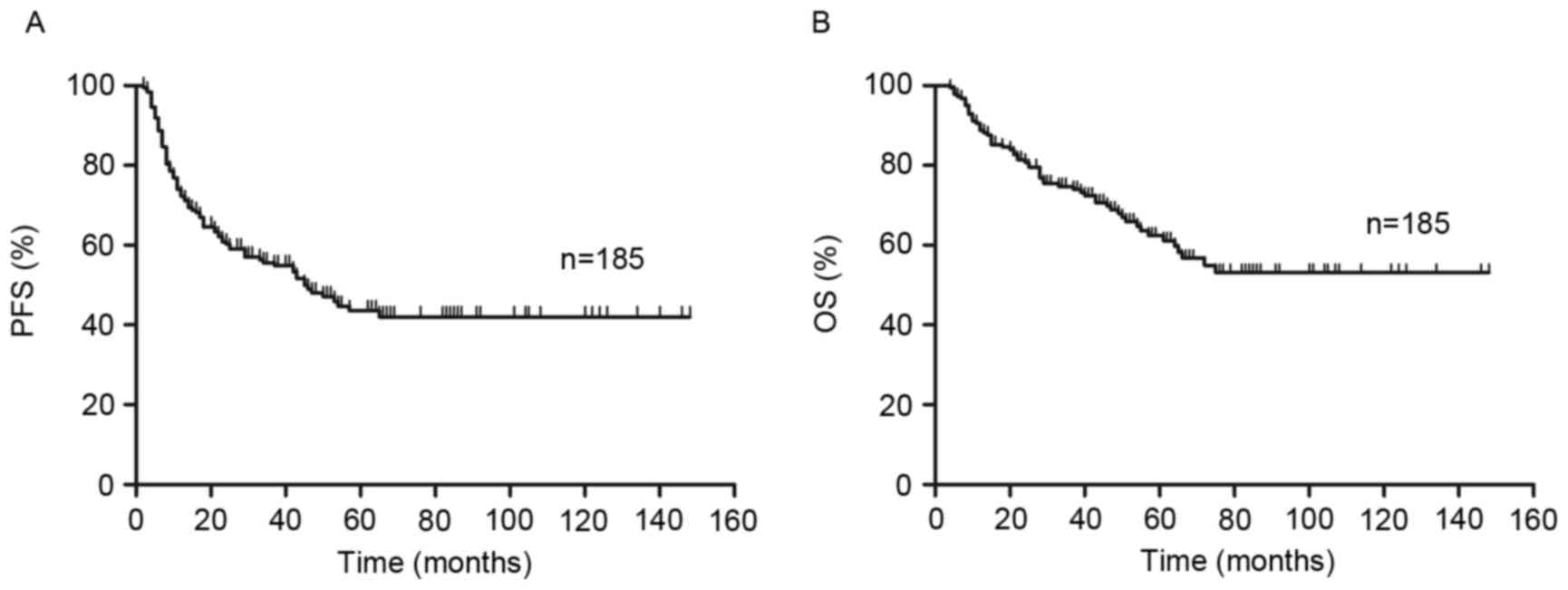
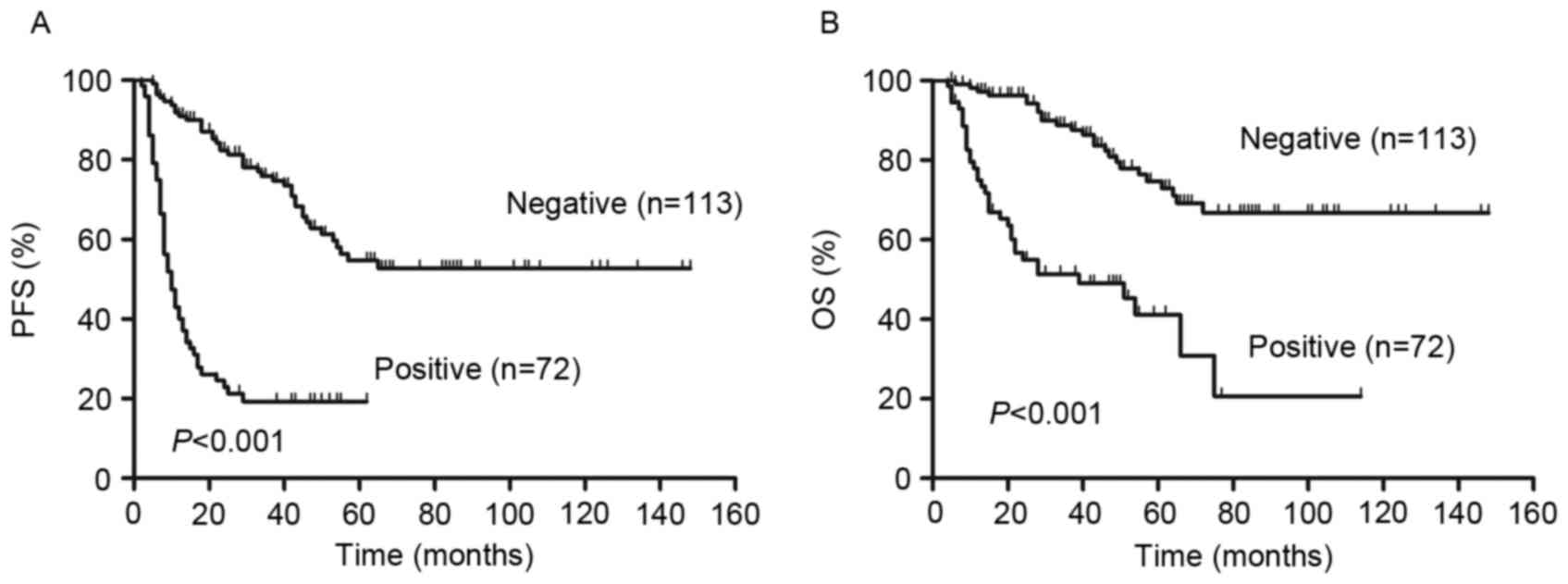
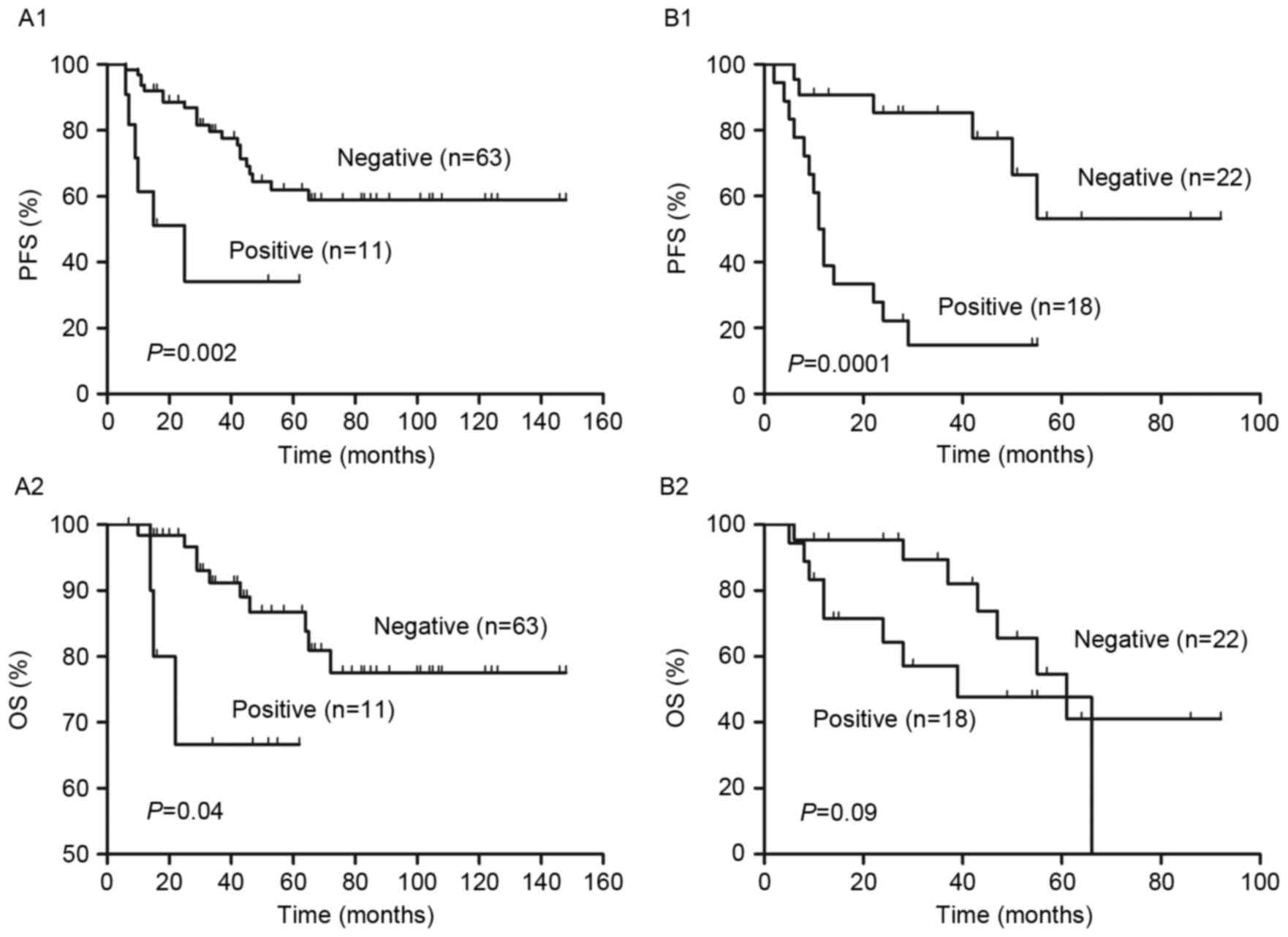
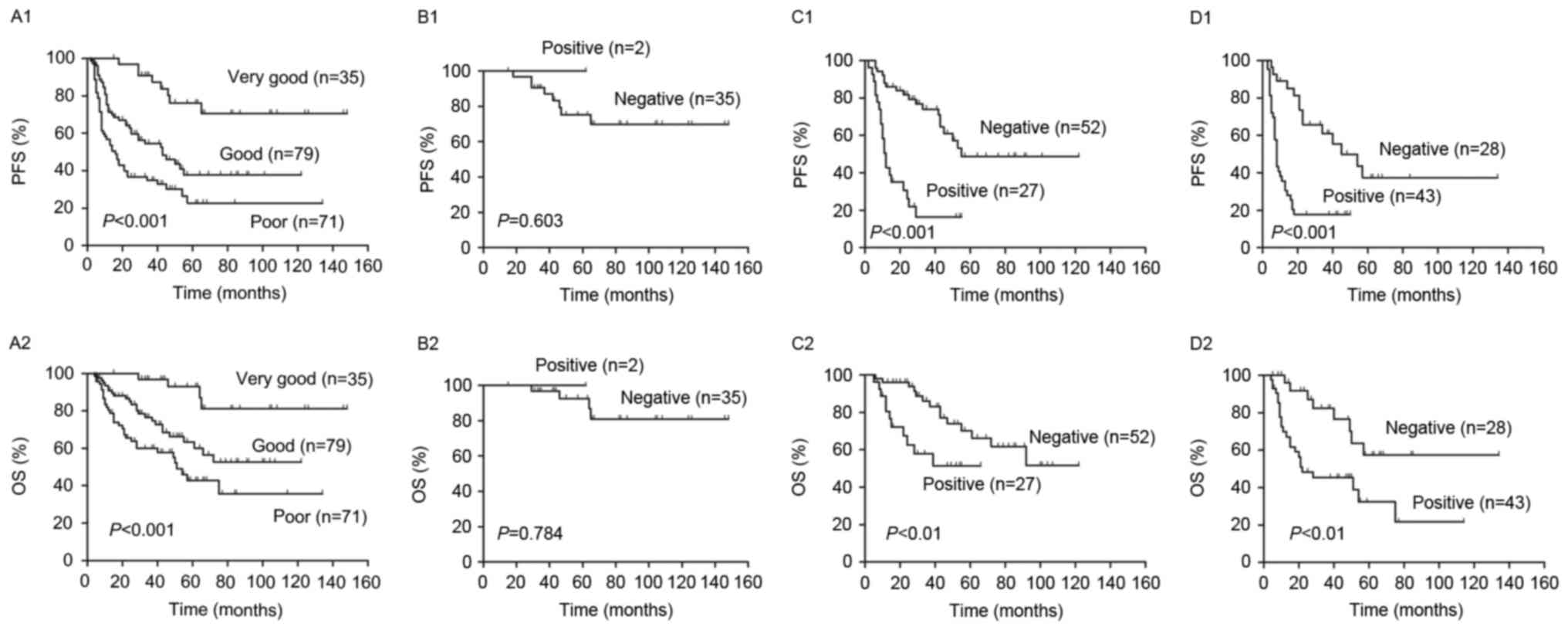
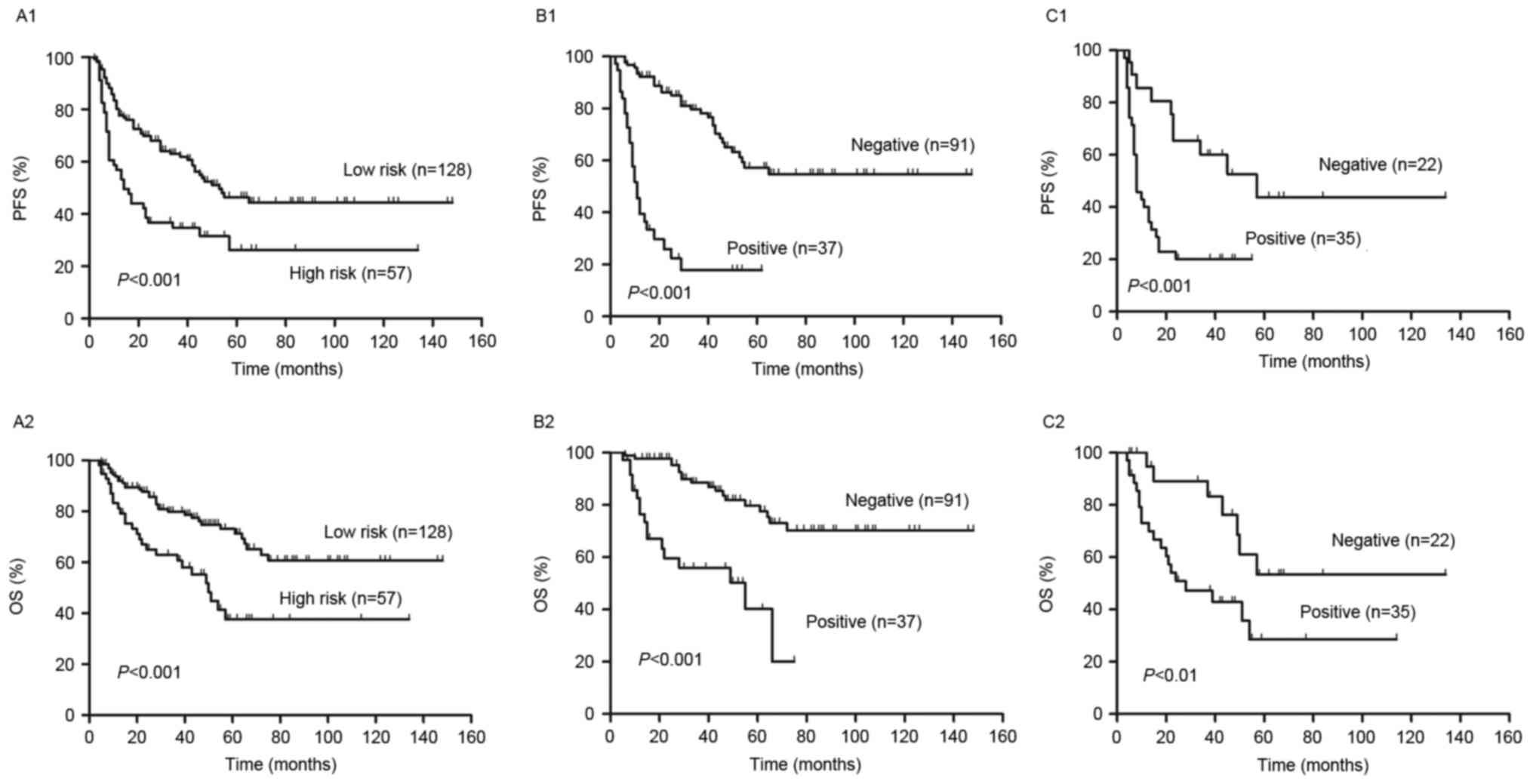
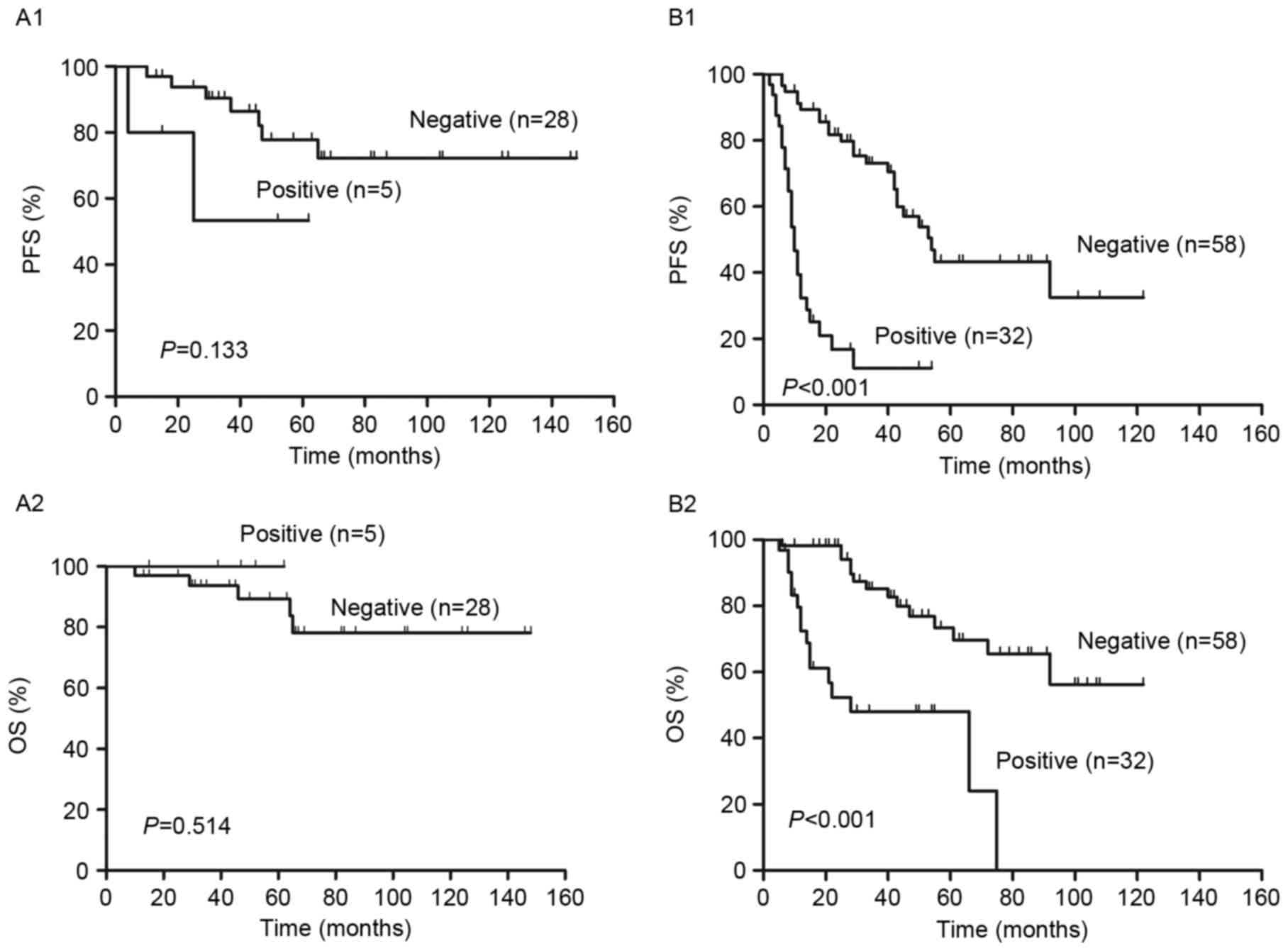
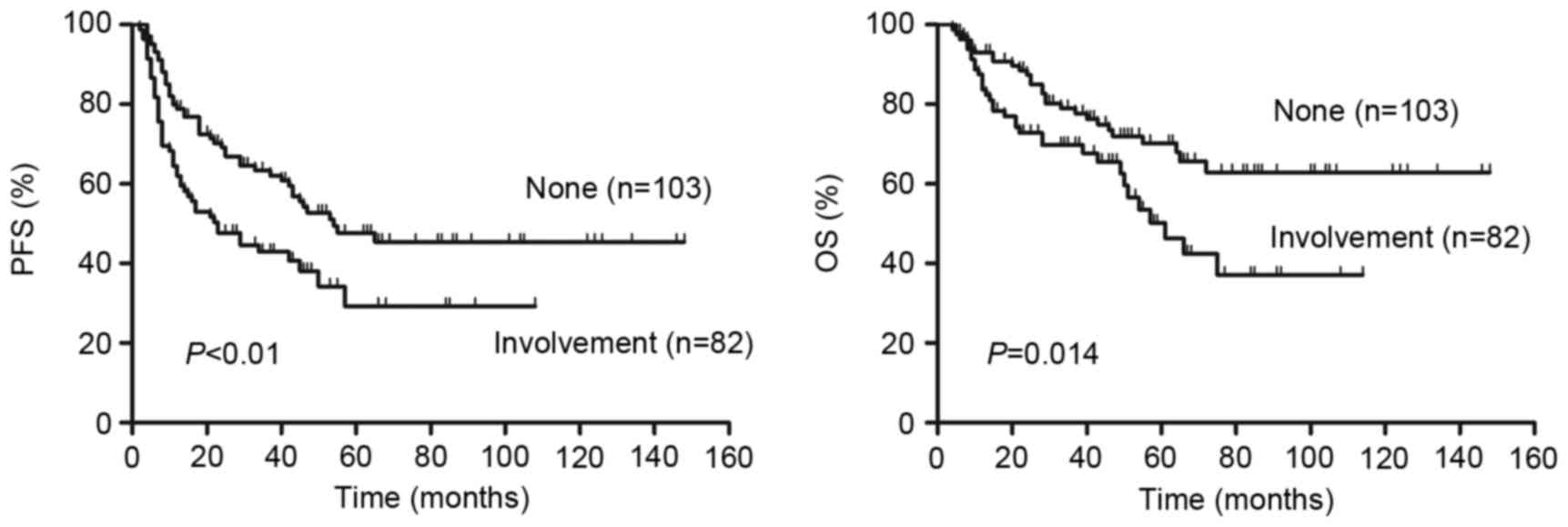
|
1
|
No authors listed: A clinical evaluation
of the International Lymphoma Study Group classification of
non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Classification
Project. Blood. 89:3909–3918. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Coiffier B: Diffuse large cell lymphoma.
Curr Opin Oncol. 13:325–334. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Coiffier B, Lepage E, Briere J, Herbrecht
R, Tilly H, Bouabdallah R, Morel P, Van Den Neste E, Salles G,
Gaulard P, et al: CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with
CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma.
N Engl J Med. 346:235–242. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ziepert M, Hasenclever D, Kuhnt E, Glass
B, Schmitz N, Pfreundschuh M and Loeffler M: Standard international
prognostic index remains a valid predictor of outcome for patients
with aggressive CD20+ B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era. J Clin
Oncol. 28:2373–2380. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pfreundschuh M, Schubert J, Ziepert M,
Schmits R, Mohren M, Lengfelder E, Reiser M, Nickenig C, Clemens M,
Peter N, et al: Six versus eight cycles of bi-weekly CHOP-14 with
or without rituximab in elderly patients with aggressive CD20+
B-cell lymphomas: A randomised controlled trial (RICOVER-60).
Lancet Oncol. 9:105–116. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Campo E, Swerdlow SH, Harris NL, Pileri S,
Stein H and Jaffe ES: The 2008 WHO classification of lymphoid
neoplasms and beyond: Evolving concepts and practical applications.
Blood. 117:5019–5032. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dybkær K, Bøgsted M, Falgreen S, Bødker
JS, Kjeldsen MK, Schmitz A, Bilgrau AE, Xu-Monette ZY, Li L,
Bergkvist KS, et al: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma classification
system that associates normal B-cell subset phenotypes with
prognosis. J Clin Oncol. 33:1379–1388. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Barrans SL, Carter I, Owen RG, Davies FE,
Patmore RD, Haynes AP, Morgan GJ and Jack AS: Germinal center
phenotype and bcl-2 expression combined with the International
Prognostic Index improves patient risk stratification in diffuse
large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 99:1136–1143. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Colomo L, López-Guillermo A, Perales M,
Rives S, Martínez A, Bosch F, Colomer D, Falini B, Montserrat E and
Campo E: Clinical impact of the differentiation profile assessed by
immunophenotyping in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
Blood. 101:78–84. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Linderoth J, Jerkeman M, Cavallin-Ståhl E,
Kvaløy S and Torlakovic E: Nordic Lymphoma Group Study:
Immunohistochemical expression of CD23 and CD40 may identify
prognostically favorable subgroups of diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma: A nordic lymphoma group study. Clin Cancer Res.
9:722–728. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Young J, Badgery-Parker T, Dobbins T,
Jorgensen M, Gibbs P, Faragher I, Jones I and Currow D: Comparison
of ECOG/WHO performance status and ASA score as a measure of
functional status. J Pain Symptom Manage. 49:258–264. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Greene FL: The American Joint Committee on
Cancer: Updating the strategies in cancer staging. Bull Am Coll
Surg. 87:13–15. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
International Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Prognostic Factors Project: A predictive model for aggressive
non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 329:987–994. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sehn LH, Berry B, Chhanabhai M, Fitzgerald
C, Gill K, Hoskins P, Klasa R, Savage KJ, Shenkier T, Sutherland J,
et al: The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a
better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with
diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood.
109:1857–1861. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou Z, Sehn LH, Rademaker AW, Gordon LI,
Lacasce AS, Crosby-Thompson A, Vanderplas A, Zelenetz AD, Abel GA,
Rodriguez MA, et al: An enhanced International Prognostic Index
(NCCN-IPI) for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated
in the rituximab era. Blood. 123:837–842. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C,
Lossos IS, Rosenwald A, Boldrick JC, Sabet H, Tran T, Yu X, et al:
Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene
expression profiling. Nature. 403:503–511. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Terasawa T, Nihashi T, Hotta T and Nagai
H: 18F-FDG PET for posttherapy assessment of Hodgkin's disease and
aggressive Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: A systematic review. J Nucl Med.
49:13–21. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Terasawa T, Lau J, Bardet S, Couturier O,
Hotta T, Hutchings M, Nihashi T and Nagai H:
Fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography for
interim response assessment of advanced-stage Hodgkin's lymphoma
and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A systematic review. J Clin
Oncol. 27:1906–1914. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cheson BD, Fisher RI, Barrington SF,
Cavalli F, Schwartz LH, Zucca E and Lister TA: Alliance,
Australasian Leukaemia and Lymphoma Group; Eastern Cooperative
Oncology Group; European Mantle Cell Lymphoma Consortium:
Recommendations for initial evaluation, staging, and response
assessment of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: The Lugano
classification. J Clin Oncol. 32:3059–3068. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Casasnovas RO, Meignan M,
Berriolo-Riedinger A, Bardet S, Julian A, Thieblemont C, Vera P,
Bologna S, Brière J, Jais JP, et al: SUVmax reduction improves
early prognosis value of interim positron emission tomography scans
in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 118:37–43. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fuertes S, Setoain X, Lopez-Guillermo A,
Carrasco JL, Rodríguez S, Rovira J and Pons F: Interim FDG PET/CT
as a prognostic factor in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Eur J Nucl
Med Mol Imaging. 40:496–504. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nols N, Mounier N, Bouazza S, Lhommel R,
Costantini S, Vander Borght T, Vekemans MC, Sonet A, Bosly A,
Michaux L, et al: Quantitative and qualitative analysis of
metabolic response at interim positron emission tomography scan
combined with International Prognostic Index is highly predictive
of outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma.
55:773–780. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Delbeke D, Coleman RE, Guiberteau MJ,
Brown ML, Royal HD, Siegel BA, Townsend DW, Berland LL, Parker JA,
Hubner K, et al: Procedure guideline for tumor imaging with 18F-FDG
PET/CT 1.0. J Nucl Med. 47:885–895. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Meignan M, Gallamini A, Haioun C and
Polliack A: Report on the second international workshop on interim
positron emission tomography in lymphoma held in Menton, France,
8–9 April 2010. Leuk Lymphoma. 51:2171–2180. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Meignan M, Gallamini A, Meignan M,
Gallamini A and Haioun C: Report on the first international
workshop on interim-PET-scan in lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma.
50:1257–1260. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Habermann TM, Weller EA, Morrison VA,
Gascoyne RD, Cassileth PA, Cohn JB, Dakhil SR, Woda B, Fisher RI,
Peterson BA and Horning SJ: Rituximab-CHOP versus CHOP alone or
with maintenance rituximab in older patients with diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 24:3121–3127. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, Brunning
RD, Borowitz MJ, Porwit A, Harris NL, Le Beau MM,
Hellström-Lindberg E, Tefferi A and Bloomfield CD: The 2008
revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of
myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: Rationale and important
changes. Blood. 114:937–951. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC,
Gascoyne RD, Delabie J, Ott G, Müller-Hermelink HK, Campo E,
Braziel RM, Jaffe ES, et al: Confirmation of the molecular
classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by
immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood. 103:275–282.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kwon SH, Kang DR, Kim J, Yoon JK, Lee SJ,
Jeong SH, Lee HW and An YS: Prognostic value of negative interim
2-[18F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose PET/CT in diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma. Clin Radiol. 71:280–286. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang DH, Min JJ, Song HC, Jeong YY, Chung
WK, Bae SY, Ahn JS, Kim YK, Bom HS, Chung IJ, et al: Prognostic
significance of interim 18F-FDG PET/CT after three or
four cycles of R-CHOP chemotherapy in the treatment of diffuse
large B-cell lymphoma. Eur J Cancer. 47:1312–1318. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Itti E, Lin C, Dupuis J, Paone G,
Capacchione D, Rahmouni A, Haioun C and Meignan M: Prognostic value
of interim 18F-FDG PET in patients with diffuse large B-Cell
lymphoma: SUV-based assessment at 4 cycles of chemotherapy. J Nucl
Med. 50:527–533. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|